Missed questions
1/1010
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
1011 Terms
What is the primary function of pulmonary surfactant?
To reduce surface tension in the alveoli, increasing lung compliance and preventing alveolar collapse
How does pulmonary surfactant affect alveolar compliance?
It increases compliance by lowering surface tension, making alveoli easier to expand during inhalation
How does decreased surfactant affect alveolar surface tension?
It increases surface tension, making alveoli more likely to collapse
Radiation causing electron ejection can lead to what types of atoms?
free radicals
what is the primary purpose of aldosterone?
To regulate sodium and potassium levels in the body, thereby controlling blood pressure and fluid balance.
Aldosterone is most active when what ionic conditions are present?
Low sodium and high potassium levels.
Where is aldosterone released from?
the adrenal glands, specifically the adrenal cortex
What are the ionic effects of aldosterone release?
K+ secretion increases and Na+ reabsorption occurs in the kidneys. Blood Na+ increases and blood K+ decreases as a result.
What happens when too much aldosterone is secreted?
hypertension
How does secretion differ from reabsorption?
Secretion involves the active transport of substances from the blood into the renal tubules, while reabsorption refers to the process of taking substances from the renal tubules back into the blood.
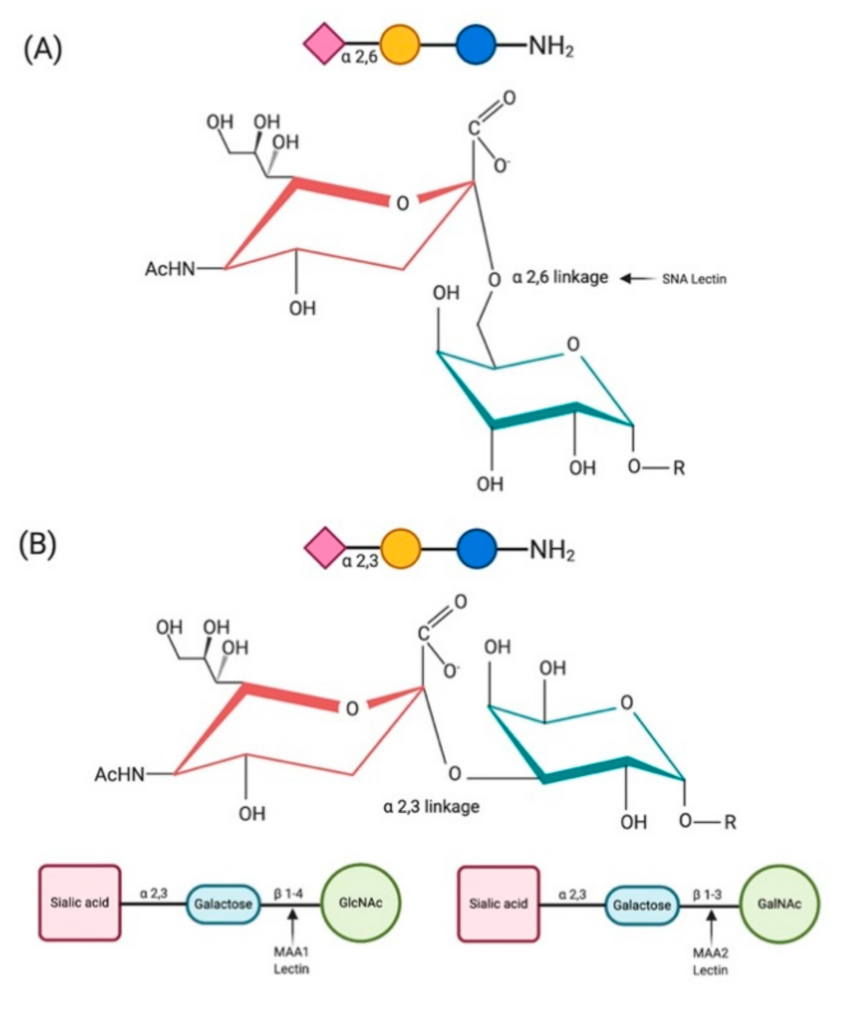
What is the difference between alpha 2,6 and alpha 2,3 linkage?
Alpha 2,6 linkage involves sialic acid residues attached to the 6th carbon of galactose, while alpha 2,3 linkage involves attachment to the 3rd carbon.
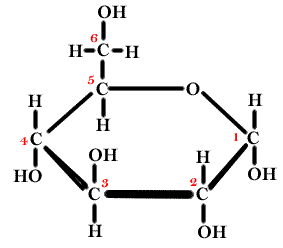
Number the carbons in this monosaccharide
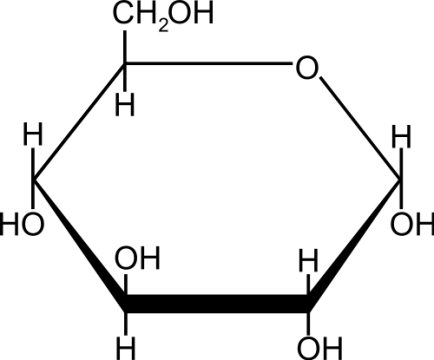
from 1 to 6 starting at the aldehyde or ketone group.
What do antiviral therapies target?
Antiviral therapies primarily target specific stages in the viral life cycle, such as viral entry, replication, and assembly, to inhibit viral reproduction.
what are examples of post-transcriptional modifications?
5’ methylguanosine cap of mRNA, polyadenlylation, and splicing of introns.
what are examples of post-translational modifications?
Phosphorylation, glycosylation, ubiquitination, and acetylation, which alter the protein's function and activity after synthesis.
What is bacterial transduction?
a form of horizontal gene transfer in bacteria in which bacteriophages (viruses that infect bacteria) transmit genomic material
What is bacterial conjugation?
horizontal gene transfer process in bacteria in which plasmid DNA is transferred from one bacterium to another through a pilus. Needs F factor for donor cell.
What is bacterial transformation?
Transformation involves direct uptake of genetic material from the environment
What is binary fission?
Binary fission is the asexual reproduction process in bacteria where a single cell divides into two identical daughter cells
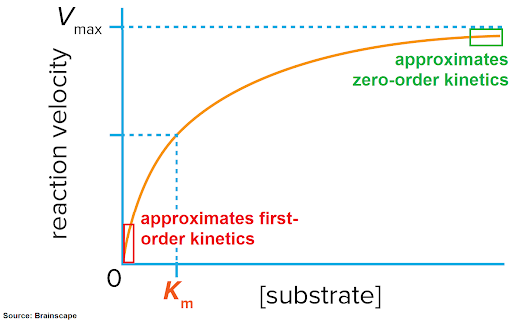
At low concentrations of substrate, what is the reaction order?
The reaction is first-order, meaning the rate is directly proportional to the concentration of reactants present.
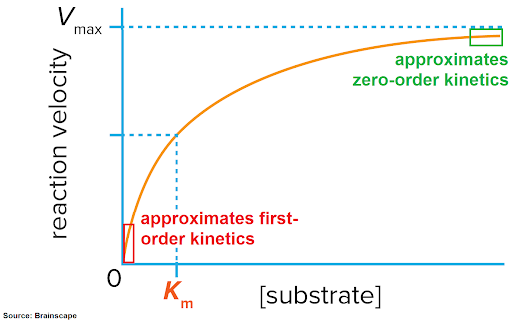
At high concentrations of substrate, what is the reaction order?
The reaction order becomes zero-order, indicating that the rate of reaction is independent of the concentration of substrates present.
What is the least likely mutation for deamination or methylation to cause?
Conversion of purine to pyrimidine an vice versa due to differences in ring structure
Which is heavier: DNA or RNA?
RNA due to the extra 2’ hydroxyl compared to the hydrogen in DNA
SN2 reaction is favored by what type of solvent?
Polar aprotic solvent
SN2 reaction is favored by what type of nucleophile?
A strong, negatively charged nucleophile that isn’t bulky
What is passive immunity?
transfer of active humoral immunity in the form of ready-made antibodies, from one individual to another. Usually provides temporary protection
cell-mediated immunity
a type of immunity that involves the activation of T cells and does not involve antibodies.
Natural immunity
refers to the antibody protection an individual gets after their body has been exposed to a particular pathogen
What can happen to DNA viruses that can’t directly happen to RNA viruses?
DNA viruses can be spliced into a viral vector
What would be expected of the expression of universal emotions in all cultures?
All cultures would display any one of those emotions using the same facial expressions
What is a mimetic organization?
organizations that try to copy another organizations
Looking glass self
A social psychological concept that suggests a person's self-concept is influenced by how they believe others perceive them, often leading to self-fulfilling prophecies.
egocentric bias
Tendency to overstresss changes between the past and present in order to make oneself appear more favorable or competent.
attributional bias
the tendency to attribute positive events to oneself and negative events to external factors.
automation bias
the tendency to favor suggestions from automated systems or technologies, leading to reliance on those systems even in the face of contradictory evidence.
intergenerational mobility
describes upward or downward movement in social class between two or more generations.
intragenerational mobility
describes changes in social class that occur within one lifetime
social reproduction
phenomenon in which poverty tends to beget poverty, and wealth tends to beget wealth across generations
Meritocracy is an organization defined by what?
the belief that social status is achieved through individual effort and abilities, rather than predetermined factors like class or wealth
fundamental attribution error
refers to the tendency to overemphasize personal characteristics and underestimate situational factors when explaining someone else's behavior.
Can you increase action potential strength?
No, AP’s are all or nothing, only their frequency can be increased
What are interneurons?
Interneurons are a type of neuron that connect sensory and motor neurons, are not afferent or efferent
Construct validity
is the degree to which a test or instrument measures the concept it is intended to measure
researcher bias
refers to the tendency of researchers to unintentionally influence the results of their study based on their expectations or beliefs.
reliability
likelihood that results could be replicated
Bandura’s Social cognitive theory
is a psychological model that emphasizes the role of observational learning, imitation, and modeling in behavior development.
biological perspective
A viewpoint in psychology that emphasizes the importance of physiological and genetic factors in influencing behavior, cognition, and emotional responses
Maslow’s humanistic theory
is a psychological perspective that emphasizes self-actualization and the fulfillment of human needs, arranged in a hierarchy.
Rorschach inkblot test
is a projective psychological test consisting of 10 inkblots printed on cards, which are used to measure personality traits and emotional functioning. Both subjective and projective
Dopamine irregularities are related to what disorders?
neuropsychiatric disorders like schizophrenia (dopamine overactivity) and Parkinson’s disease (low dopamine)
what disorders are related to serotonin dysregulation?
Depressive disorders and anxiety disorders
impression management
involves controlling information about oneself for personal benefit and is characterized by techniques such as flattery, boasting, self-promotion, conformity, and ingratiation
webers law
states that the change in a stimulus that will be just noticeable is a constant ratio of the original stimulus.
What does weber’s law say about the relationship between a stimulus and an individual’s ability to detect it?
there is a linear relationship between the intensity of a stimulus and its detection
Ratio level of measurement
is a level of measurement that has a true zero point, allowing for the comparison of both differences and ratios between measurements.
self efficacy is usually influenced by what?
internal locus of control which is the belief that one can influence their own outcomes.
self esteem is usually influenced by what?
external locus of control, which is the belief that outside forces influence one's outcomes.
what type of information does the frontal lobe process?
Information related to reasoning, problem-solving, and planning. It also processes emotions, personality, and higher-level cognitive functions.
What type of information does the temporal lobe process?
Information related to memory, emotion, and auditory processing (as well as other sensory information)
Moderating vs confounding variable
Moderating variables influence the strength or direction of a relationship between two other variables, while confounding variables provide an alternative explanation for the observed relationship
Proactive interference would be lower in people with difficulty forming new memories because_____
They would find it hard to remember new information they are presented with and old memories would less likely interfere
confabulation
is the fabrication of false memories without the intention to deceive, often occurring in individuals with memory disorders.
context effect
refers to the influence of environmental characteristics on a person’s perception of a stimulus. For example, a participant may have better recall when the original learning and recall take place in similar environments.
false alarm in signal detection theory
describes a situation where a person incorrectly identifies a signal or event, believing it to be present when it is not.
What is a miss in the signal detection theory?
A failure to identify a signal or event that is actually present, often measured in signal detection theory.
de ja vu
example of a context effect in which a person believes they have experienced an event before
Pearson correlation coefficient
a statistic that measures the strength and direction of a linear relationship between two variables. Ranges from -1 to 1 (1 is perfect positive correlation, -1 is perfect negative correlation; 0 indicates no correlation)
Where is sperm produced?
the Sertoli cells of the seminiferous tubules in the testes.
Where are leydig cells located?
in the interstitial tissue of the testes, surrounding the seminiferous tubules
What is the function of leydig cells?
Leydig cells produce testosterone, which is essential for male reproductive development and function.
What is bone resorption?
the process by which osteoclasts break down bone tissue, releasing minerals and other substances into the bloodstream.
What reproductive hormone inhibits bone resorption or the breaking down of bone?
Estrogen
Internal consistency
refers to how well the items of a test that assess a certain construct of interest correlate with each other
implicit vs explicit attitudes
Implicit attitudes are subconscious beliefs or feelings toward a subject, while explicit attitudes are conscious and easily articulated views
Covert vs overt
refers to the distinction between hidden behaviors or expressions (covert) and those that are openly displayed (overt) in social contexts.
exchange theory
behavior patterns in societies reflect individuals who make choices that maximize their benefits and minimize their costs from the relationships they maintain.
role theory
The framework that explains how individuals perform behaviors expected of them based on their social roles within groups and society.
The recency effect
the tendency to recall items near the end of a list
Positive priming
exposure to one stimulus influences the response to another stimulus, often enhancing the recognition or recall of related information.
The serial position effect
people are more likely to retain pieces of information from the beginning and end of a list and includes both primacy and recency effects
enzyme linked receptors
a type of membrane protein that acts as both a receptor and enzyme and when a ligand binds, it triggers intracellular enzymatic activity (like tyrosine kinase receptor)
How many times to GPCR membrane proteins pass through the membrane?
7 times
What impact can GPCR’s have on camp activity?
They can activate or inhibit adenylate cyclase, which regulates the levels of cAMP in the cell
How many subunits do GPCRs have?
3 different protein subunits (heterotrimeric)
What are the types of g proteins in GPCR’s
Gs, Gi, and Gg, each of which has distinct functions in signal transduction.
What is the function of the gs g protein component?
It stimulates adenylate cyclase, increasing cAMP levels in the cell.
What is the function of gi g protein component?
It inhibits adenylate cyclase, decreasing cAMP levels in the cell
What is the function of the gq g protein component?
It activates phospholipase C, leading to an increase in inositol trisphosphate (IP3) and diacylglycerol (DAG), which subsequently increase intracellular calcium levels.
When a gpcr is activated, what subunit exchanges GDP for GTP?
The alpha subunit
What are the steps of GPCR activation?
agonist binding to the receptor, conformational changes in the receptor, exchange of GDP for GTP on the alpha subunit, activation adenylate cyclase, activation of cAMP, and phosphorylation of PKA
Adenylate cyclase catalyzes what reaction?
The conversion of ATP to cAMP
What happens when someone is hyperventilating?
Co2 levels decrease, o2 levels increase, blood pH increases
What organs does glucagon target?
liver and to a small extent kidneys
Electrons in the etc are passed from what potential?
High to low reduction potential energy
What complexes in the etc pump protons?
Complexes I, III, and IV
What is a FISH analysis?
A technique used to detect and localize the presence or absence of specific DNA sequences on chromosomes, commonly used in genetics and cancer to identify chromosomal abnormalities.
An acidic buffer will only include what components?
A weak acid and its conjugate base
What is a buffer?
A solution with a weak acid, weak base and their conjugate base and acid respectively. The solution resists changes in ph
Henderson Hasselback equation
ph= pka+ log[A-]/ [HA]
What is the bicarbonate buffer system?
It maintains blood ph by using carbonic acid (H2CO3) and bicarbonate (HCO3-) to regulate acidity and alkalinity.