Ch. 3 Overview of Human Embryology and Development
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
Embryology
Study of individual origin and development.
Prenatal period
Time from conception to birth.
Embryonic period
First 8 weeks post-fertilization.
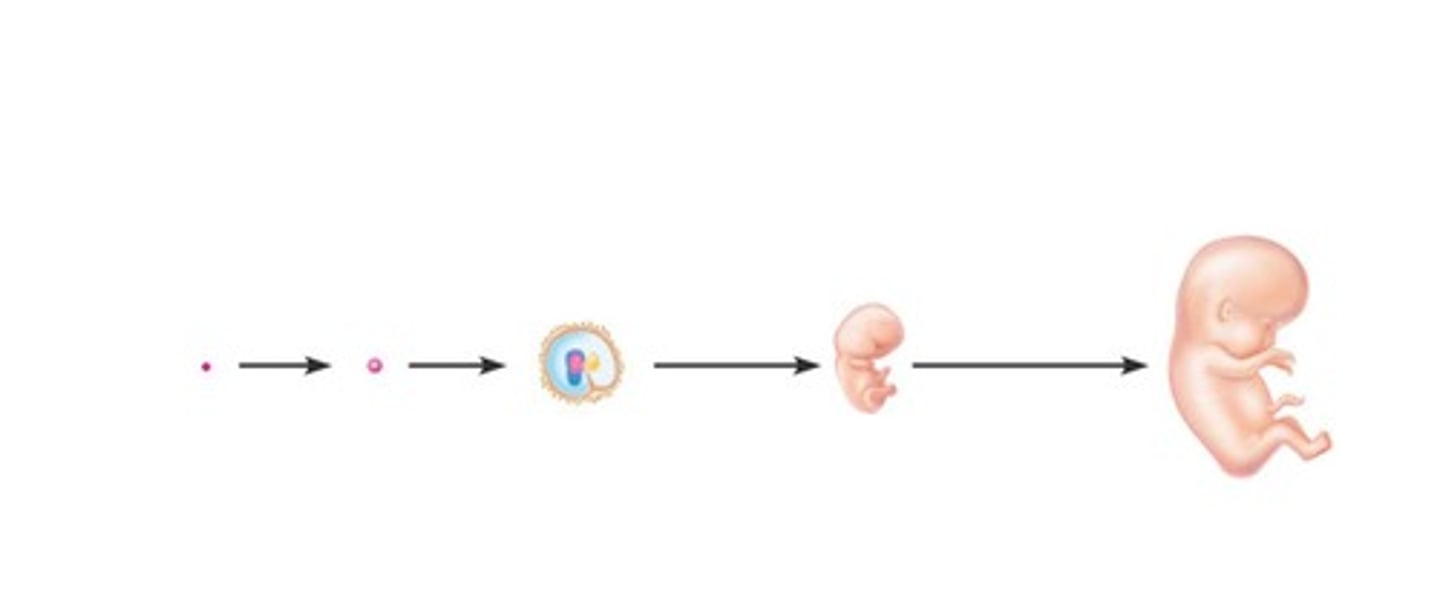
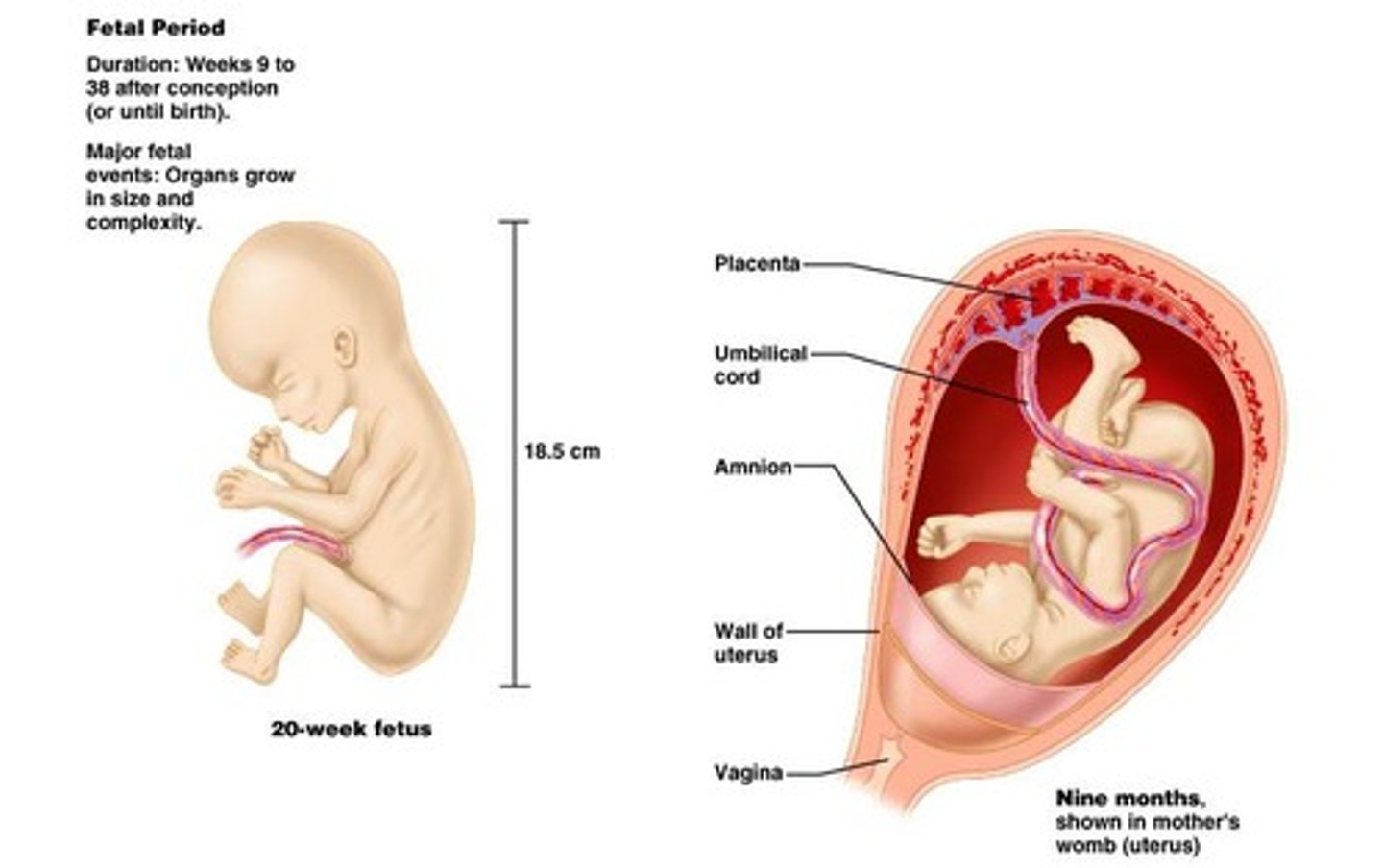
Fetal period
Remaining 30 weeks of development.
Zygote
Fertilized oocyte that develops into an embryo.
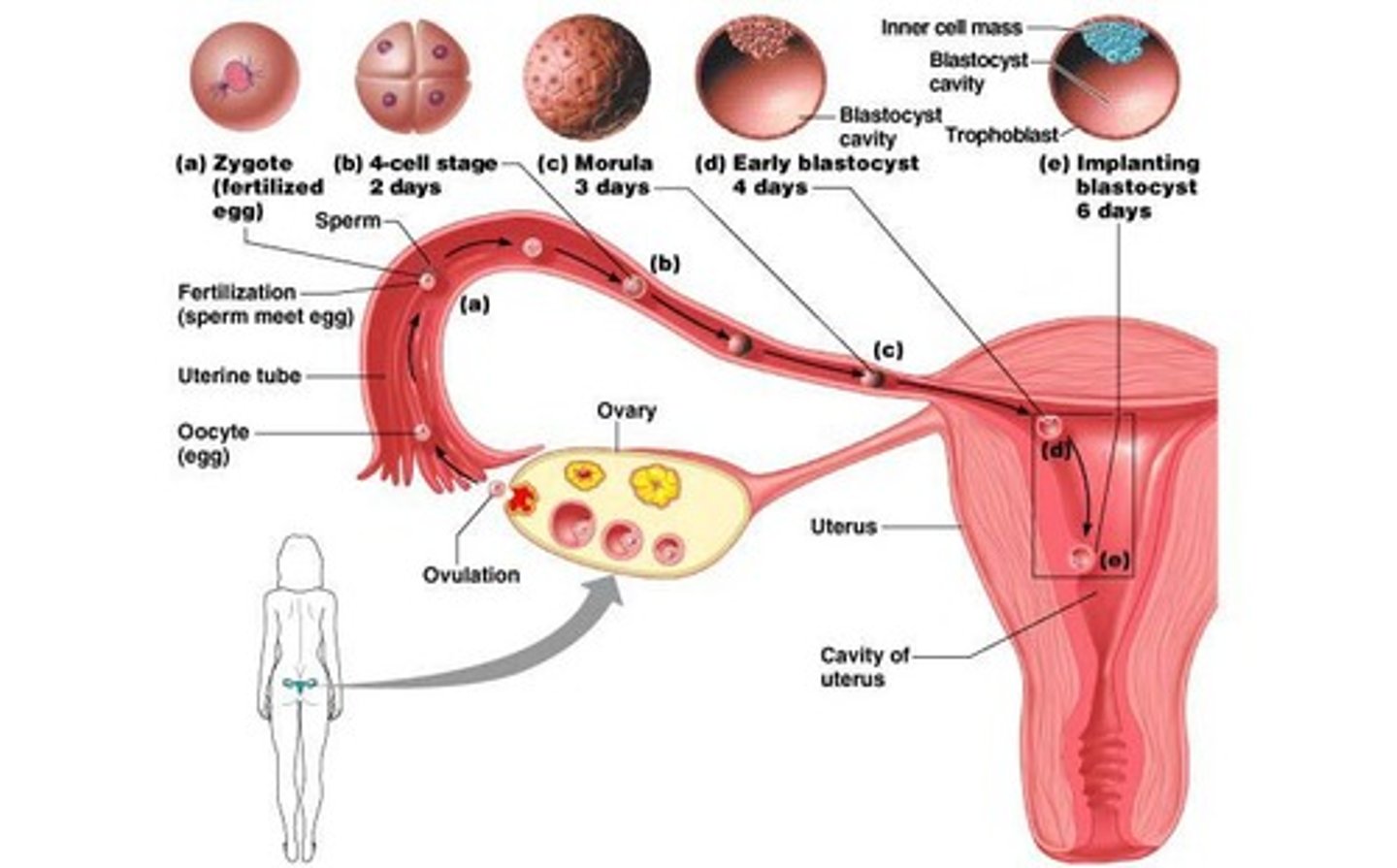
Blastomeres
Daughter cells formed from the zygote.
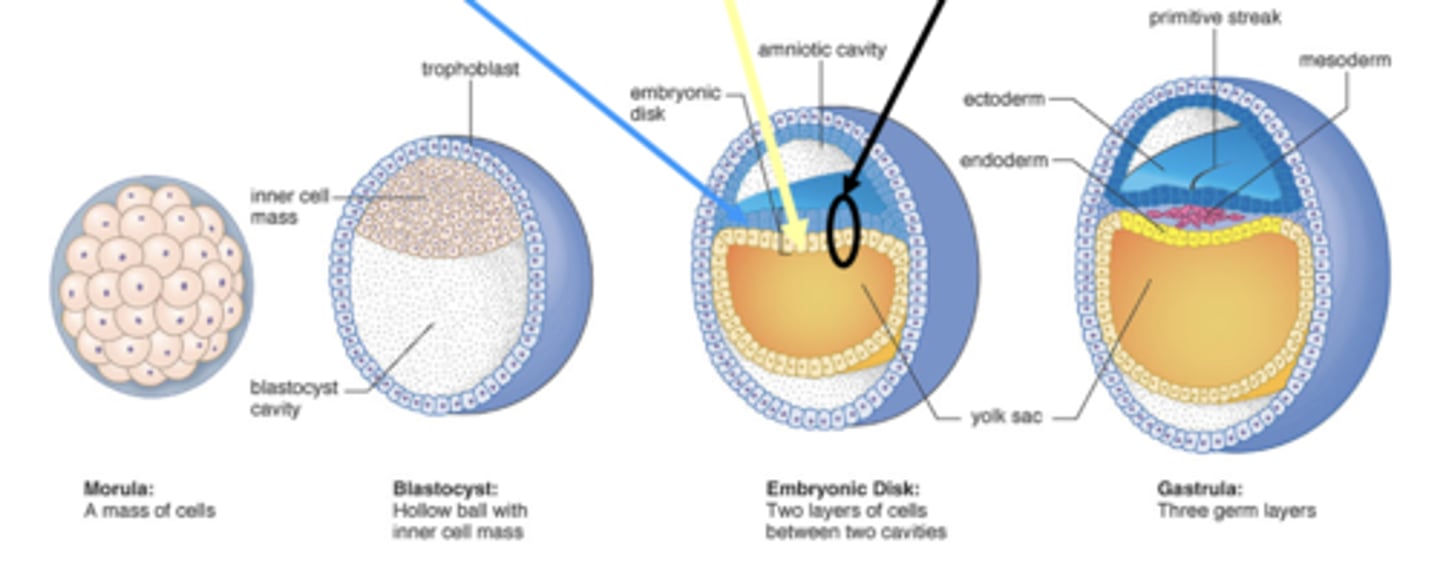
Morula
Cluster of 12-16 blastomeres.
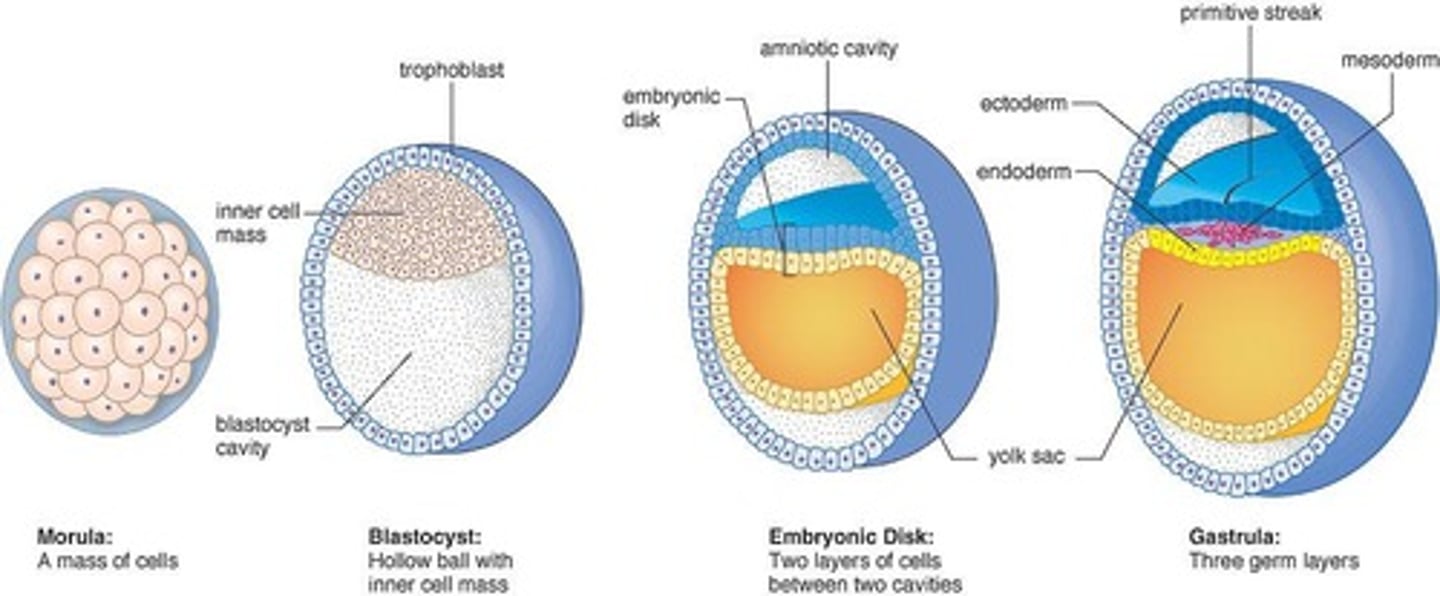
Blastocyst
Fluid-filled structure with about 60 cells.
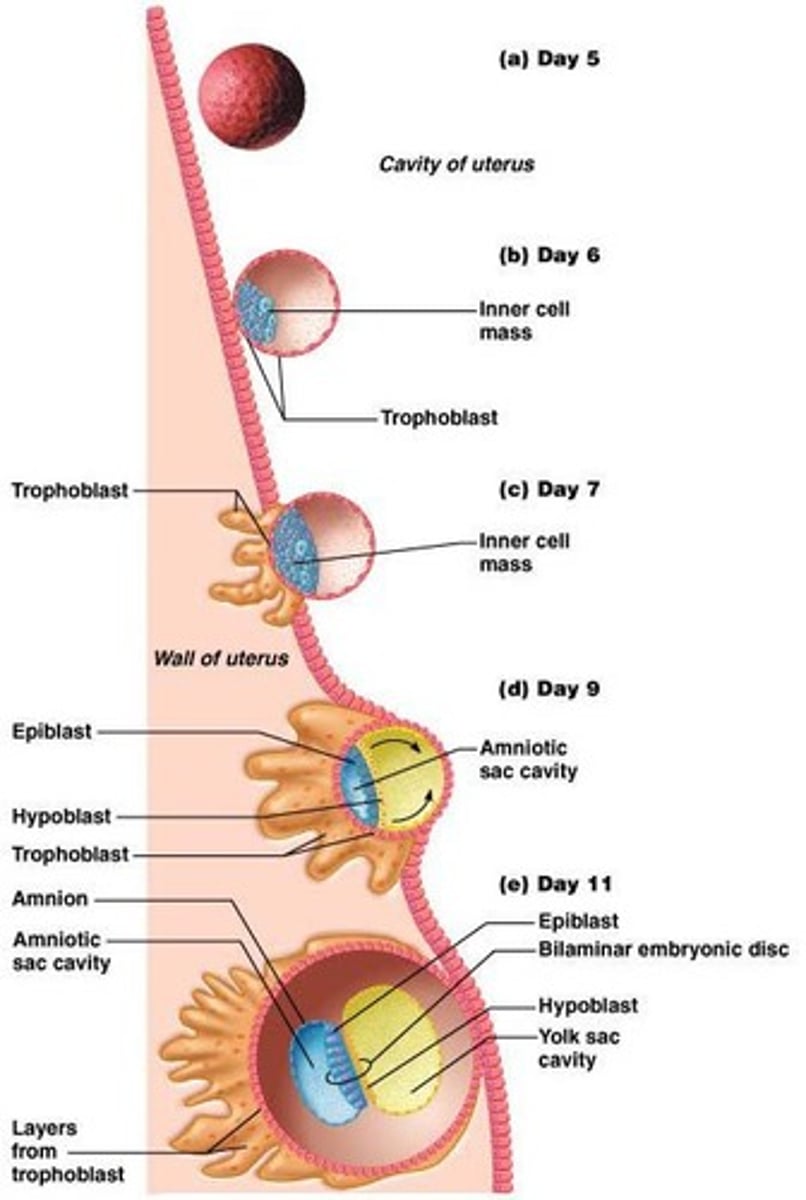
Cleavage
Cell division without growth.
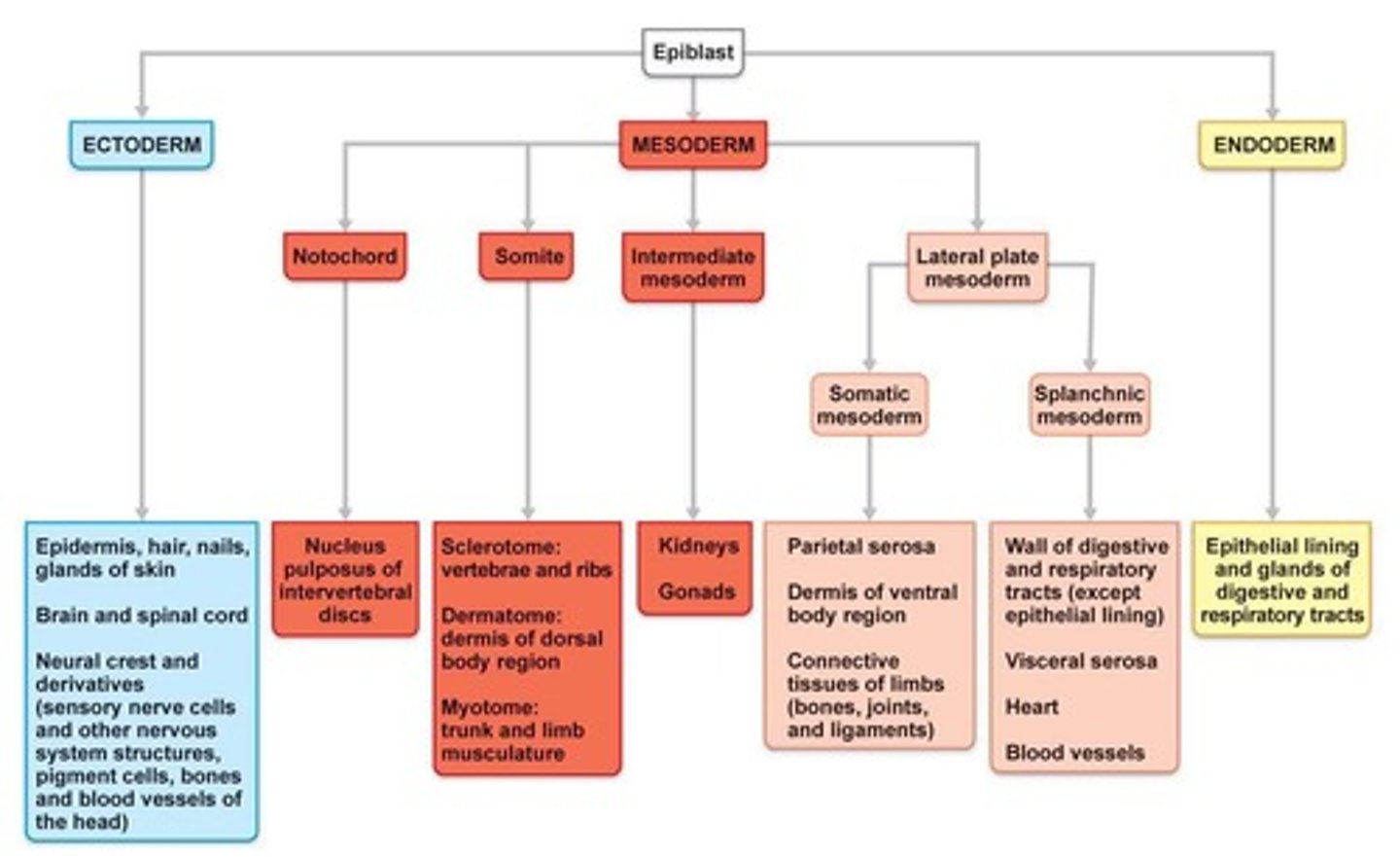
Bilaminar embryonic disc
Inner cell mass divided into two sheets.
Epiblast
Upper layer of the bilaminar embryonic disc.
Hypoblast
Lower layer of the bilaminar embryonic disc.
Amniotic sac
- Formed by an extension of epiblast
- Outer membrane: forms amnion
- Inner membrane: forms the amniotic sac cavity filled with amniotic fluid
Yolk sac
Forms digestive tube; extension of hypoblast.
Primitive streak
Site where epiblast cells migrate inward.
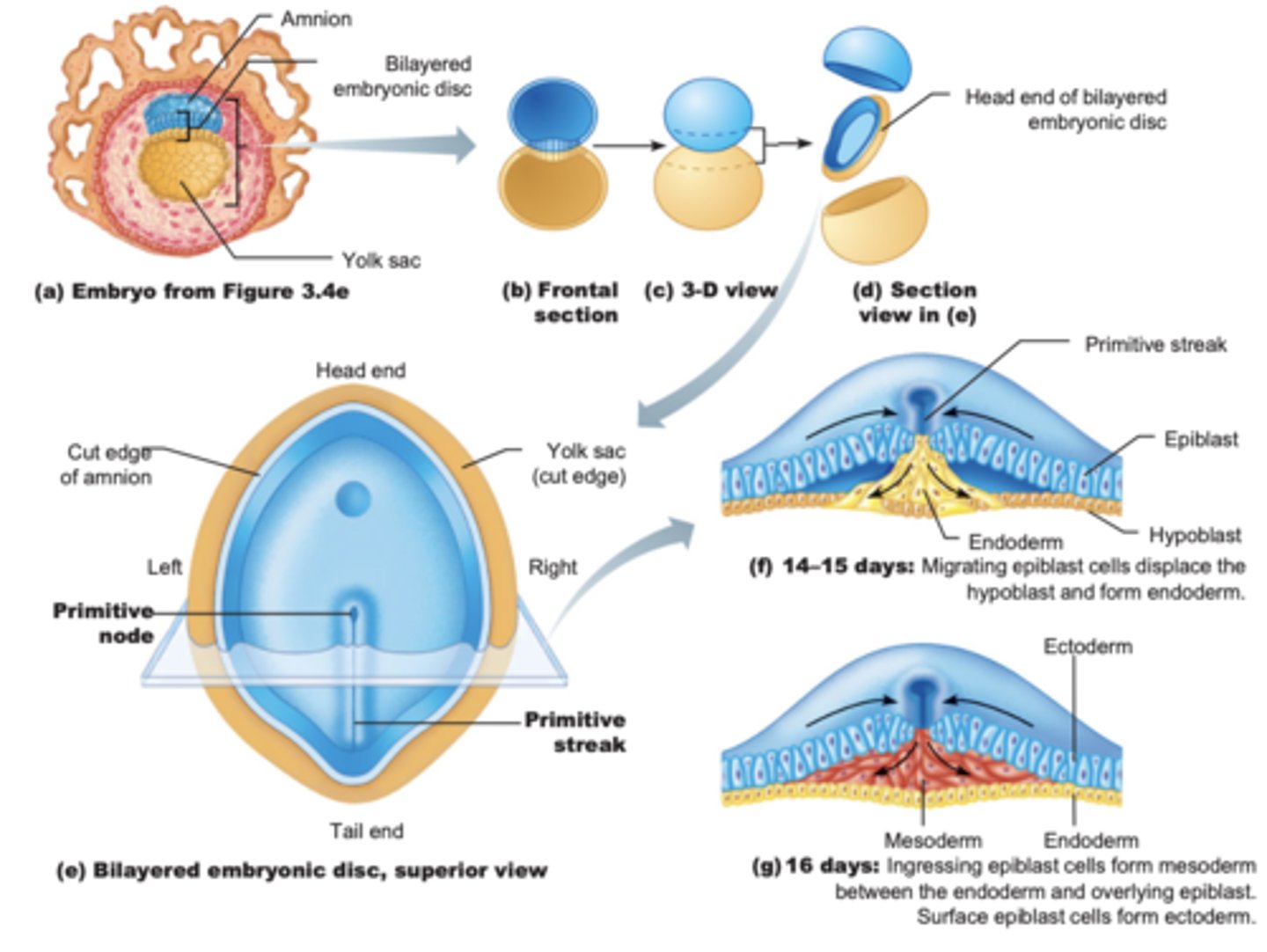
Gastrulation
Process forming three germ layers.
Endoderm
First migrating cells replace hypoblast.
Mesoderm
Cells between epiblast and endoderm. Next group of migrating cells.
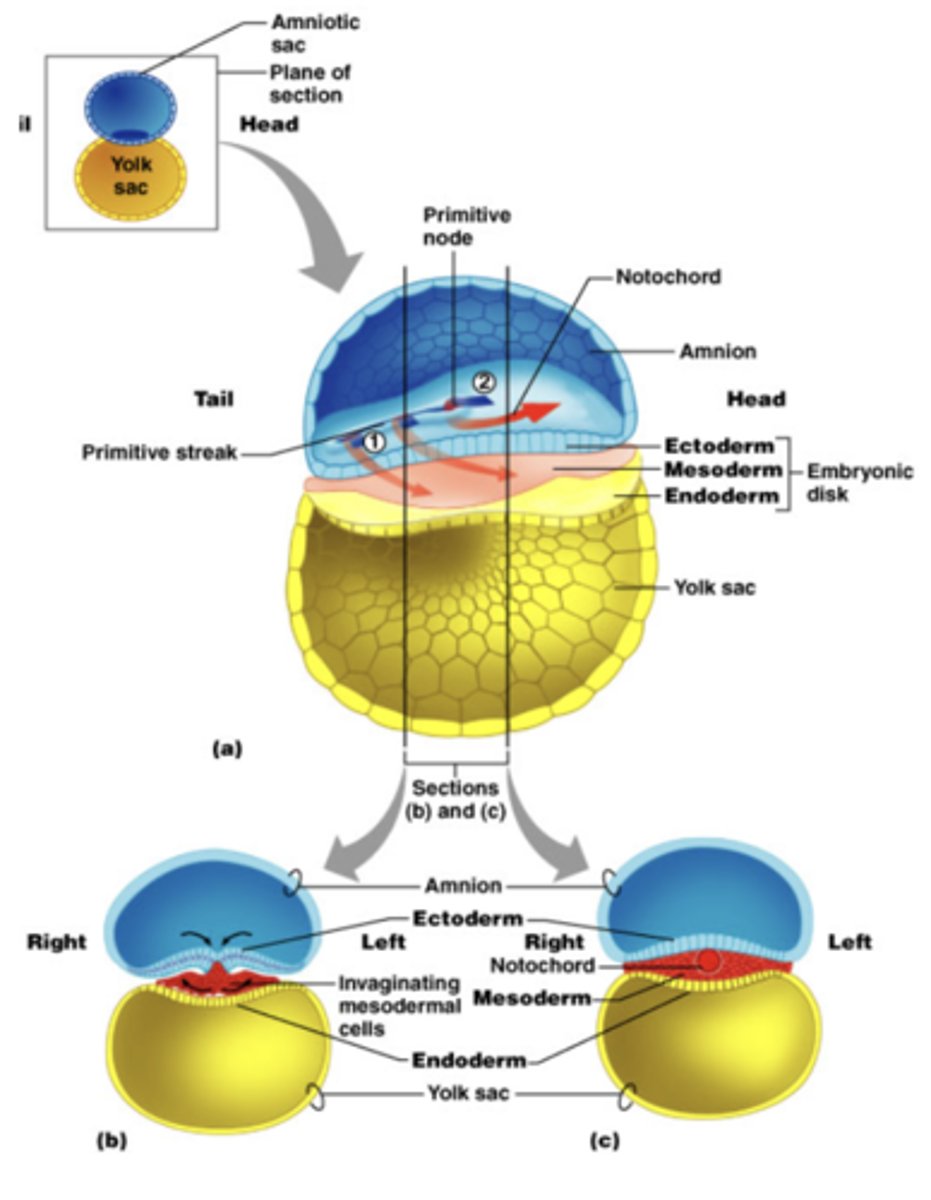
Ectoderm
Surface cells left at surface that do not migrate inward, formed from epiblast cells.
Neurulation
Ectoderm forms brain and spinal cord.
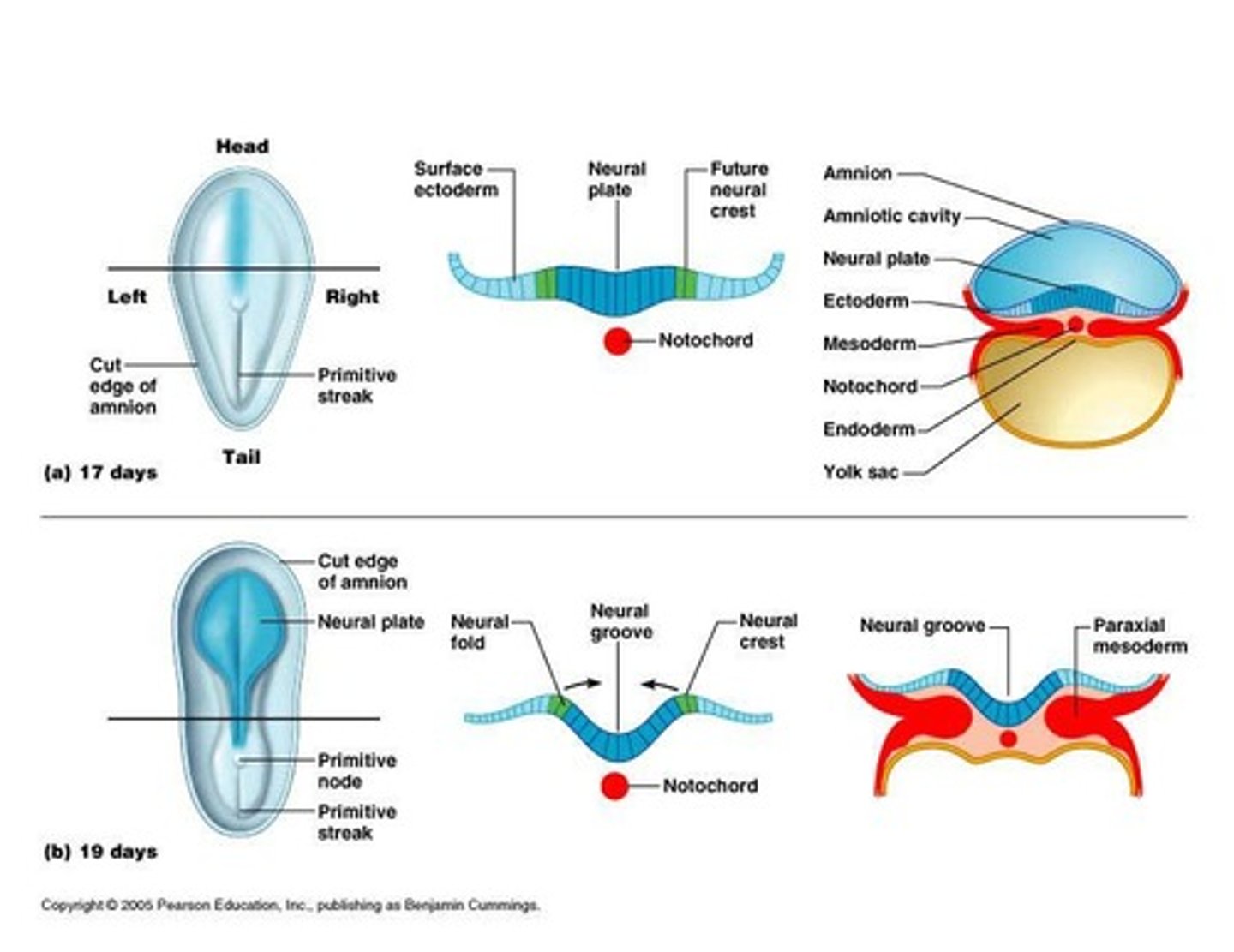
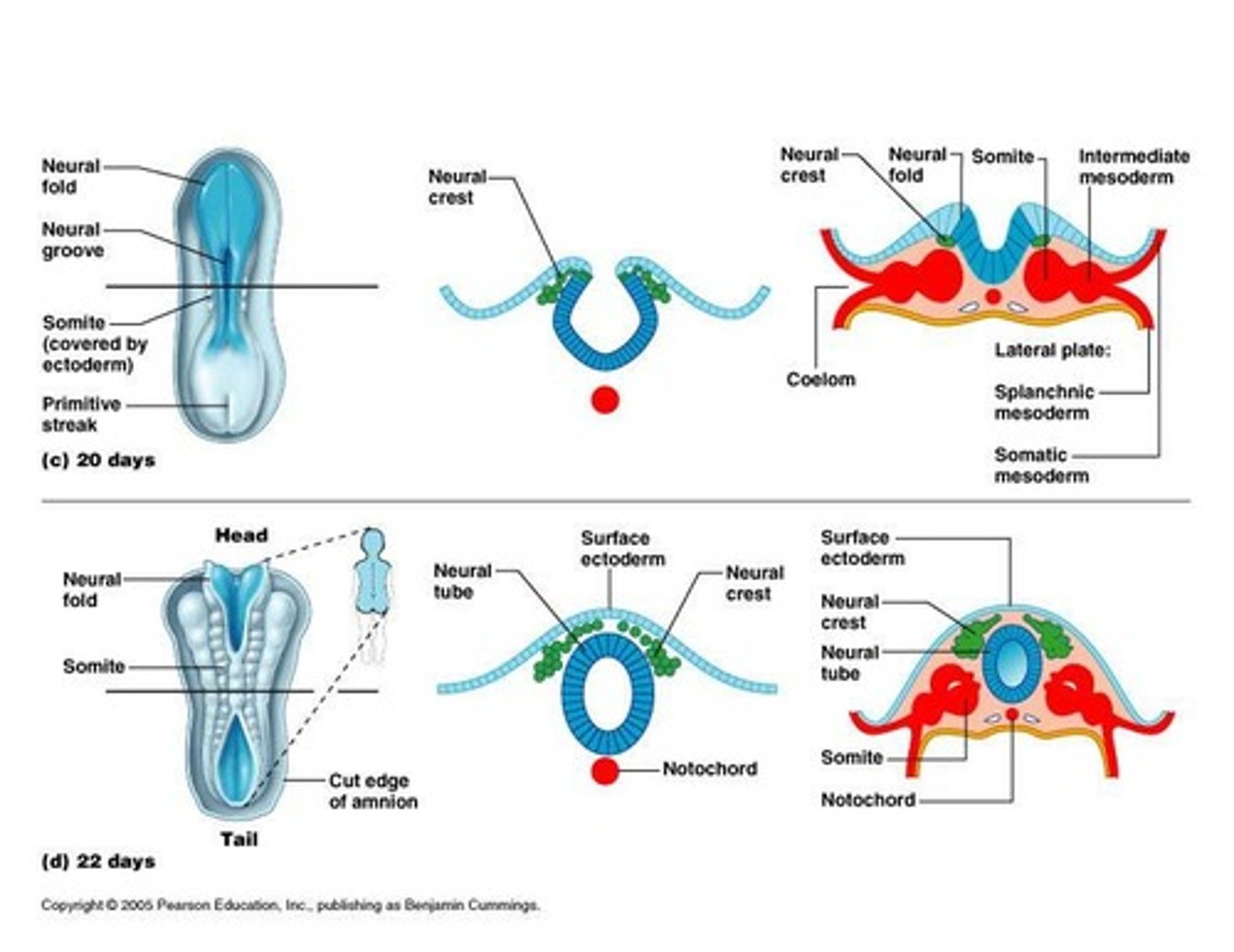
Neural tube
Hollow tube forming from the neural plate, cranial part of the neural tube becomes the brain
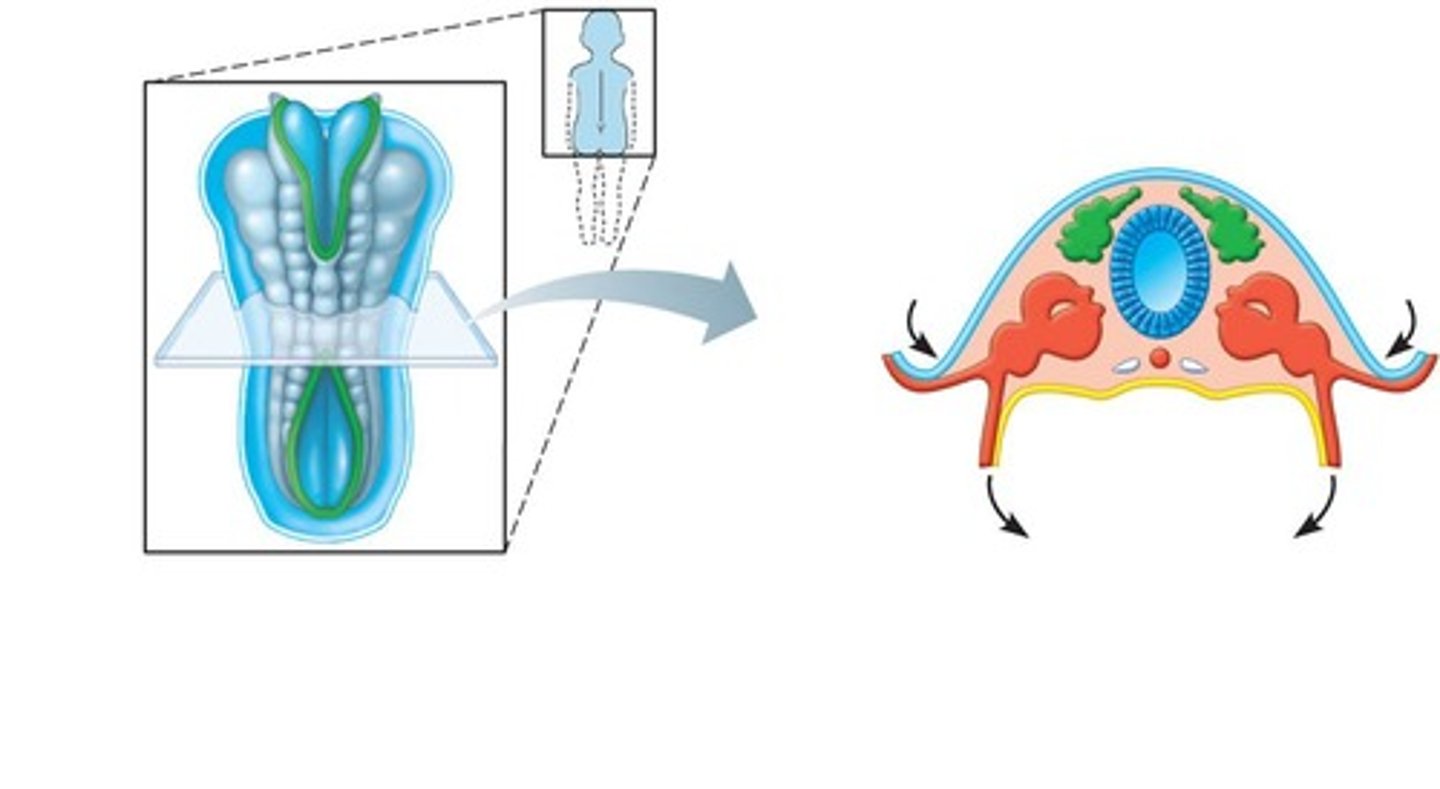
Somites
First body segments forming vertebrae, ribs, and axial muscles. Paraxial mesoderm
Ossification centers
Sites where bone formation begins.
Surfactant
Substance that prevents lung collapse.
Neural plate
ectoderm thickens
Neural groove
ectoderm folds inward
Neural crest
Forms sensory nerve cells, ganglia, and melanocytes
Intermediate mesoderm
begins as a continuous strip of tissue just lateral to the paraxial mesoderm (urogenital system)
End of second month
All organs have appeared and the placenta is fully functioning, embryonic development complete
Fetal development
Beginning of third month, head growth begins to slow and body increases in length, ossification centers appear in bones, sex can be determined
5-7 months
Mother begins to feel fetal movement, lungs lack surfactant
8-9 months
Fetus usually rotates so head is pointed down toward cervix