Earth Systems - 8 ✅
1/66
Earn XP
Description and Tags
https://studykit.app/decks/4855e1a3-75fe-400f-9129-ef7b4ce19442 - Volcanoes
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
what we can see, cool solid rock, oceanic or continental
(also what number)
Crust
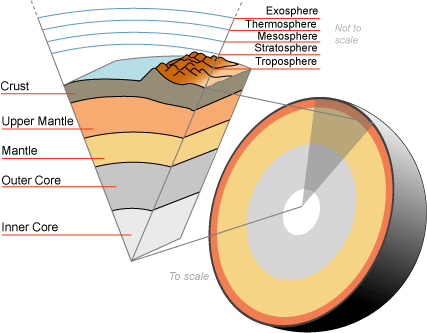
solid, moves slowly, very hot (500C-4,000C)
(also what number)
Mantle
Outer Core
very hot liquid
iron and nickel
Inner Core
hot solid
mostly iron, some nickel
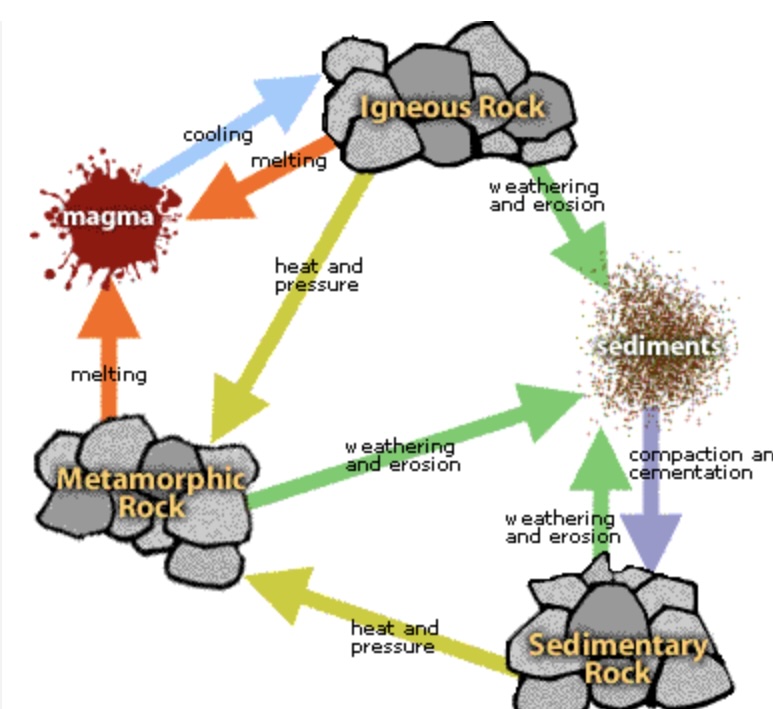
The formation of solid rock happens through
a) sedimentation
b) erosion
c) weathering
a
______ breaks down a rock into smaller pieces
Weathering
What example is this?
The small rock fragments are carried away by a river current.
*MOVED
Erosion
Occurs when the transported sediment settles out of the carrying agent and accumulates in a new location. (sand dunes, island)
Deposition
water, wind
solar heating and cooling
water freezing in cracks
Mechanical weathering
acid rain
lichen - destroy rocks
Chemical Weathering
T/F - Mechanical Weathering is the direct force and does not change it’s chemical composition.
T
T/F - Oxidation is an example of chemical weathering
Substance combines with O
T
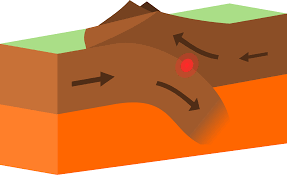
Select the Convergent Plate Boundary
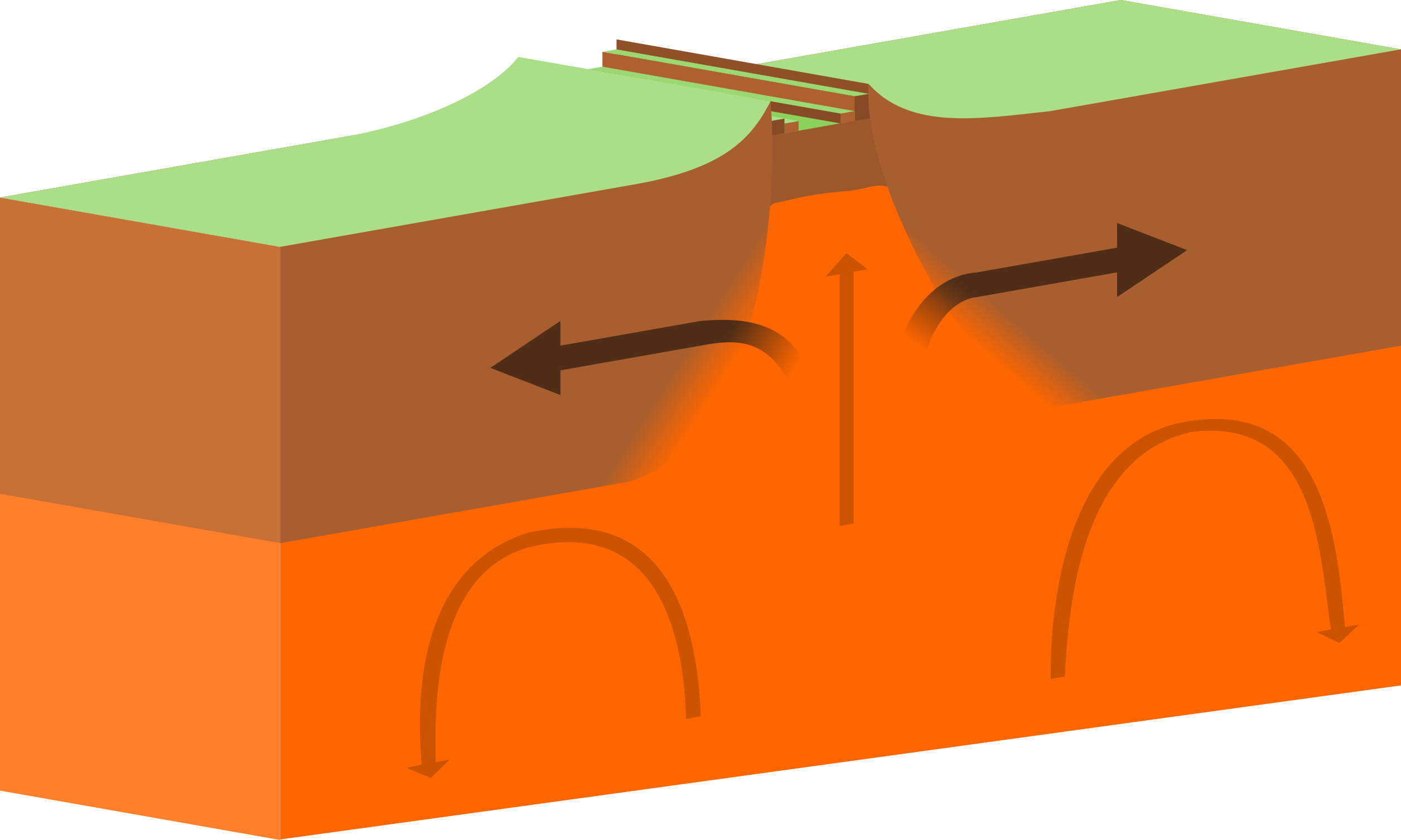
Select the Divergent Plate Boundary
Select the Transform Plate Boundary
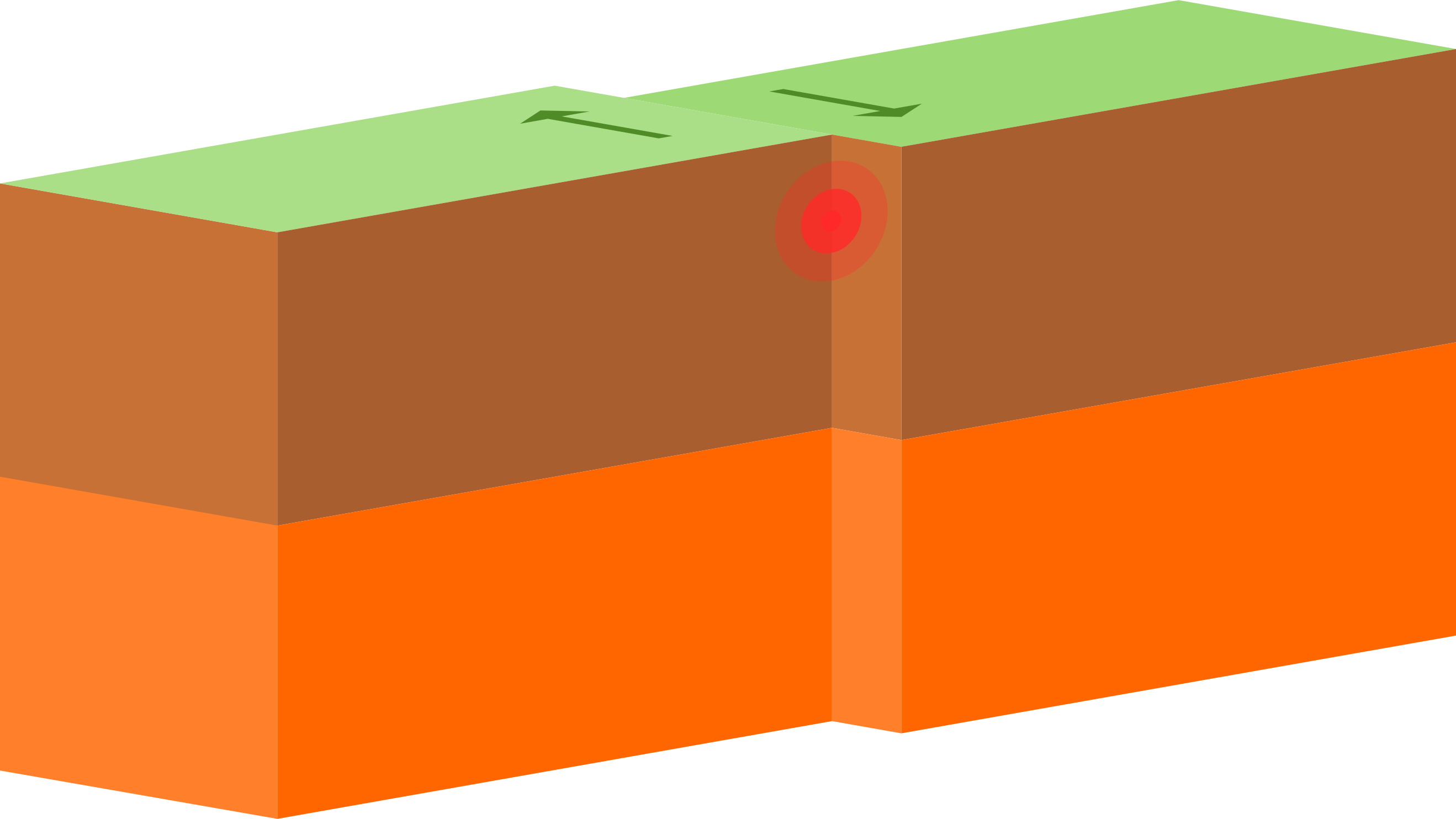
T/F -Transform boundary constructs the new lithosphere.
F, divergent
Mountains and trenches (subduction) forms from?
Convergent
Rift valleys and ridges form from?
Divergent
List 2 things that Transform Boundaries create
earthquakes
fault lines
measures the amplitude of seismic waves and determines the magnitude of an Earthquake.
seismometer
measures the magnitude (size) made by an earthquake. This records the numerical part 1-10.
Richter Scale
What is the difference between magma and lava?
a) Magma is molten rock that is underground and lava is molten rock that is above ground.
b) When molten rock is underground, it is called magma. When molten rock is on or above Earth's surface, it is called lava.
c) Magma is molten crustal material and lava is molten mantle material.
d) Magma is molten rock that is above ground and lava is molten rock that is underground.
e)Magma is molten mantle material and lava is molten crustal material.
a
Volcanoes form from an _____ eruption.
A caldera forms from an ____ collapse that sometimes occurs after an eruption.
outward
inward
A small collapse is a crater, what is the shape?
bowl
Less viscous are fast/slow volcano erruptions
fast
T/F - Mafic lava is highly viscous and an example is Basalt.
F, less
Hadean Eon
formed from debris
What eon? - Single cell life forming and earth’s crust is forming
Archean eon
Proterozoic Eon
Multicellular life (plants + animals)
What eon? - current, evolution of animals and life, known for Pangea
Phanerozoic Eon
What and When does Pangea exist?
A supercontinent that existed at the time of the Dinosaurs.
Before the Hadean Eon, layers of the Earth formed through _____ (attracting cosmic dust and forming creations)
accretion
T/F - Older organisms have less Carbon-14 in fossils, so they use Carbon Dating for younger fossils.
T
Why was the Cambrian Explosion significant?
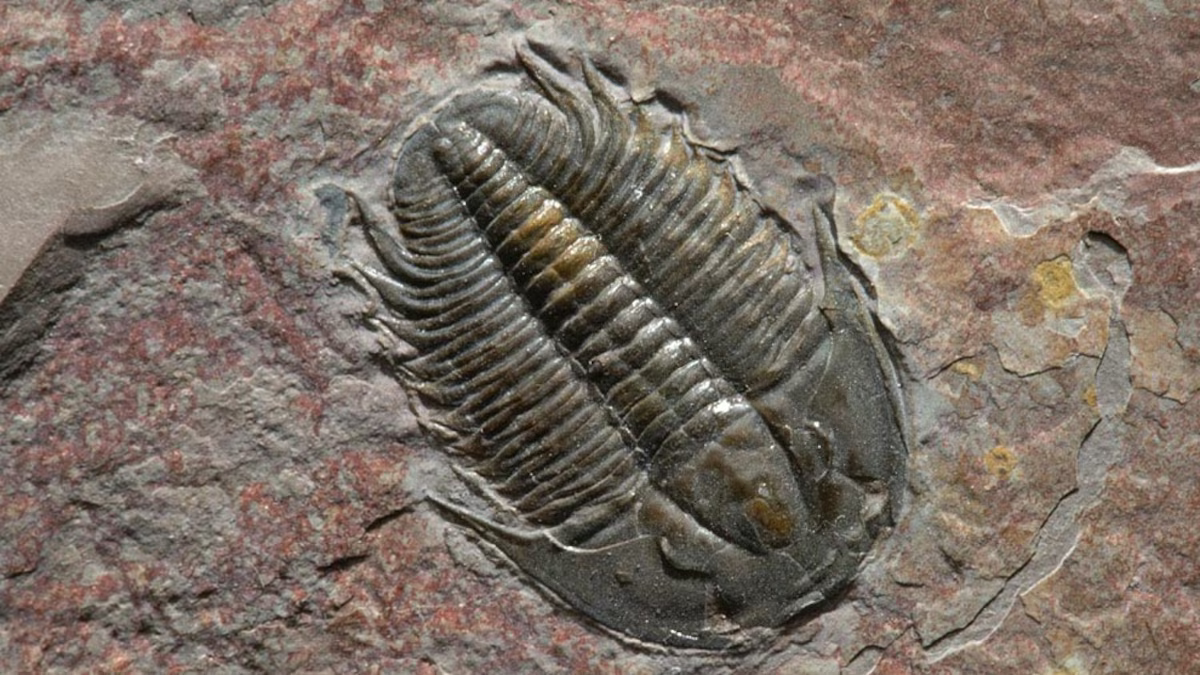

explosion of biodiversity
Weathering is an example of a Destructive Process, why?
breaks down rocks and minerals
This scientist discover the continental drift theory, lava cools → iron alings (magnet) with earth’s magnetic field
a) Issac Newton
b) Aristotle
c) Alfred Wegner
d) Galileo
c
"Gluing sediments together" (The sticking together of sediments)
Cementation
If heat and pressure is applied to a sedimentary rock, what will happen?
a) igneous rock
b) erode
c) metamorphic rock
c
Magma or lava cooling will create a _____.
igenous rock
Weathering and Erosion is associated with what rock?
sedimentary rock
YOU’RE CAPABLE AND INTELLIGENT! (look at rock cycle 😁 )
How does the asthenosphere (mantle) move tectonic plates?
convection currents
Put the eons in order from youngest - oldest
1-4
Phan
Phro
Arch
Hade
A person who finds fossils is called
paleontologist
What is the primary way carbon dioxide is naturally taken out of the atmosphere?
photosynthesis
The atmosphere surrounding Earth is composed of approximately 78% nitrogen. How do multicellular organisms obtain this atmospheric nitrogen?
Nitrogen-fixing bacteria release forms into the soil.
___ (broken) to form a new rock, visible layers, sandstone
Sedimentary
cooling of magma or lava, air pockets or crystals, basalt and granite
igneous
changed by heat, pressure, or chemical reactions, banding/stripes, marble
metamorphic
What is the cooling of intrusive igneous rocks, and can you see crystals?
slow cooling, crystals
T/F - Extrusive igneous rocks are fast cooling, hence no crystals.
T
A process that squeezes, or presses, sediments into sedimentary rocks
Compaction
Chemical or physical process that breaks down rocks into smaller pieces.
Weathering
Epicenter
the point on Earth directly above the other term
Focus
is the point of origin inside the Earth where the rupture occurs
What do you identify the epicenter with?
Triangulation
amplitude (vibrations) of earthquake
Seismometer
Richter Scale
used to express magnitude
T/F - The Richter scale relies on the seismometer to create the magnitude (size).
T
Where do plates glide across?
Asthenosphere
Shield Volcanoes are formed by ___ magma and produce of low viscosity (runny)
mafic
Photosynthesis is the biggest component that removes [carbon or nitrogen?] from the atmosphere.
carbon
what process allows humans and plants to use nitrogen?
nitrogen fixation
With which of the following substances could radiometric carbon dating be used?
a) an arrowhead thought to be from 1,200 BCE
b) a leather sandal thought to be from 45,000 BCE
c) a piece of petrified wood thought to be from 80,000 BCE
d) a ceramic vase thought to be from 1,000 BCE.
b, using Carbon-14 isotopes must be younger than 60,000 years
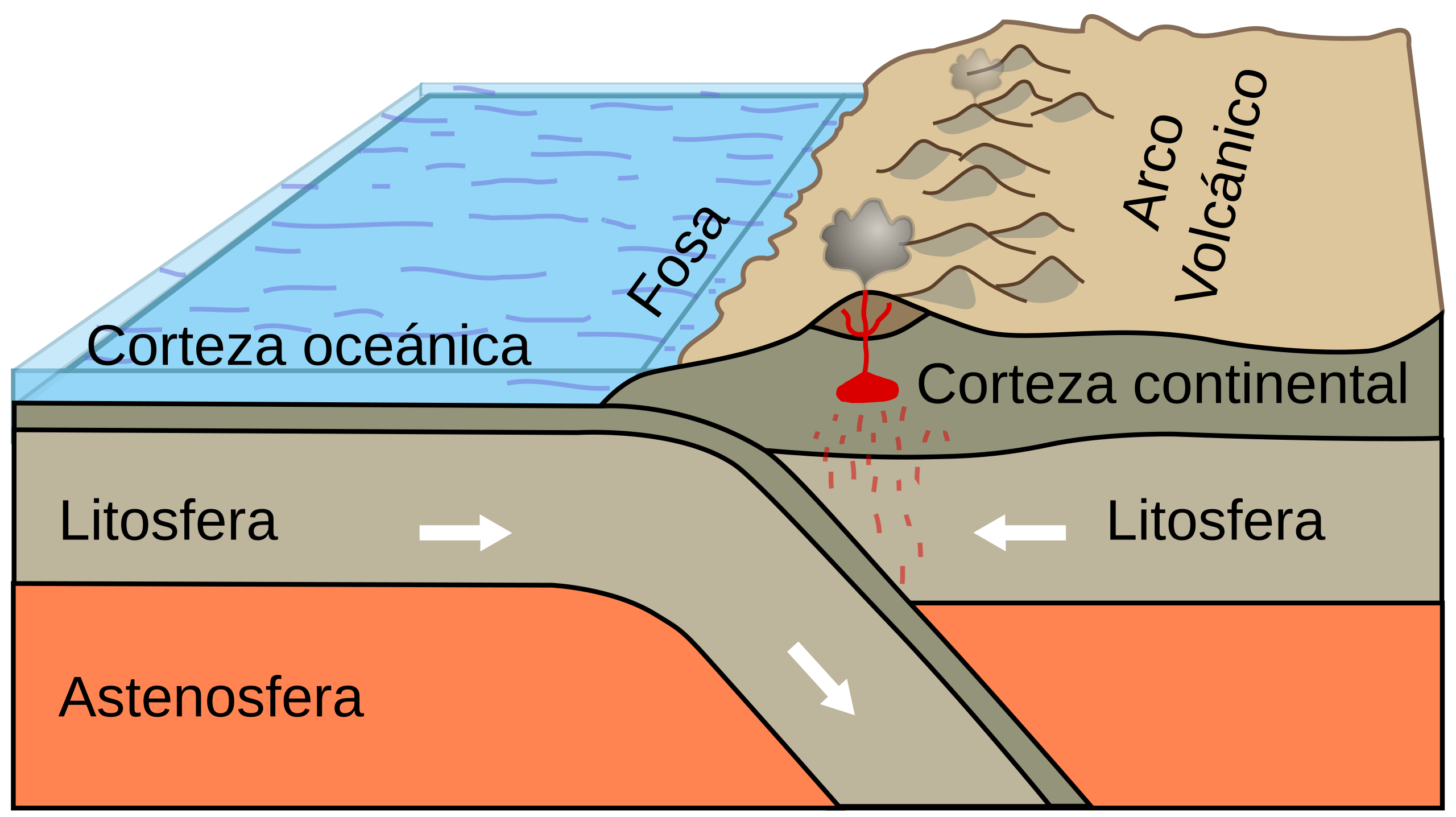
The denser (term) plate gets pushed under (subducted) the lighter (term) plate.
Volcanic mountain ranges on land, ocean trenches,
Oceanic-Continental Convergence
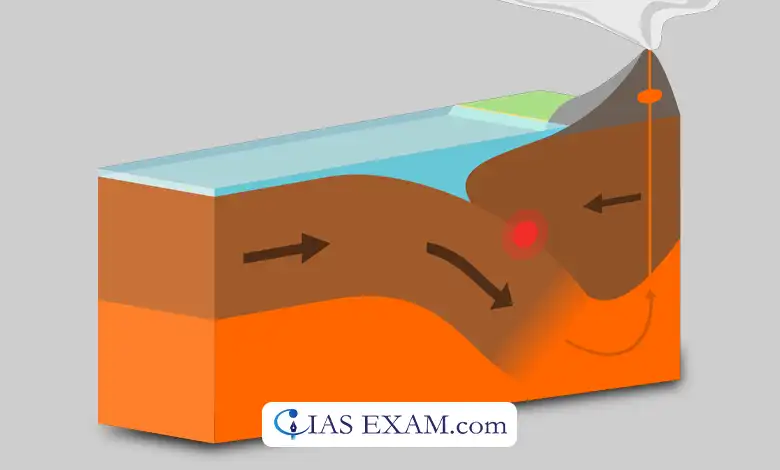
One term gets subducted under
Volcanic on islands, ocean trenches
Oceanic-Oceanic Convergence
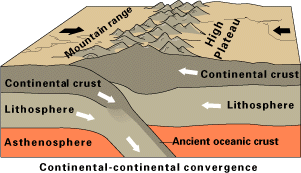
neither get subducted, crumple and fold
Faults, Mountains, earthquakes
Continental-Continental Convergence