Economics 6th lecture
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
What is the overall goal of healthcare systems?
Equity( s a fair way to distribute healthcare?)
Similar healthcare services for similar health conditions
Does not depend on irrelevant factors (e.g.age, gender, etc.)
efficiency
Macro-efficiency
How much to spend on healthcare?( its abt allocative resources)
During negotiations on how to allocate the government budget for the next four years, a heated debate emerges between the minister for education and the minister of defence. The minister for education is angry that too many resources are dedicated to new missiles, while there are still not enough teachers.
micro-efficiency
is about whether it is more efficient to spend resources in one policy area, rather than another. I.e. macro-efficiency.
is about the most efficient way to allocate resources within a particular policy areas.
Why state intervention?
Challenges of private provision ( private hospitals, doctors)
Imperfect information
Bounded rationality / willpower
Bounded rationality/willpower
Can I process all that info (without becoming a doctor)?
Difficult to screen prices if you’re bleeding on the road...
Procrastination in seeking care
Imperfect information
How much care do I need?
Do I receive good care?
What is a normal price?
Challenges of private insurance
certainty rather than risk
moral hazard
adverse selection
Certainty rather than risk ( challenge of private insurance)
E.g. chronic diseases; pre-existing conditions; etc.
In these cases, often not possible to buy insurance in markets
Adverse selection
With higher prices, only ‘bad risks’ will buy voluntarily (driving up prices even more...)
Cream-skimming drives out those with high risks
Moral Hazard
Patients can influence the probability of requiring treatment after having been insured(e.g. taking fewer health precautions; consulting your GP with every cough or itch; over-use of elective treatments; etc.)
Patients and doctors can influence the cost of medical treatment => THIRD PARTY PAYMENT PROBLEM
Third part payment problem
Result is overconsumption of healthcare
With ‘zero private costs’ for patients and doctors, they have an incentive to consume more than optimal given positive social costs of healthcare
Healthcare providers and consumers engage in overconsumption when they don’t face the cost of healthcare
because insurance company has imperfect information about decisions made by doctors and patient
because doctors are paid a fee for service by the insurer
Why would the state intervene in private insurance?
When treating healthcare insurance as normal, you probably end up with inefficient and inequitable coverage
Private healthcare systems
market-based provision and insurance
Public healthcare systems
government runs provision and insurance
Mixed healthcare systems
government-led; but role for market-competition
How to evaluate healthcare systems? ( what makes them most successful)
cost containment
equitable access to healthcare
minimizing waiting lists
offering consumer choice
Is there a role for markets in healthcare?
They are in charged of empirically-informed evaluation of healthcare systems
Reasons for rising healthcare spending
Medical technology advances
Demographic change
The third-party payment problem
Medical technology advances ( Reasons for rising healthcare spending )
technology improves, but it also gets more expensive
When not to use it?
Allocative efficiency?
Demographic change
population aging
Elderly generally require more care and more expensive treatment
Explain the third party payment problem
it appears whenn healthcare providers and consumers engage in overconsumption when they don’t face the cost of healthcare
Equitable access to healthcare (challenge of healthcare system)
Low income
Geographical inequalities
Medical conditions
Containing waiting list (challenge of healthcare system)
Delayed diagnosis and treatment
Different waiting times across socio-economic groups
Consumer choice ( challenge of healthcare system)
Better compliance with treatment
Different tastes
Improve responsiveness
Why there is no perfect health system?
because we do not live in first-best world – so some level of inefficiency and inequity is unavoidable.
The description of private healthcare systems
health system as any other marketplace
competition welcome
Competition in healthcare provision
and insurance
USA ( but there are no country that completely rely on private healthcare systems)
price mechanisms - low quality
adverse selection
many people are not able to pay it
What is the biggest problem in private healthcare systems?
Adverse selection, that leaves many without healthcare insurance, exposing them to high medical expenses ( usa)
What do companies do when there is a Third-party party payment problem within the health care system?
insurance companies often restrict the provision (known as ‘managed care’)
The check list of private healthcare system
cost containment - PROBLEM
equitable access - PROBLEM
waiting list - OK
choice - OK
Medicare
65+ (as well as pregnant women, disabled, etc.) underserved groups by private provisions
healthcare reform in USA
mid 1960s
Medicaid
low income households
What was the problem during the health system reforms ?
Rising healthcare expenditure - Public finance, but still private provision (3rd party payment problems)
Early reforms of public programs to control costs
From retrospective to prospective payment
e.g. DRG (diagnosis-related groups) - fixed prices
Managed Care
Through managed care, insurance companies aim to control the decisions made by patients and healthcare providers.
Prior authorization - insurance company needs to improve in advance if a drug or surgery is needed
Deductibles - the amount the household needs to pay by it pocket ( to co ja mam 386euro)
Managed Care aims at mitigating moral hazard; Yet strict application reduces access.
It refers to those strategies used by healthcare insurers to mitigate the challenges of third-party-payment problems (this by having more control over the decisions made by patients and healthcare providers).
Obamacare ( 2010) Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act
Steering outcomes in the health insurance market through regulation and subsidies; for example
a) Prohibiting refusal of pre-existing conditions - no refusal to potential clientsb) Individual mandate
Public healthcare systems
finance through general taxation
no fee for services
UK, several Scandinavian countries
How do public healthcare systems deal with market failures?
well
Coverage is universal: treatment is free and no one is denied access
Controlling costs is easier:
Tax -financing allows for budget control
Public financing and no fee for service: less Third-Party Payment Incentives
What are the drawbacks of public healthcare system ?
Inadequate healthcare spending can create problems( especially when the govermnet is under pressure)
Long waiting lists are a reoccurring challenge ( strikes)
Limited consumer choice – few opportunities to go elsewhere
UK healthcare reforms
Pre 1990s UK healthcare reforms
NHS is organized through centralized top-down planning by the government ( made by politicians )
Proposed reforms in uk healthcare system since 1990s
Introducing more choices for patients & more competition on the supply side (quasi-markets)
Critics: patients are not informed – so competition will create opportunities for over-treatment
Advocates: choice and competition will
increase responsiveness (hence higher quality
for lower costs)
Mixed Healthacre systems ( description)
Germany, the Netherlands, Canada
Market-based competition to increase efficiency Yet public intervention to reduce problems with market failures
The third payment party problem ; (
Generally private provision and fee for service
yet public financing
Social insurance and tax financing
What is the biggest problem in mixed healthcare systems?
Cost containment is the main challenge - Public financing for private provision and fee for service (Third-party payment problem)
Managed care (e.g. deductibles)
Regulation (e.g. budget caps)
Healthcare reforms in the Netherlands
Tradition: Private provision + public and private insurance
Unequal access ( those who earned more were getting private insurance and those who did not were using the public one)
Escalating healthcare expenditure ( rosnace wydatki na opieke zdrowotna)
What was the report by Dekker Commission (1987)
He reported that the system too inefficient and inflexible
Insufficient incentives to reduce costs
Recommended market-based reform
What was the healthacre reform in the Netherlands?
2006 Health Insurance Act (Zorgverzekeringwet)- Managed competition in healthcare provision as well as in healthcare insurance!
2006 Health Insurance Act (Zorgverzekeringwet)
Introducing market elements, but in a heavily regulated manner:
Private insurers have to compete for patients (on price/package content)
But they cannot refuse patients (to avoid adverse selection, so they do not include only healthy people ( avoiding cream-skimming))
Competition based on premium encouraged, but no differentiation between risks allowed (‘community rating’)
Buying insurance is mandatory (to avoid adverse selection)- those with lower risks still need to stay in a risk pool
Basic package of coverage is set by law
Co-payment and deductibles allowed (to mitigate moral hazard)
the overall of healthcare systems
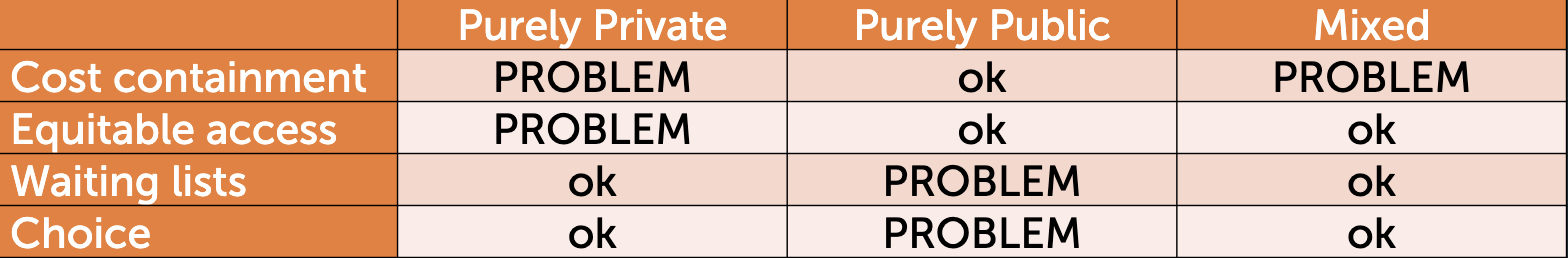
What is the risk of mixed health care systems?
Underspending
Longer waiting lists and pressure on access
Reduced quality of care
Job policymakers of healthcare systems?
Choosing the least bad option based on previous theory and experience
Do markets have a role to play in healthcare provision?( mixed healthcare systems)
Market failures in healthcare provision and insurance are prevalent; so purely market-based health systems have predictable problems (high costs; low coverage)
state intervention is desirable!!
Is State intervention needed in mixed healthcare systems?
One takeaway- public financing is always necessary (both equity and efficiency)
Another takeaway - public provision is not always necessary
Will introducing market elements (like competition between providers or insurers) bring better results
Where does the main payment for healthcare services take place in a private healthcare system with private health insurance?
Healthcare providers (hospital) ←> healthcare insurer
the provision of healthcare services ( USA)
healtcare providers(hospital)←>consumers(patiens)
What was the main conclusion of the 1987 Dekker Committee report, which shaped healthcare reforms in the Netherlands throughout the coming decades?
The whole system had become too inefficient and inflexible; without incentives to replace expensive care with less expensive but equally effective care.
How to resorve the problem proposed by 1987 Dekker Committee report?
the Committee recommended a market-based reform that would offer insurers and providers more room for entrepreneurship and consumers more freedom of choice.
Why do countries with mixed healthcare systems tend to face third-party-payment challenges?
Private providers ask a fee-for-service, which is paid for through public insurance.
Third-party payment challenges emerge when providers receive a fee-for-service (hence an incentive to overprescribe) and insurers have imperfect information of the decisions made by providers (as would be the case in a mixed system with public insurance yet private provision).
Which of the following is NOT a good rationale for expanding consumer choice in healthcare systems?
Governments seek to help people dealing with bounded rationality.
What are the good rationale for expanding consumer choice in healthcare systems?
Governments seek to encourage responsiveness of providers. ( if they are unhappy let them choose someone different)
Governments seek to encourage compliance with treatments.
Governments seek to accommodate people with different preferences.
Which of the following healthcare systems is most likely to keep rising healthcare spending under control?
A public system run completely by the government, where healthcare providers receive fixed salaries (so no fee for service)
From the perspective of a healthcare insurer, for whom of the following people is ‘adverse selection’ most likely to be an issue?
The middle-aged women who lost her mother and grandmother to cancer.
Adverse selection is about the ability to hide information before setting up a contract. Physical disabilities, age and weight are more difficult to hide than information about family history.
magine that you work as a policy officer in the department for healthcare.
You receive the results from a survey by the consumer association, showing that 40% of people do not seek healthcare because they are overwhelmed by the range of private healthcare options. They call for a large-scale information campaign to inform people about these options.
Based on insights from welfare economics, which of the following policy responses is most effective?
Explore other policy options, since a large-scale information campaign is not likely to address the issue.
The underlying market failure is bounded rationality (failing to make a rational decision as a result of information overload and limited capacity to process all this information). An information campaign is not addressing bounded rationality (and providing more information could even make the problem worse).
technical efficiency
ensuring that resources are used in the most efficient way to achieve desired outcome : wealth money
Ensures that goods and services are produced in the most cost-effective way, minimizing the use of resources and reducing production costs.
Productive efficiency (micro-efficiency)
Achieving the best outcomes with given resources : ensuring hospitals and healthcare use budget effectively
how to spend your resources
how to spend your resources?
Allocative efficiency (micro-efficiency)
where we put resources to have the best outcome
where to spend your resources?