Viral Diseases and Global Health week 3
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
immunolagy week 3
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
The three factors in the Epidemiological Triad are the A ______, the H___, and the E__.
agent, host, environment
The __ in the Epidemiological Triad refers to the pathogen that causes the infection, such as a virus, bacteria, or parasite.
agent
Dengue virus is mostly spread to people by the bite of infected mosquitoes, mainly Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus. After the mosquito drinks blood from an infected person, the virus grows inside its __________ and then spreads to other parts of its body, including the __________ __________.
midgut, salivary glands
How is the Dengue virus transmitted to humans?
A) Through contaminated water
B) By inhalation of viral particles
C) Via the bite of infected Aedes mosquitoes
D) Through direct contact with infected blood
Via the bite of the infected Aedes mosquitoes
Which of the following is an example of a viral disease with high global prevalence?
A) Tuberculosis
B) Dengue
C) Malaria
D) Cholera
Dengue
What is the primary vector for the transmission of Dengue virus?
A) Anopheles mosquito
B) Aedes aegypti mosquito
C) Culex mosquito
D) Tsetse fly
Aedes aegypti mosquito
Which of the following statements is incorrect regarding the fundamental characteristics of viruses?
A. Viruses lack ribosomes and must utilise host translational machinery to synthesise proteins.
B. Viral replication depends entirely on the metabolic and enzymatic systems of the host cell.
C. Viruses can possess either DNA or RNA genomes, but never both simultaneously.
D. Some viruses can carry out autonomous replication in specialised host-free environments under laboratory conditions.
E. All viruses are composed of nucleic acid enclosed within a protein capsid, and some have additional lipid envelopes.
Some viruses can carry out autonomous replication in specialised host-free environments under laboratory conditions.
What is the term for a disease that occurs at a constant level within a population?
A) Sporadic
B) Endemic
C) Epidemic
D) Pandemic
Endemic
Which stage of Dengue infection is characterized by high fever and viremia?
A) Febrile phase
B) Critical phase
C) Recovery phase
D) Latent phase
Febrile phase
Considering both the immune response and microbiological principles, which of the following interventions is most effective in preventing viral infections at the population level?
A. Antibiotics, which prevent bacterial co-infections that often complicate viral infections and reduce the severity of the disease.
B. Vaccines, which stimulate both humoral and cell-mediated immunity, create long-lasting memory responses to specific viral antigens and reduce viral transmission within populations.
C. Antiviral drugs, which directly inhibit viral replication and can reduce viral load, offering long-term prevention of viral infections in healthy individuals.
D. Rehydration therapy, which is used primarily to manage symptoms of gastrointestinal viral infections, reduces morbidity but does not prevent the initial infection.
E. Microbiome modulation, which involves altering the gut microbiota to improve immune function and prevent viral infections through non-specific mechanisms.
Vaccines, which stimulate both humoral and cell-mediated immunity, create long-lasting memory responses to specific viral antigens and reduce viral transmission within populations.
Which laboratory finding is most commonly associated with Ebola Virus Disease?
A) Lymphocytosis
B) Hypernatremia
C) Thrombocytopenia
D) Hypoglycemia
Thrombocytopenia
Which species was responsible for the 2014 West African Ebola outbreak?
A) Sudan ebolavirus
B) Taï Forest ebolavirus
C) Zaire ebolavirus
D) Reston ebolavirus
Zaire ebolavirus
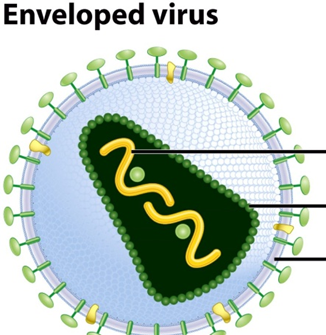
where is the Genome
yellow section
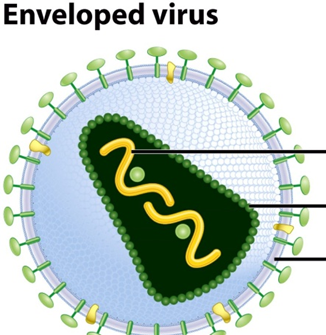
The protective protein shell surrounding the viral genome is called the __________.
capsid
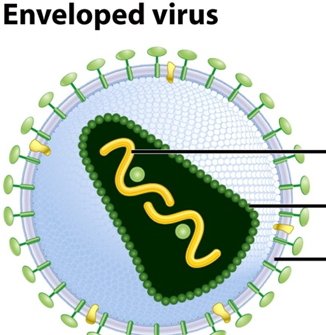
The wavy strand inside the virus represents the __________ __________, which can be DNA or RNA.
genetic material
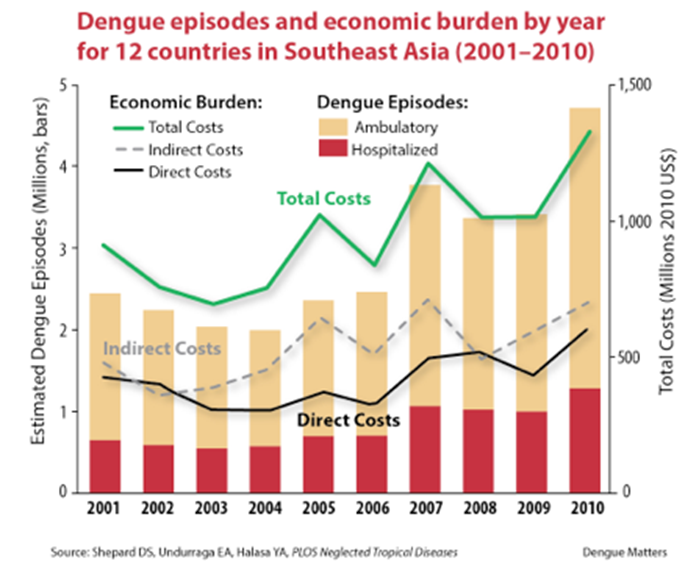
Economic Impact due to Dengue virus
loss of productivity due to illness and disability
Which of the following statements best describes the molecular characteristics and replication strategy of the Ebola virus?
A. Ebola virus is a non-enveloped, double-stranded RNA virus that replicates in the host cell nucleus using host RNA-dependent RNA polymerase.
B. Ebola virus is an enveloped, negative-sense, single-stranded RNA virus that relies on its own RNA-dependent RNA polymerase for cytoplasmic replication.
C. Ebola virus is a segmented, positive-sense RNA virus that uses host reverse transcriptase to integrate into the host genome.
D. Ebola virus is a circular, double-stranded DNA virus that encodes its own DNA polymerase for replication in the cytoplasm.
E. Ebola virus is an enveloped, positive-sense RNA virus that directly serves as mRNA upon entry into the
Ebola virus is an enveloped, negative-sense, single-stranded RNA virus that relies on its own RNA-dependent RNA polymerase for cytoplasmic replication.
Which of the following clinical features is least likely to be observed during the early phase of Ebola Virus Disease?
A. High-grade fever and chills due to cytokine release
B. Severe myalgia and arthralgia related to viral replication and tissue damage
C. Profound jaundice caused by early hepatocellular failure
D. General malaise and fatigue resulting from systemic immune activation
E. Headache associated with vascular inflammation and cytokine effects
Profound jaundice caused by early hepatocellular failure
What is the primary method used to diagnose acute Ebola virus infection?
A) ELISA
B) RT-PCR
C) Western Blot
D) Immunofluorescence assay
RT-PCR
The incubation period for Ebola virus disease typically ranges from __________ to __________ days.
2 to 21
Ebola infection, the serum levels of __________ are often elevated more than ALT, indicating multi-organ involvement.
AST
One of the hallmark complications in fatal Ebola cases is __________, which results from widespread vascular damage and immune activation.
DIC
Ebola virus belongs to the __________ family and is characterized as an enveloped, non-segmented, negative-sense RNA virus.
Filoviridae