Patterns of Global Climate Change
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
Ecosystem
All living and non-living components in a certain community, along with all the interactions taking place between them
Biotic factors
Living parts of an ecosystem
Abiotic factors are
Non-living parts of an ecosystem, e.g. Light, water, salinity, pH
Earth's 4 systems
Hydrosphere - Water
Atmosphere - Air
Lithosphere/Geosphere - Soil and land
Biosphere - All living things and ecosystems
The carbon cycle
CO2 in air --> Photosynthesis --> Dead organisms and waste products --> Factory + vehicle combustion emissions --> CO2 in air
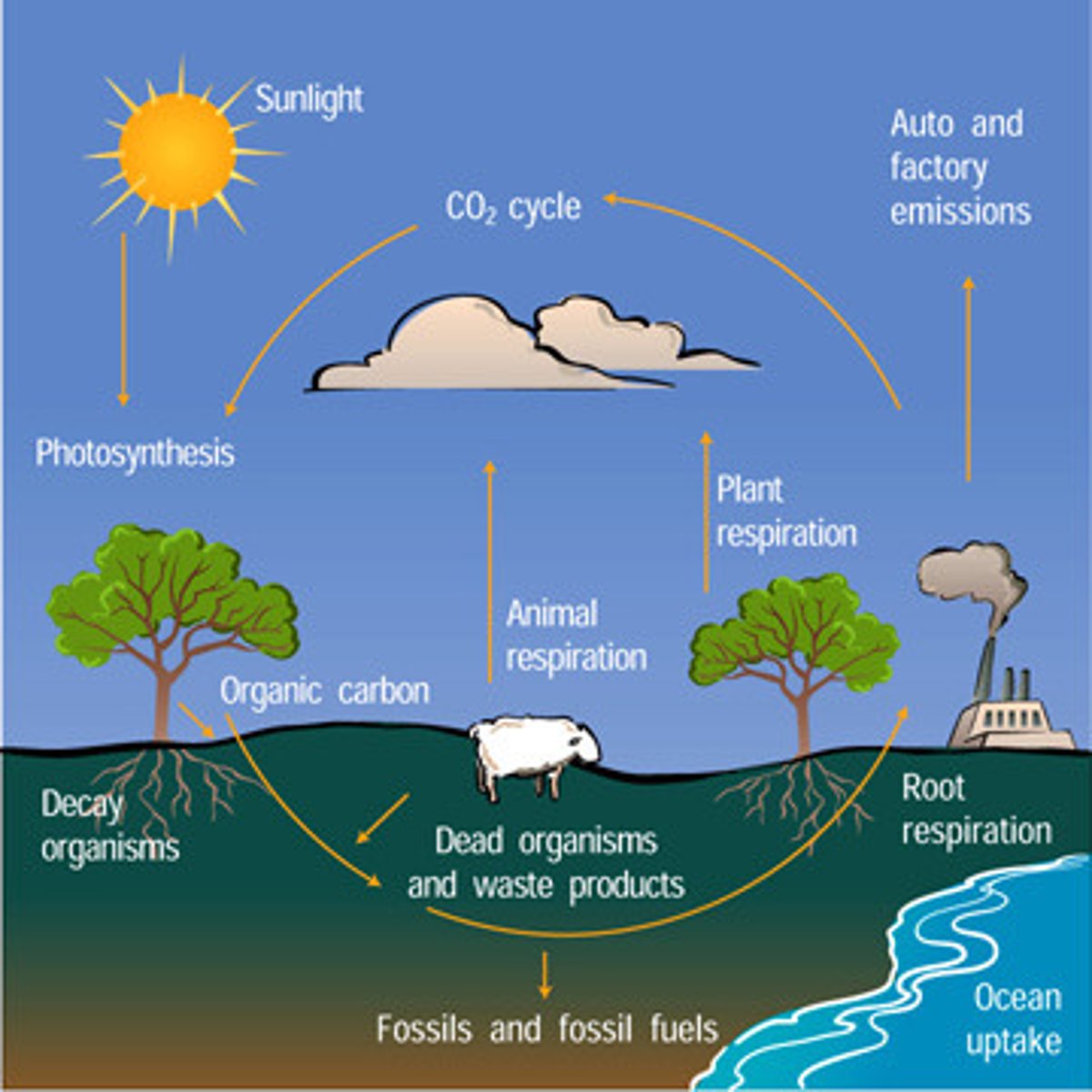
Photosynthesis
How plants convert the sun's light energy into chemical energy, takes place in Chloroplast of a cell
Photosynthesis word equation
carbon dioxide + water --light--> glucose + oxygen
Photosynthesis chemical equation
6CO2 + 6H2O --light--> C6H12O6 + 6O2
Cellular Respiration
the process by which cells in every organism use oxygen to produce energy from food, takes place in Mitochondria
Cellular Respiration word equation
glucose + oxygen --> carbon dioxide + water + energy
Cellular Respiration chemical equation
C6H12O6 + 6O2 --> 6CO2 + 6H20 + Energy (ATP)
What is the greenhouse effect?
Greenhouse gases trap some infrared radiation in the atmosphere, keeping the Earth warm
What is the Enhanced Greenhouse Effect?
Global warming due to increased greenhouse gases in Earth's atmosphere due to humans
Methane emitting activities
- Agriculture (cattle)
- Mining of natural gas
- Wastewater treatment
- Decomposition in landfill
Renewable energy
An energy source that won't run out, or will replenish faster than it is used
Green energy
A sustainable energy source that doesn't produce pollutants
Solar energy pros and cons
PROS: Renewable, green
CONS: Weather dependent, large land use
Wind energy pros and cons
PROS: Renewable, green
CONS: Weather dependent, bird disrupting
Hydropower pros and cons
PROS: Green
CONS: Steep valley needed, disrupts fish, weather dependent
Biodegradable
Able to be broken down naturally by bacteria
What is nuclear energy?
Energy made by splitting a uranium atom
How do the different spheres store carbon?
Atmosphere - Carbon and methane in the air
Lithosphere - Coal and oil deposits and rocks like limestone
Biota - Proteins, carbohydrates and lipids.
Hydrosphere - Dissolved carbon dioxide
Biosphere
All living things and ecosystems, where materials are cycled within the different spheres through the nitrogen, carbon and phosphorus cycles.
Atmosphere layers (from highest to lowest)
Exosphere - Escaping gases into space, no protection to biosphere
Thermosphere - High energy radiation from sun is absorbed here
Mesosphere - Meteorites burn up here
Stratosphere - Ozone layer absorbs UV radiation
Troposphere - Higher Oxygen Pressure, weather events
Hydrosphere
All water, 97% in oceans, 3% freshwater in ice, underground and atmosphere
Lithosphere/Geosphere
Earth’s rocky crust (made of igneous, sedimentary and metamorphic rock), and the soil. Provides nutrients to biosphere.
Nitrogen cycle
Nitrogen moves through biosphere and is used for DNA, proteins, and chlorophyll. Bacteria are involved in waste breakdown and nitrification/denitrification.
Phosphorus cycle
Phosphorus moves between lithosphere and hydrosphere through food chains. Found in rocks, dissolved, in fertiliser, and in biota for growth and CO2 absorption
Factors influencing climate change
Deforestation
Mining
CFCs
Increases in human population (agriculture)
Industrial wastes
Travel
Deforestation effects
More CO2
Impact element cycles
Likelihood of desertification (ecosystem becomes fry and arid; sun’s energy can’t evaporate water and instead heats ground and lower atmosphere
CFCs
Chlorofluorocarbons, once used greatly in refrigeration. React with ozone (O3), and destroy it. Stronger greenhouse gas than CO2.
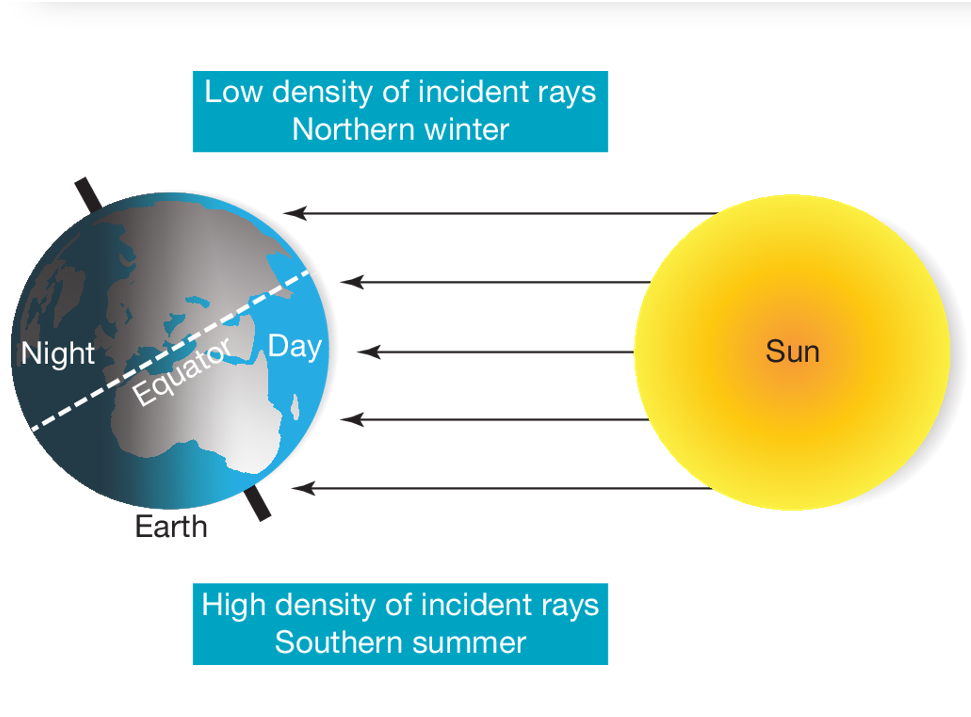
Variation in climate patterns is caused by
Tilt of Earth’s axis (amount of sun reaching Earth’s surface)
Differing land and water abilities to absorb and emit thermal radiation
Features of land
Earth tilt summary
23.5 degrees. Affects way sun passes through atmosphere and length of daylight
Heat absorption rate
Water heats and cools slower and less than land.
Land features
Temperature of air (altitude)
Sandy vs fertile soil
Snow reflects
Dark foliage absorbs
Albedo affect
Snow and clouds reflect heat, water absorbs. Therefore less ice = more heat
What causes wind?
Convection currents made by cold and warm air moving
La Nina vs El Nino
La Nina - Strong trade winds push warm water to Asia
El Nino - Weak trade winds bring warm water to America, leading to droughts in Australia
Main greenhouse gases and sources
Carbon Dioxide - Electricity and fuel, manufacturing and agriculture
Methane - Fossil fuel use and production, wetlands, agriculture
Nitrous Oxide - Fossil fuel combustion
Water Vapour - Warming of environment
Different types of biodiversity
Genetic diversity - variations within a species (colour, metabolic rate, leaf structures)
Species diversity - Variety of species on Earth (bugs, beetles, rhino beetle)
Geosequestration
Separating CO2 from other gases at fossil fuel plants and storing it underground.
Sustainable forests
Absorb carbon, release oxygen. When carbon storage plateaus, harvesting trees and turning them into wood products locks carbon, preventing immediate release into atmosphere.
Renewable resource examples
Solar, wind, geothermal, hydropower, bioenergy
Afforestation vs reforestation
Afforestation is planting trees where they were not previously, reforestation is planting trees back where they have been lost.
Water cycle
Evaporated (water bodies) and transpirated (plants) water condenses into clouds, which deposit as snow and ice and precipitate as rain. There is also surface and subsurface flow (Infiltration to percolation).