Biology Cell Division Mitosis/Meiosis
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
Karyokinesis
involves the division of the nucleus.
Cytokinesis
involves the division of the cytoplasm.
Somatic cell
Body cells
Produced through mitosis
Contains diploid number of chromosomes and each cell contains 2 set of chromosomes
2n = 46
Gamete
Reproductive cells
Produced through meiosis
Haploid number of chromosome, one cell one set
n = 23
G1 phase
Cells grow.
Cell components such as mitochondrion and endoplasmic reticulum are produced at this stage.
Proteins used in the cell cycle are also synthesised during this time.
At this stage, the nucleus looks big and the chromosome is in the form of chromatin.
S phase
DNA synthesis occurs in the S phase.
The DNA in the nucleus is replicated.
Each chromosome multiplies into two identical chromosomes known as sister chromatids.
Both chromatids contain the same copy of the DNA molecule.
Both chromatids are joined at the centromeres.
G2 phase
The cells will continue to grow and remain active metabolically during the G2 phase.
Cells gather energy and make final arrangements to enter the next stage of cell division.
After the interphase stage, the cell will enter the M phase.
M phase
M phase is made up of mitosis and cytokinesis.
Mitosis involves prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase
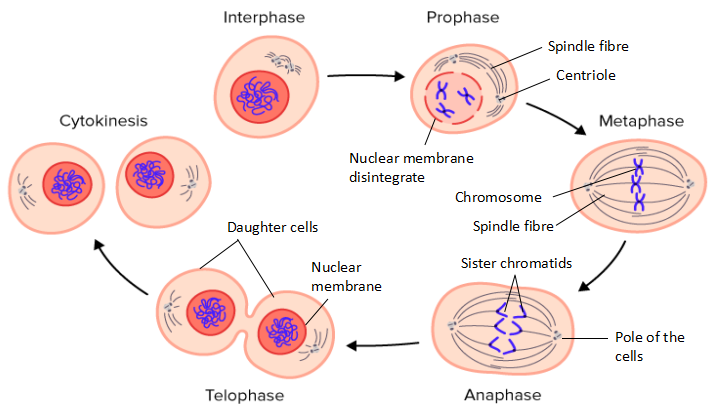
Prophase (1)
In the nucleus, chromatin starts to shorten and thicken to form a chromosome structure that can be seen through a light microscope.
The chromosome is seen to be made up of two identical threads called sister chromatids.
Both sister chromatids are joined at the centromere.
The nucleus membrane disintegrates, the nucleolus disappears, the centriole moves to the opposite poles and the spindle fibres start to form.
Metaphase (2)
Centrioles are at the opposite poles of the cell.
The spindle fibres maintain the chromosomes at the equatorial plane.
The chromosomes become aligned in a single row on the equatorial plane.
Metaphase ends when the centromere begins to divide.
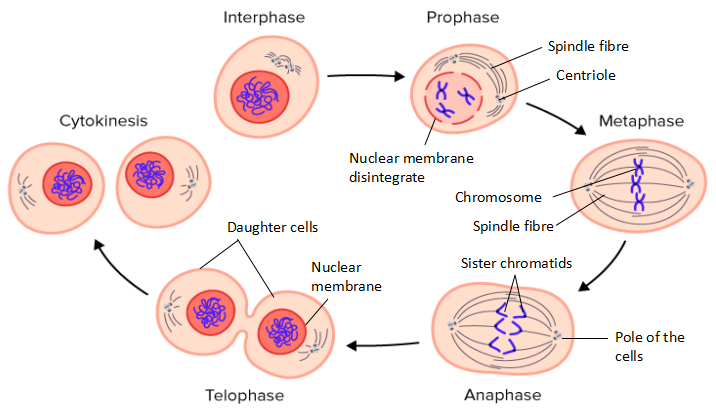
Anaphase (3)
The centromere divides into two and the sister chromatids separate.
Spindle fibres shorten, contract and the sister chromatids are attracted to the opposite pole cells.
Anaphase ends when the chromatid arrives at the pole of the cell.
Telophase (4)
When the chromatids are at the opposite poles, they are now called the daughter chromosome.
Each pole contains one set of complete and identical chromosomes.
Chromosomes are shaped again as fine chromatin threads.
Nucleoli are formed again.
Spindle fibres disappear.
A new nucleus membrane is formed.
The telophase stage is followed by cytokinesis.
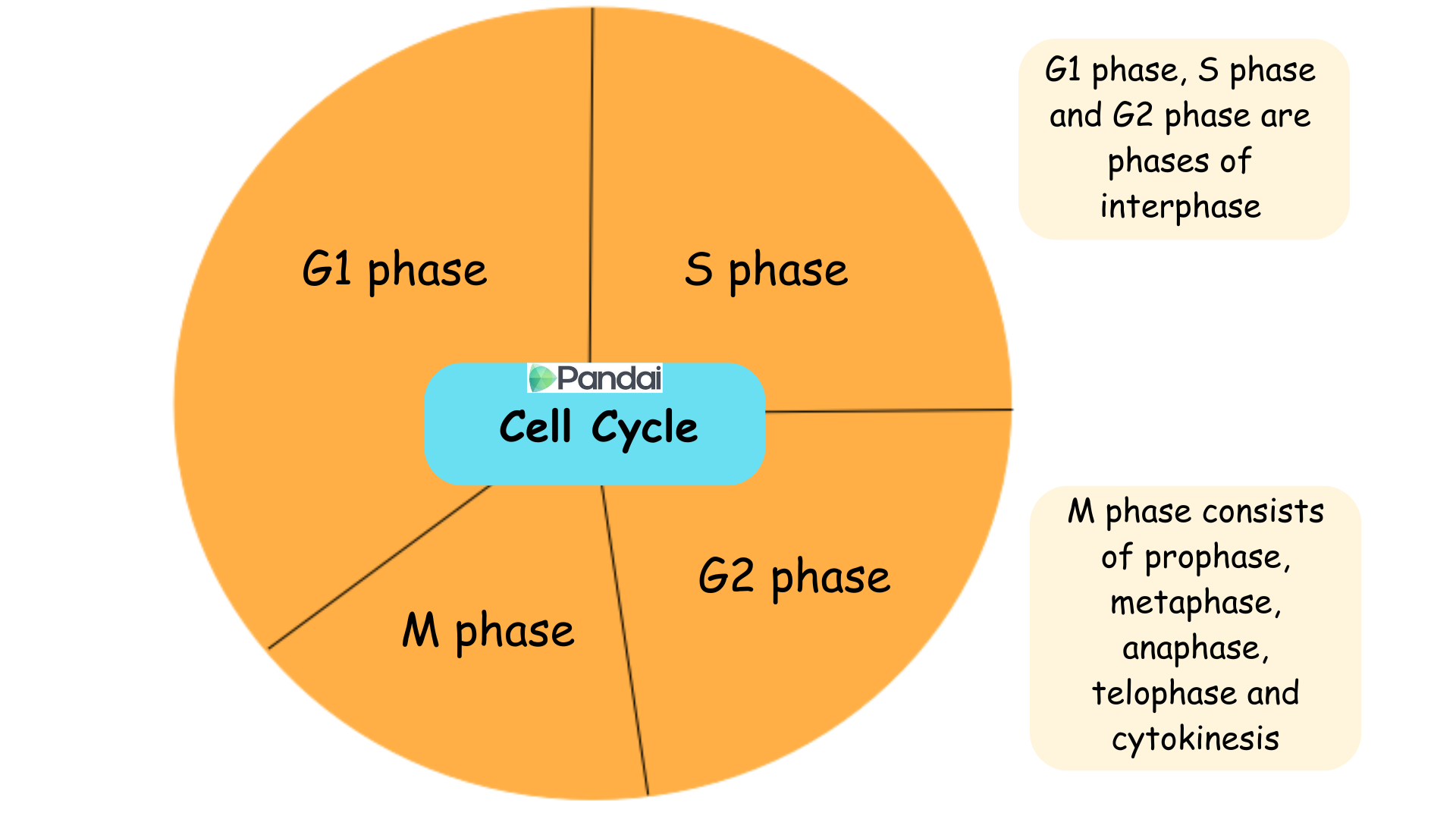
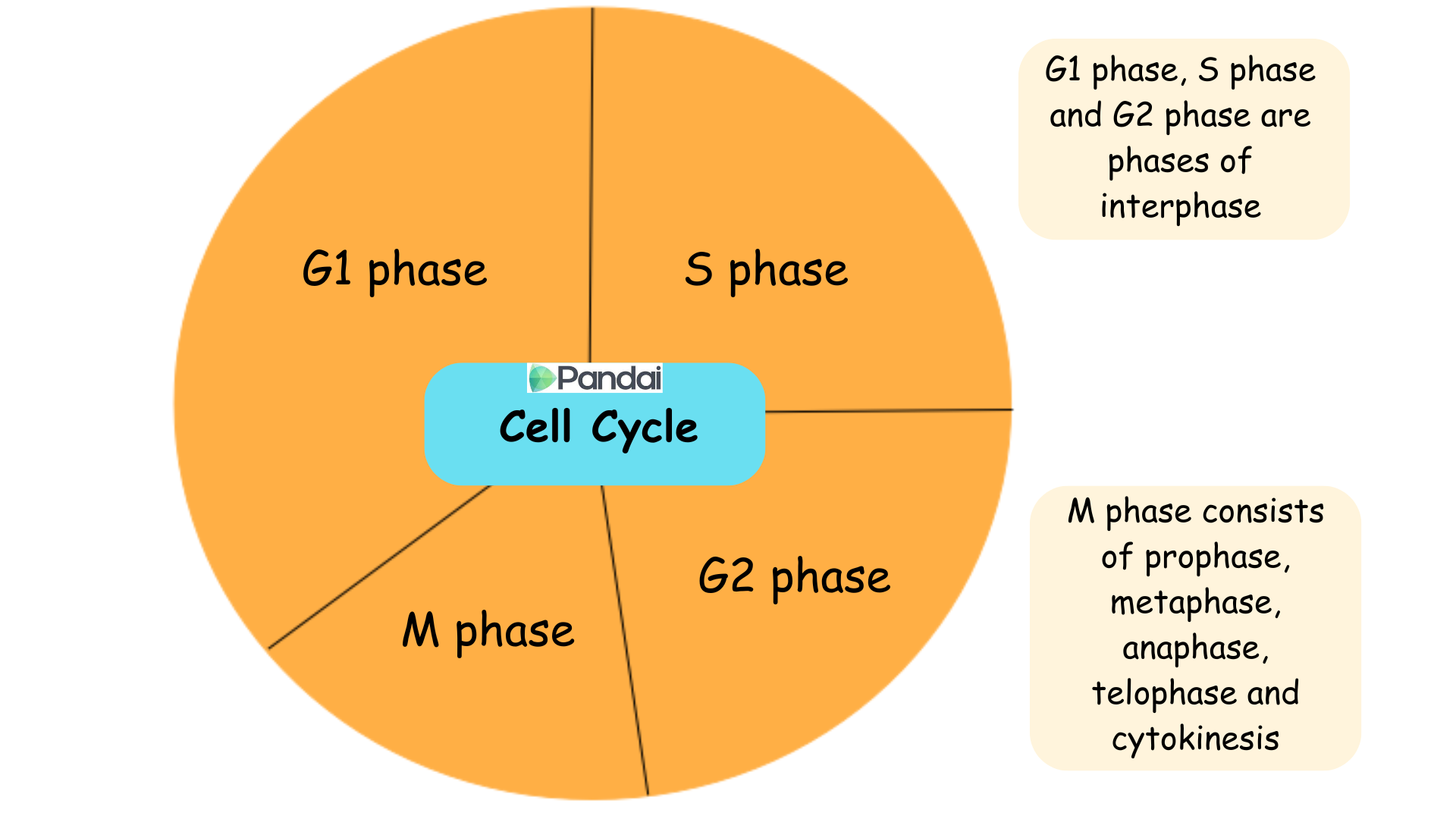
Cell cycle
The cell cycle refers to the sequence of events that involves DNA multiplication and cell division to produce two daughter cells.
The cell cycle consists of interphase and M phase.
Interphase is the longest phase in the cell cycle.
This phase is made up of the G1, S and G2 phase.
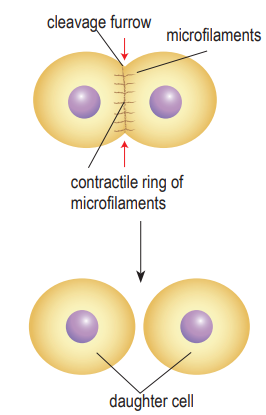
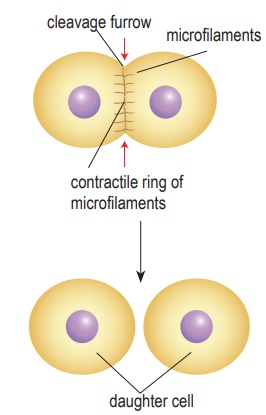
Cytokinesis (animal cell)
Cytokinesis occurs in animal cells when the plasma membrane constricts in the middle of the cell between the two nuclei.
Microfilaments at the point of constriction will contract, causing the cell to constrict until it splits to form two daughter cells.
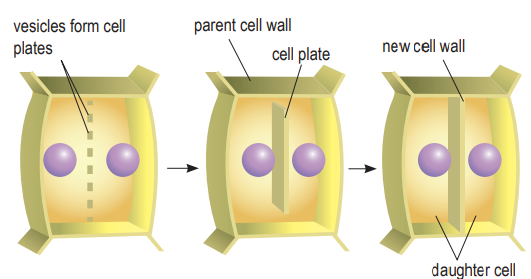
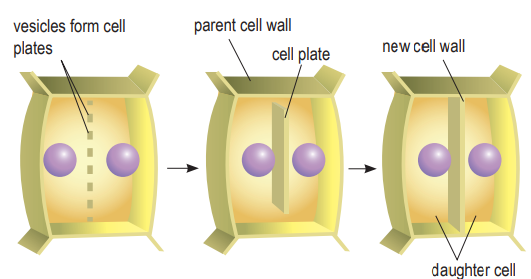
Cytokinesis (plant cell)
Cytokinesis in plant cells also begins when the formed vesicles combine to form cell plates at the centre of the cell.
The cell plates are surrounded by a new plasma membrane and a new cell wall substance is formed among the spaces of the cell plates.
The cell plates expand outwards until they combine with the plasma membranes.
At the end of cytokinesis, cellulose fibres are produced by the cells to strengthen the new cell walls.
Two daughter cells are formed.
Each cell has a diploid condition
The Necessity of Mitosis
Mitosis is important for the following life processes.
For embryo development and organism growth, mitosis ensures that rapid cell growth occurs.
Through the mitosis process, the lizard is able to grow a new tail (regeneration) if the tail breaks.
When the body is injured, mitosis will produce new cells to replace cells that are dead or damaged.
Mitosis aids organisms such as hydra to produce new individuals through the formation of new buds.
In agriculture, the technique of culturing plant tissues is used to produce young plants through the culturing of parent cells without going through the fertilisation process.
Stem cell therapy uses stem cells from bone marrows to treat damaged cartilage.
The culturing technique uses stem cells from animals which are then cultured in laboratories to produce meat.
Meiosis
Meiosis is the process of cell division that occurs in reproductive organs to produce gametes that contain half the number of chromosomes (haploid) of the parent cells (diploid).
Meiosis occurs in the testis (male) and ovary (female) for animals and humans
Prophase I
Chromatin shortens, thickens and forms visible chromosomes.
The pairing of homologous chromosomes (synapsis) forms bivalent (or known as a tetrad, that is four chromatids for each homologous chromosome).
The crossing over process that is an exchange of genetic material between non-identical chromatids takes place.
Crossing over produces a combination of genes that are new in chromosomes.
The point where the chromatids cross over is called chiasma.
At the end of prophase I, the nucleus membrane and nucleoli will start to disappear.
Both centrioles will move towards the opposite pole cells.
Spindle fibres are formed among the centrioles.