Honors Chemistry Unit 9 Study Review
1/44
Earn XP
Description and Tags
The electron, more in depth, flashcards to help any student know the rules and regulations, perfectly, for their test! Please note, you will need to practice using equations mentioned, this is because practice problems are not listed below. Also, practice short-hand and full electron configurations / drawings! These flashcards mainly focus on the memory and basics of the electron.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
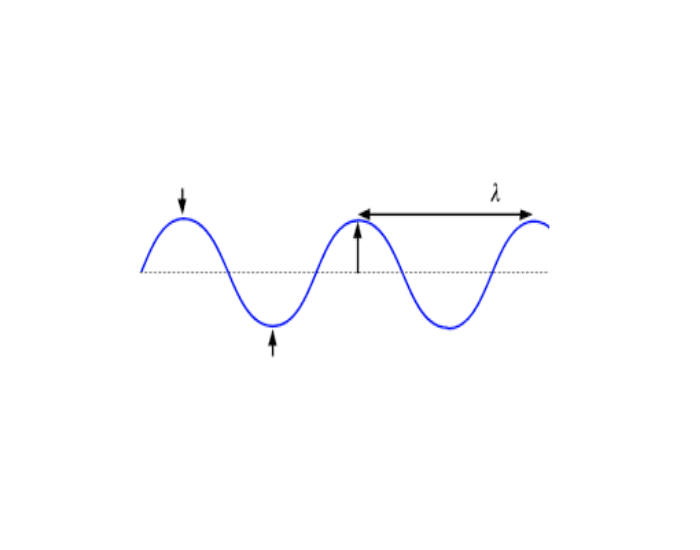
Fill in the blank. (What is left to right, what is up and down?)
Left to right - Wavelength
Up and down - Amplitude
For the visible spectrum, which color has the shortest wavelength?
longest wavelength?
highest energy?
lowest energy?
Violet
Red
Violet
Red
For the electromagnetic energy spectrum (EMR), what increases to the left, and what increases to the right?
Left is energy increasing
Right is wavelength increasing
Which radiation has the highest energy associated with it? (On the EMR)
Gamma Rays
Which radiation has the longest wavelength associated with it?
Radiowaves
The SI unit of wavelength is?
What can wavelength also be expressed by?
SI unit of wavelength is “m" (mass)
It can also be expressed by “nm” (nanometers)
The SI unit of frequency is?
s^-1 (s to the power of -1) (per second)
What is the relationship between energy and wavelength? (Inverse or direct)
Inverse (As one increases, the other decreases)
What is the relationship between energy and frequency? (Inverse or direct)
Direct (Both increase, together)
Who theorized that energy is QUANTIZED in multiples of hv (v = frequency)
Max Planck theorized that energy is quantized in multiples of hv (h = Planck’s Constant, v = frequency)
What are the two formulas to get energy?
Make sure to list what each variable is.
E = hv (h = Planck’s constant, v = frequency, and e = energy)
E = hc / λ (h = Planck’s constant, c = speed of light, e = energy, and λ = wavelength)
What is the formula used to get frequency?
Make sure to list what each variable is.
V = c / λ (c = speed of light, λ = wavelength, and v = frequency)
In 1900, Max Planck heated solids up to very high temperatures and observed that they emitted light (EMR). What is the name of this phenomenon?
Black Body Radiation (You can attempt to remember this by seeing the letters B, R, and P are very similar.)
Can Black Body Radiation be explained by classical physics?
No, this is because classical physics assumes that radiant energy is continuous. Black Body Radiation is quantized, not continuous.
According to Planck, EMR is quantized and can only be emitted or absorbed in certain amounts of multiple of what?
hν energy (h - nu)
Rutherford’s model of the atom proposed a central nucleus with all the positive charges. Where were the negative chargers or electrons located in THIS model?
In Rutherford’s model of the atom, the electrons were randomly distributed.
Niels Bohr applied Planck’s theory of quantized energy to Rutherford’s model of the atom. How did he explain the location of the electrons?
Remember how to draw and label Bohr’s model of the atom.
Bohr theorized that electrons were not randomly distributed, but instead occupied certain allowed orbits, each corresponding to quantized energy levels.
(You should label where the protons are. The red line in this picture is not relevant.)
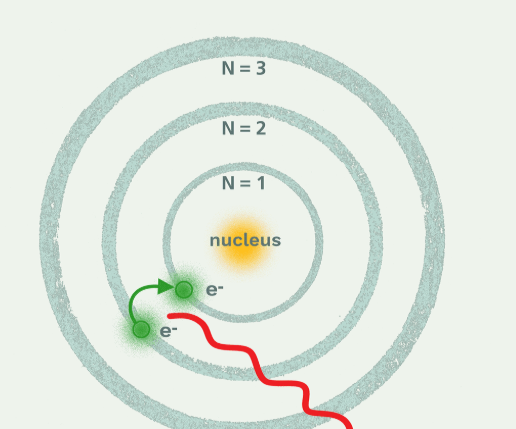
According to Bohr’s model, how were electrons able to move?
An electron could move if it were able to emit or absorb an hv energy or multiple of hv energy.
Electrons closest to the nucleus are said to be in what state?
Ground state
If an electron is not in the ground state, what state is it said to be in?
Excited state
Bohr’s theory worked only for what atom?
Why did it fail beyond this atom?
Hydrogen atom
It failed beyond this atom because it did not treat the electron as a wave.
In 1927, who gave a wave equation? State who, the equation, and what each variable means.
In 1927, Louis DeBroglie gave his wave equation: λ = h / mv
λ = wavelength, m = mass, v = velocity, and h = Planck’s constant
Fill in the blank: We don’t notice the wave nature of mass in motion in the (blank) world because the large m in the denominator means the wavelength is (blank and blank). This equation becomes important in the (blank) world because then the teeny tiny mass in the denominator means the wavelength is (blank and blank).
Marcoscopic world, short and unnoticeable
Microscopic world, long and noticeable
Fill in the blank:
This equation led the Austrian physicist (blank) to develop a new physics known as (blank).
Erwin Schrodinger developed quantum mechanics.
Erwin Schrodinger gave an equation that accounted for what?
When we solve this equation, we get four quantum numbers which give us information about electrons.
For the particle (mass) and wave nature of the electron.
Which orbitals are lobe shaped?
P orbitals
Which orbitals are spherically shaped?
S orbitals
Which orbitals are DONUT and lobed shaped?
D orbitals
Which orbitals are similar to D orbitals, but there are 7 orientations in space?
F orbitals
Which quantum number gives the shape of the orbital?
Angular momentum, L
Which quantum number gives the orientation of the orbital in space?
Magnetic quantum, mₗ (m sub l)
Which quantum number can have values from 1 to infinity?
Principle quantum, n
Which quantum number describes the spin orientation of the orbital?
Electron spin quantum, mₛ (m sub s)
Which quantum number determines the size of the oribtal?
Principle quantum, n
If n = 3, then what are the possible values for the other quantum numbers?
Please make sure to practice multiple of these problems for better understanding.
l = 0, 1, 2
mₗ = -2, -1, 0, +1, +2
mₛ = + ½ , - ½
How many electrons can go into each shell (s, p, d, and f)?
s shell = 2
p shell = 6
d shell = 10
f shell = 14
Which has more energy, 3d or 5s?
5s
Tip: Remember we always occupy the lowest energy orbitals first. Therefore, as we write an electron configuration, we go from lowest to highest. In this case, 3d would come before 5s, so 5s has more energy than 3d.
What is the Pauli Exclusion Principle?
No 2 electrons in the same atom can have the same four quantum numbers.
What is the Aufbau Principle?
Electron configurations are prepared as a result of a building up (adding on from one atom to the next) according to the Periodic Table.
What is Hund’s Rule?
When electrons go in orbits, they spin up before pairing and spinning down.
Tip: Think about how you would draw an electron configuration!
Because of the work of these scientists and applying the Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle, can we now determine EXACTLY where the electron is located in an atom?
No, we cannot determine exactly where the electron is located in an atom.
What is Heisenberg’s Uncertainty Principle?
This principle states that it is impossible to know both the momentum and the position of the electron at the same time. Why? The electron behaves as a wave, a continuum.
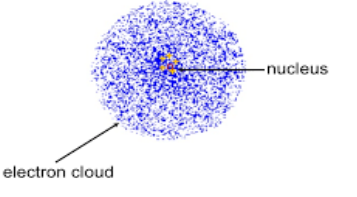
How does the current model of the atom show electrons? Please note that you need to know how to draw this.
The current model of the atom shows electrons in a dense cloud like atmosphere, surrounding the nucleus.
When an electron gains energy, is EMR absorbed or emitted?
When an electron loses energy, is EMR absorbed or emitted?
When an electron gains energy, EMR is absorbed.
When an electron loses energy, EMR is emitted.
Who is said to be the father of modern-day quantum mechanics?
Erwin Schrodinger