🍂🍃Physics year 10🍃🍂
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Balanced forces
Forces that are equal in size and opposite in direction
They cancel each other out
No change in motion or shape
Object may be still or moving at a constant speed
Example: A book resting on a table (gravity pulls down, table pushes up)
Unbalanced Forces
Forces that are not equal
Cause a change in motion (speed up, slow down, change direction)
Example: Two dogs pull a toy — if one dog pulls harder, the toy moves
Representing the forces on an object
Forces are shown with arrows
Arrow length = size of force
Arrow direction = direction of force
If the object is not moving or not accelerating, forces are balanced
Applied Force
A push or pull by a person, animal, or machine
Example: Holding a soccer ball — your hand applies a force upward
Balances gravity, so the ball doesn’t fall
Free Body Diagram
Object is shown as a square or box
Arrows show forces acting on it
Helps find the net force
Balanced Forces in Free Body Diagram
Equal length arrows in opposite directions
Forces cancel → net force = 0
No movement or constant speed
Support Force
The upward force from a surface
Balances gravity when something rests on a surface
If object doesn’t sink → support force
Net force
The sum of the forces acting on a single object
If the forces are balanced, the net force is zero → no change in motion.
If the forces are unbalanced, the net force is not zero → the object will accelerate (speed up, slow down, or change direction).
add any forces acting in the same direction and subtract any forces acting in opposite directions.
units of net force are newtons (N).
10 N force right, 6 N force left → Net force = 4 N to the right
5 N up, 5 N down → Net force = 0 N (balanced)
Newton’s first law of motion
Law of inertia- An object will remain at rest or move with constant velocity unless acted on by a net force
Explains why things don’t change speed or direction without a force
Properties of inertia
Inertia is not a force
It doesn't make something move or stop
It's a property of all objects with mass,
Moving vs stationary objects and inertia
Inertia is the natural tendency of an object to keep doing what it's already doing
An object at rest → stays at rest
A moving object → keeps moving at the same speed and direction
Inertia means an object resists changes to its motion
Velocity
Velocity = speed + direction
A change in velocity means a change in speed, direction, or both
Inertia keeps an object’s velocity the same unless a net force acts on it
Newton’s Second Law of Motion
Newton’s 2nd Law: F = ma
(Force = mass × acceleration)
Proportional Relationships
When the force acting on an object increases, the acceleration also increases.
→ This means acceleration is directly proportional to force.
(More force = more acceleration)When the mass of an object increases, the acceleration decreases (if the same force is applied).
→ This means acceleration is inversely proportional to mass.(More mass = less acceleration)
Force Units
1 Newton (N) = 1 kg × 1 m/s² (f=ma)
Standard units:
Force (F) → Newtons (N)
Mass (m) → Kilograms (kg)
Acceleration (a) → Metres per second² (m/s²)
Simulation uses:
millinewtons (mN) = 0.001 N
grams (g) = 0.001 kg
F = ma still works if you divide both mass and force by 1000
Why More Mass Needs More Force
More mass = more inertia
Inertia = resistance to change in motion
A greater force is needed to accelerate a larger mass
So: same force → smaller object accelerates more
Newton’s Third Law
Every action has an equal and opposite reaction.
Forces always come in pairs.
These pairs are called action-reaction forces.
Action-Reaction forces must be:
equal in size
opposite in direction
of the same type
acting on different objects
e.g. a horse pulls a cart (action), the cart pulls back on the horse (reaction). They don’t cancel out because they act on different things.
Labelling forces
Each label should have the following form:
Fforce type, x on y
For example, you hit a nail with a hammer. We could represent the force like this:
Fapplied, hammer on nail
Action reaction forces vs balanced forces
Equal and opposite forces only cancel out when they act on the same object.
This is when we say that they are balanced.
But, the pairs of forces described by the third law always act on different objects.
What is speed?
Speed describes how far something travels in a certain amount of time.
It does not describe whether something is "fast" or "slow".
It's a measurement of motion.
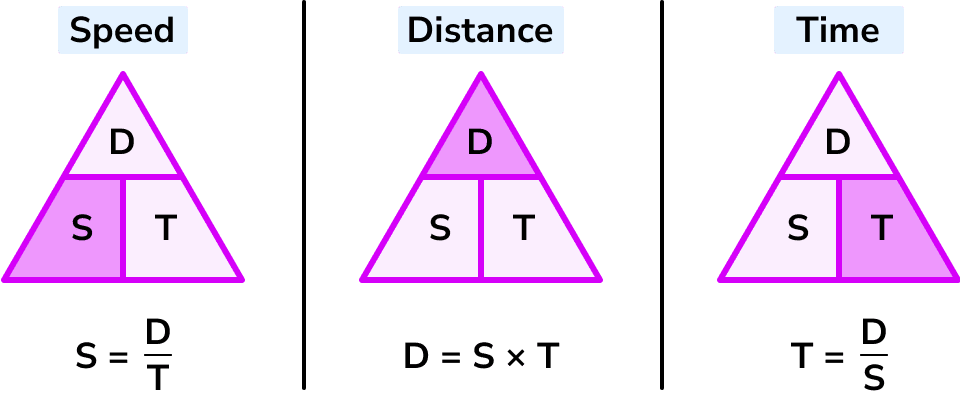
Speed Formula
speed= distance travelled/time taken
Converting between units of speed
To convert km/h → m/s, divide by 3.6
To convert m/s → km/h, multiply by 3.6
Units of speed- option 1
Speed- m/s
Distance- m
Time- s
Units of speed- option 2
Speed- km/h
Distance- km
Time- h
Instantaneous speed
An objects speed at any instant of it’s motion.
Average speed
The average of the instantaneous speeds over the whole distance travelled.
Average speed=Distance/Time
Transposing speed equation
What does a distance–time graph show?
How far an object has travelled over time.
x axis= time
y axis= distance
gradient= speed

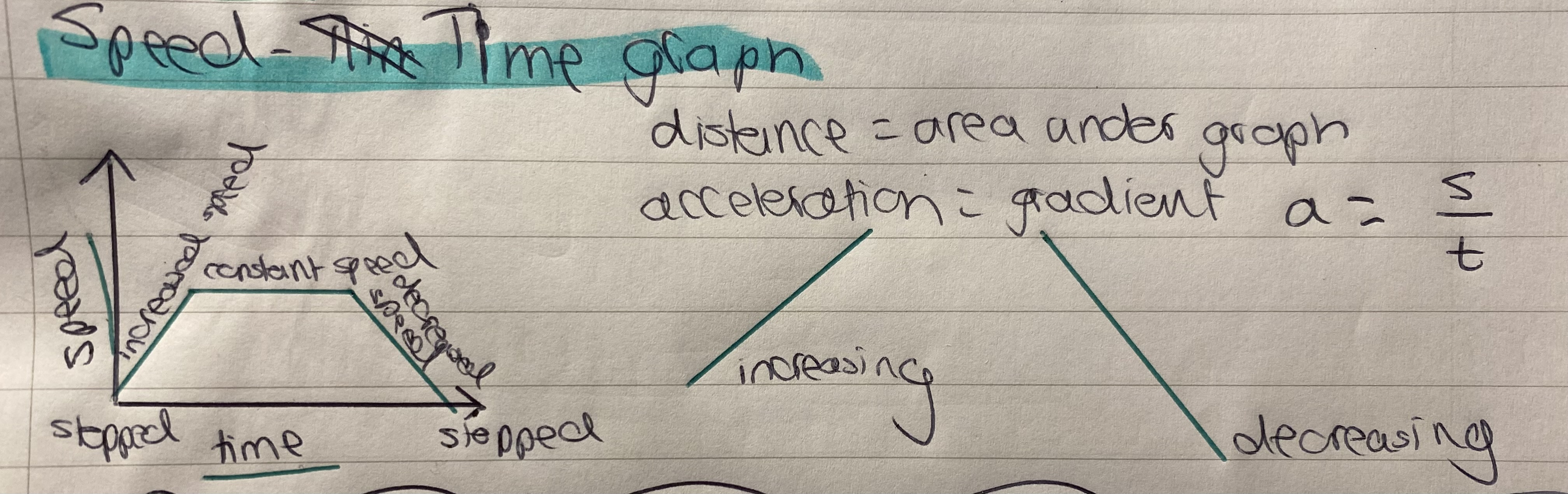
How to read a distance-time graph
Upward curve (steepening) = Speeding up
Curve flattening out = Slowing down
Straight line = Constant speed
Flat horizontal line = Stopped
How does the slope of a distance–time graph relate to speed?
The steeper the slope, the greater the speed.
The slope = speed.
How do we calculate average speed between two times?
Speed=gradient
s= rise(distance)/run(time)
speed= d2−d1/ t2-t1
Change in distance/ change in time

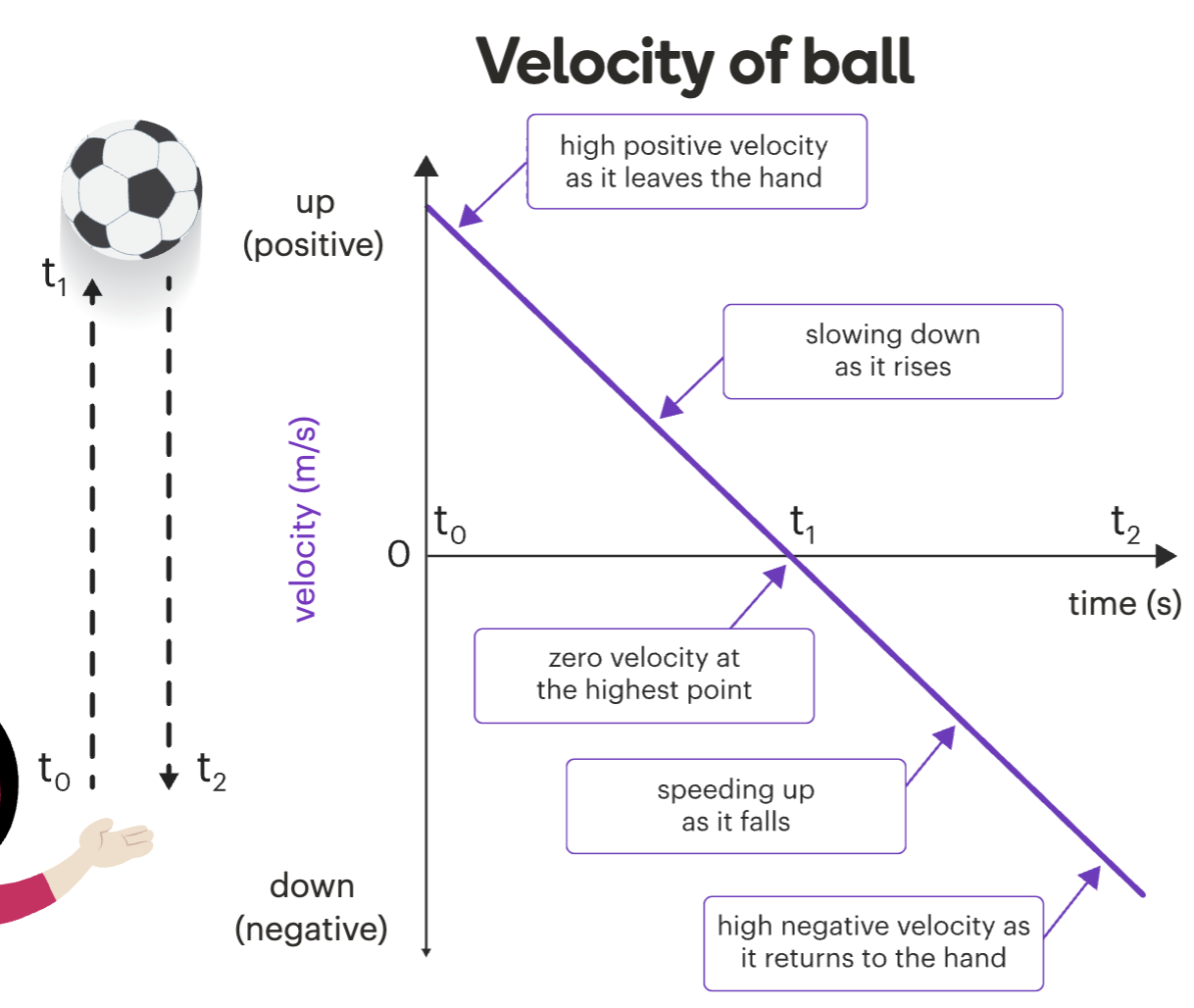
What does a speed–time graph show?
How fast an object is moving at each moment.
How to read a speed-time graph
Upward slope (line going up)
→ Acceleration (speed is increasing)Downward slope (line going down)
→ Deceleration (speed is decreasing)Horizontal line (flat)
→ Constant speedLine at zero (on the time axis)
→ Object is stopped / not moving
Distance
Total distance travelled during the motion
Displacement
Straight line distance from an object’s starting point
has magnitude(size) and direction.
e.g. it's 120 km by a slow and winding road between Snake Gully and Gusville. But the map shows Gusville is only 70 km east of Snake Gully.
So, the displacement from snake gully to Gusville is 70km east
Scaler quantity
Has magnitude(size) but not direction
Distance is a scalar quantity
Speed is a scalar quantity, because it is measured using distance and time, which are both scalar quantities.
Vector quantity
Has magnitude(size) and direction
Displacement is a vector quantity.
Velocity is a vector quantity
Velocity formula
Velocity= displacement/time
e.g. A map shows Gusville is only 70 km east of Snake Gully.
If it takes a driver 2 hours to get between the towns, then their average velocity is: 70/ 2
= 35km east
What's the difference between average speed and average velocity?
Speed = uses distance
Velocity = uses displacement
They’re often different!
Positive and negative velocity
Choose a direction as positive.
Move that way = positive velocity
Move opposite = negative velocity
( Right and up is often positive, left and down is often negative)
What is Acceleration?
Acceleration = any change in velocity
Velocity = speed + direction
It is a vector quantity
So, acceleration happens when:
🚀 Speed increases
🐢 Speed decreases
🔄 Direction changes
Acceleration Formula
Acceleration= change in velocity/time taken
a= v2-v1/t2-t1

Standard units of acceleration
a= m/s/s, m/s2 , or ms-2
v= m/s or ms-1
t=s
Positive vs Negative Acceleration
Positive acceleration = speeding up
Negative acceleration = slowing down (also called deceleration)
⚠ But if you're moving in a negative direction, negative acceleration can mean speeding up in that direction!
Velocity-Time graphs: slope
The slope (tilt) tells you the acceleration:
Upward slope = Positive acceleration (speeding up in + direction)
Downward slope = Negative acceleration (slowing down or speeding up in – direction)
Flat line = Constant velocity- same speed and direction (zero acceleration)
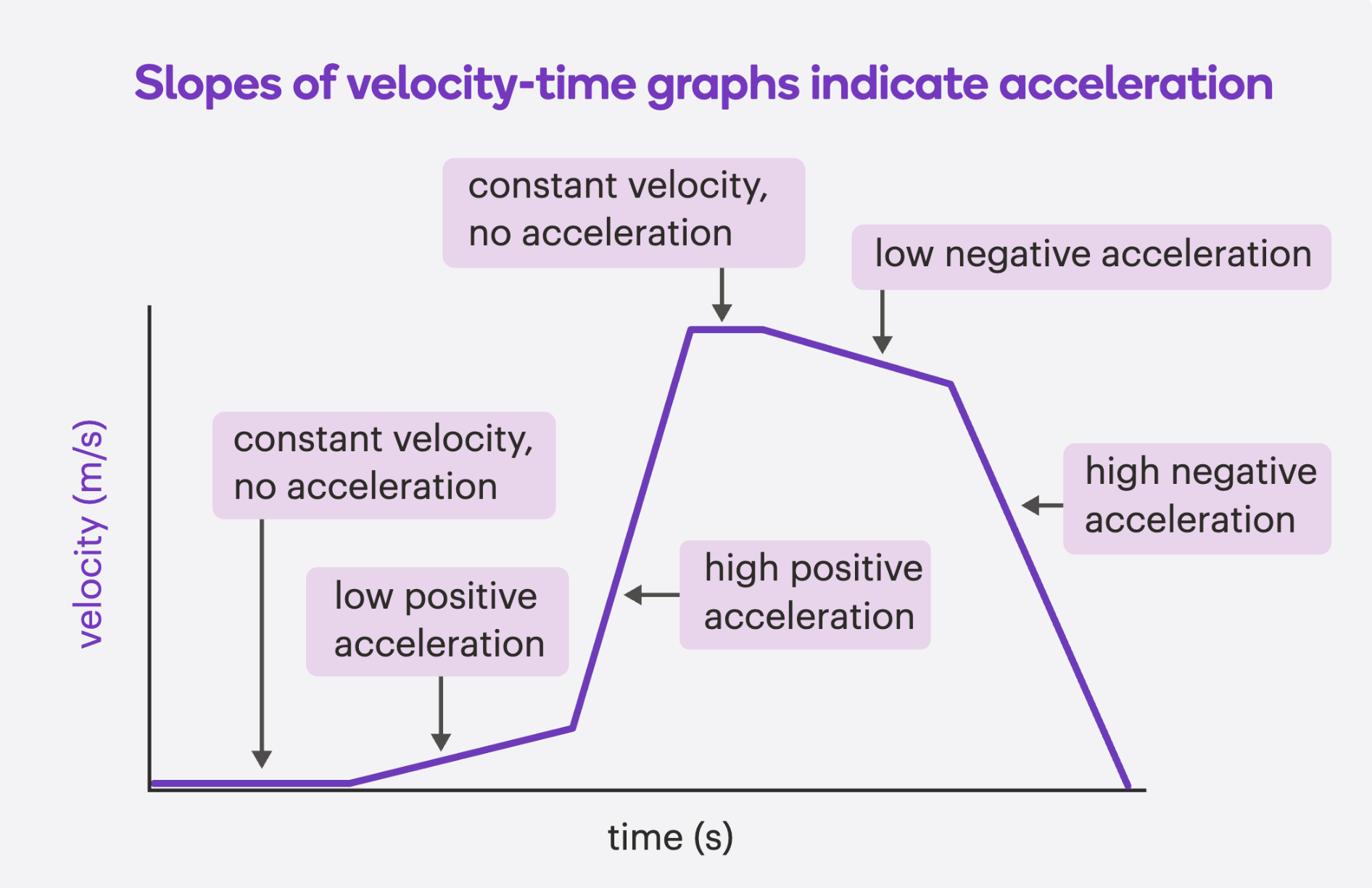
Velocity-Time graphs- other important info
On a velocity-time graph:
Area under the line = distance travelled
Slope of the line = acceleration
Steeper = faster acceleration or deceleration
Flat = no acceleration
What is acceleration due to gravity?
The same force that acts on all objects on Earth.
Acceleration due to gravity (g) has a value of about 10 m/s/s down.
It always acts downwards towards the centre of the Earth, no matter the direction the object is going
Why would an object have a negative acceleration even when going up?
Because gravity pulls it down the whole time,
Slows it down going up
Speeds it up coming down
What does a straight, sloping line mean on a velocity-time graph?
Constant acceleration
Negative slope = acceleration is downward
Line goes through 0 when an object changes direction