fundamentals of nervous system
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
what are 3 functions of the nervous system and how are they connected
1) sensory input, receptors that detect stimuli. 2) Integration, process + interpret that input. 3)motor output, acting out the message. They connect like a half circle.
what are the 2 main parts of the nervous system, what are the functions of these parts
1) central nervous system (CNS)- brain, spinal cord, integration happens here. 2) peripheral nervous system (PNS)- all spinal + cranial nervous, sensory impute and motor output happens here
what are 2 subdivisions of the peripheral nervous system and what is there function
1) sensory(afferent)- conducts impulses from receptors in the CNS. 2) motor(efferent)- conducts impulses from the CNS to the effecters
what type of sensory fibers convey info from the skin, skeletal muscles and joints to the CNS
somatic sensory fibers
What type of sensory fibers convey info from the organs within the ventral body cavity to the CNS
visceral sensory fibers
what are the 2 subdivisions of the motor division and what parts of the body do they conduct impulses to? what division is voluntary and which is involuntary?
1)somatic nervous system- conducts impulses from CNS to skeletal muscles 2)autonomic nervous system(ANS)- conducts impulses from the CNS to cardiac muscle, smooth muscle and glands
what are 2 types of cells that make up nervous tissue
1)neurons 2)neuroglia (glial)
neuroglia cells, astrocytes in the CNS
-support and brace the neurons and anchor them to their nutrient supply lines, guide things that migrating, participate in information processing in brain, control environment around neurons.
neuroglia cells, microglial in the CNS
monitor nearby neurons health, have a protective role
neuroglia cells, ependymal in the CNS
line the central cavities of the brain and spinal cord with cilia, circulates cerebral spinal fluid that acts as a cushion
neuroglia cells, oligodendrocytes in the CNS
line up along thicker nerve fibers and act as insulation, creates myelin sheath
satellite cells in the PNS are like what cells in the CNS
astrocytes
Schwann cells in the PNS are like what cell in the CNS
oligodendrocytes
besides their ability to conduct nerve impulses, what 3 other characteristics do neurons have
1) extreme longevity: they live forever, you die with what you are born with. 2) amitotic: they don’t divide/ don’t do mitosis 3) high metabolic rate: doing collier respiration at a faster rate (requires a lot of oxygen)
what is the function of dendrites
convey incoming messages toward the cell body
what in the function of the axon
generate nerve impulses and send them
what is the purpose of myelin sheath and which part of a neuron contains it
-purpose: protects and electrically insulates axons and increases the transmission speed of nerve impulses
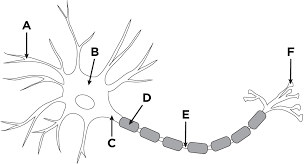
A
Dendrites
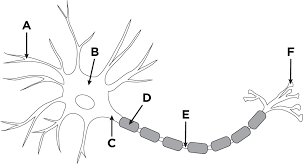
B
cell body (soma)
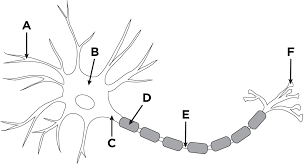
F
Axon terminal
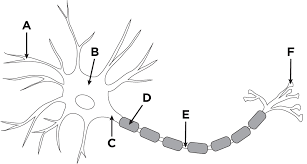
D
Schwann cell
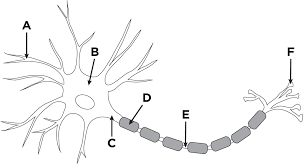
C and E
axon