Pulmonary Function Testing (PFT)
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
what does spirometry measure?
airflow and lung volumes
why do we measure spirometry?
- to determine the amount of residual volume
- to assess if the lungs are affected by disease progression
what is tidal volume?
the amount of air inhaled and exhaled during normal breathing
what is inspiratory reserve volume?
the amount of air that can be inhaled maximally above normal tidal volume
what is expiratory reserve volume?
the amount of air that can be forcefully exhaled past tidal volume
what is residual volume?
the amount of air left over aver maximal expiration in the lung
can residual volume be measured via spirometry?
nope
what is total lung capacity?
all 4 lung volumes combined
TV + IRV + ERV + RV
what is functional residual capacity?
amount of air remaining after expelling a tidal breath
Expiratory Volume + Residual volume
what is inspiratory capacity?
Inspiratory reserve + tidal volume
what is vital capacity?
the difference between maximal inspiratory and maximal expiratory volumes
what is the most common type of PFT?
spirometry
what is forced vital capacity (FVC)?
the volume air that can be forcibly expired after a maximal inspiration
what is forced expiratory volume in 1 second? (FEV1)
this is the volume of air that can be forcefully expired in 1 second after maximal inspiration
what corrects the differences in lung size and capacities?
FEV1/FVC
what is FEV 25-75?
this is maximal expiratory flow rate between 25-75% of FVC
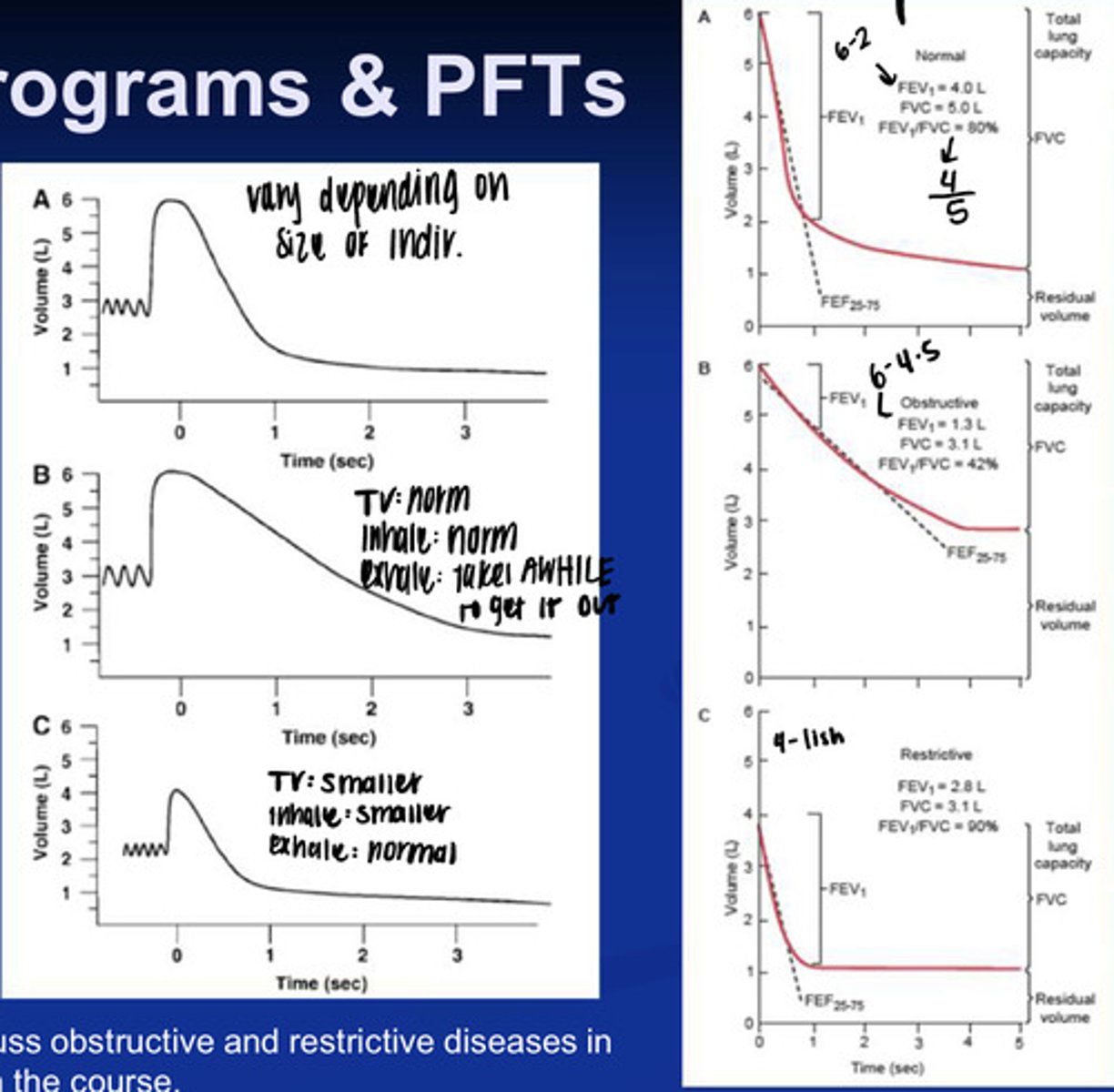
what is an obstructive lung disorder? what might this look like on a graph?
- this is a disorder causing trouble getting air out of the lungs (COPD, Emphysema, etc).
- so for this one you'd have a decrease in the amount of air you can forcefully expire after max inspiration (Decreased FEV1)
- you'd have a decrease in the Forced vital capacity (because you cant push much out)
- and a decrease in the FEV1/FVC because you aren't pushing much air out
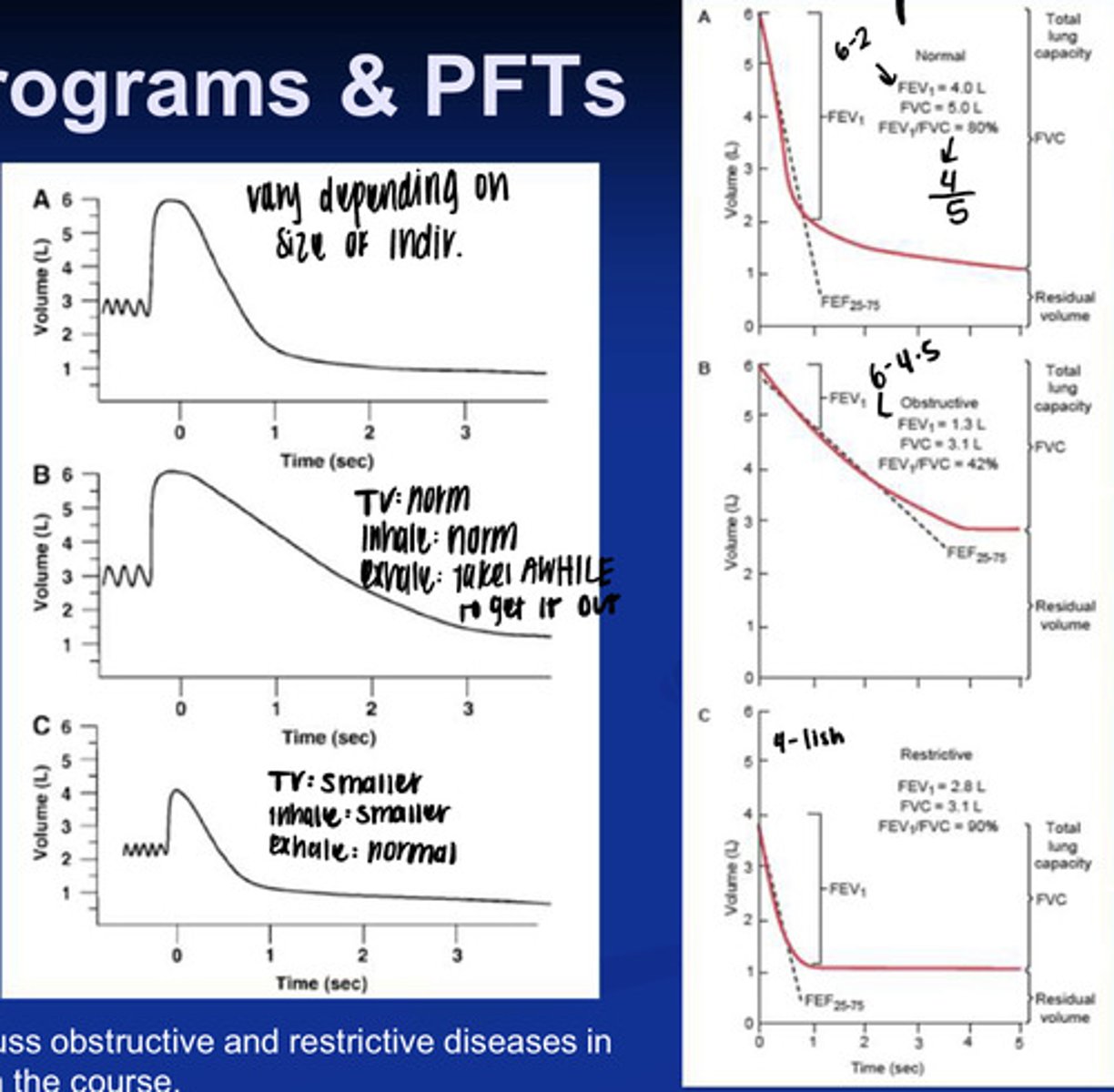
what is a restrictive lung disease? what does it look like on a graph?
- this is the inability to get air IN the lungs
- so you would have a decrease in FVC1 because you dont have much air from inspiration to begin with
- you would have a decrease in FVC because you didnt inhale as much
- you would have an increase in FEV1/FVC
if you are resting and healthy, what is your diffusion exchange like?
- it is not limited by diffusion
- equal PAO2 and Blood PaO2
if you are doing maximal exercise what happens to diffusion exchange?
- you see an increase in cardiac output, and decreased time for blood to be in capillaries so your exchange may be limited to diffusion rate
- basically your blood doesn't stay in the capillaries long enough for gas exchange to occur
what is the purpose of a DLCO test?
to estimate diffusion capacity of the lungs
how is a DLCO test performed?
a single breath or steady state technique
what does DLCO mean?
- this is the diffusing capacity for carbon monoxide (CO)
what is the diffusion like for carbon monoxide?
hemoglobin binds to CO with very high affinity. CO will bind as fast as it crosses the interface and its exchange is always diffusion limited.
what are some factors that can affect DLCO values?
- Body size
- age
- sex
- lung volume
- exercise
- body position
- PaO2 changes
how does body size affect DLCO?
because lung size increases, causing diffusion area and volume of pulmonary capillary blood vessels to increase
how does age affect DLCO?
it decreases by 2% each year after age 20
how does sex play a role in lung volume?
10% greater DLCO in men
how does lung volume play a role in DLCO values?
an increase in lung volume can cause an increase in the volume of pulmonary capillary blood vessels and an increase in diffusion area with a decrease in diffusion distance
how does exercise play a role in DLCO values?
an increase in perfusion causes a dilation of pulmonary capillaries which increases the area of diffusion and volume of pulmonary capillary blood
how does body position play a role in DLCO values?
changes in posture increase the pulmonary capillary flow due to gravity
Supine > Sitting > Standing
how does PaO2 change play a role in DLCO values?
- an increase in PaO2 causes a decrease in DLCO by lowering the rate at which CO binds with Hemoglobin
if lungs collapse, you need to do what?
increase transpulmonary pressure
once you get the airways open with a large increase in pressure what happens?
the change in volume becomes linear and you dont have to have as much pressure to increase volume
normally inspiration starts at what percent of TLC?
50%
what is lung compliance?
the amount that lung volume increases in response to changes in transpulmonary pressure
if you have high lung compliance you can do what?
expand the volume of the lungs with minimal changes in pressure
if you have low lung compliance what do you need?
a lot more pressure to change volume
what governs lung compliance?
- surfactant (surface tension)
- elastic properties of the chest wall
if it was just the chest wall, what would happen?
you would have expansion out
if it was just the lungs what would happen?
you would have collapse in
what does breathing require?
a contraction of respiratory muscles against resistance
at rest, what % of energy usage does it take to breathe? (if healthy)
5%
during exercise, what % of energy usage does it take to breathe? (if healthy)
20%
what is the work needed to counter the lungs elastic recoil during inspiration (proportional to lung compliance)
elastic work
what is moving air out through airways against resistance?
resistive work
what is pulmonary work?
the amount of force needed to change the transpulmonary pressure gradient X air volume moved per unit of time
if you decrease compliance you work harder or easier to inhale?
harder
what is a PT implication of a patient dealing with restrictive or obstructive lung disease?
if all of their effort and energy use is going toward breathing, the patient may not have much left to participate in PT.