Labor Econ Final
1/60
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Every Question from the tests & Chp 15-16 Notes
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
Normative
Employers should not be required to offer pensions to their employees.
Positive
Employers offering pensions benefits will pay lower wages than they would if they did not offer a pension program.
Positive
If the further immigration of lower-skilled foreigners is prevented, the wages of lower-skilled immigrants already here will rise.
Normative
The military draft compels people to engage in a transaction that they would not voluntarily enter into; it should therefore be avoided as a way of recruiting military personnel.
Positive
If the military draft were reinstituted, military salaries would probably fall.
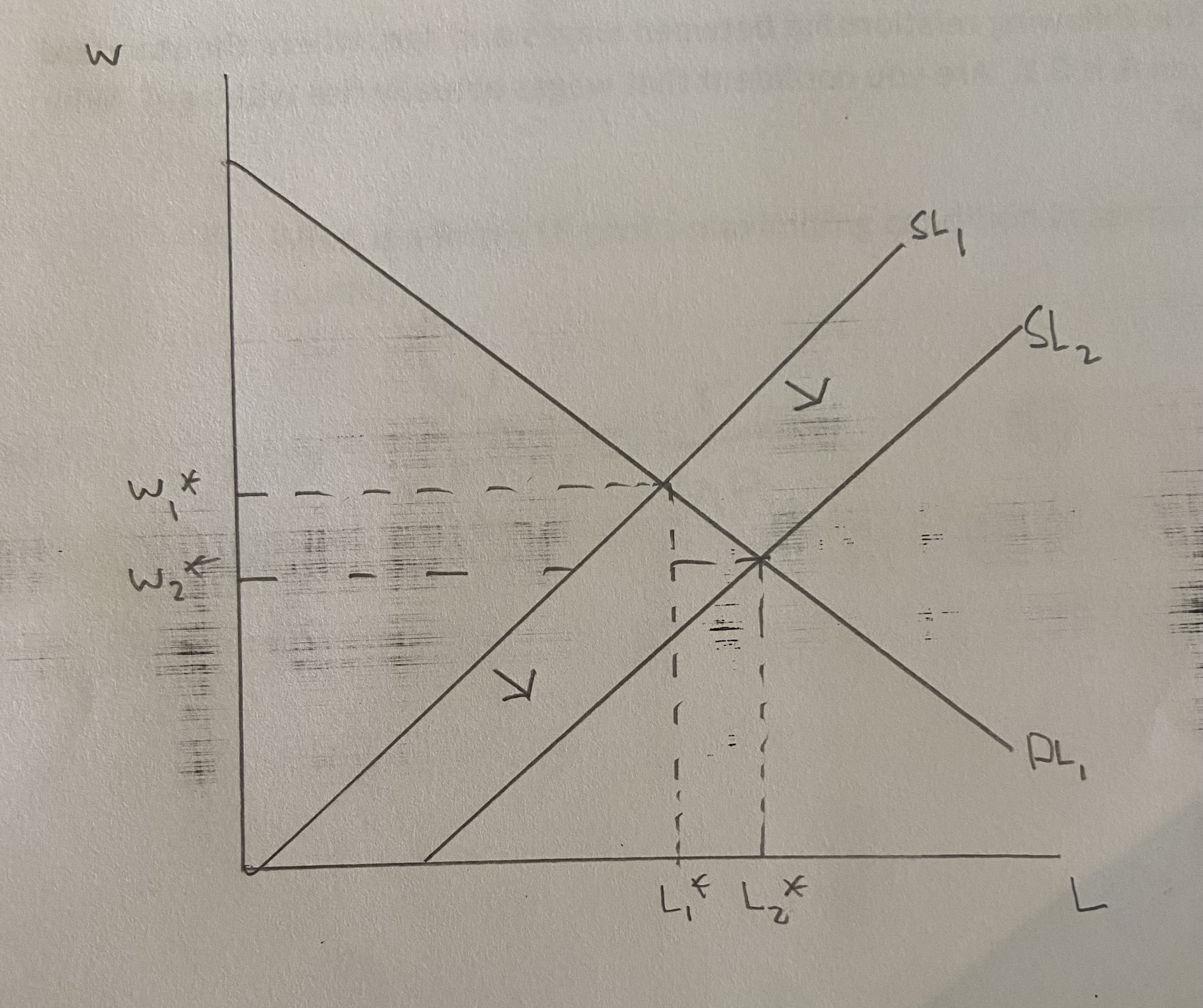
Using a supply-demand diagram, show how an increase in the immigration of unskilled workers to the U.S would affect the equilibrium wage and employment level of unskilled workers in the U.S. Be sure to label everything.
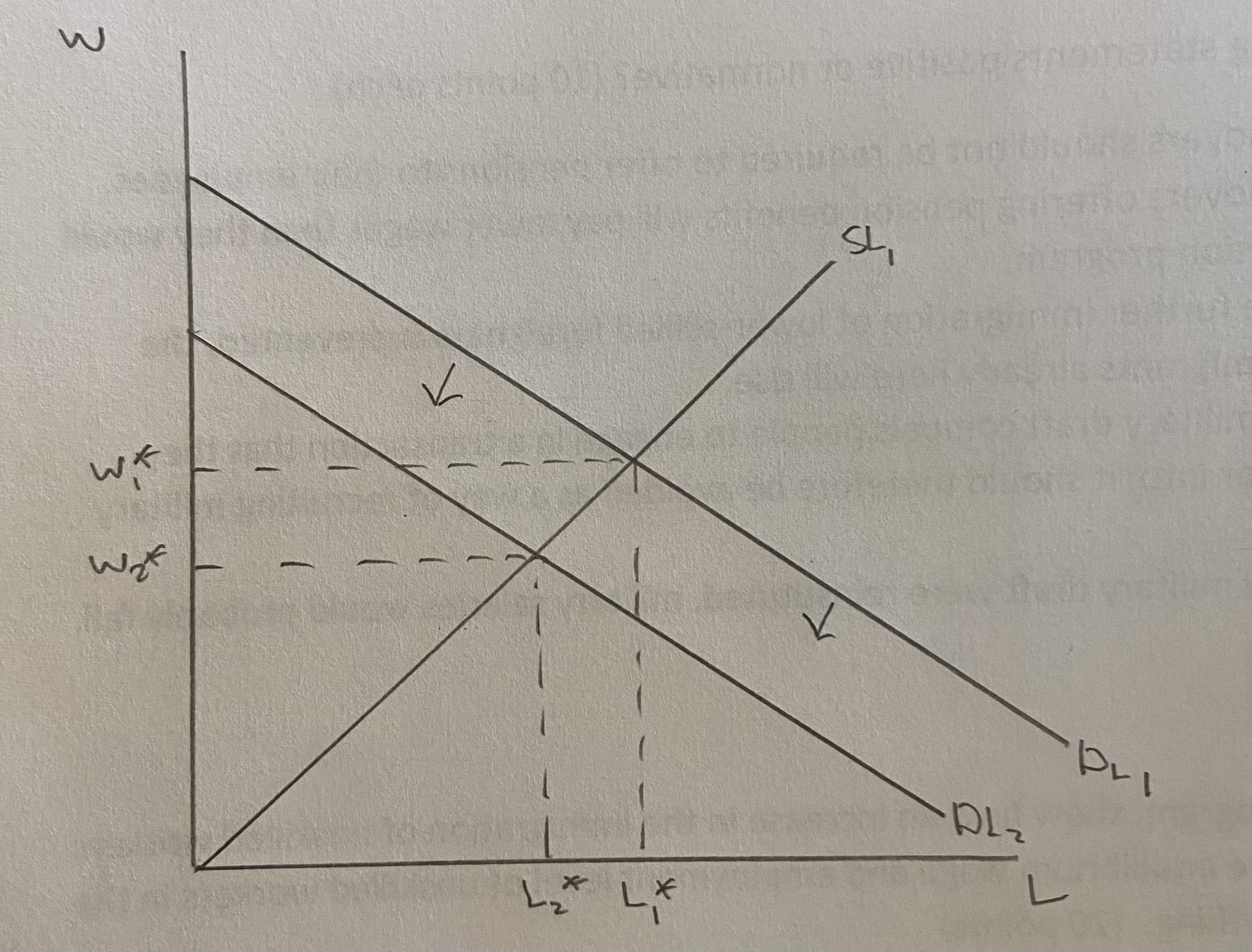
What would happen to the wages and employment level of engineers if the government expenditures on research and development programs were to fall? Show the effect graphically.
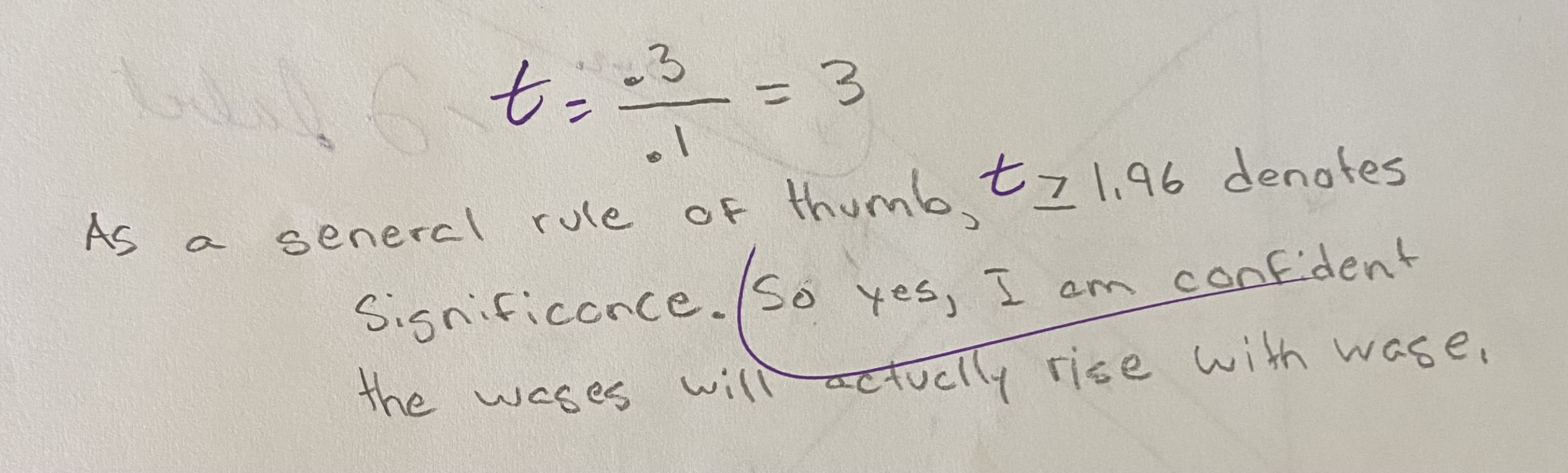
Suppose you estimate the following relationship between wages and age, where the standard error of the coefficient on Ai is 0.1. Are you confident that wages actually rise with age? Why or why not? Wi= -1 + 0.3Ai
P=MC
What is the profit-maximizing condition for a firm in the output market?
W/P = MP(L)
What is the short run profit-maximizing condition for a firm in the labor market?
W/MP(L) = r/MP(K)
What is a firm’s LR profit-maximizing condition in the terms of hiring labor and capital?
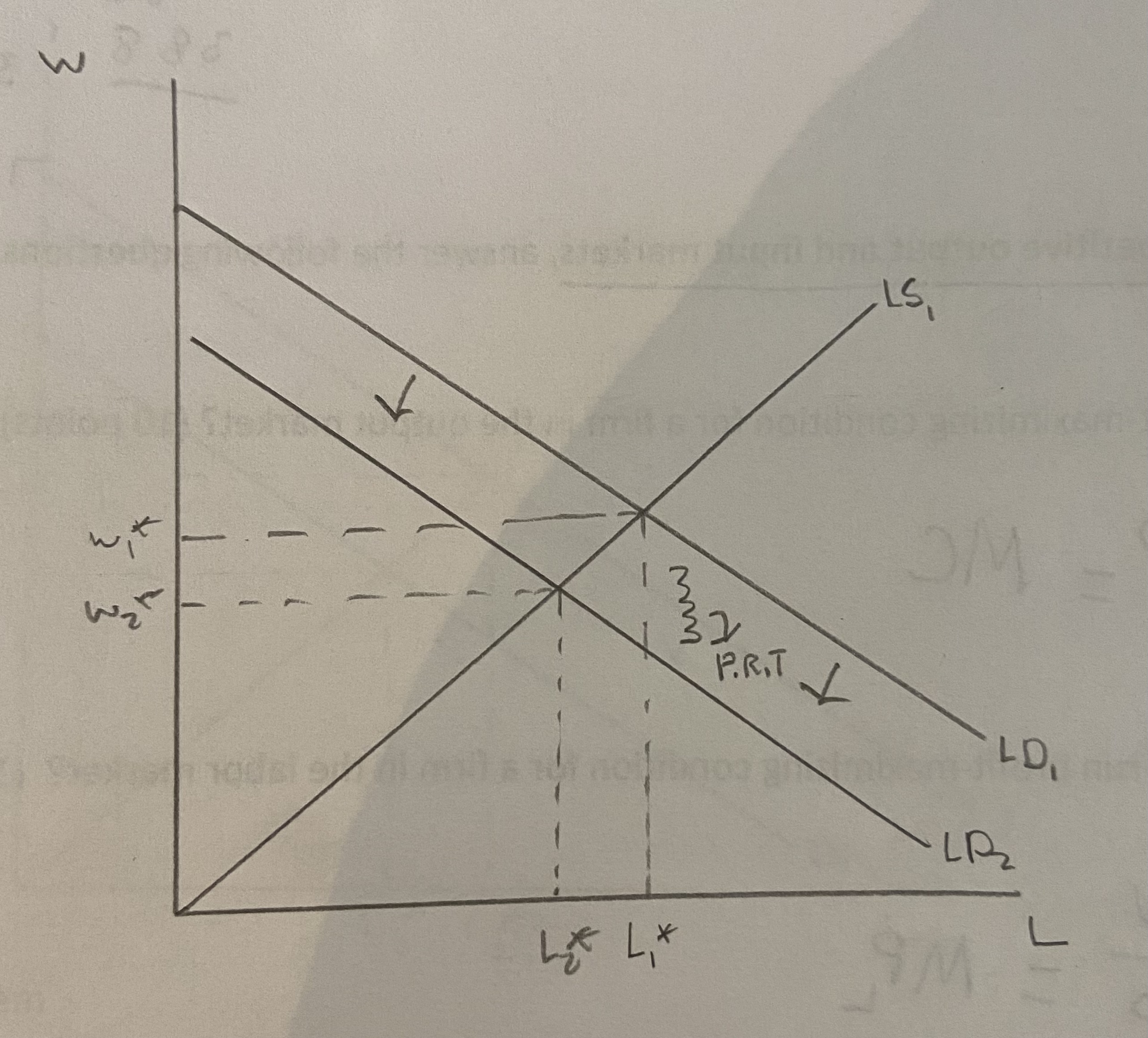
Using a supply and demand diagram, how does a payroll tax affect the equilibrium wage and level of employment?
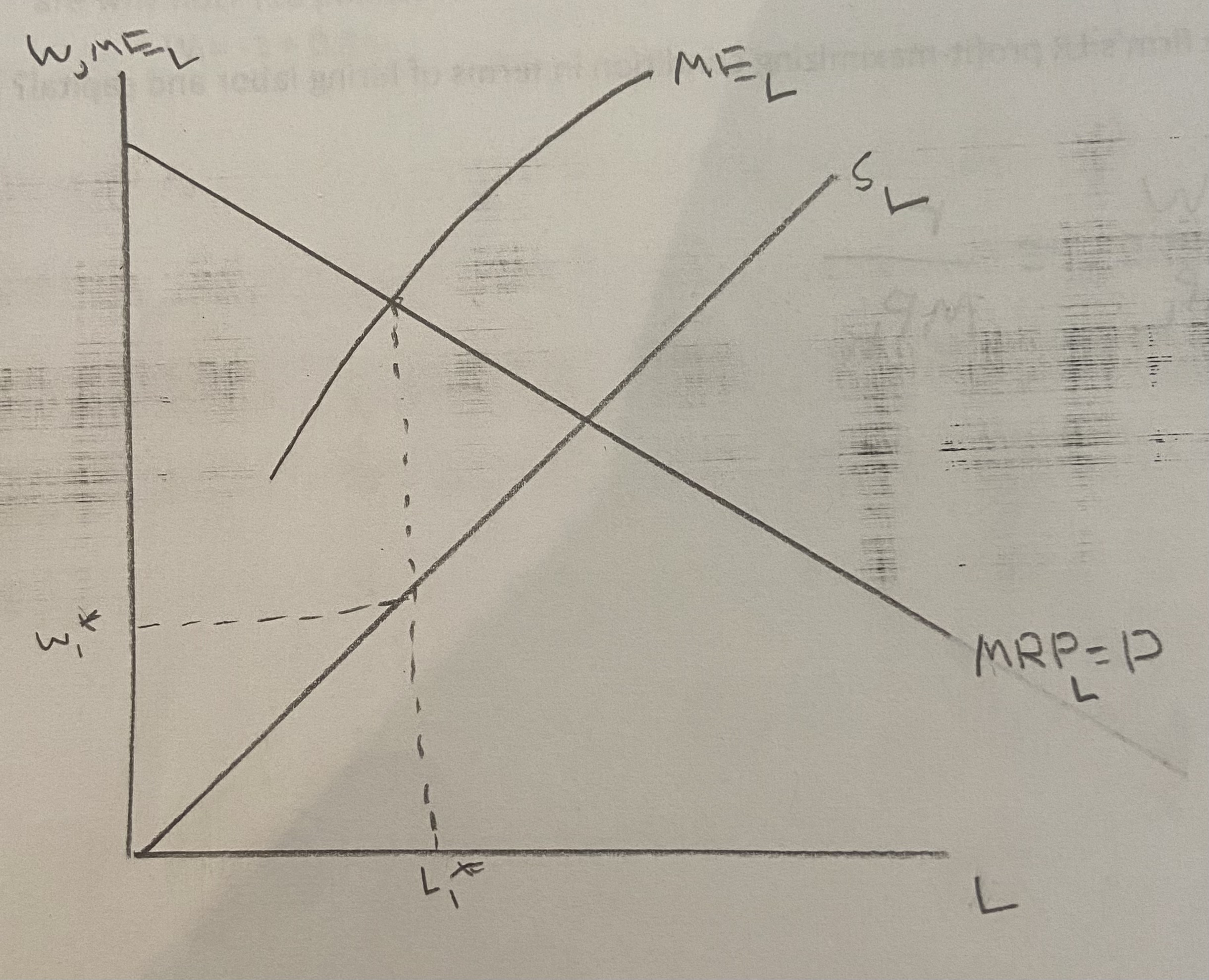
Using a graph, show how firms choose the level of employment and the wage to maximize profits under monopsonistic conditions.
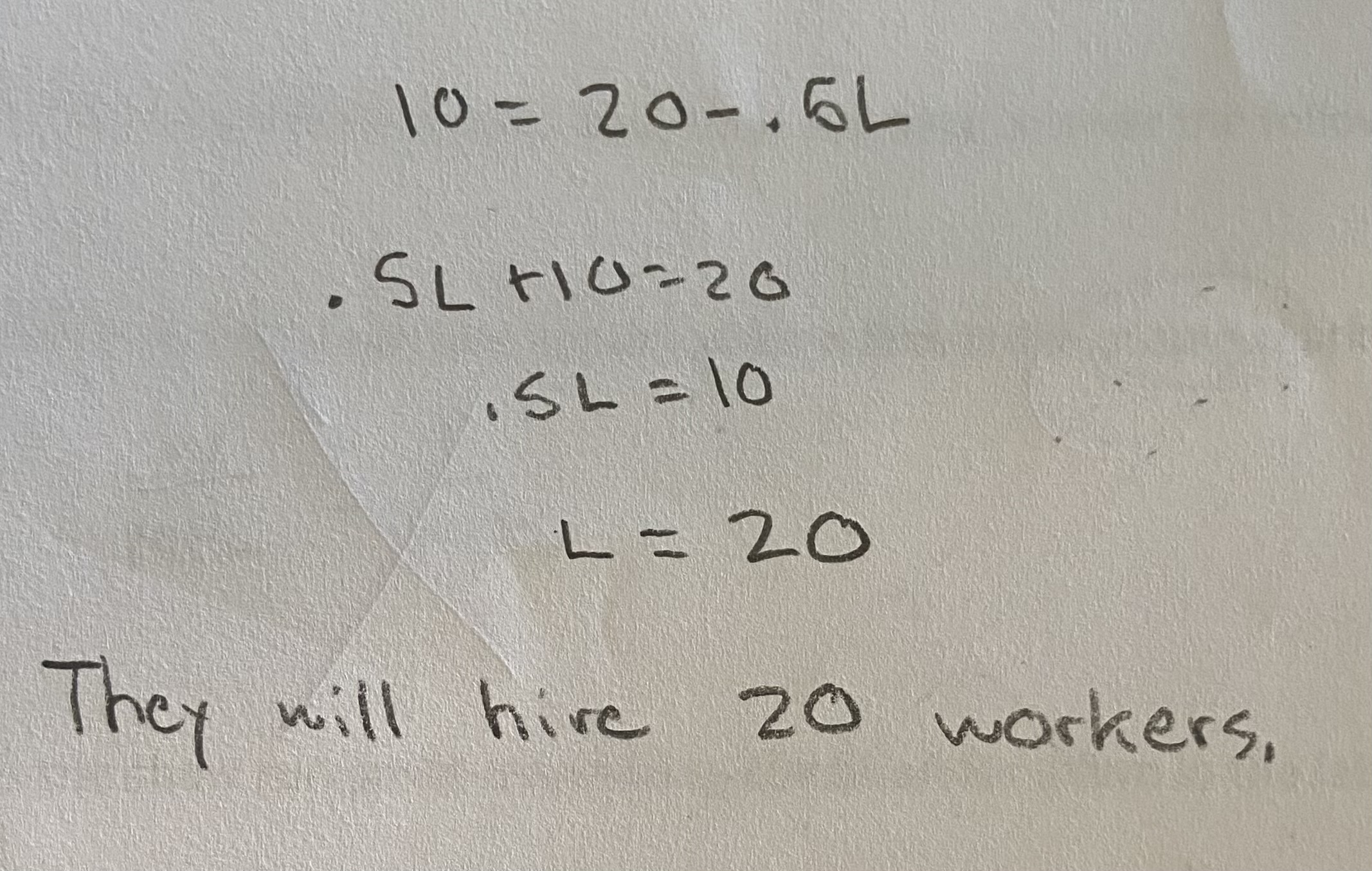
The marginal revenue product of labor at the kicak sawmill is MRPL= 20 - 0.5L, where L = the number of workers. If the wage of the sawmill workers is $10 per hour, how many workers will the mill hire?
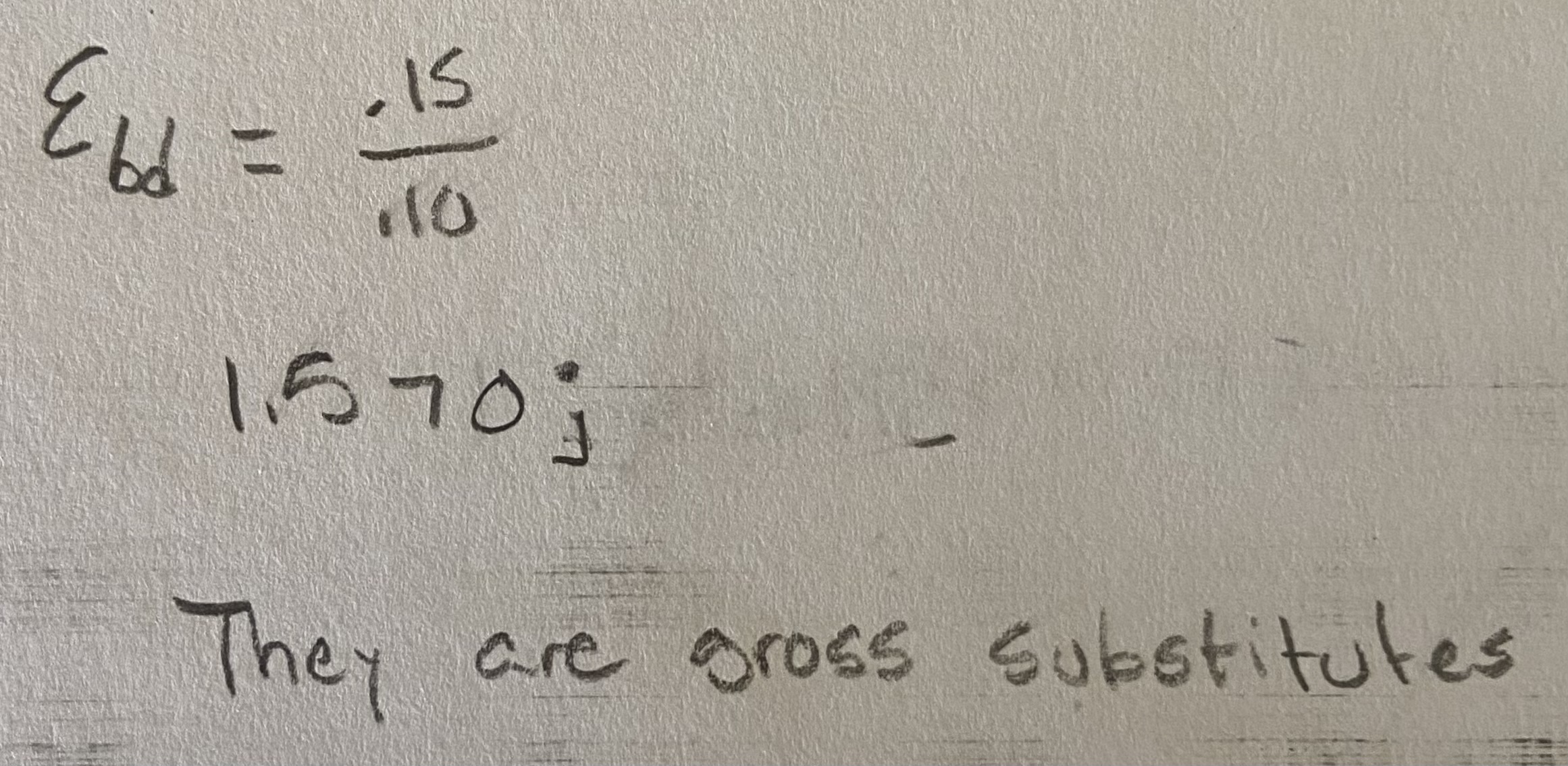
When the cost of dough-making machines fell by 10 percent, the demand for assistant bakers fell by 15 percent. What is the cross-wage elasticity of demand for assistant bakers in this case? Are assistant bakers and dough-making machines gross substitutes or gross compliments?
1) They don’t intersect
2) Convex to origin
3) Downwards sloping
What are the three characteristic of indifference curves that we discussed in class?
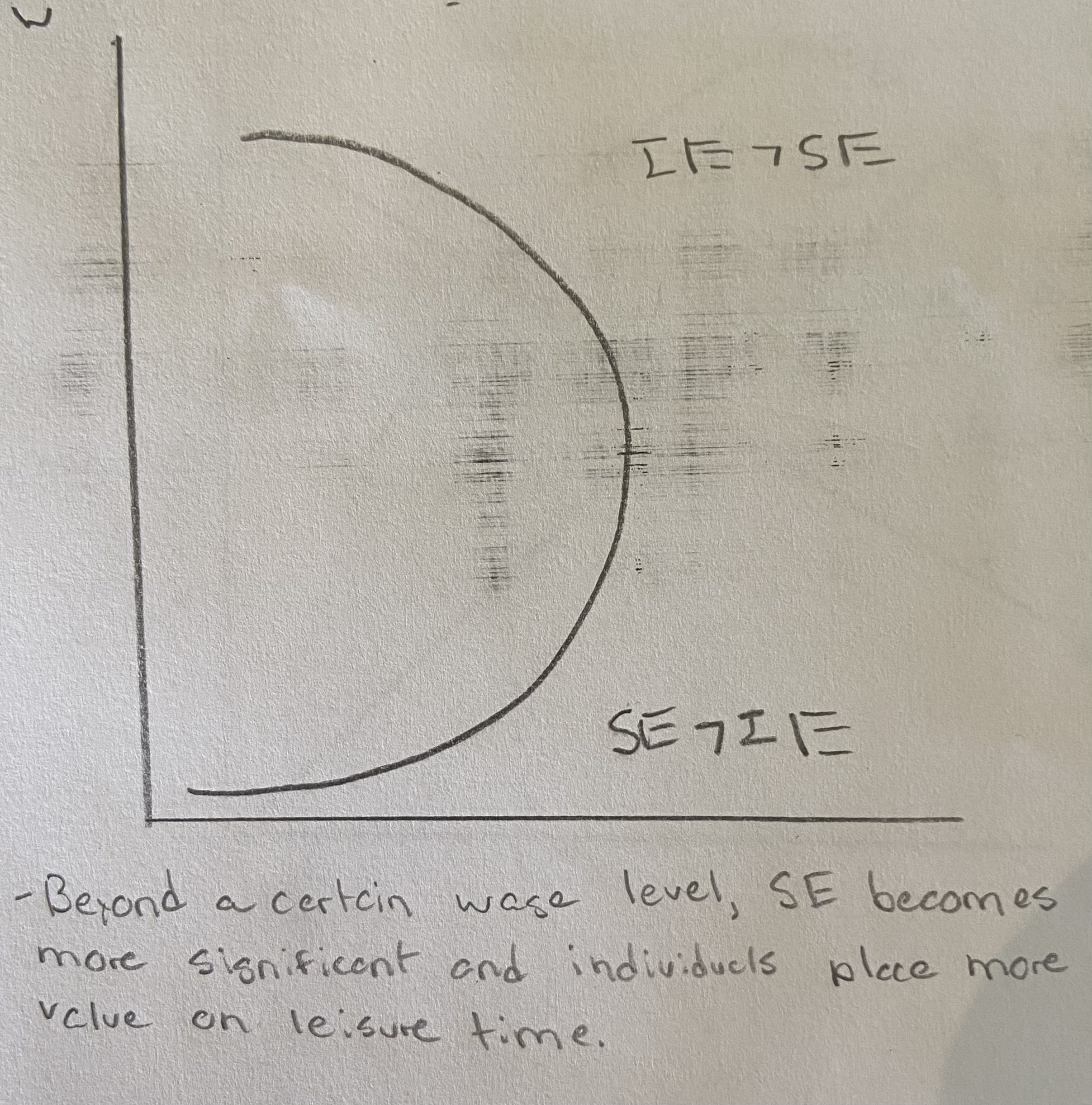
Graph and discuss in words how a person could have a backwards bending labor supply curve.
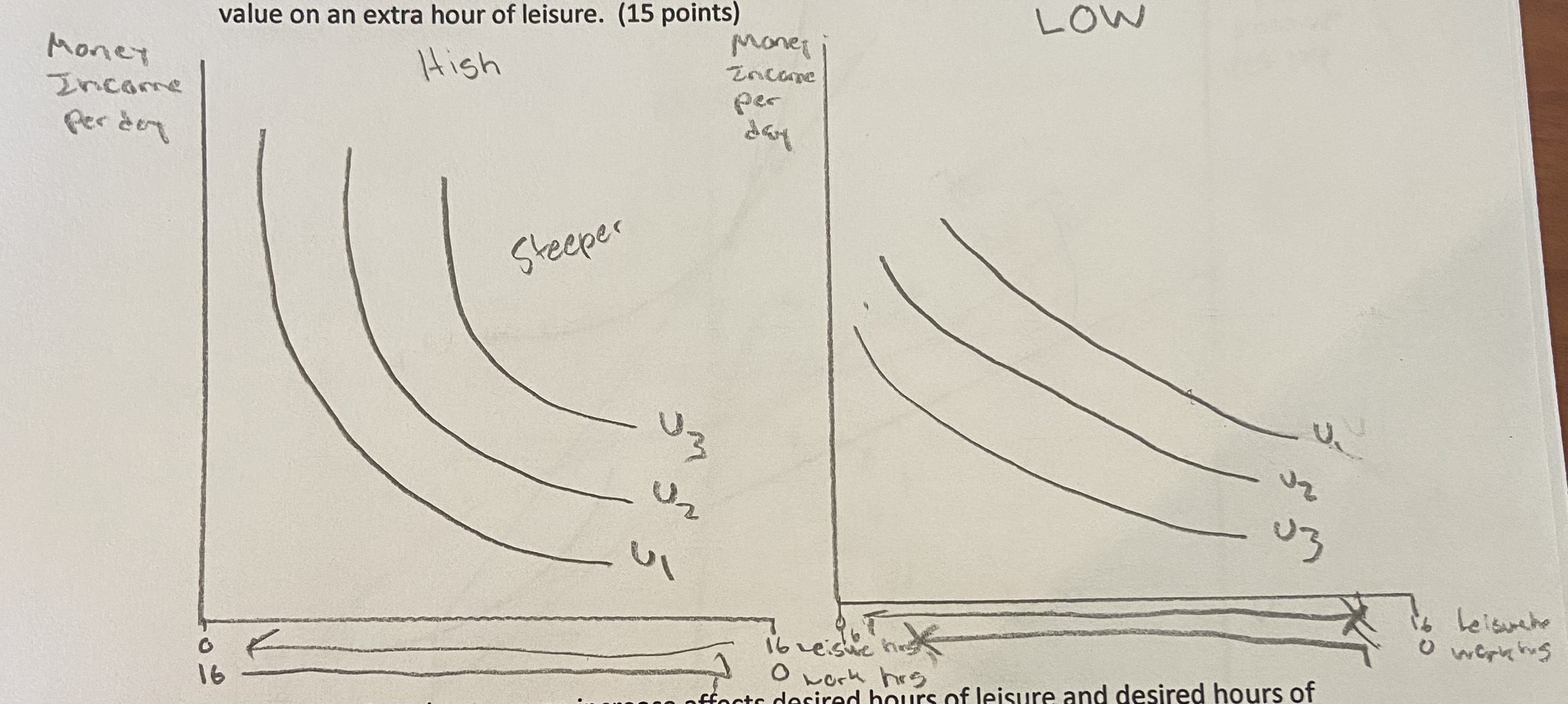
On two separate graphs, compare the indifferences curve maps of a person who places a high value on an extra hour of leisure and the indifference curve maps of a person who places a low value of an extra hour of leisure.
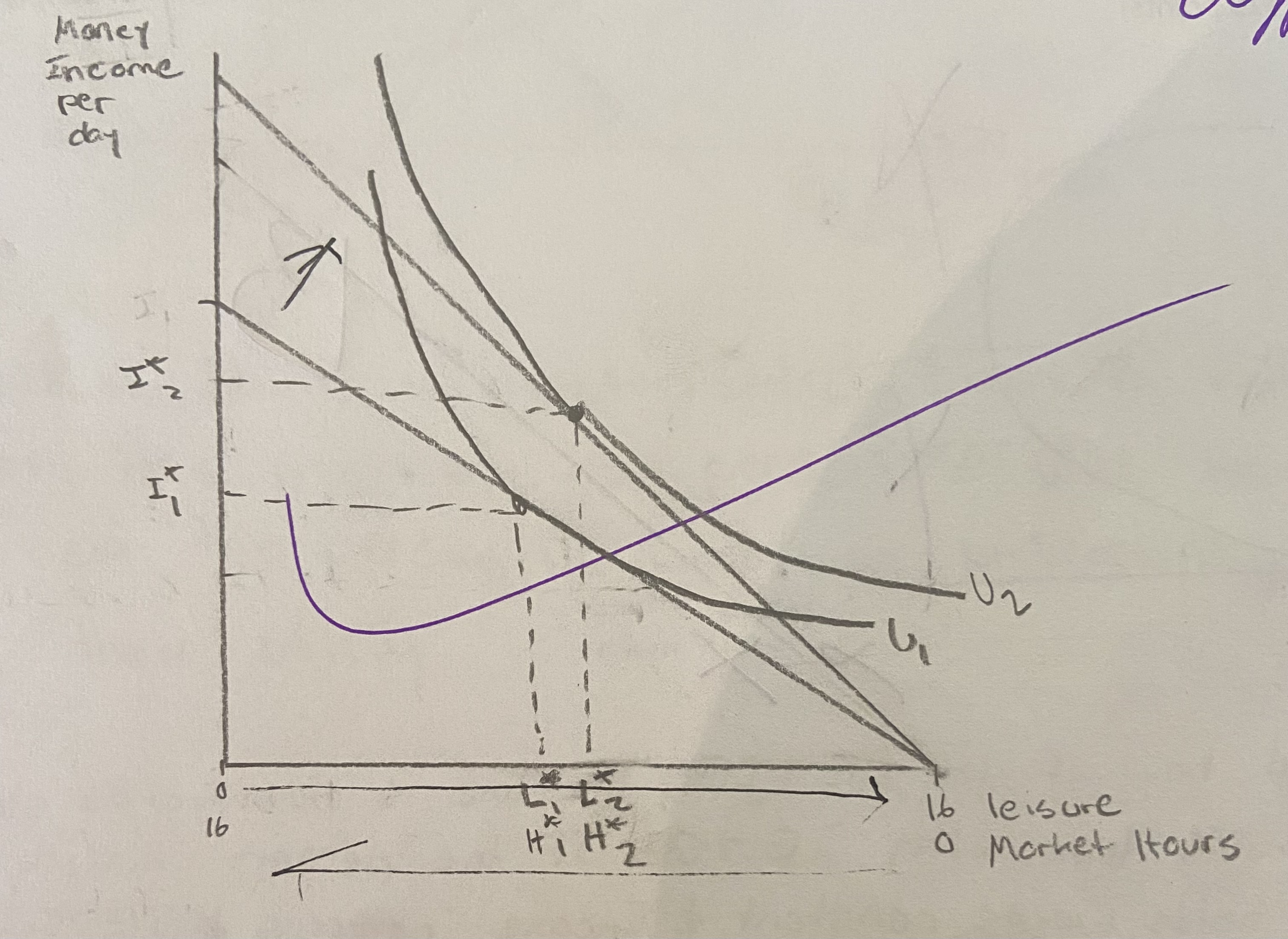
Graphically show how a wage increase affects desired hours of leisure and desired hours of market work, assuming the income effect is larger than the substitution effect.
Graphically show how the increased education of women in the post-WWII period increased women’s labor force participation.
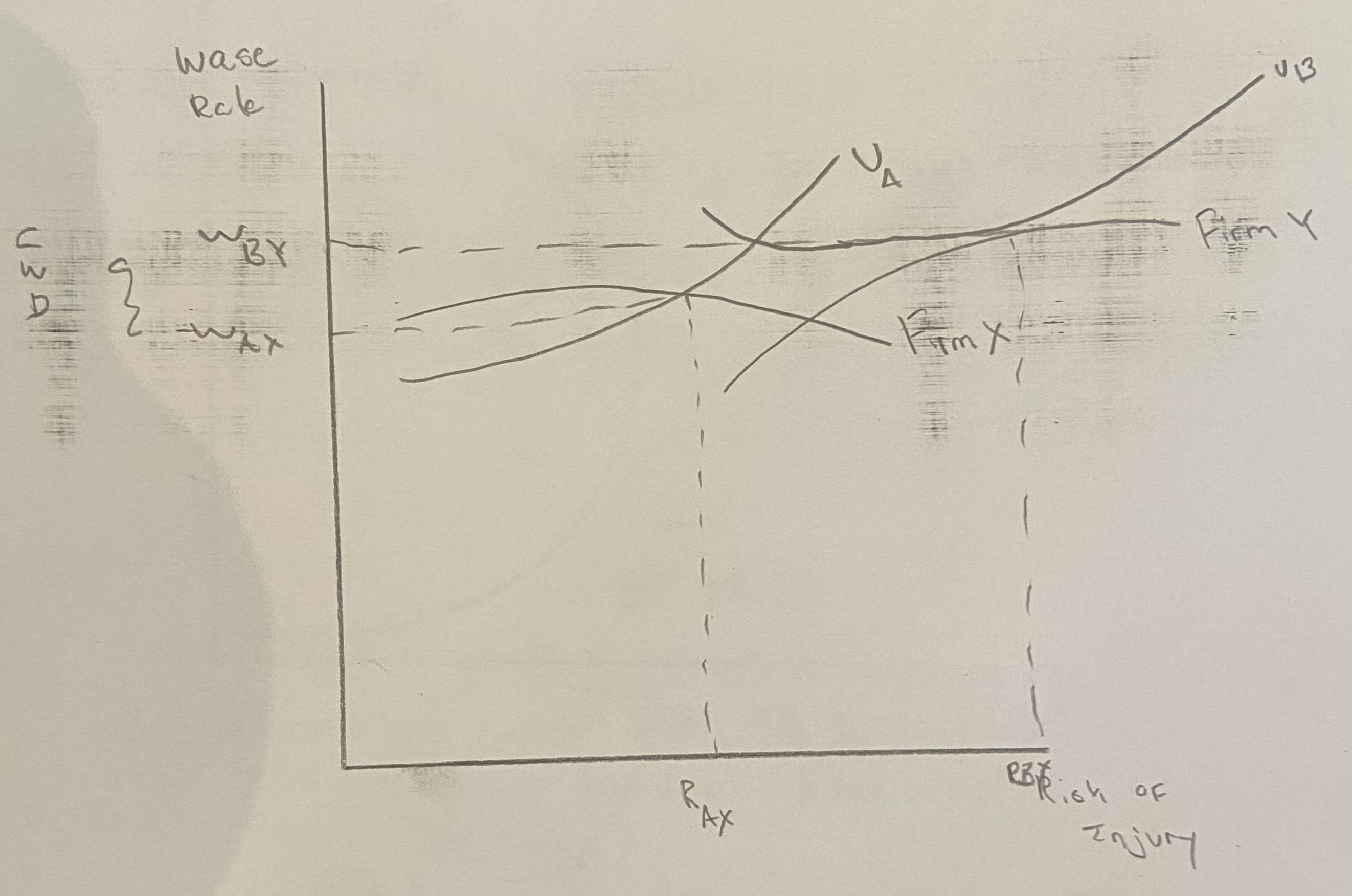
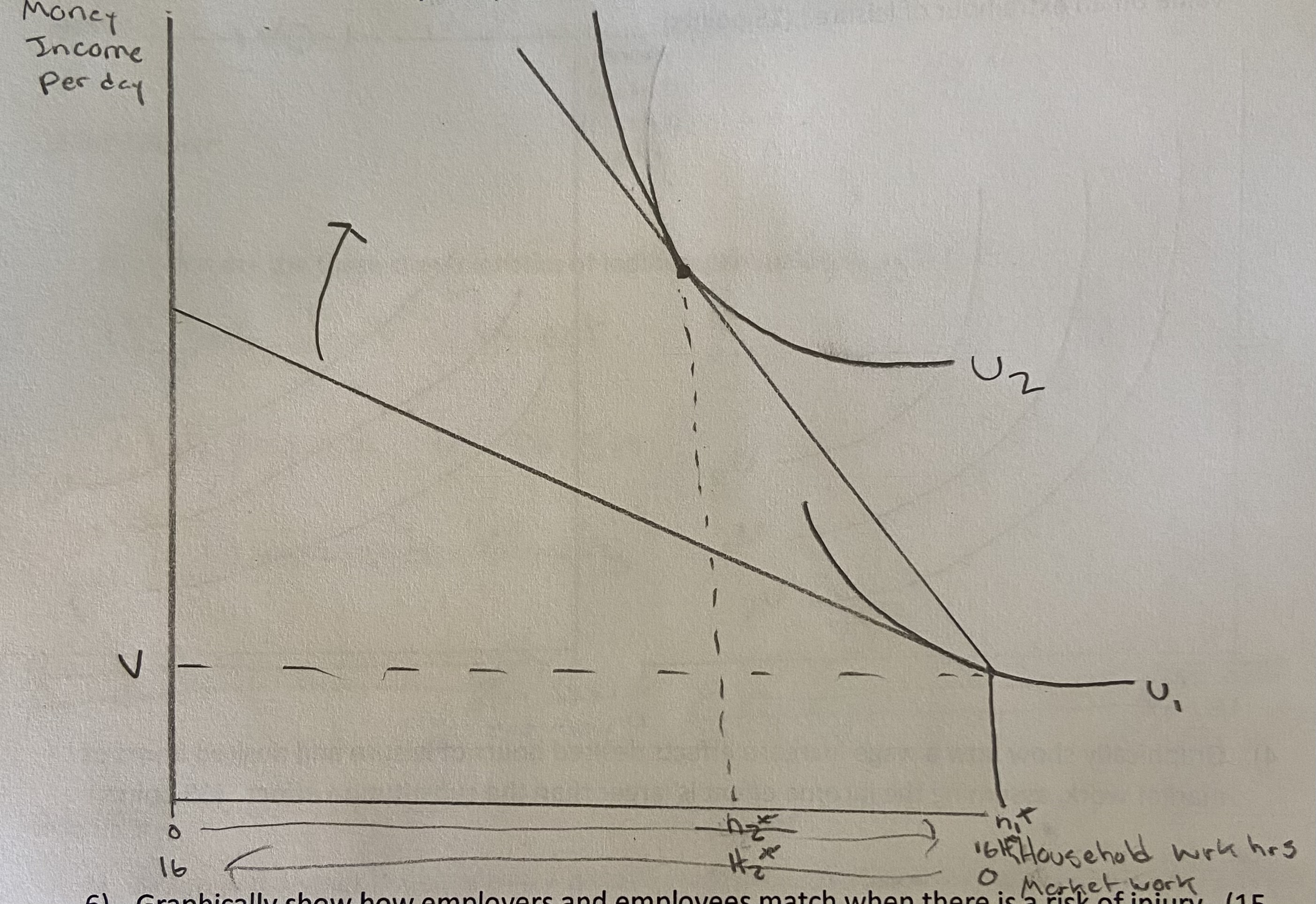
Graphically show how employers and employees match when there is a risk of injury.
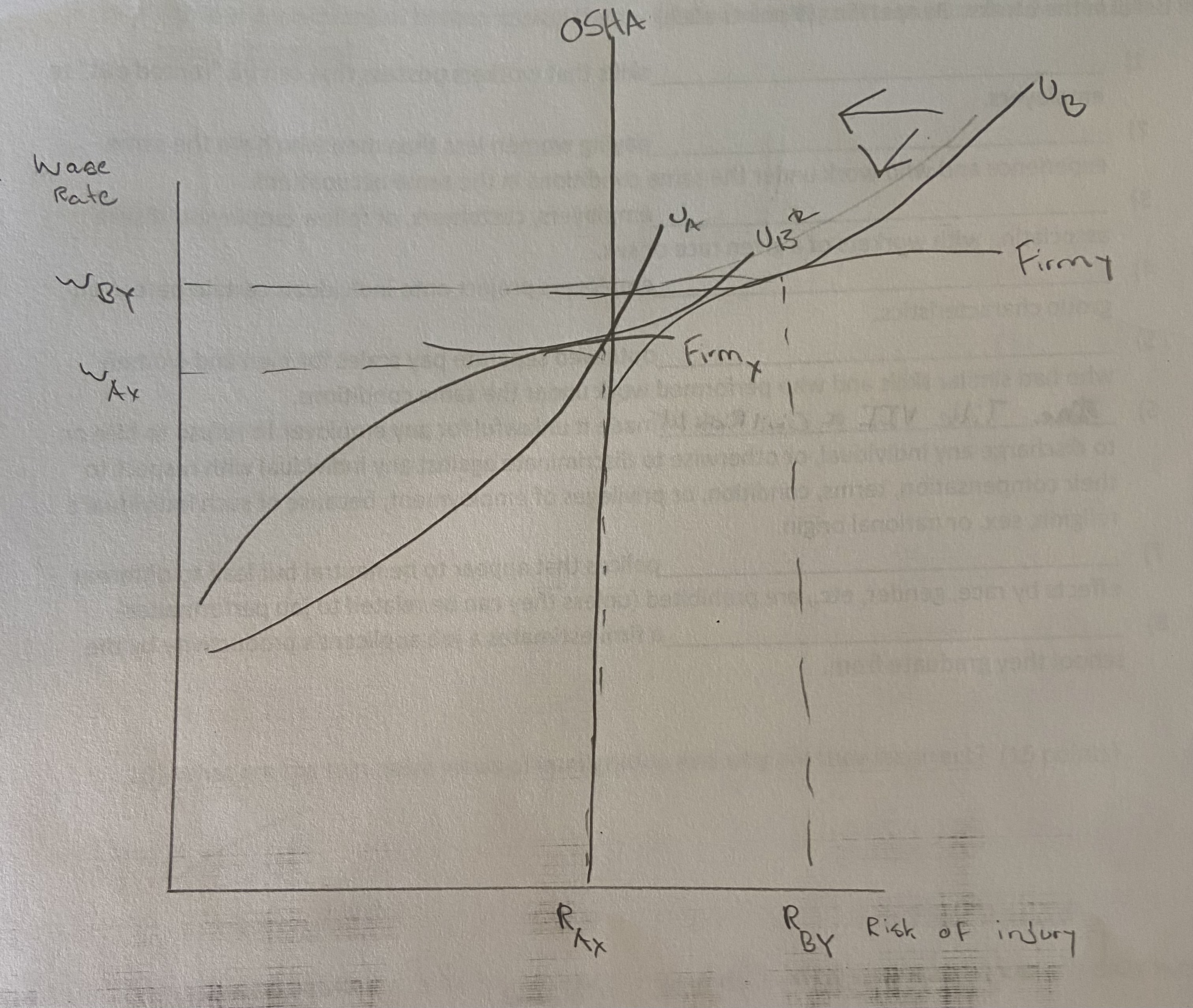
Graphically show how OSHA regulations can reduce a worker’s utility and drive a firm our of business.
Human Capital
Skills that workers possess that can be “rented out” to employers
Wage Discrimination
Paying women less than men who have the same experience and who work under the same conditions in the same occupations
Personal Prejudice
Employers, customers, or fellow employees dislike associating with workers of a given race or sex.
Statistical prejudgement
Employers project onto individuals a certain perceived group characteristics.
Equal Pay Act of 1963
Outlawed separate pay scales for men and women who had similar skills and who performed work under the same conditions.
Title VII of Civil Rights Act
Made it unlawful for any employer to refuse to hire or to discharge any individual, or otherwise to discriminate against any individual with respect to their compensation, terms, conditions, or privileges of employment because of such individual’s religion, sex, or national origin.
signaling
A firm estimates a job applicant’s productivity by the school they graduate from.
1) As college becomes more expensive, attendance will decrease, all else equal.
2) As the wage between High School grads and College grads widens, college attendance will increase, all else equal.
3) Most college students are young (large T), all else equal.
4) Those who have a high r rate are less likely to attend college (more present oriented, all else equal.)
List four predictions of human capital theory related to college attendance that we discussed in class.
1) Every employed undocumented immigrant deprives a citizen of a job —> If supply were reduced to domestic supply only, NOT ALL jobs lost will go to natives.
2) Undocumented immigrants only work jobs U.S citizens won’t work —> If the wage us high enough, U.S citizens will work almost EVERY job.
what are the two naive view of immigration and why are they incorrect?
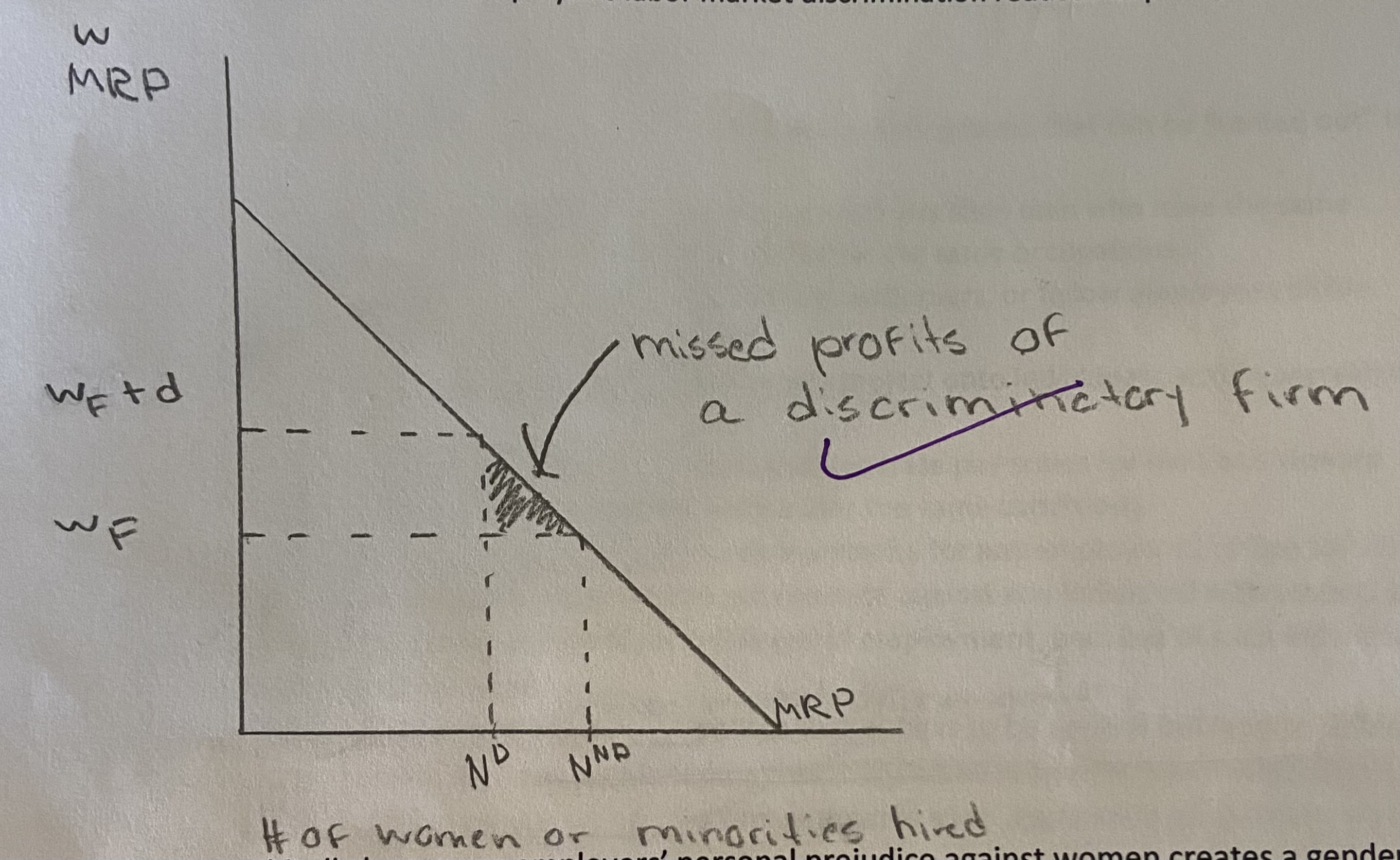
Show graphically how an employer’s labor market discrimination reduces its profits.
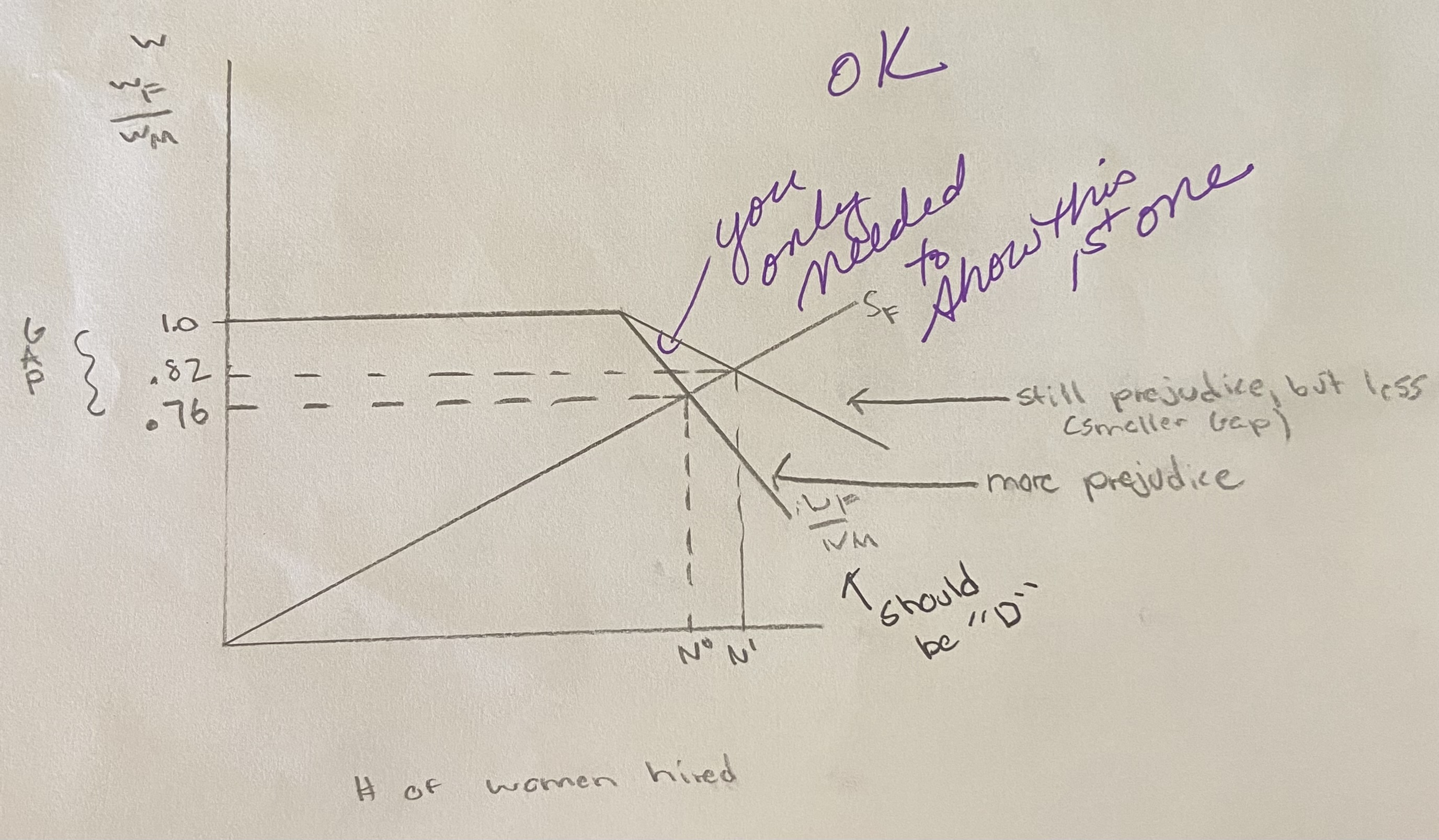
Show graphically how some eployers’ personal prejudice against women creates a gender wage gap.
Industrial Union
Represents most or all of the worker in an industry or firm regardless of their occupation
National Labor relations board
entity that has the power by law both to conduct union certification elections and to investigate claims against employers.
Right to work
Laws that prohibit the “union shop” requirement that a person become a union member as a condition of employment.
Efficient contracts
set of wage-employment combinations that at least one of the parties prefers and that would leave the other no worse off.
structural unemployment
Unemployment that arises when there is a mismatch between the skills demanded and supplied in a given area or an imbalance between the supplies of and demanded for workers across areas.
1) Firms need to operate successfully in the input and output markets
2) Substitution of capital for labor when increased compensation for workers happens.
state the two constraints on union objectives
1) Changes in the industrial mix
2) Competitive pressures
3) Regional shifts in employment
List the three reasons discussed in class for the decline of unionization of private sector workers in the U.S
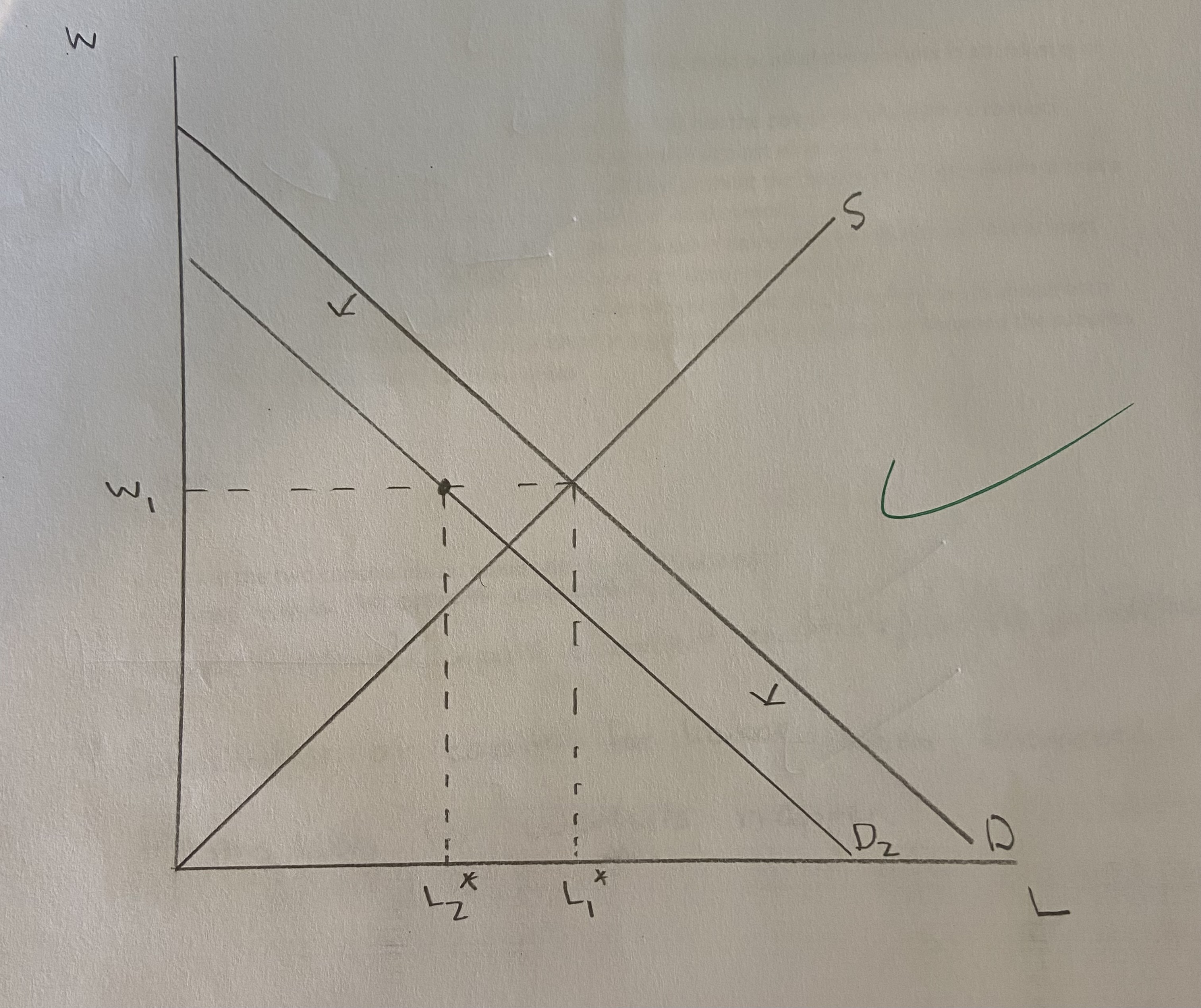
Use a demand-supply diagram to show how demand-deficient (cyclical) unemployment is created.
The Mist —> survivors: David, Billy, Amanda, and Dan.
BONUS QUESTION
The variance of the distribution: (Summation(Ei-E(BAR))²/N)
Measure of inequality
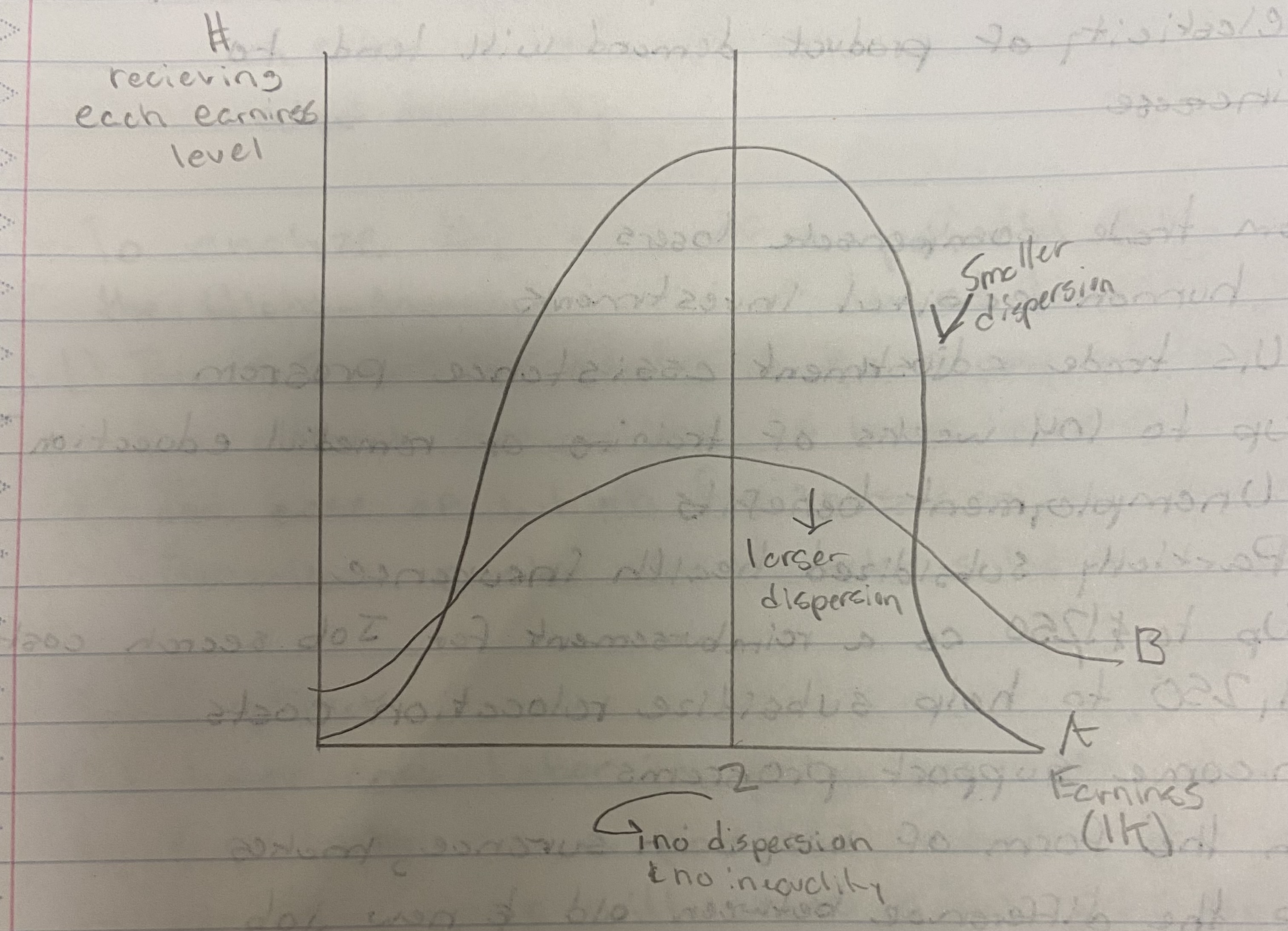
What does the variance of the distribution graph look like?
Ei= earning of person i in the population
n = the number of people in the population
E(BAR) = average level of earnings in the population
What do the inequality variables represent?
1) It tends to rise as earnings grow larger
2) If all earnings double, this measure would 4x
3) Variance is a better measure of the absolute than of the relative dispersion of earnings
What is a problem of using the variance of the distribution to measure inequality?
The coefficient of variation (St. D/Mean)
What is another measure of inequality?
1) Ranking the population by earnings level and establish into percentile a given earnings level falls
2)Compare the earnings level associated with each percentile and look at the ratio of earnings in 2 percentiles like the 80th and 20th to indicate how far apart the two ends of the distribution are & compare the ratios over time.
What are the most widely used measures of inequality?
1) The supply of less educated workers might’ve risen faster than the supply of college graduates, driving down the wages of less skilled workers
2) The demand for more educated workers might’ve increased relative to the demand of less educated workers
3) Changes in institutional forces such as the minimum wage or decline in unions, might’ve reduced the relative wage of less educated workers.
What are the three possible causes for the widening gap between the wages of highly educated and less educated workers?
Geographical dispersion of the various steps in the production process.
What is product sharing?
Comparative advantage, relative opportunity cost that determines who makes what.
Why does trade take place?
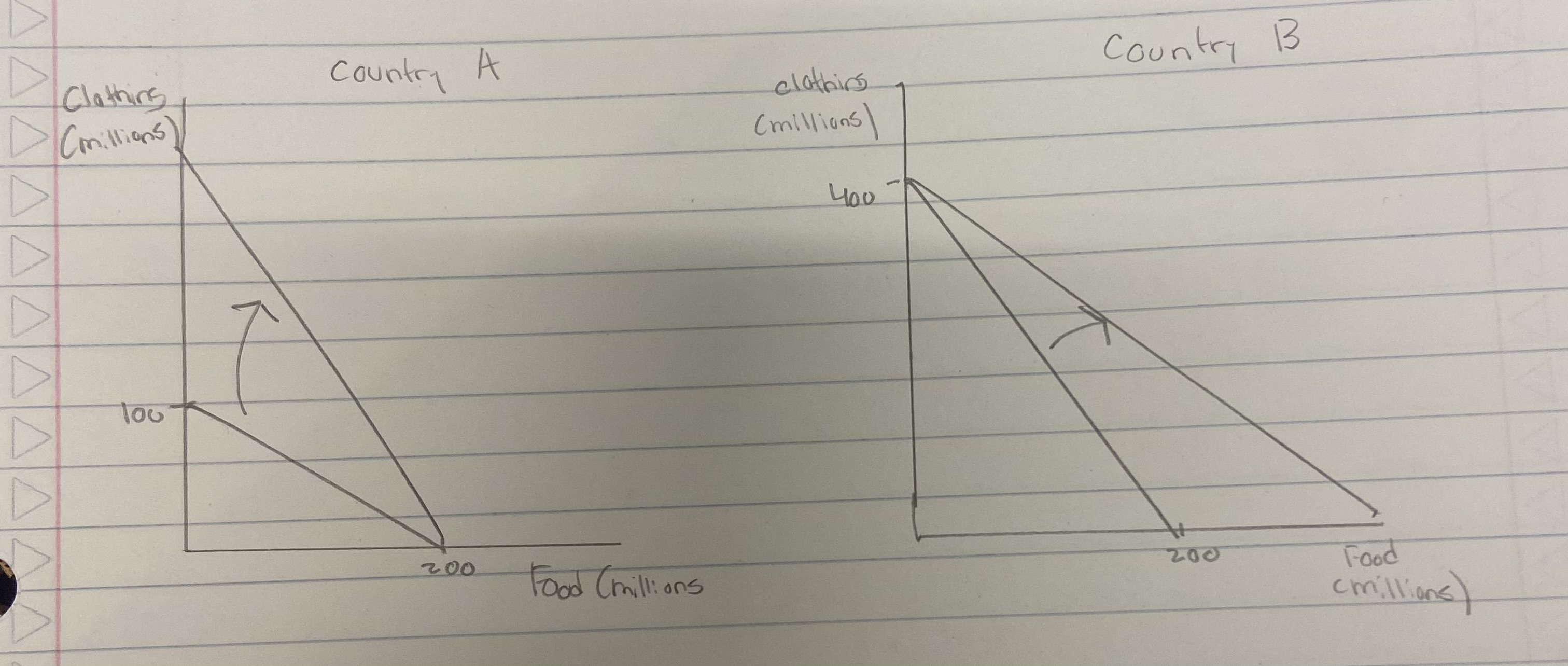
What does a trade graph of two countries look like?
1) Conditions in the product market
2) The prices and productivities of other factors of production
What is the demand for a given type of labor derived from?
1) Increase in trade —> Increase in imports & exports
2) An increase in exports will increase the demand for workers in the export sector which increases wages and employment
3) An increase in imports will decreases the demand of domestically produced goods and services which decreases demand, employment, and wages for workers in the input sector
What are the product demande shifters?
1) Many U.S firms have relocated all or parts of their production to poorer areas of the world
2) This production sharing has increased competition U.S workers face (cheaper labor)
3) When the cost of an alternative factor of production falls, there is a cross-wage effect on the demand for U.S labor, a combination of the substitution and scale effect
What are the shifts in the supply of alternative factors of production?
Wu.s/MPu.s = Wforeign/MPforeign
When does Profit Maximization occur with the SE?
1) The S.E will be greater if the supply of U.S workers to relevant occupations is more elastic
2) The ease of which foreigners can be substituted for Americans greater ease = greater substitution
what are the two Hick-Marshall laws of derived demand?
If lower-cost labor in poorer countries is substituted for U.S labor in a particular industry, the resulting fall in production will cause output price to decrease and a demand for all workers to increase.
How can the scale effect be seen?
1) Elasticity of demand for the final product in the industry cutting its labor costs
2) Share of foreign labor in total cost
What two factors does the size of the scale effect depend on?
1) Greater ability to substitute foreign labors for domestic labors will increase S.E, all else equal
2) As foreign made goods and services are allowed to compete with those produced domestically, elasticity of product demand will tend to increase
Decreasing barriers to international transactions will increase the elasticity of demand for labor by what two ways?
U.S trade adjustment assistance program
up to 104 weeks of training or remedial education
unemployment benefits
partially subsidized health insurance
1,250 USD for job search costs & relocation
Income support programs
In the form of wage insurance, makes up the difference between old and new job
Focused on older workers
Subsidized employment
Government can become the employment of last resort
How does the united states compensate “losers” of foreign trade?