advanced chemistry test: nuclear radiation
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
1
New cards
nuclear chemistry
study of the structure of atomic nuclei and the changes they undergo
2
New cards
wihlem roentgen
found that invisible rays were emitted by electrons hitting the surface of certain materials. lead to the discovery of x-rays.
3
New cards
henri becquerel
discovered phosphorescent uranium salts produced emissions that darkened photographic plates
4
New cards
phosphorescence
the study of if minerals emit light after being exposed to it
5
New cards
marie and pierre curie
discovered that becquerel's results (darkening of photogenic plates) occurred due to the uranium present in the uranium salts
6
New cards
radioactivity
process which of materials gives off radioactive rays
7
New cards
isotopes
atoms of the same element that have a different number of neutrons
8
New cards
radioisotopes
isotopes with unstable nuclei
9
New cards
radioactive decay
unstable atoms lose energy by emitting radiation
10
New cards
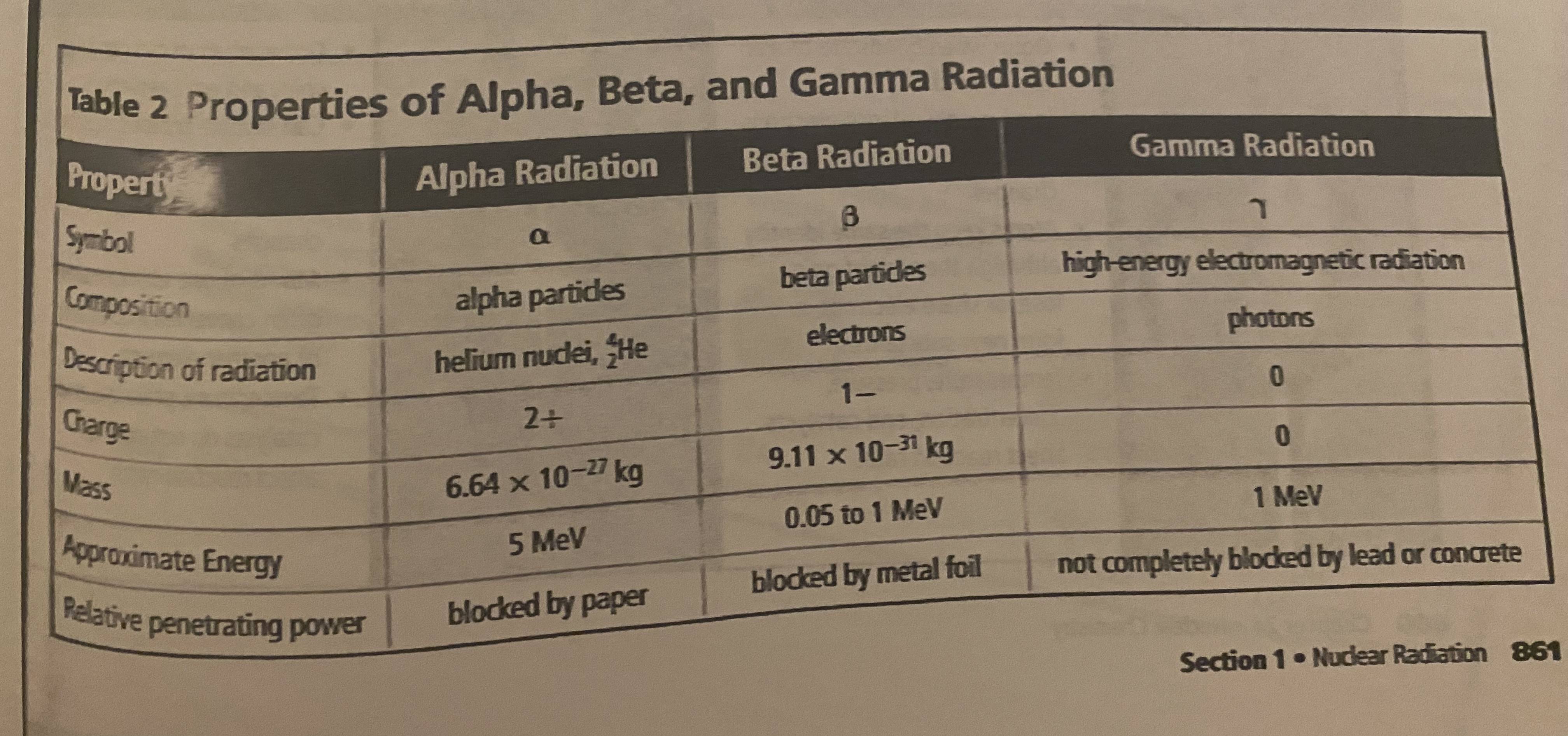
alpha, beta and gamma
most common types of radiation
11
New cards
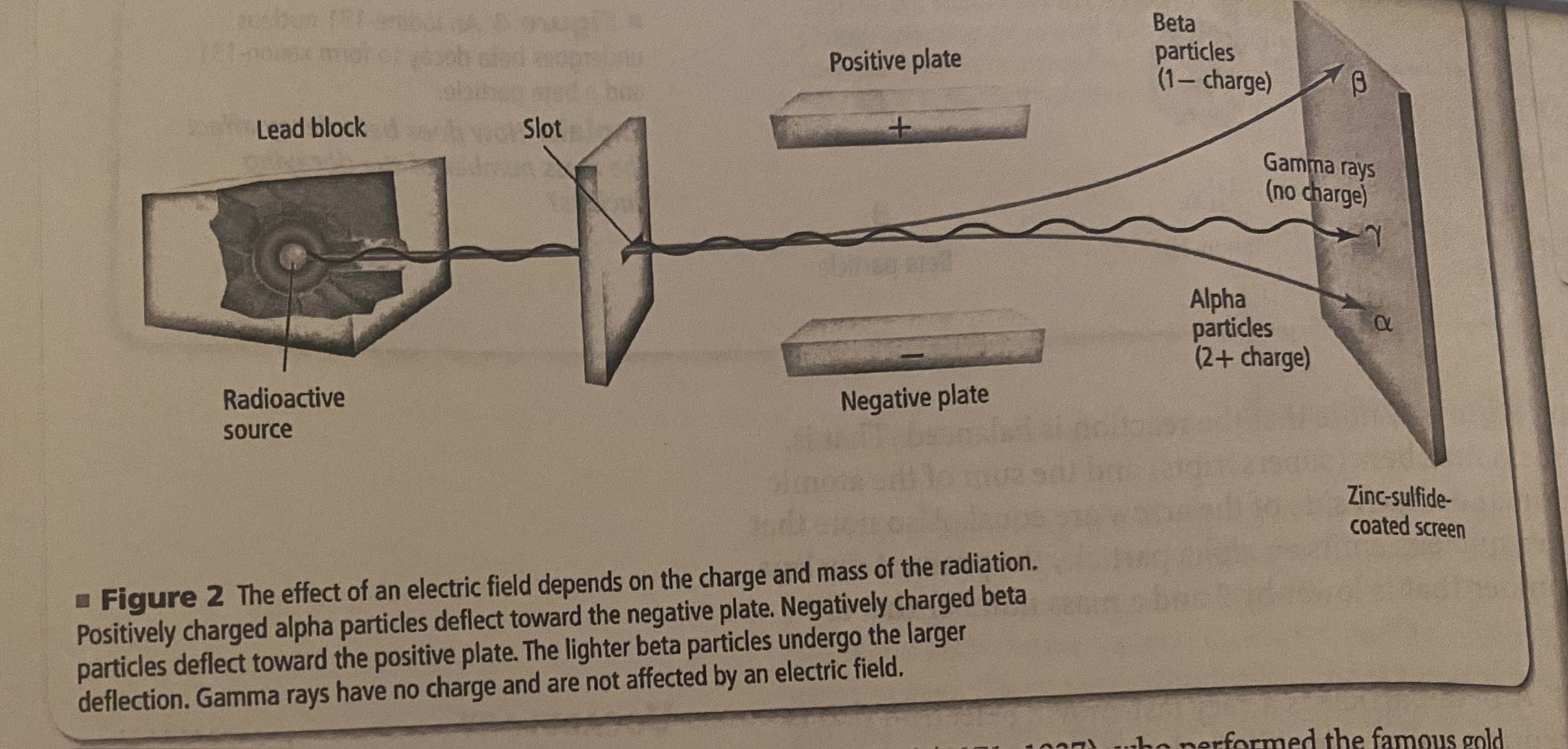
ernest rutherford
performed famous gold foil experiment that helped define modern atomic structure
12
New cards
alpha particles
same composition of He nucleus (2 protons, 2 neutrons), charge is 2+ due to presence of two protons. relatively slow moving compared to other forms of radiation.
13
New cards
alpha radiation
stream of alpha particles
14
New cards
when a radioactive nucleus emits an alpha particle...
the product nucleus has an atomic number that is lower by 2 and a mass number that is lowered by 4
15
New cards
beta particles
very fast-moving electron that is emitted when a neutron in an unstable nucleus converts to a proton
16
New cards
beta radiation
stream of fast-moving beta particles
17
New cards
n -----> p + e-
atomic number changes occur because a neutron is converted into a proton (increased by 1)
18
New cards
gamma rays
photons, (high energy and short wavelength) electromagnetic energy. no mass and no charge so no change in atomic number. accompany alpha/beta radiation because they account for most of the energy loss that happens in the nucleus as it decays.
19
New cards
transmutation
reaction where an atom's atomic number is changed
20
New cards
nucleons
protons and neutrons
21
New cards
penetrating power
the ability to pass through matter
22
New cards
band of stability
area of a graph where all stable nuclei are found (all above or below are radioactive and undergo decay in order to gain stability)
23
New cards
beta decay
(above) unstable because it has too many neutrons compared to protons
24
New cards
alpha decay
occurs to all nuclei with more than 82 protons