Labor and Delivery: Second Half
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
educate, prepare, breathing, lessens, blocking, placenta, pudendal, nitrous, epidural
Labor Pains
-Natural birth → ________ patients regarding the experiences of labor and delivery in order to ________ them for the event
May try ________ exercises, meditation/relaxation, water, massage to help cope with the pain
-Analgesic drugs → relieves/_________ pain without total loss of feeling or movement
-Anesthetic drugs → relieves pain by _________ all feeling
-Systemic analgesia → narcotics or sedatives cross the ________
-Local anesthesia → ________ nerve or perineal block for episiotomy or laceration repair
-Inhaled agents → _______ oxide
-Regional (neuraxial) anesthesia → ________ or spinal
L3-4, opioid, sensation, hypotension, back, depression
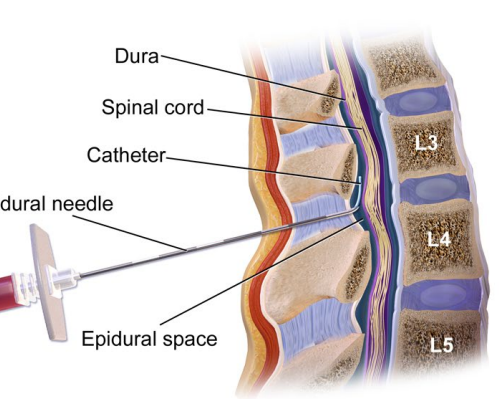
Epidural
-Epidural catheter is placed in ___-_ interspace
-Provides continuous infusion of medication, which is a local anesthetic plus ______
-Does not remove all __________ completely
-Side effects → ___________, fetal bradycardia, fever, ____ soreness, headache, maternal respiratory ____________ if level too high, hematoma
subarachnoid, cesarean, rapid, hypotension
Spinal Anesthesia
-One time does of opioid and/or local anesthetic into ____________ space
-Often used for _________ delivery
-_____ onset and dense sensory block
-Similar side effects as epidural though greater risk for ______________
emergent, aspiration, hypoxia, intubate
General Anesthesia
-Used for __________ cesarean deliveries
-Concern for risk of maternal ___________ and risk of ______ to mother and fetus during anesthesia induction
-_______ and secure airway
exhaustion, membranes, full, position, empty
Indications for Operative Vaginal Delivery
-Indications → prolonged 2nd stage, maternal ___________, and need to hasten delivery
-Safe application if → ruptured _________, ____ dilation, engaged fetal head at least +2 station, known fetal __________, no evidence CPD, _____ bladder, adequate anesthesia, and experienced operator
head, dilated, membranes, 34, bleeding
Contraindications to Operative Vaginal Delivery
-Absolute → unengaged fetal ____, unknown fetal position, incompletely ______ cervix, intact ____________, or cephalopelvic disproportion suspected
-Relative → estimated fetal weight > 4,500 (macrosomia), gestational age < __ weeks, certain fetal conditions (_______ disorders, demineralization disorders), and operator inexperience or lack of immediate backup for cesarean
scalp, suction, pelvis, contractions
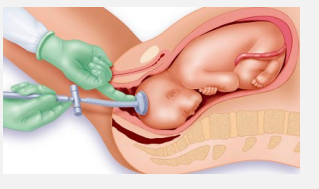
Vacuum Assisted Vaginal Delivery
-Vacuum consists of vacuum cup placed on fetal _____ and a ________ device that is connected to the cup
-Exertion on the cup and consequently on the fetal scalp is made parallel to the axis of the maternal ______ along with maternal pushing and uterine ___________
cephalic, head, pelvis
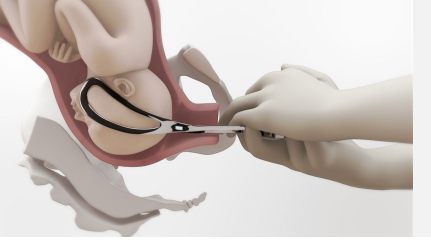
Forceps Delivery
-Metal blades with _______ curvature that are placed around the ____ of fetus
-Most have a curvature as well that conforms to the maternal ______
-Two forceps connect at lock between shank and handle
laceration, head, facial, canal
Complications of Operative Vaginal Delivery
-Vacuum assisted → scalp ________/bruising, cephalohematoma
-Forceps → lacerations or bruising on fetal ____ or face, ______ nerve palsy, intracranial damage, and lacerations of the birth _____
placental, body, skin, muscles, sphincter, epithelium
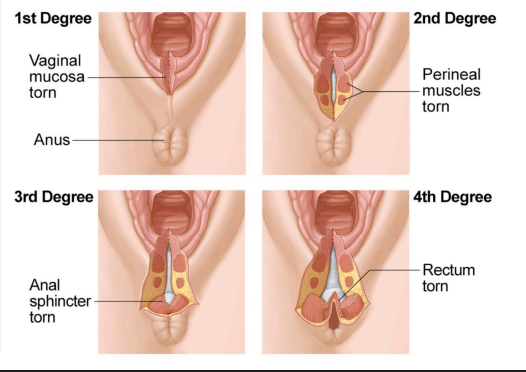
Perineal Lacerations
-Lacerations are repaired after _________ delivery
-Most common site is the perineal ____
-Classification System
1st degree = injury to perineal _____ only
2nd degree = injury to perineum involving perineal ________
3rd degree = injury to perineum involving anal _________ complex
4th degree = injury to perineum involving anal sphincter complex and anal ___________
bleeding, distorted, continuous
Laceration Repair
-For periclitoral, periurethral, labial, and 1st degree lacerations, repair if ___________ or anatomy ____________
-Clinical judgement for 2nd degree laceration repairs
___________ suturing preferred over interrupted
-Experienced provider must repair all 3rd and 4th degree lacerations
sphincter, operative, weight, antibiotic, pain, constipation, incontinence, fistula, sexual
3rd/4th Degree Perineal Lacerations
-OASIS → obstetric anal _________ injuries
-Risk factors → _________ vaginal delivery, midline episiotomy, and increased fetal birth _______
-Consider dose of __________ at time of repair
-____ control and avoid ___________
-Short term risks → wound breakdown and infection
-Long term risks → pelvic floor injury, fecal and urinary ___________, recto-vaginal _______, persistent pain, and _______ dysfunction
-May offer primary cesarean delivery next pregnancy
perineum, midline, dystocia
Episiotomy
-Incision made in __________ → either mediolateral or ________
-Indications → need to hasten delivery or impending/ongoing shoulder ________
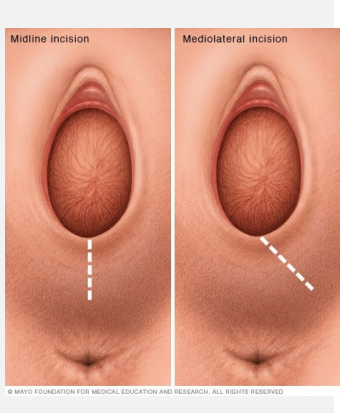
anterior, pubic symphysis, impacted, deliver, none, obesity, epidural
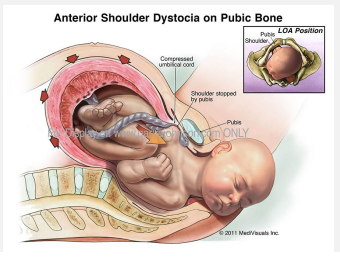
Shoulder Dystocia: Background
-Occurs when, after delivery of the fetal head, the baby’s ________ shoulder gets stuck behind the mother’s _____ __________
-Anterior shoulder gets lodged up against maternal symphysis pubis → shoulders are ___________, unable to get under the pubic symphysis to deliver
-Risk Factors
#1 risk factor/cause is ____
Possible risk factors are GDM, history of dystocia, maternal _______, prolonged 2nd stage, operative delivery, macrosomia, multiparity, post-term pregnancy, _______ use, and inability of the fetus to rotate after head is delivered
retraction, expulsion, not, fail, episiotomy, hemorrhage, Erb’s, asphyxia
Shoulder Dystocia: Turtle Sign and Complications
-Represented by the _________ of the fetal head after _________
Suggestive of shoulder dystocia but ___ diagnostic
Shoulder dystocia is not diagnosed until the usual attempts at the delivery of the head ____
-Maternal complications → need for _________, laceration, and postpartum __________
-Fetal complications → fracture of clavicle/humerus, ____ palsy, _________/neonatal encephalopathy
Erb’s Palsy is a brachial plexus paralysis that usually resolves by 18 months
Neonatal death due to asphyxia is rare
drills, 5000, 6-10, help, traction, dorsal
Management of Shoulder Dystocia
-Must anticipate it
Practice via _____, call for help, remain calm, take charge
Highly anticipate for the patients who have estimated _____g babies (without DM) or 4500g (with DM)
-Deliver within _____ minutes
-Call for ____
-Try gentle ________ first
Apply pressure on the fetal vertex in a _______ direction helps move the anterior shoulder
Done before anyone suspects shoulder dystocia
help, episiotomy, McRoberts, suprapubic, internal, posterior, fours
Management of Shoulder Dystocia: HELPERR Algorithm
-H → call for ____
-E → evaluate for __________
-L → legs → __________ → hyperflex legs and abduct the hips
-P → _________ pressure → not fundal
-E → enter → _______ maneuvers such as Woods screw
-R → remove → delivery of _______ arm
-R → roll the patient onto all _____
hyperflex, abduct, vertical, rotating, anterior
Maneuvers for Shoulder Dystocia: McRobert’s
-Initial maneuver performed upon recognition
-_________ legs and _____ the hips
-Goal is to bring pelvic inlet and outlet into more _______ alignment while flattening the sacrum and _______ the pubic symphysis
-Disimpact ________ shoulder
suprapubic, disimpact, posterior, fundal, wrist, pressure, forearm
Shoulder Dystocia Maneuvers: Suprapubic Pressure and Delivery of Posterior Arm
-Suprapubic pressure → moderate __________ pressure is often the only additional maneuver necessary to ________ the anterior fetal shoulder
Direct force on ________ shoulder to rotate it anteriorly
No _____ pressure
-Posterior arm → bring the fetal ______ within reach and exert ________ with the index finger at the antecubital junction. Sweep the fetal _________ down over the front of the chest
posterior, anteriorly, counterclockwise, anterior, posterior, sling, traction
Shoulder Dystocia Maneuvers: Rubin, Woods Corkscrew, Axilla Sling
-Rubin Maneuver → practitioner placed hand on back surface of ________ shoulder, then rotates it _________ toward fetal face
-Woods Corkscrew → _____________ rotation of the ______ shoulder to move toward the more favorable pelvic diameter or clockwise rotation of the _________ shoulder
-Posterior Axilla Sling → French catheter is threaded to make a _____ around posterior shoulder. Apply moderate _______ to the sling to deliver shoulder
knees, traction, upward, increases, fracture, ramis, anteriorly, cesarean, abdominal
Shoulder Dystocia Maneuvers: Gaskin, Fracture Clavicle, Last Resorts
-Gaskin → patient on hands and ______. Apply gentle downward _______ on posterior shoulder or _______ traction on anterior shoulder
________ pelvic dimensions and may allow fetal position to shift, freeing the impacted shoulder
-Fracture Clavicle → ______ the clavicle if less invasive measures fail
The anterior clavicle is pressed against the ___ of the pubis
Avoid puncturing the lung by angling the fracture __________
-Zavenelli → cephalic replacement and then proceed with emergent ________ delivery
-Symphysiotomy → _________ rescue, where you cut the symphysis pubis
ultrasound, sutures, 28, multiple, anomaly, fibroids
Malpresentation: Diagnosis and Risk Factors
-Diagnosis → gold standard is __________
You may be able to feel ______ on the fetal head upon pelvic exam
Start Leopold’s maneuvers at __ weeks for fetal presentation assessment
-Risk Factors → multiparity, ________ gestation, polyhydramnios, uterine ______, abnormal uterine growth such as ________, placenta previa, or preterm labor
occiput, pelvis, anterior, transverse, posterior
Vertex Presentation
-Fetal position → relationship of the fetal _______ to maternal ______
-L/R OA → left/right occiput _______ (what you want)
-L/R OT → left/right occiput _________
-L/R OP → left/right occiput _________
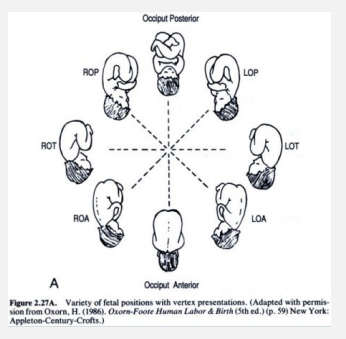
feet, cervix, buttock, head, feet, knees
Breech Presentation
-Either the bottom or ____ are the first body parts that make contact with the _____
-Complete → ________ and feet are next to each other with bent knees
-Frank → buttock first, feet by the ____
-Footling → _____ first, single or double
-Kneeling → ______ first
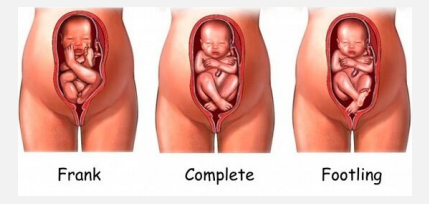
horizontally, perpendicular, shoulders, elbow
Transverse Presentation
-Fetus lies ___________ in the pelvis, so it is _____________ to the mother
-The presenting part is usually the _________ but can be iliac crest, hand, or ______
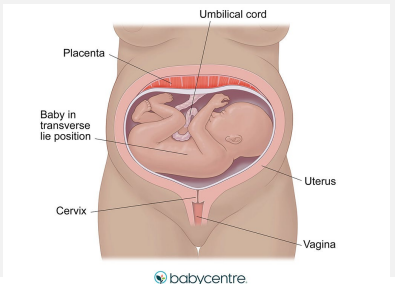
extremity, hand, cord, traumatic
Compound Presentation
-Prolapse of fetal ________ alongside a presenting part
____ up by the head
-Increased risk of ____ prolapse
-Risk of _______-vaginal delivery
Perineal tears

hyperextension, extension, chin
Brow, Chin, Face Presentations
-Face → ____________ of the fetal head, so clinician is unable to feel sutures on vaginal exam
-Brow → caused by partial ________ of the fetal head
-Mentum (____) → prolonged labor is common
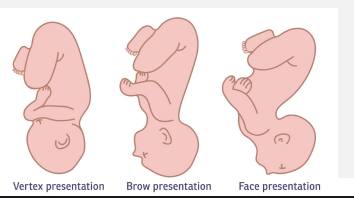
pressure, singleton, 36, intact, induction, cesarean, distress, myometrium, epidural
External Cephalic Version
-Attempt to change the fetal position via external _________ through the maternal abdominal wall
-Must have a __________ pregnancy, be over __ weeks gestation, membranes _____, adequate amniotic fluid, no complications, and consent
-Consider proceeding with ________ soon after if successful
-If unsuccessful, plan for ________ delivery
-Complications → pushing so hard may cause placental injury or fetal ________
-Medication → sometimes terbutaline is given to relax the __________ or an ______ for pain control or prep for cesarean
complete, preterm, flexed, entrapment
Spontaneous Vaginal Delivery: Breech
-If provider has experience with vaginal breech delivery, may consider performing
-Rarely done anymore
-May consider if → ________ or frank breech, adequate clinical pelvimetry, ________ fetus, fetus not too large, no prior C-section, or _______ head
-Major complications → head ____________
cesarean, footling, large, US
Elective Cesarean Delivery
-Malpresentation is an indication for _________ delivery
-Consider especially if double _______ breech, small pelvis, _____ fetus, previous c-section, or hyperextended head
-Confirm with __ to know if the fetus is breech or transverse
infection, forceps, trauma, hemorrhage, cord, prolapse, asphyxia, brachial plexus
Potential Complications of Malpresentation
-Maternal → prolonged labor, PROM leading to _________, need for _____ delivery or cesarean, ______ to birth canal during delivery from manipulation, or intrapartum/postpartum ___________
-Fetal → compression of ____, ________ of the umbilical cord, entrapment of fetal head in incompletely dilated cervix, aspiration and ________ at birth, birth trauma from manipulation and/or instruments to free fetal head like ______ _____ injury/clavicle fracture/hip injury
descends, cervix, malpresentations, long, rupture
Cord Prolapse: Background
-When the umbilical cord __________ through the ______ before the baby
-Risks → fetal _____________, premature infants, multiparous women, ____ umbilical cord, polyhydramnios, unengaged presenting part, and ______ of membranes at high fetal station
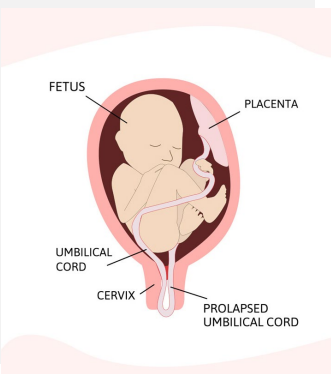
ruptured, decelerations, palpable, pressure, Trendelenburg, delivery, cesarean
Recognition and Management of Cord Prolapse
-Diagnosis →
In setting of ______ membranes
On electronic fetal monitoring, fetal ____________, fetal bradycardia
________ cord felt on vaginal exam
-Management →
Relieve _________ off the cord by using hand to maintain pressure on the fetal presenting part to keep it lifted off the cord
_____________ position
May be able to reduce the cord or have patient deliver through it if ________ imminent
Most often to OR for emergent __________ delivery
macrosomia, previa, complete, rupture, herpes
Contraindications to Vaginal Delivery
-Relative → fetal _________, >2 prior c-sections, partial placenta _____, non-reassuring fetal heart tracings
-Absolute → vasa previa, _________ placenta previa, narrow pelvis, malpresentation, classical uterine scar, history of uterine ________, cord prolapse, and active genital ________
uterine, first, failure, increased, request
Cesarean Delivery
-Delivery of fetus through abdominal and ______ incisions
-Primary → _____ cesarean delivery, common indication is ________ to progress
-Repeat → the higher the number, the ________ risk of placenta accreta and previa, and uterine rupture
-Elective → no other indication other than patient _________
progress, scar, dystocia, preeclampsia, fibroid, breech, prolapse, conjoined
C-Section Indications
-Maternal
Failure to ________, cephalopelvic disproportion, previous uterine ____, history of shoulder _______/4th degree laceration/vesicovaginal fistula, severe __________, pelvic tumors/obstructing ______/HSV, severe aortic stenosis, and cerebral palsy
-Fetal
Malpresentation (______, transverse, compound), complete placenta previa, vasa previa, placenta accrete, placental abruption, cord ________, macrosomia, fetal intolerance of labor, failed operative vaginal delivery, and ________ twins
vaginal, rupture, pain, FHR, station, decrease
Trial of Labor After Cesarean
-If successful, results in _______ birth after cesarean
-If considering, ensure known type of prior hysterotomy, in-house OB and anesthesiologist, informed conset
-Greatest concern is risk of ______ of prior uterine scar
-Signs of rupture → sudden severe abdominal ____, maternal sensation of “pop”, ___ decelerations or bradycardia, loss of fetal station, and sudden _______ in pressure on IUPC