BIOL L tissues
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
82 Terms
simple squamous
single layer of flattened cells
epithelial simple squamous
provide for rapid diffusion of gasses and dissolved solutes across membranes
simple squamous
located in the alveoli of the lungs, the endothelial cells of capillaries, glomeruli of kidneys
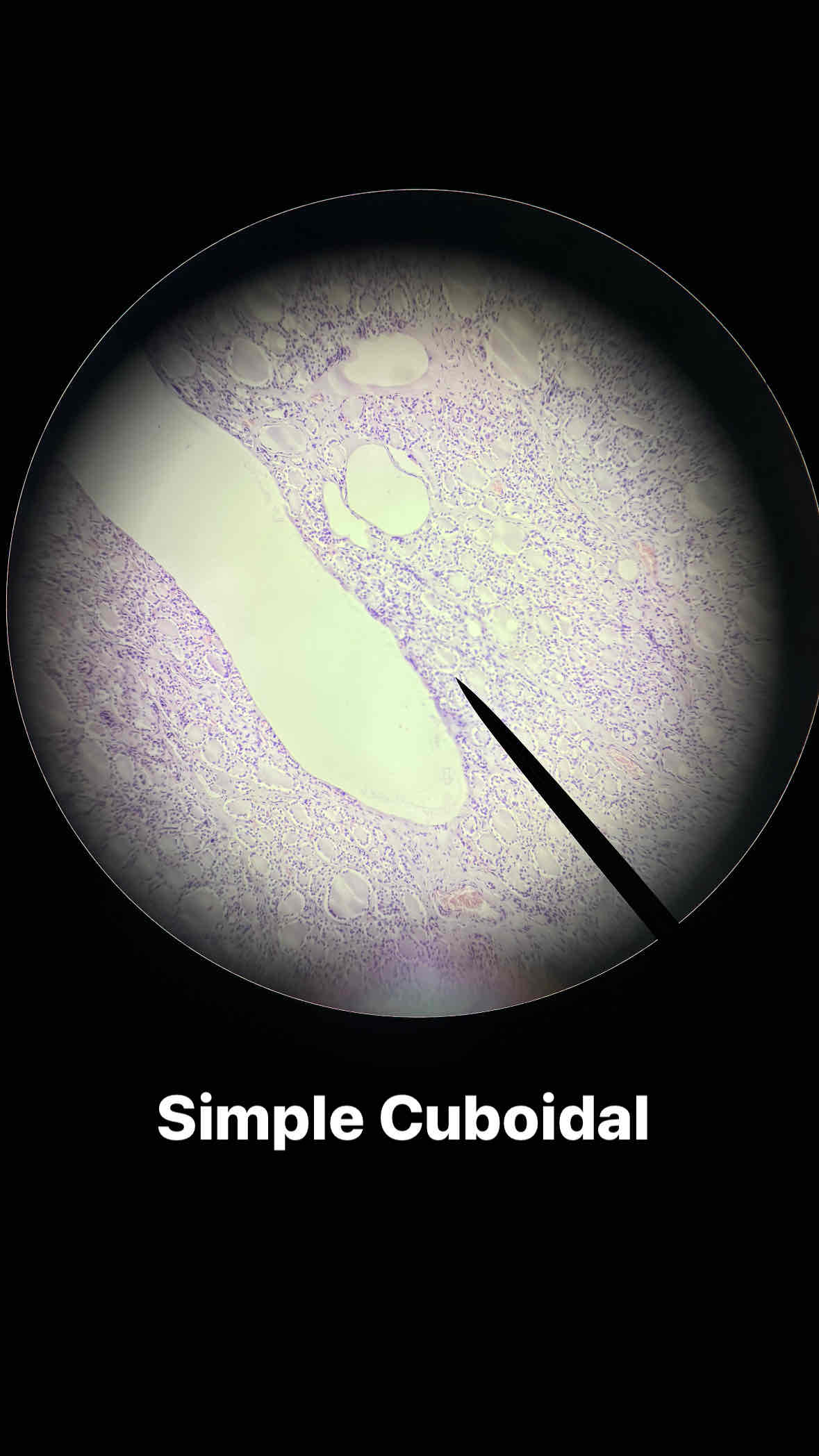
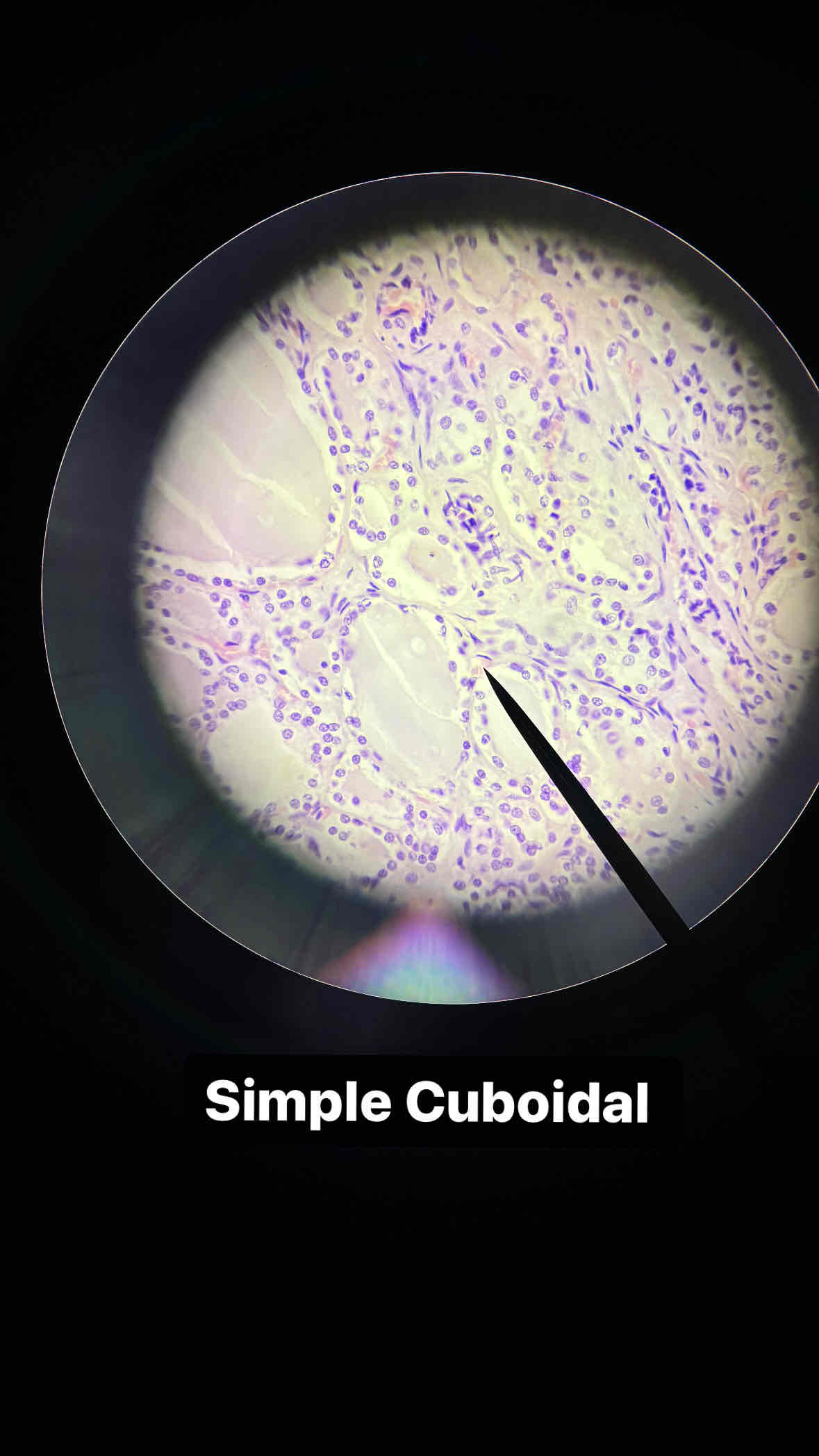
simple cuboidal
single layer of cube-shaped cells
simple cuboidal
secretes and absorbs, sometimes ciliated-driven movement of materials
simple cuboidal
lines the lumens of small secretory ducts, kidney tubules; portions of bronchioles; reproductive ducts, and ureters
simple columnar
secretes and absorbs, sometimes ciliated-driven movement of materials; often possess microvilli to increase surface area of apical membrane
simple columnar
lines the intestinal tract and the lumens of some secretory ducts, lines bronchi and uterine tubes
stratified squamous
multiple layers of flattened cells
stratified squamous
protection from abrasive forces
stratified squamous
located in keratinized type forms the upper portion of the skin; non-keratinized type forms the wet surfaces of the esophagus, mouth, vagina, and rectum
stratified cuboidal
multiple layers of square cells
stratified cuboidal
protection; secretion of mucus
stratified cuboidal
located in sweat glands, mammary glands, and salivary glands
stratified columnar
multiple layers of tall cells
stratified columnar
protection; secretion of mucus
stratified columnar
rare in the body; some found in male urethra and ducts of large glands
Cell
the smallest structural and functional unit of life in an organism consisting of many working components with the ultimate purpose of maintaining homeostasis
homeostasis
the process by which an internal environment is kept constant despite a constantly changing external environment
organelles
in order to maintain homeostasis, cells contain different types of ? that serve different functions
false
all cells are created equal or have the same type and number of organelles
mitosis
a process how most human cells reproduce through in which the cell cleaved in two after key components have been duplicated
interphase
initially, cells begin in ? during which time the cell grows and DNA is duplicated
four phases of mitosis are:
prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase
prophase
DNA condenses into 23 distinct pairs of chromosomes, nuclear membrane disperses, each pair is joined together by a protein bridge called a centromere
centromere
protein bridge that joins together each pair in prophase
metaphase
chromosomes align themselves midway between poles
anaphase
chromosome pairs separate and move toward opposite poles
telophase
Nuclear membrane begins to form and chromosomes decondense into chromatin, and cell membrane begins to "pinch" eventually cleaving in two (known as cytokinesis)
histology
study of tissues
squamous
flat; function = diffusion
cuboidal
cubed; function = secretion or absorption
columnar
tall; function = secretion or absorption; if ciliated, then to also help with movement of materials
simple
one layer
stratified
numerous layers
epithelial tissue
very cellular, highly mitotic, avascular (no blood vessels), polar, regenerative
epithelial tissue
lines body cavities and parts of the body exposed to the outside world
simple squamous
simple cuboidal
stratified squamous
simple columnar
connective tissue proper loose
lymphocytes, mast cells, macrophages, fibroblasts, leukocyte, adipocytes
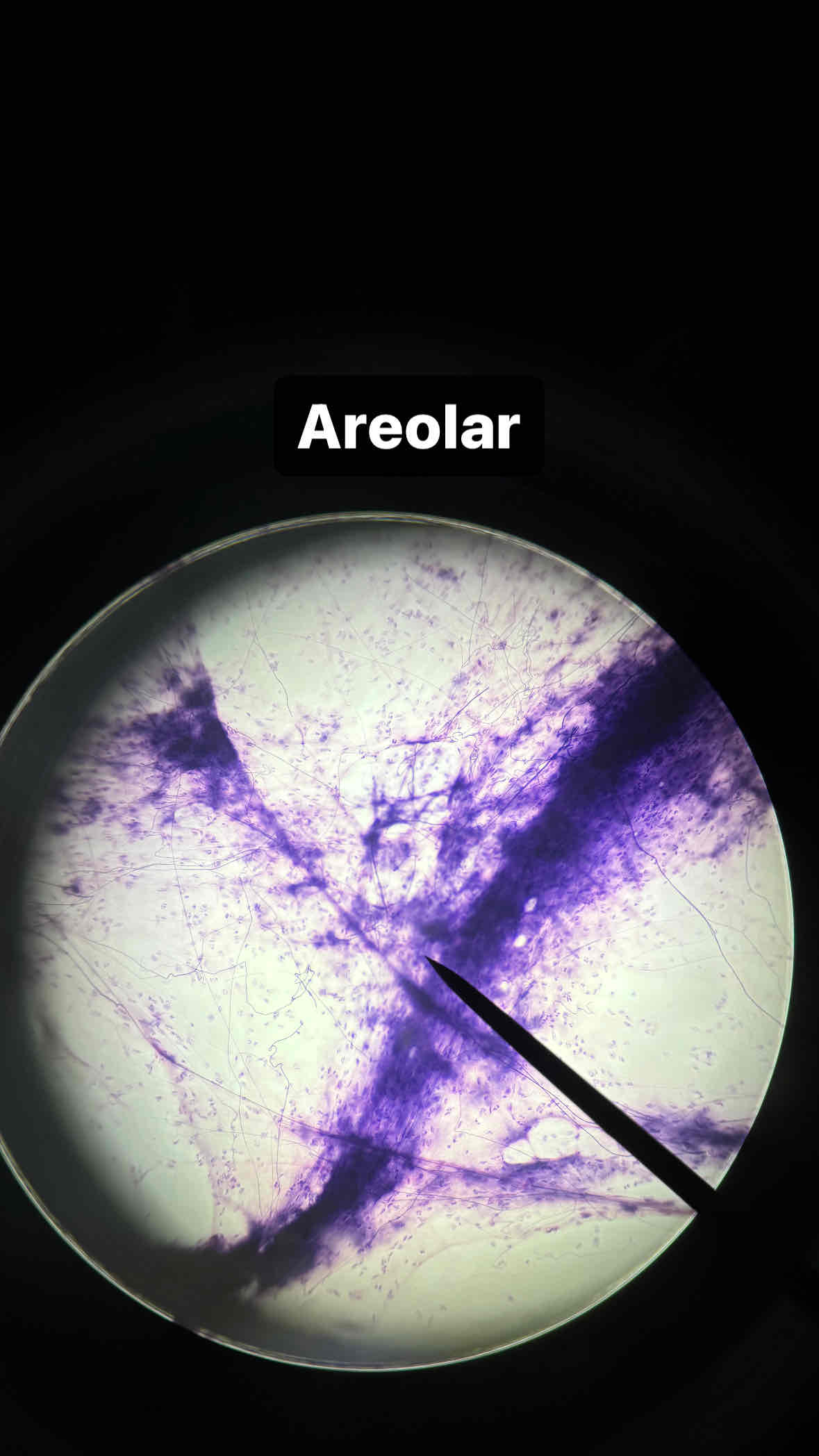
loose areolar connective tissue
fibroblast; collagen, reticular, and elastic
loose areolar connective tissue
function = wraps and cushions organs; holds and conveys tissue fluid during inflammation
loose areolar connective tissue
location: under epithelia, packages organs, surrounds capillaries
loose adipose connective tissue
adipocytes; function = energy storage; soft padding between moving organs and joints; heat conservation
loose adipose connective tissue
Location: Surrounds organs/joints; dermis of the skin; female breast
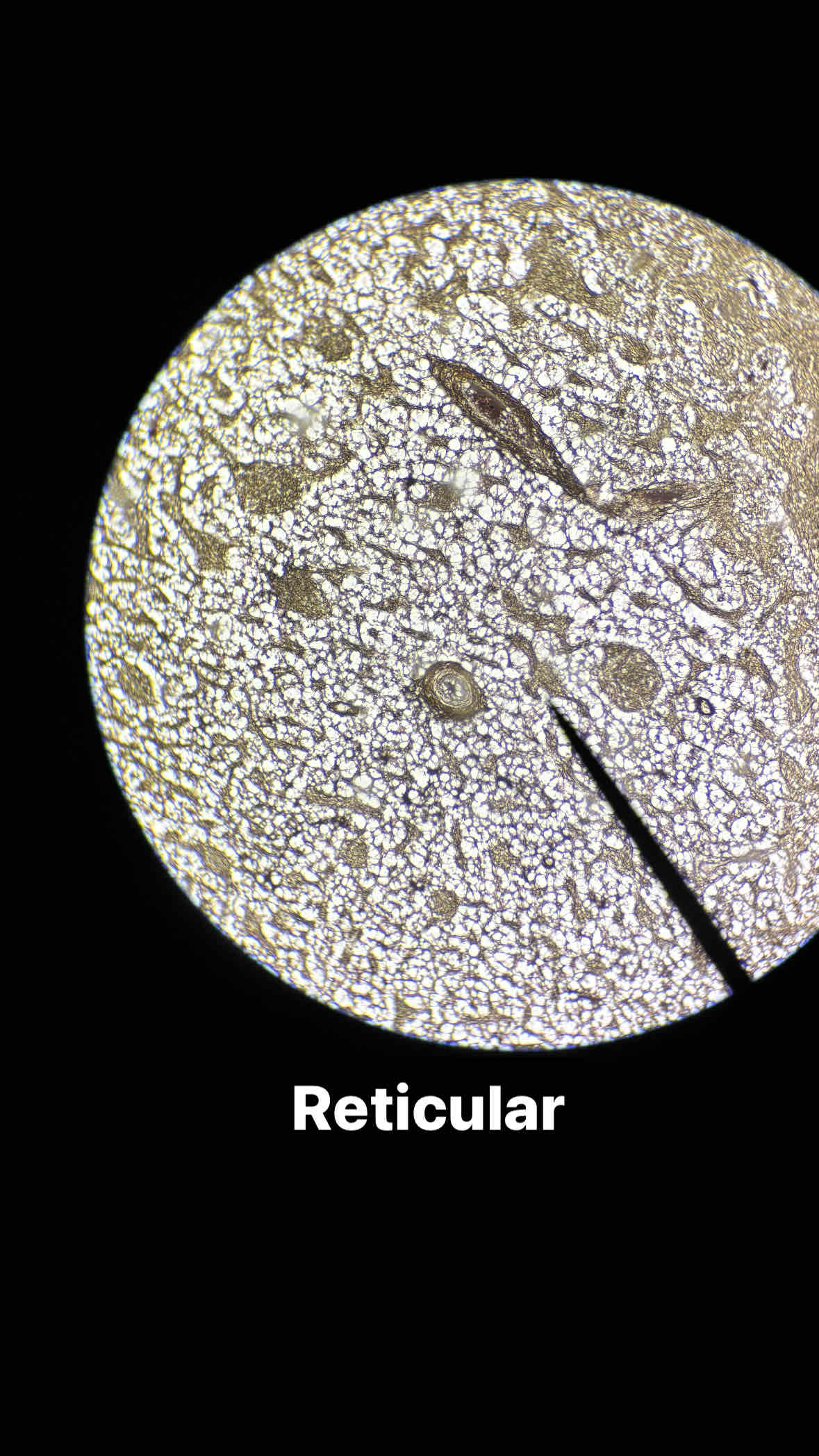
loose reticular connective tissue
function = fibers create a skeleton like framework to support other cell types
loose reticular connective tissue
Location: Spleen, lymph nodes, bone marrow, liver
dense connective tissue proper
fibroblasts secrete collagen
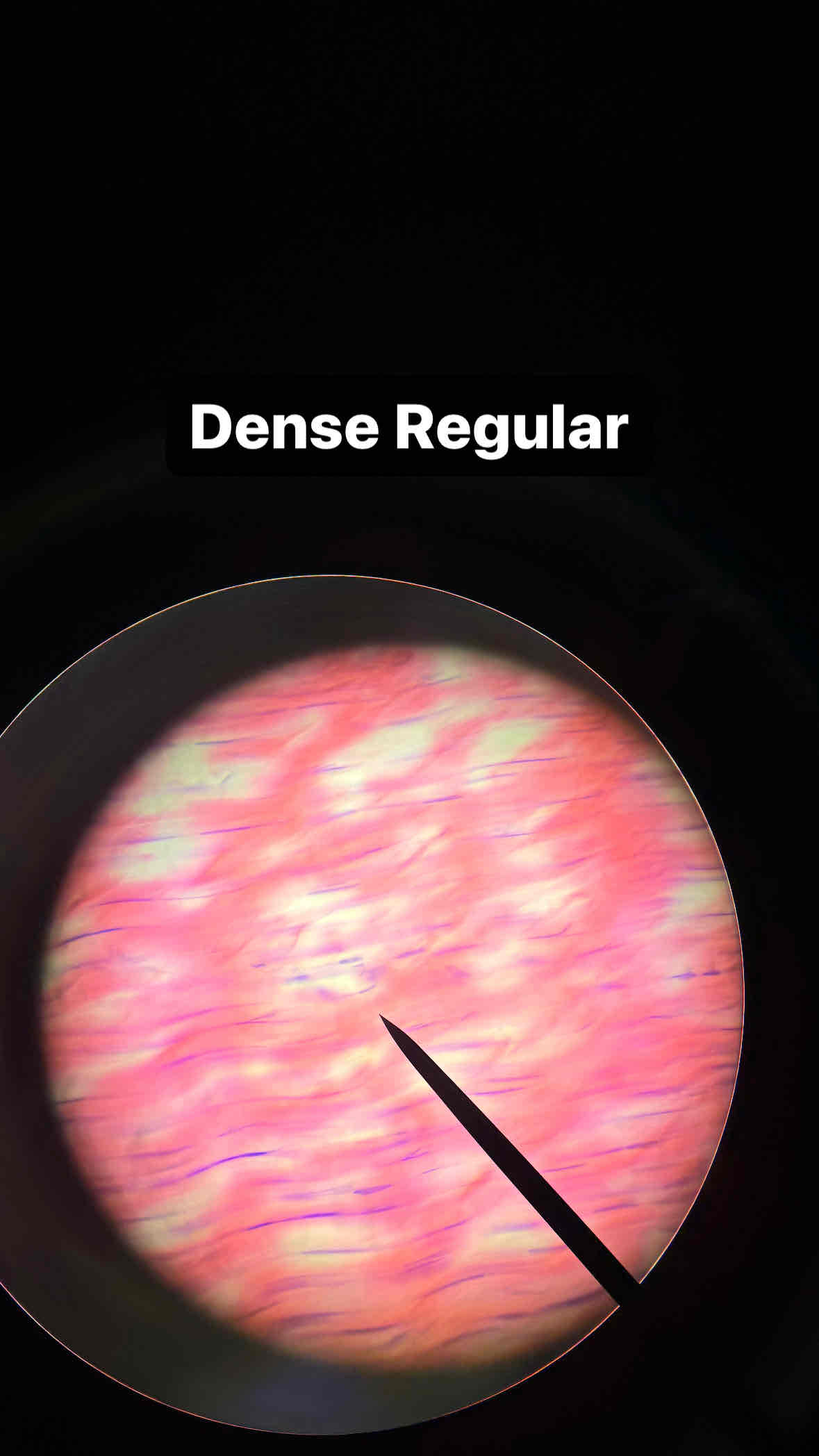
dense regular connective tissue
Function: Forms tendons and ligaments; withstands great tensile strength in one direction
dense regular connective tissue
Location: Tendons, ligaments, aponeuroses
dense irregular connective tissue
Function: Withstands tensile strength from many directions
dense irregular connective tissue
Location: Dermis of skin, joint capsules, vessels
cartilage
has chondrocytes inside lacunae
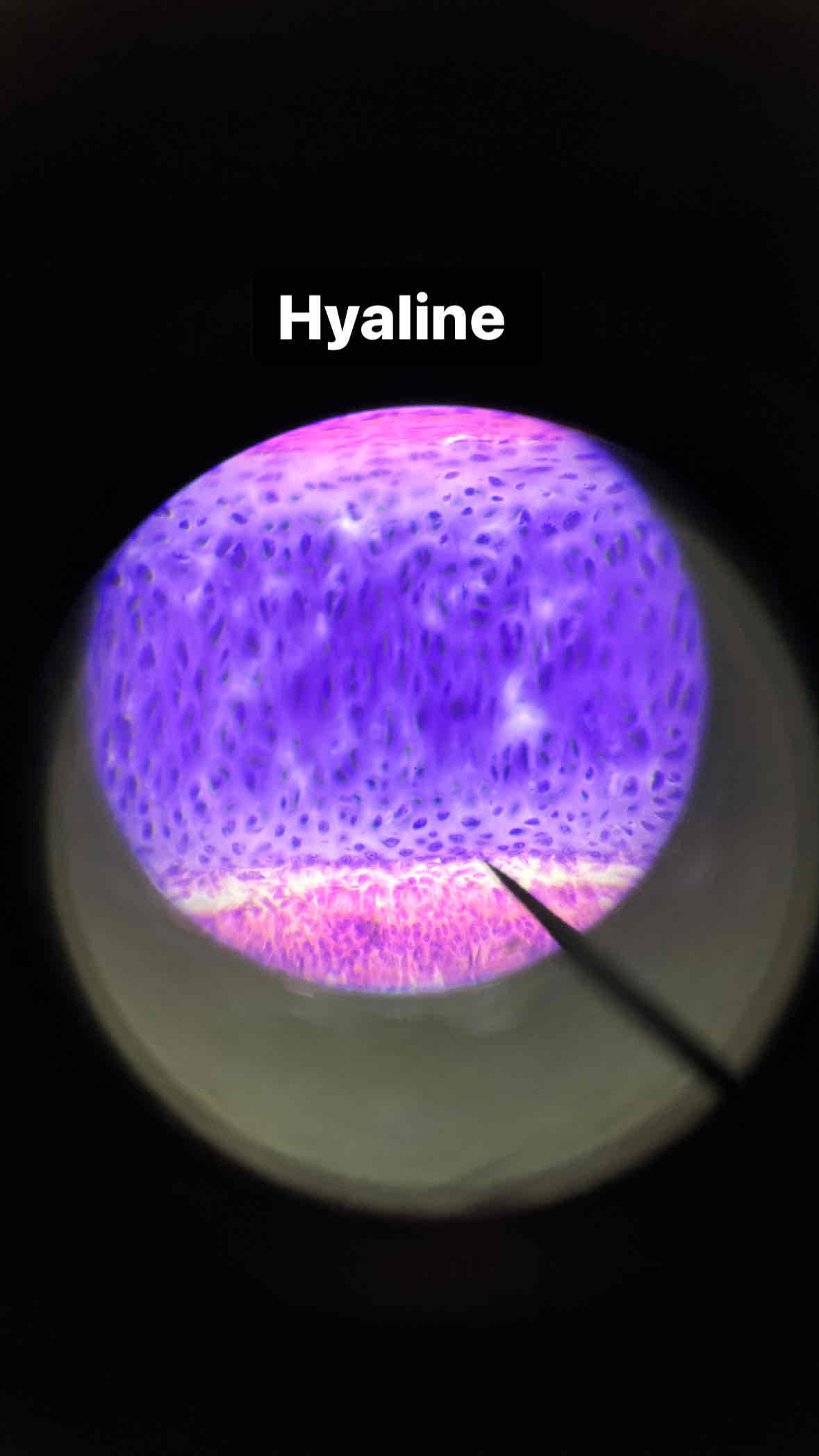
hyaline cartilage tissue
Function: Support and protection
connective cartilage hyaline tissue
Location: Trachea, larynx, costal cartilage, nose, ends of long bones
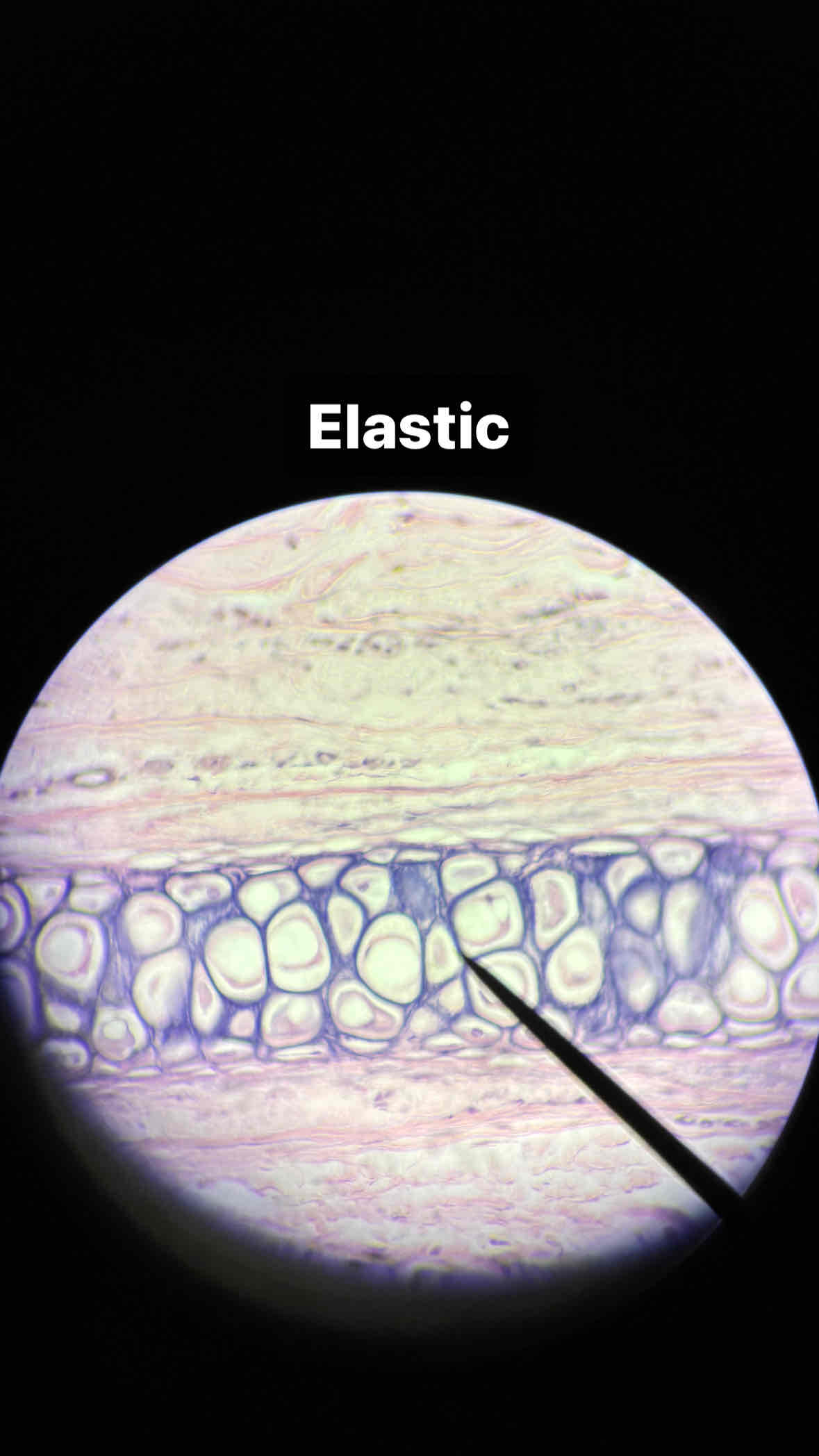
elastic cartilage tissue
Function: Provides support with flexibility
elastic cartilage tissue
location: external ear and epiglottis
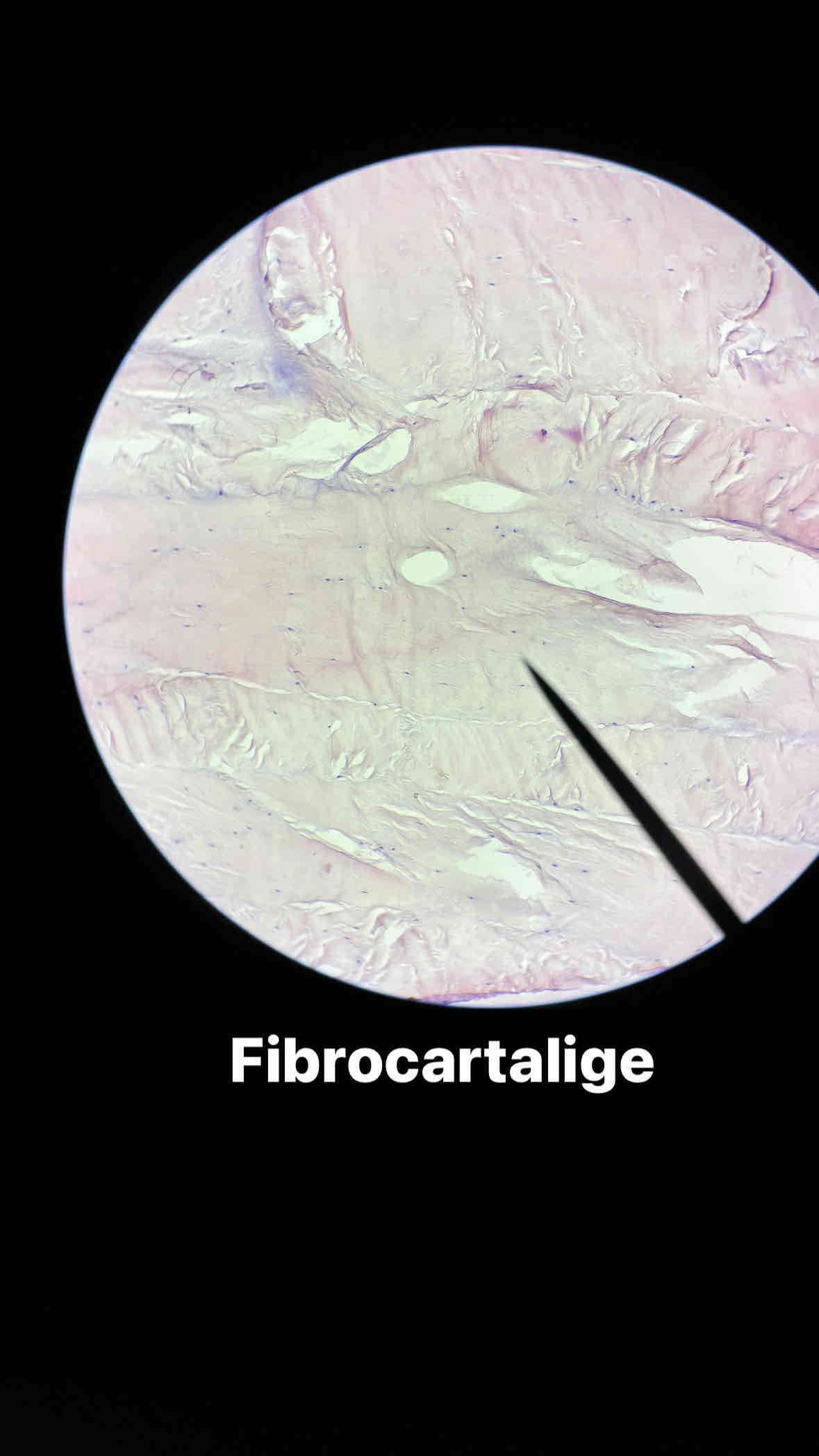
fibrocartilage tissue
Function: Absorb compressive shock
fibrocartilage tissue
location: intervertebral discs, pubic symphysis, meniscus of knee joint
bone
has osteocytes
blood
what tissue has cell types such as: erythrocytes, leukocytes, thrombocytes
bone
Function: support for the body; protection; storage of minerals
bone
location: skelton
blood
function: transport of nutrients and waste products
blood
location: within blood vessels
skeletal muscle tissue (voluntary)
function: move bones and produce heat
cardiac muscle tissue (involuntary)
function: synchronized contraction of heat to push blood throughout the body
smooth muscle tissue
function: contractions push material through a tract and adjusts diameter of blood vessels
nervous tissue
functions to transmit and process information throughout the body and can be divided into two groups based on functionality: Neurons: provide primary electrical pathways and Neuroglia: supporting cells that aid neurons
Neurons
provide primary electrical pathways
Neuroglia
supporting cells that aid neurons
connective cartilage hyaline tissue
type and subtype of tissue?
connective cartilage elastic tissue
type and subtype of tissue
connective cartilage fibrocartilage tissue
type and subtype of tissue?
connective loose reticular tissue
type and subtype tissue?
connective dense regular tissue
type and subtype of tissue?
epithelial simple cuboidal tissue
type and subtype of tissue?
epithelial simple cuboidal tissue
type and subtype of tissue?
connective loose areolar tissue
type and subtype of tissue?