Smoking Cessation
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
T/F: Tobacco use is the largest preventable cause of death and disease in the US.
True
T/F: Adults with mental illness or substance use disorder consume 40% of all cigarettes smoked in the US.
True
Ages: 24-44 years old and 45-64 are highest smokers
What percentage of current smokers smoke daily?
75%
Which of the following are community characteristics for increased risk of smoking addiction? (select all that apply)
A. Higher education
B. Lower household income
C. Under insured
D. Lower education
B. Lower household income
C. Under insured
D. Lower education

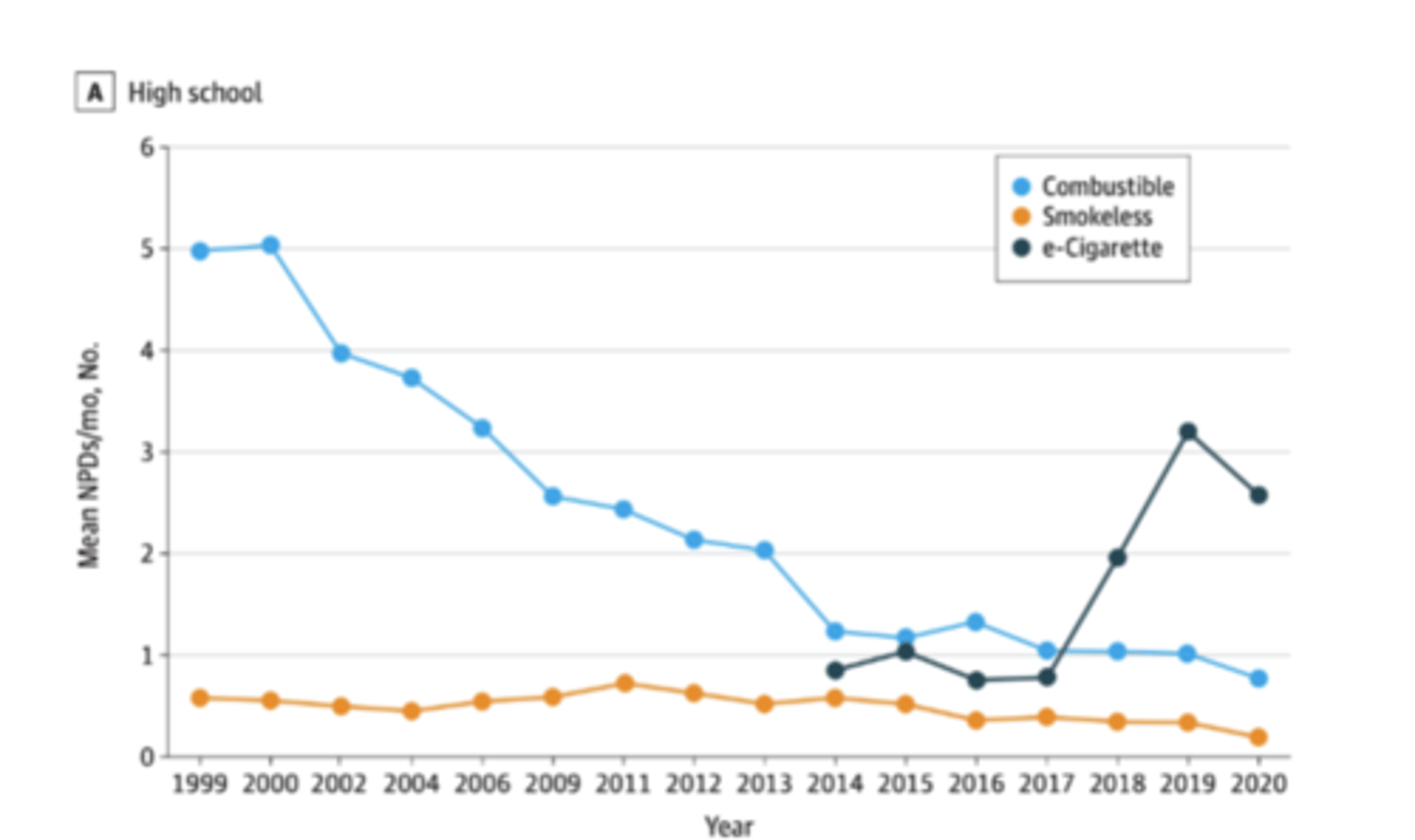
Nicotine product use trends
Drop in 2020= popcorn lungs
Pathophys of nicotine
Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor agonist= increases the release of neurotransmitters = stimulant at low doses by activating reward system
*Stimulant at low doses, neuronal depression at high doses*
Absorption of nicotine
lungs, oral mucosa, GI mucosa, and skin & metabolized via the lung and liver
T/F: smoke (combustion of tobacco) drives drug-drug interactions due to chemicals in cigarette and other forms of tobacco
True
Metabolite is cotinine(great biomarker for nicotine use/exposure)
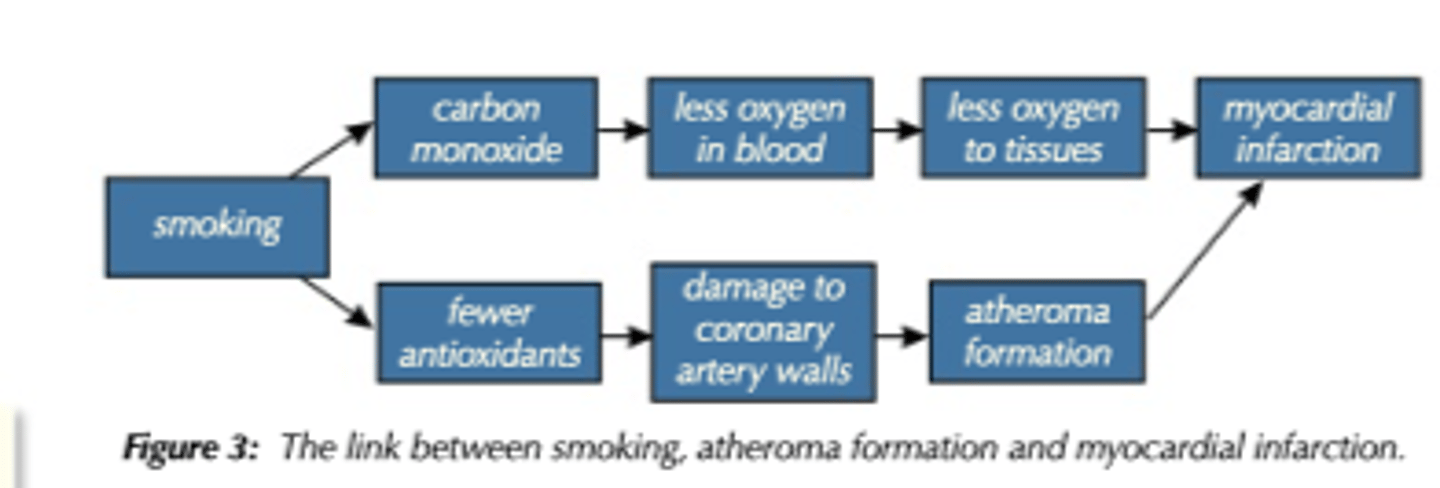
T/F: Smoking is an independent risk factor for coronary heart disease, cerebrovascular disease and total atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease
True
Immediate cardiac consequences associated with nicotine use
1. Acute increase in HR (10-15 bpm)
2. Increased BP (5-10 mmHg)
3. Increased myocardial activity, constriction of cardiovascular beds in skin and coronary arteries, dilating cardiovascular beds in skeletal muscle)
4. Increased cardiovascular disease profile
Concentration-dependent cough and airway obstruction
Nicotine and its related effects can trigger a concentration-dependent cough and airway obstruction by stimulating afferent nerve endings in the bronchial mucosa. This can result in symptoms such as nocturnal chest tightness and increased bronchial hyperactivity
more = worse effect
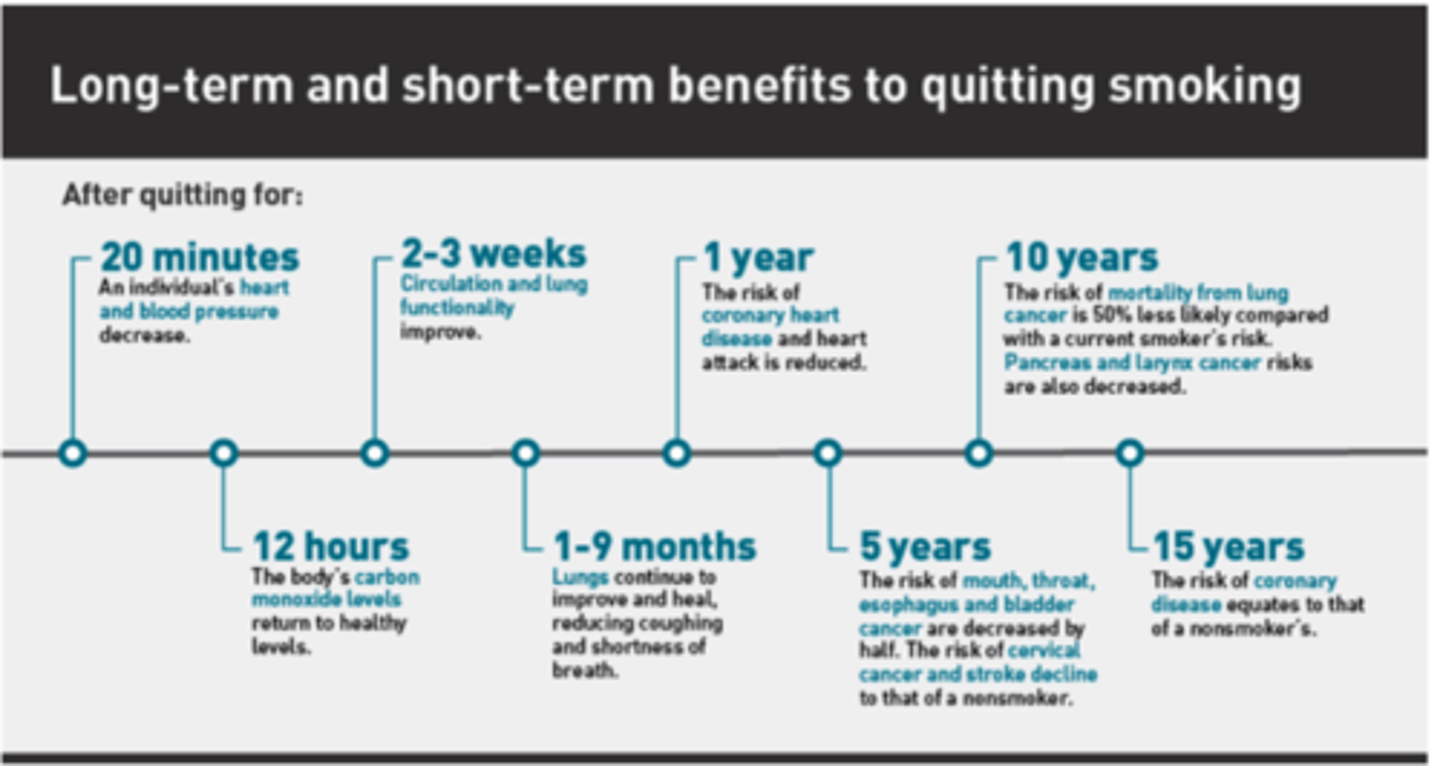
Benefits to quitting smoking
Foundations of Comprehensive Treatment
1. Behavioral counseling
2. Pharmacotherapy: medications significantly improve quit success rates
T/F: Behavioral counseling is not recommended in all smokers.
False; recommended in all smokers.
Exclusion criteria for smoking cessation pharmacotherapy?
1. Smoke less than 10 cigarettes/day: NRT only?
2. Age < 18 (needs Rx): parents must pick up
3. Pregnant women must weigh the risk versus benefits and safety
4. Contraindications to pharmacotherapy
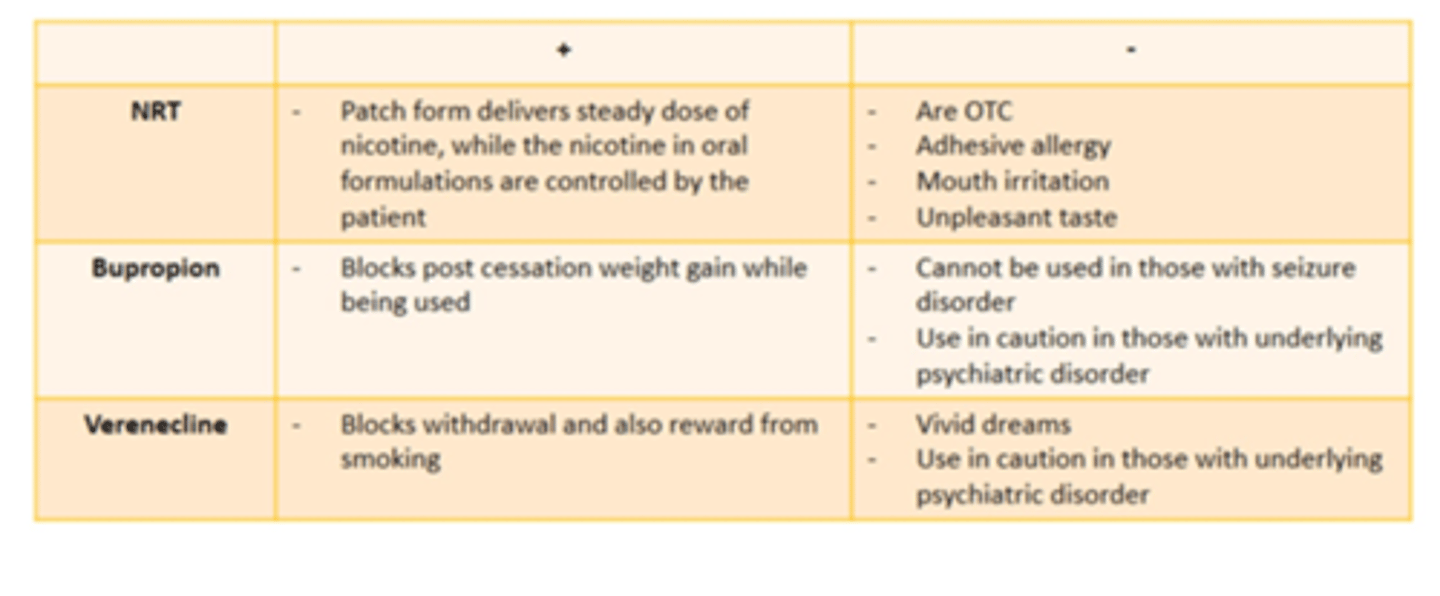
First-line pharmacotherapy for smoking cessation
1. Nicotine replacement therapy (NRT): gums, lozenges, patches, sprays, inhalers
2. Antidepressant: Buproprion 150 mg BID
3. Nicotinic receptor partial agonist (Varenicline (Chantix))
Nicotine Replacement Therapy
1. Gums
2. Lozenges
3. Transdermal Patch
4. Nasal spray: Rx only and rarely use
5. Inhaler: Rx only and rarely used

Rational for NRT
1. Mimics action of nicotine on receptors= reduce craving= allows patient to focus of behavioral and psychological aspects of cessation
2. Delays weight gain
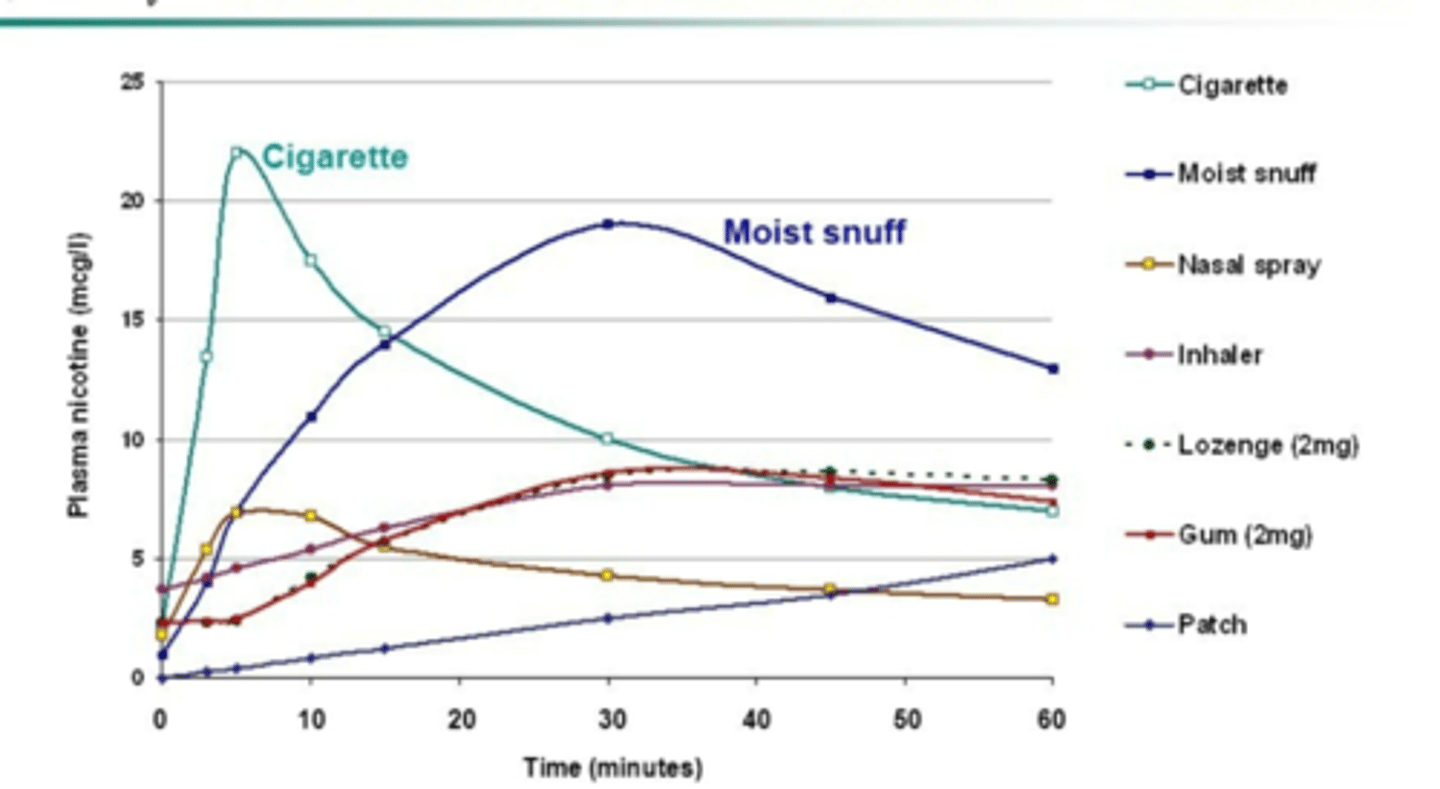
3. Slower, less variable, and more sustainable nicotine concentrations (refer to pic)
4. Reduces withdrawal
5. Less addicting than cigarettes
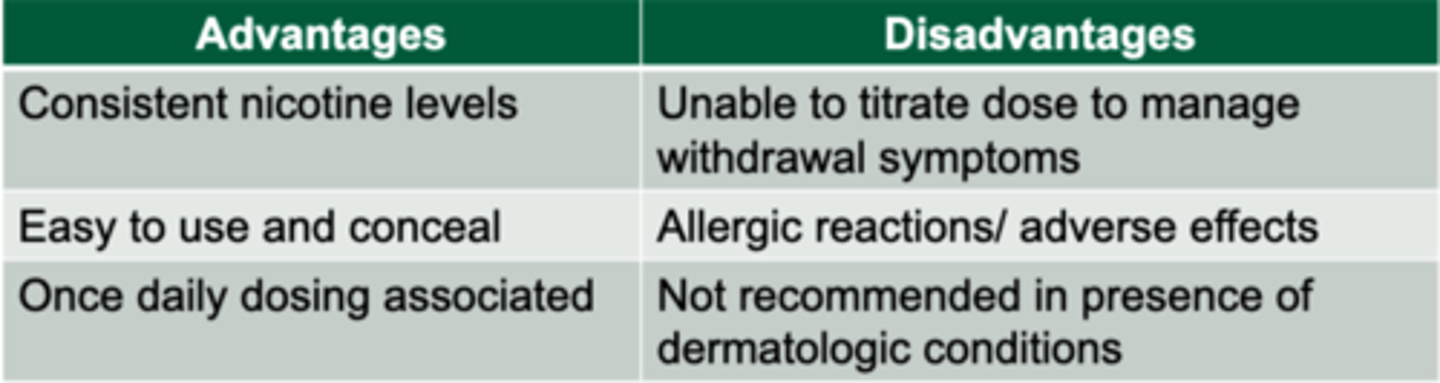
NRT still appropriate for people with
Underlying CV disease OR Uncontrolled HTN (caution with all NRT)
Ulcers (oral agents can exacerbate)
Asthma (don’t use inhaled nicotine)
Diabetes (oral agents can exacerbate due to sugar )
Sodium-restricted diet (oral agents can impact)
NRT is not appropriate for people with
Recent MI or heart attack (2 weeks)
Arrhythmias
Worsening or unstable angina
True or False: gum and lozenges are better than patches for emotional smokers
true; Emotional smokers tend to do better with lozenges and gum - so if stress or anxiety or 'issues' make them crave cigarettes or is the root of why the smoke, consider using these options over the patch and often times have more 'cravings' that need immediate NRT support
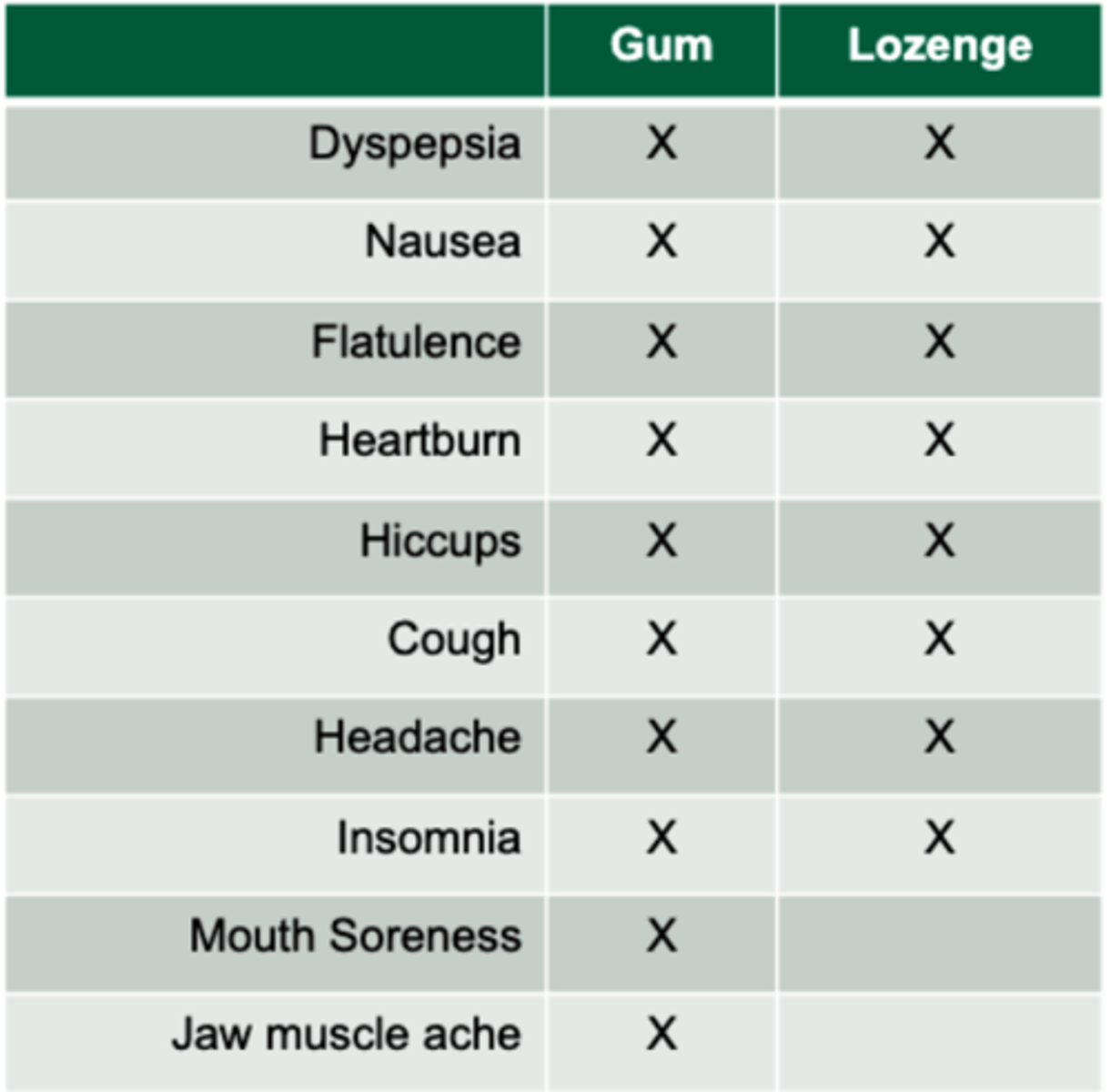
Potential adverse effects of gum and lozenges NRT
incorrect technique= lightheadedness, N/V, throat or mouth irritation
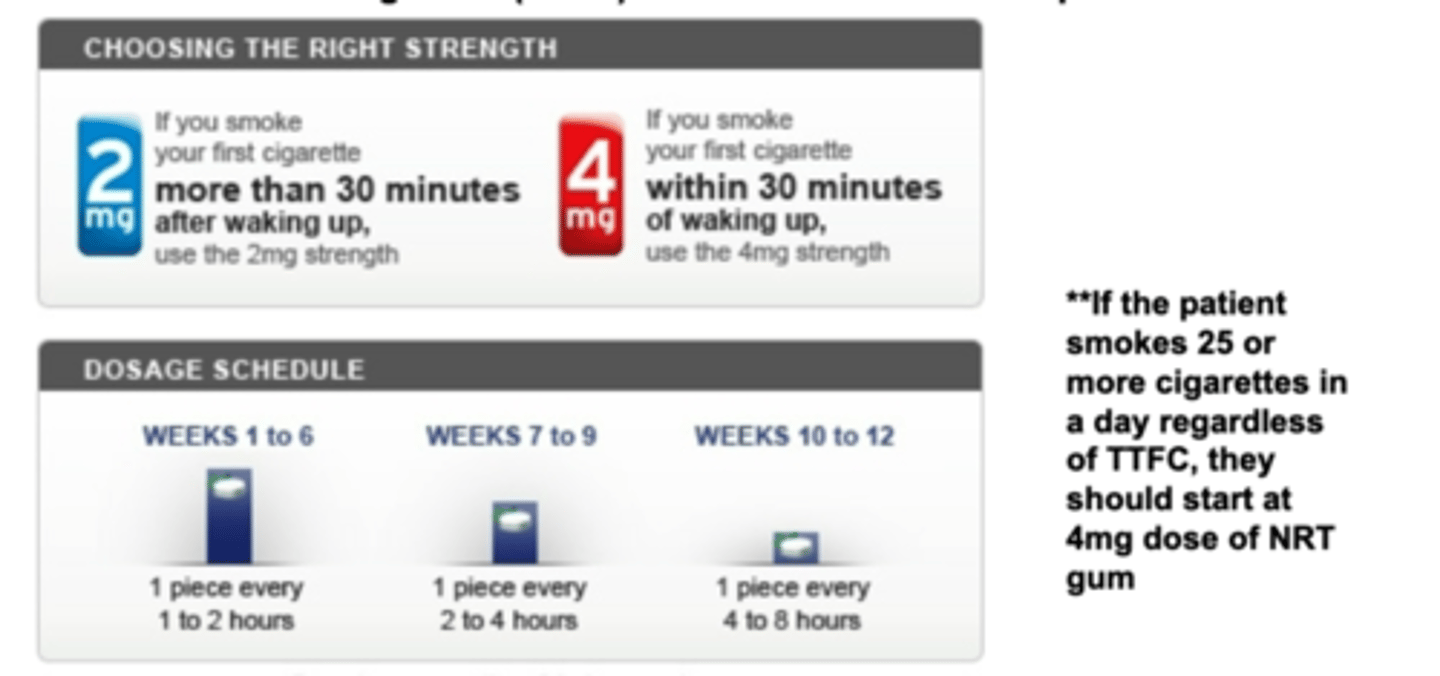
NRT gum/lozenge dosing
2 mg vs 4 mg is based on how dependent patient is on nicotine (time to first cigarette)
NRT gum technique
Avoid eating or drinking 15minutes before or while using gum/lozenge
1. Chew for a few seconds to activate = tingle
2. Park it & wait
3. Rotate and repeat
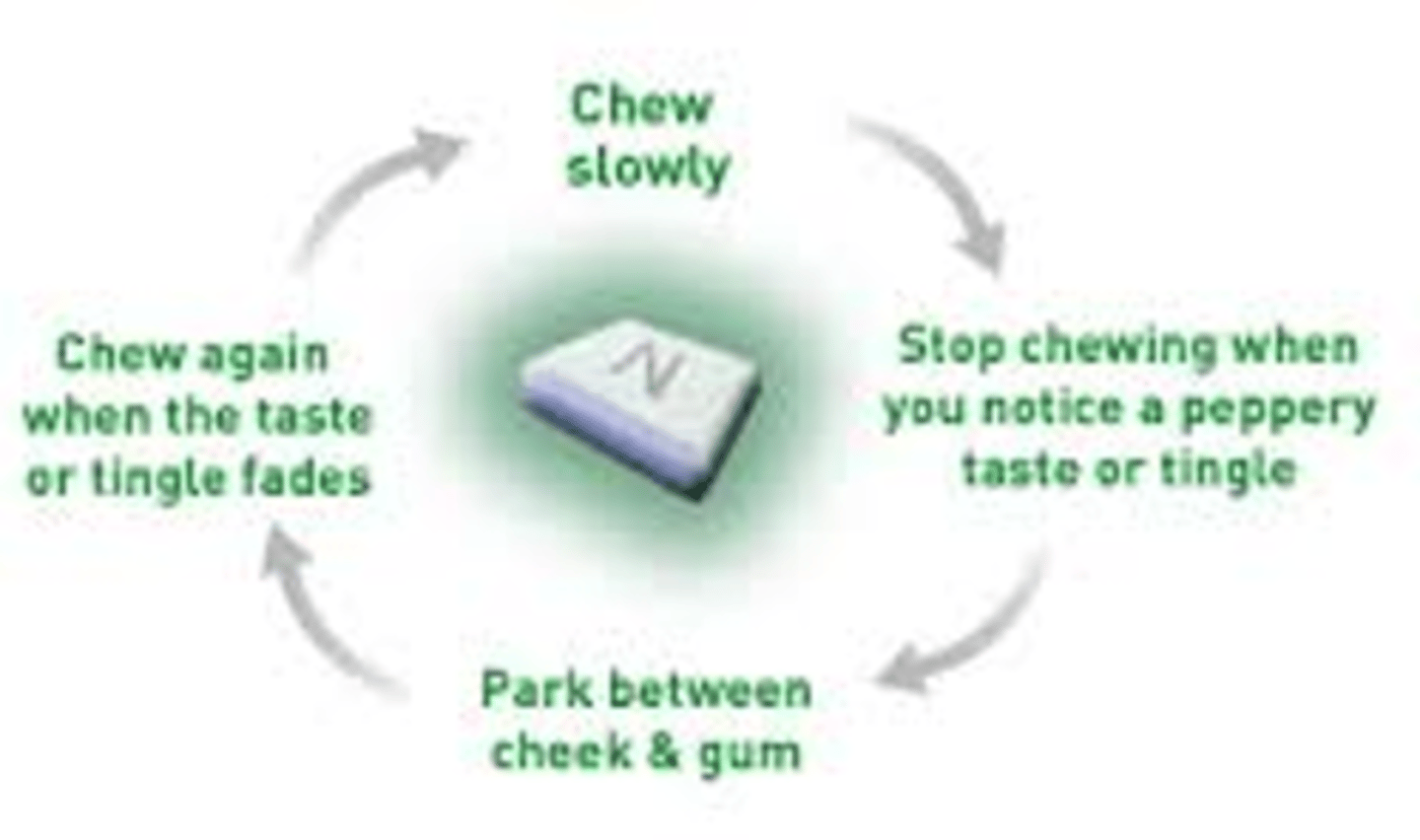
When should NRT gum not be recommended?
patients with dentures, TMJ disorders, dental work
NRT lozenge technique
Avoid eating or drinking 15minutes before or while using gum/lozenge
1. Do not chew
2. Allow to dissolve and rotate around gums
*Typically lasts for 30 minutes (mini-lozenge: 10 minutes)
T/F: you can cut a nicotine patch and wear it during an MRI
false
True or False: smokers that use nicotine as the stimulant (to stay awake, to focus when the study, to keep them motivated) they tend to do better with the patch instead of lozenges or gum
true
Nicotine patch strengths available?
7mg, 14mg, 21mg
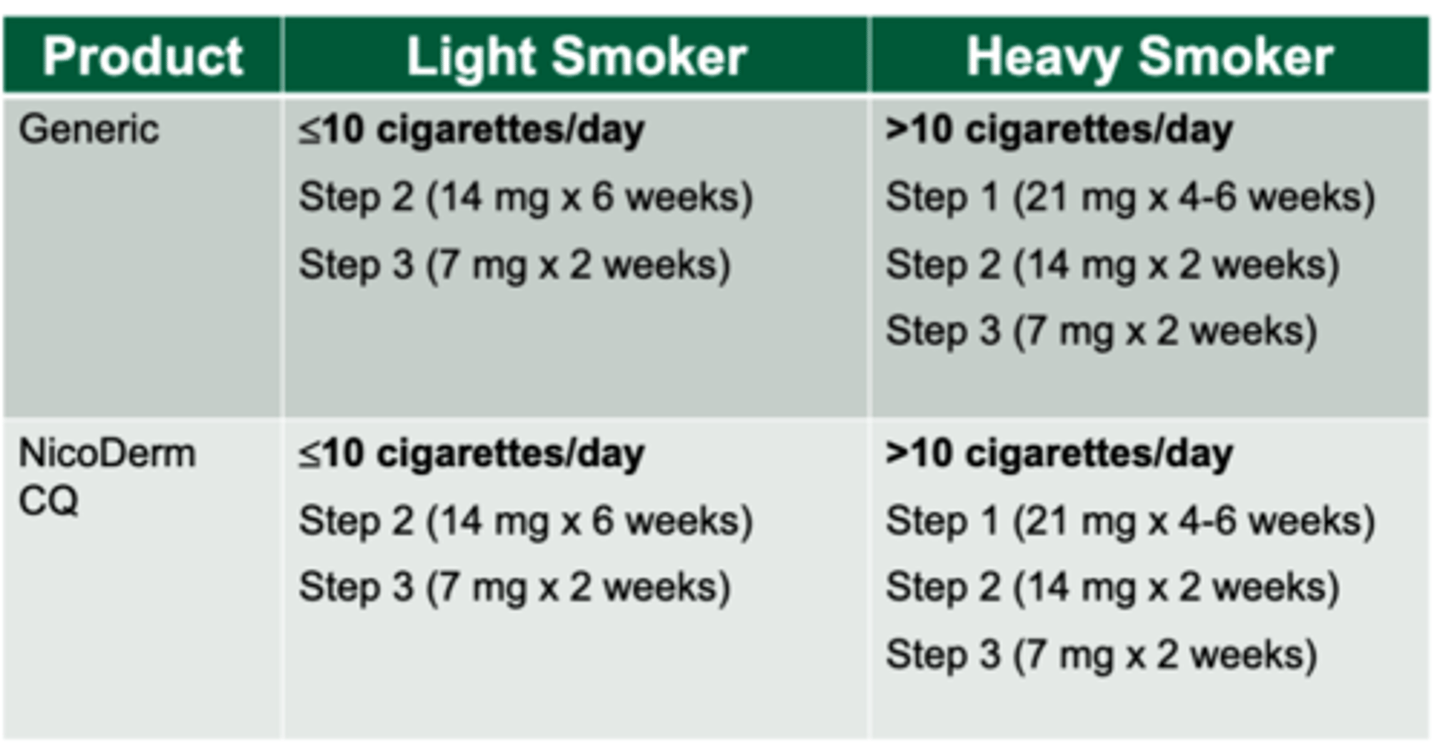
NRT patch dosing
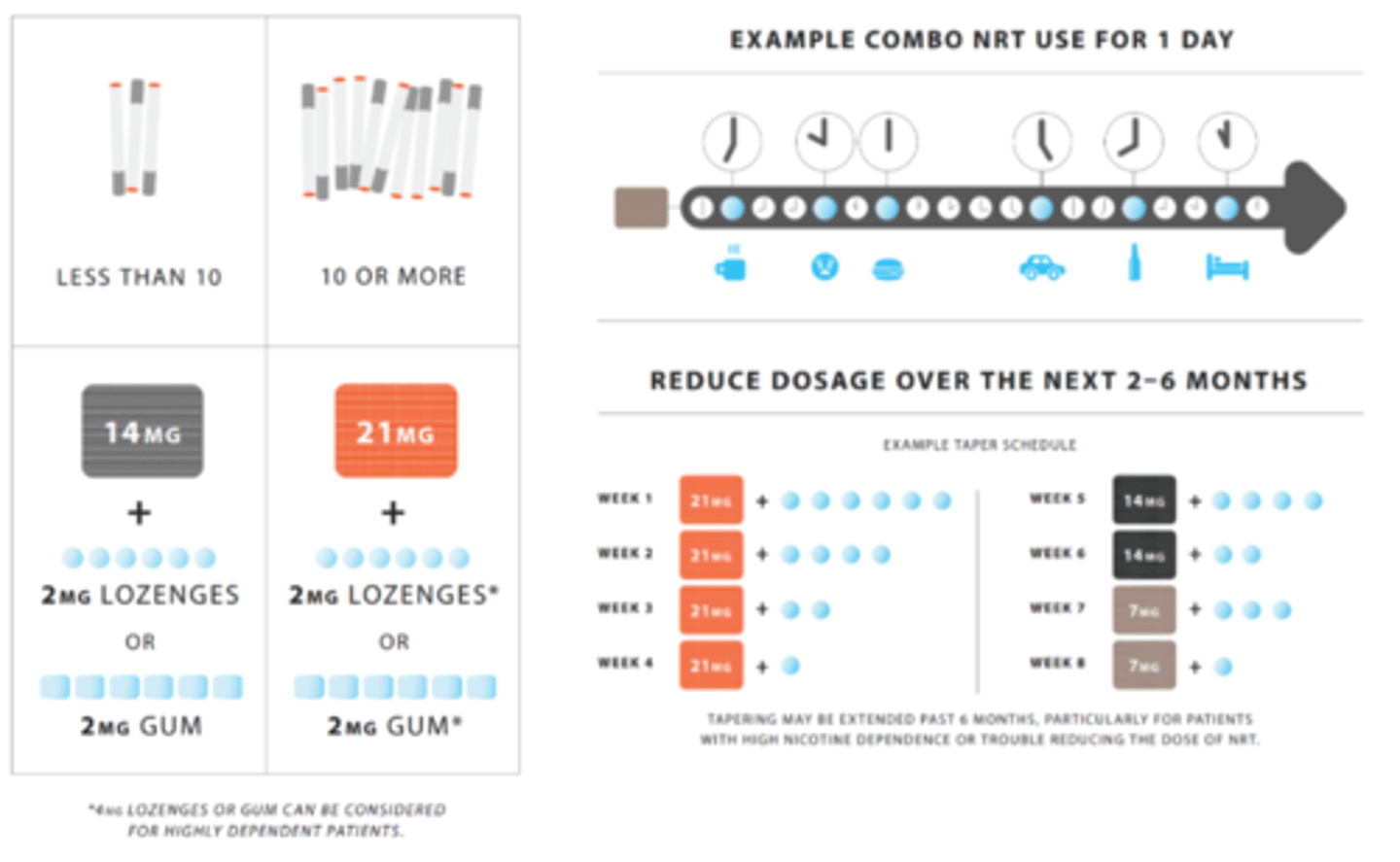
Heavy Smoker (>10 cigarettes/day)= 21 mg starting dose
Light smoker (<10 cigarettes/day)= 14 mg starting dose
*12 Week long duration of dosing schedule
*wear for 24 hours a day. Patients may bathe, swim, shower, or exercise as normal
Pack year calculation
# packs smoked per day X # of years smoking
Application of NRT patch product counseling points?
1. Wash hands before and after use
2. Press firmly for 10 seconds
3. Apply to different area daily
4. Remove each patch daily
5. Fold in half when done
6. Plastic baggy good
Combination therapy
"seatbelt": daily maintenance (patch)
"airbag": PRN for craving breakthroughs (gum or lozenge)
Adverse effects and precautions: Nicotine patches
1. Topical burning, itching, redness: may be helped by applying TCS prior to application
2. Vivid dreams
3. DO NOT USE IN patients with dermatological conditions
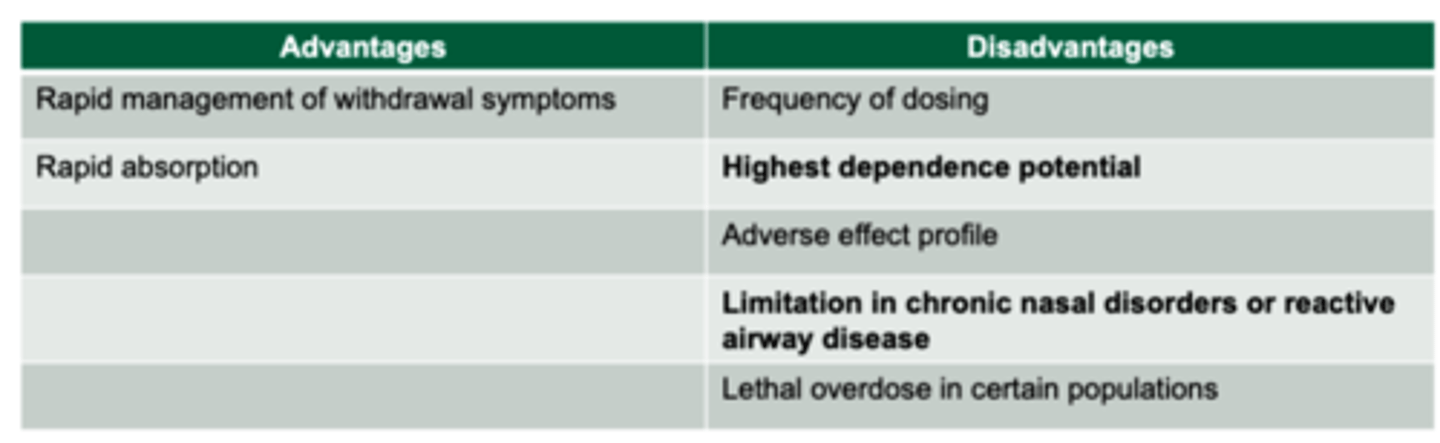
Nicotine nasal spray
Rapid absorption across nasal mucosa= Highest dependence potential
Start with 1-2 doses (1 dose= 2 sprays) per hour and increase prn
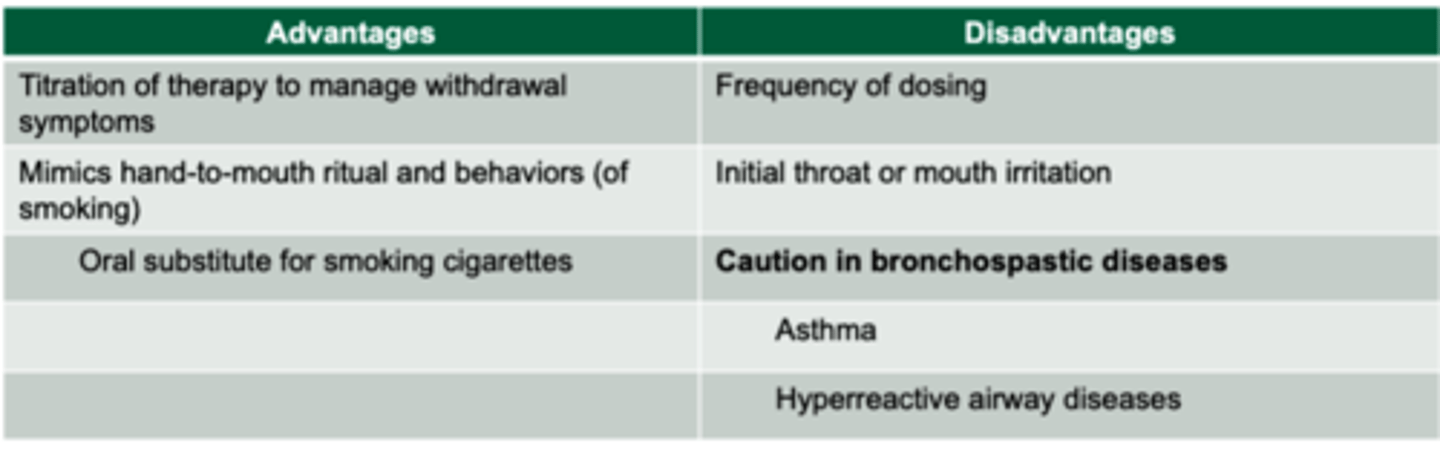
Nicotine inhaler
-Absorbed across buccal mucosa
-1 cartridge every 1-2 hours: Maximum of 16 cartridges/day
-Do not eat or drink 15 minutes before or while using inhaler= unrealistic for q 1H administration
*mainly for patients with the behavioral depending on sucking on something
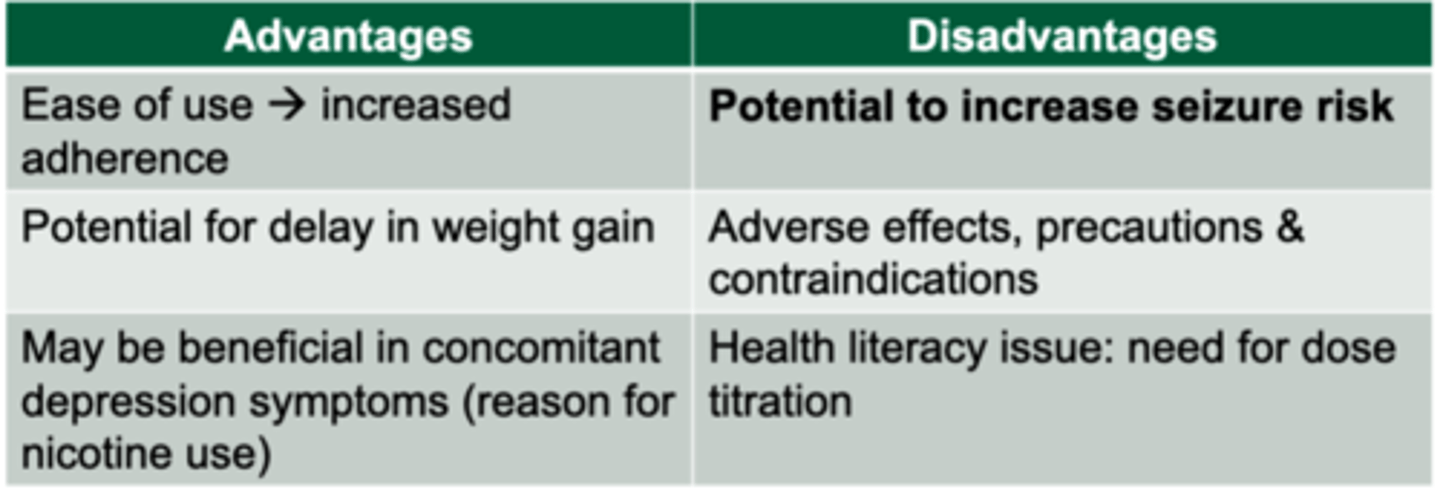
Bupropion SR
- lowers craving for cigarettes
-lowers symptoms of nicotine withdrawal
-Delays weight gain
* Contraindicated in patients with seizure disorder
MOA of bupropion SR?
Inhibits reuptake of dopamine and norepinephrine
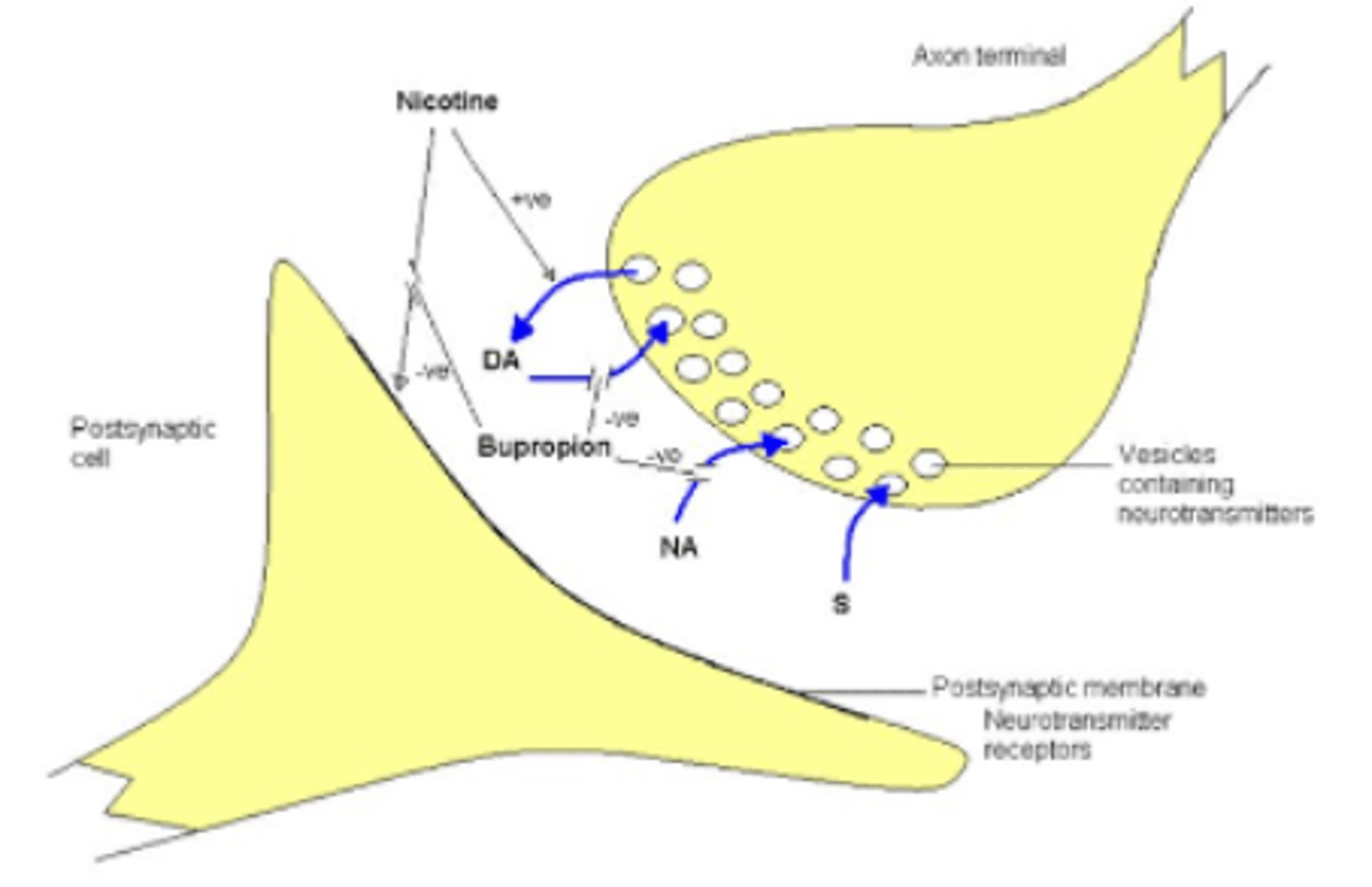
Potential adverse effects of Bupropion SR
1. Insomnia
2. Dry mouth
3. Headaches
4. Itchy
5. Pharyngitis
6. Tachycardia
8. Seizures
9. Neuropsychiatric effects
10. Suicide risk
Explain up-titration dosing for bupropion?
Days 1-3: 150 mg daily
Days 3+: 150 mg BID
Regimen lasts 7-12 wks
*begin therapy PRIOR to quit date
T/F: Bupropion is contraindicated in persons susceptible to seizures.
True
Bupropion SR black box warning
Increased risk of suicidal thinking and behavior in young adults 18 to 24 years of age
Varenicline (Chantix)
Selective a4B2 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor partial agonist= competitively inhibits binding of nicotine
Clinical effects:
- lowers symptoms of nicotine withdrawal
- decreases dopamine stimulation responsible for reinforcement and reward with smoking
Varenicline up-titration dosing schedule
Start 1 week before quit date
Days 1-3: 0.5mg daily
Days 4-7: 0.5 mg PO BID
Day 8 to end of treatment: 1 mg PO BID
*can be renally adjusted to 0.5 mg once daily
Typical treatment duration for Chantix?
12 weeks
Max 24 weeks, but not usually
Common adverse effects of varenicline? (nine)
1. Irritability
2. Insomnia
3. Abnormal dreams= NIGHTMARES
4. Nausea: minimized by taking with water/ food
5. Headache
6. Suicidal ideation
7. Depression
8. Flatulence
9. Constipation

T/F: Women 35 years and older using oral contraceptives AND smoking at least 15 cigarettes per day are at significant elevated risks for increased cardiovascular complications.
True
Consult about alternative methods• IUD, progestin only, and others.
True or False: using smoking cessation pharmacotherapy in pregnancy must be assessed using risk and benefits
True: risk of smoking are greater than risk of the medications however the safest intervention is behavioral therapy
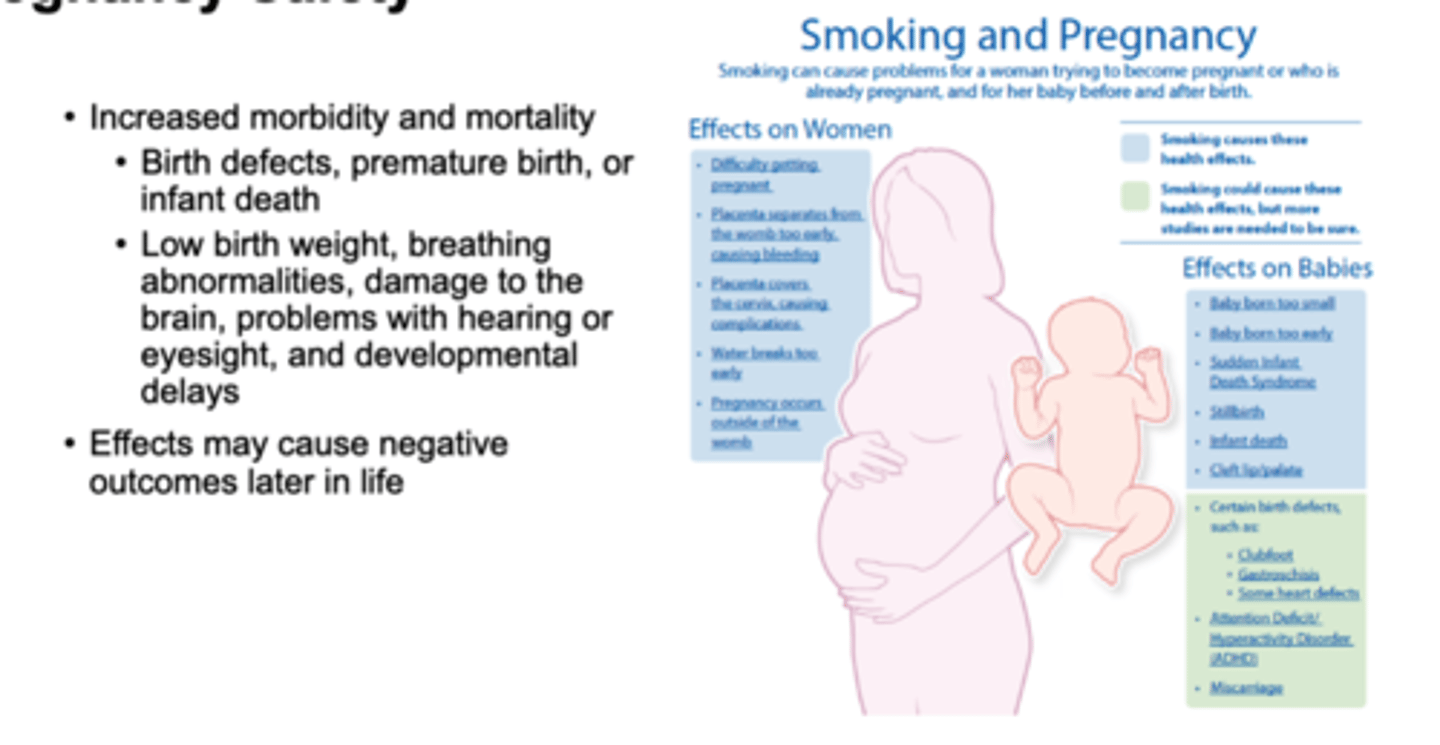
Smoking induces which CYP enzyme?
CYP1A2 which thus decreases effects of medications
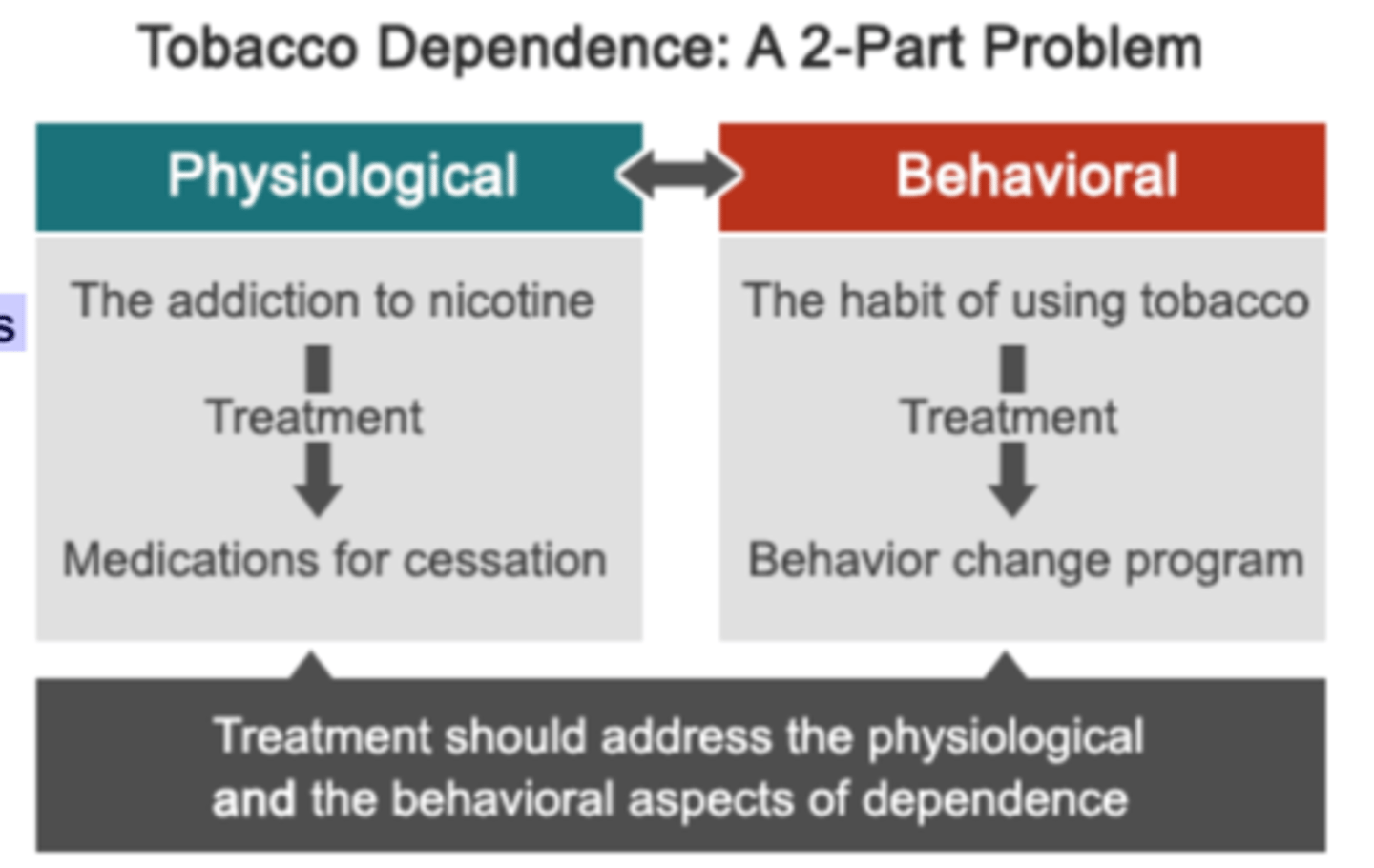
Approaches to Dependence, Treatment, and Relapse
1. Fagerstrom test for nicotine dependence= see how dependent patient is by how often they smoke
2.
Addressing dependence
Successful tobacco treatment requires multipart considerations between underlying physiological and behavioral issues
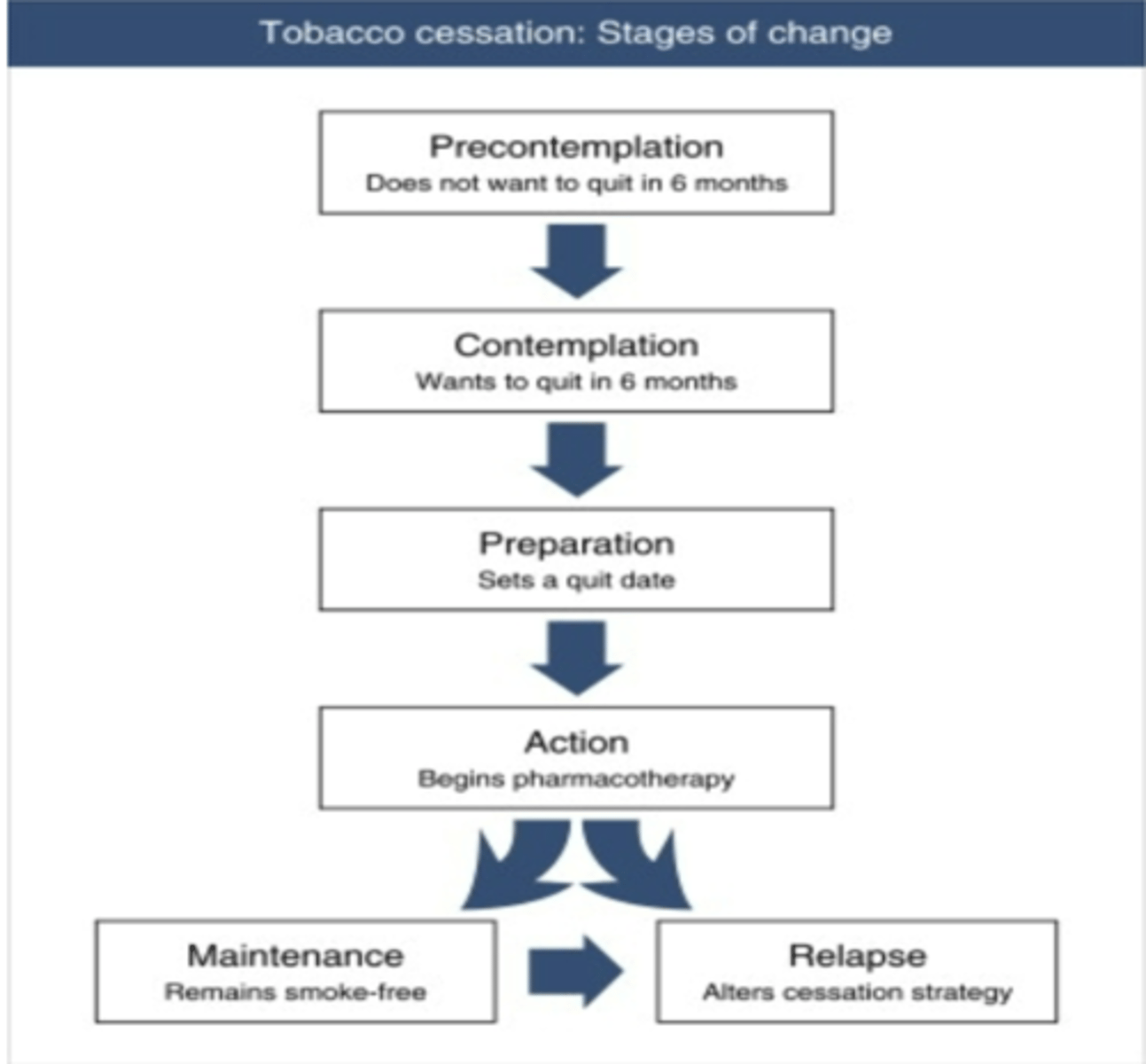
Define the "precontemplation" phase of quitting
Not really even thinking about quitting
Greater than 6 mths
Tobacco cessation: Stages of change
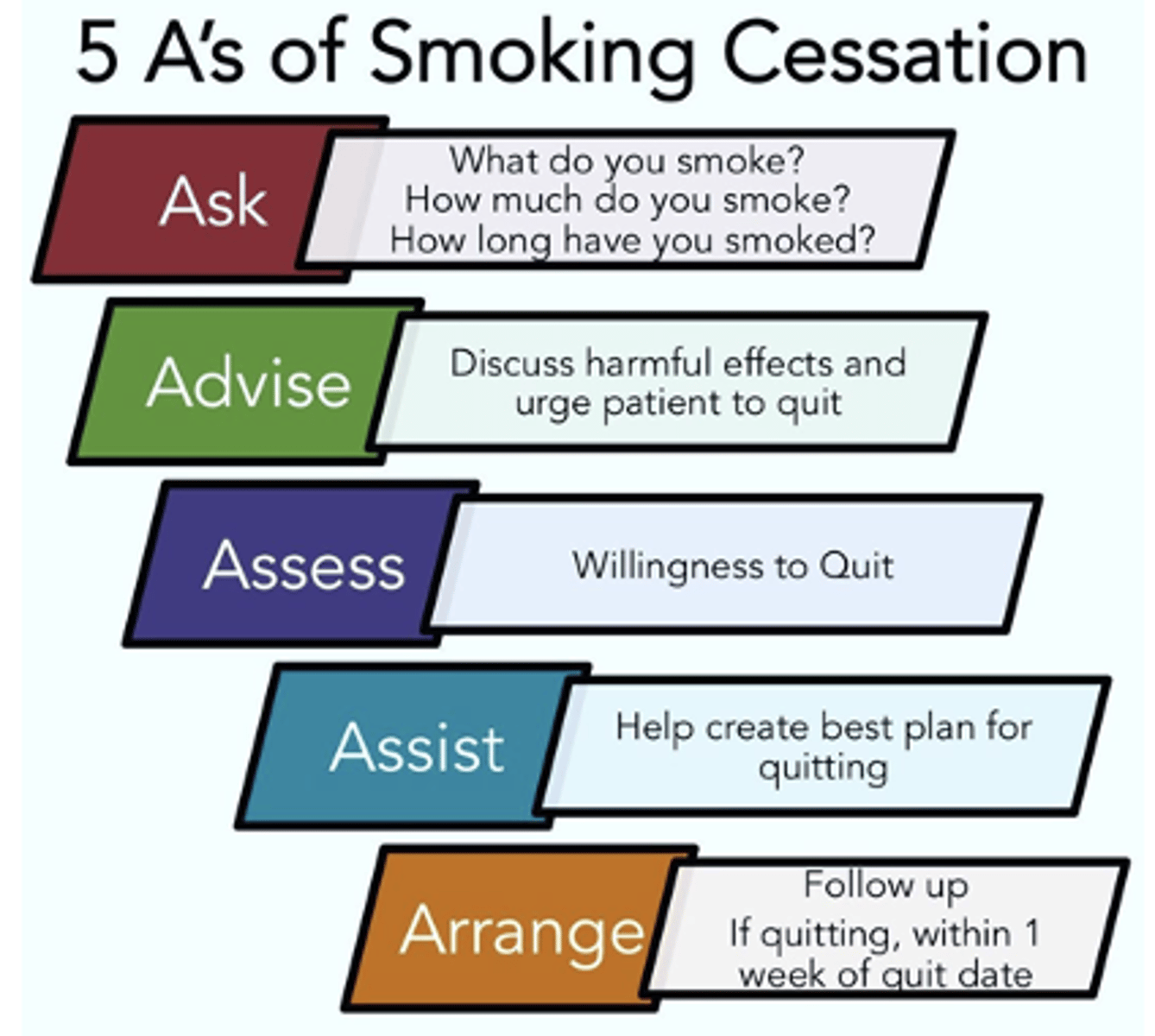
Smoking Cessation's 5 A's
At how many pack years should someone be recommended for lung cancer screening?
30 pack years