Neuroanatomy 1
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
What does the Central nervous system (CNS) consist of
Central Nervous System (CNS)
Brain
Spinal cord
What does the Peripheral nervous system consist of
Everything else
Nerves
Motor Pathways
Sensory pathways
What does the brain consist of?
Cerebellum
Cerebrum
Brain stem
Recieves a constant flow of blood from heart (approx 20%)
The two hemispheres
Left and right
Contralateral = opposite side
Ispilateral = same side
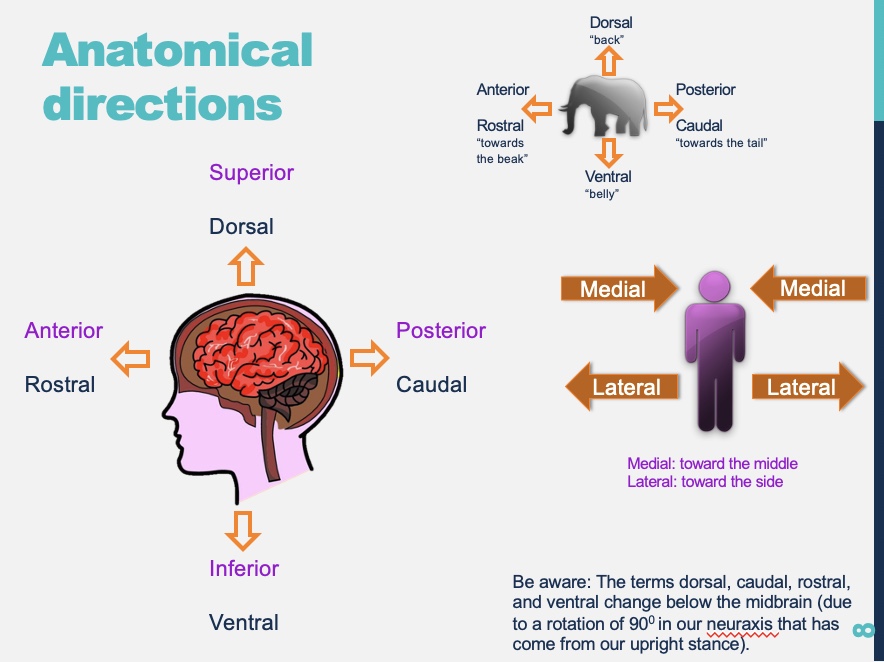
Anatomical directions
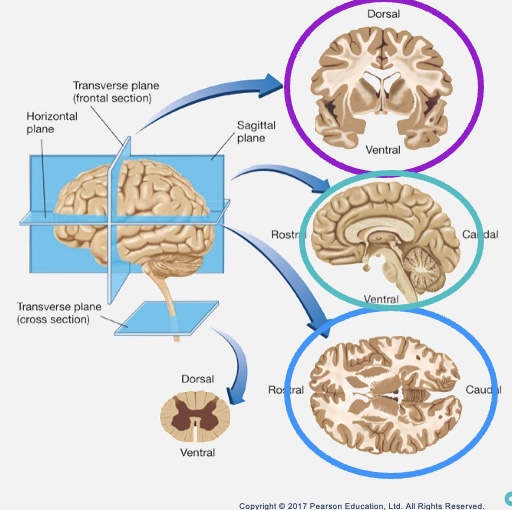
Planes and sections
Frontal (coronal) - Parallel to forhead
Saggital - arrow
Horizontal- Parallel to ground
What does grey matter consist of?
Cell bodies and dendrites
E.g. cortex, basal ganglia, thalamus
What does white matter consist of
Myelinated axons
E.g. the corpus callosum
A pathway that connect left and right side of hemisphere is called a commissure.
What is the corpus callosum?
“Hard body”
The largest fiber bundle that connects the two hemispheres of the brain
How does Meninges protect the nervous system?
3 layers of tissue that protect the brain and spinal cord (CNS)
How does Cerebrosphinal fluid (CSF) protect the nervous system
A clear fluid that fill the subarachnoid space
Functions: shock absorber, buoyancy
What are the ventricles
Hollow cavities filled with CSF
Lateral ventricles x2
Membraine called choroid plexus produces CSF by filtering blood
Third ventricle
Cerebral aqueduct
Fourth ventricle
Functions continued: exchange of materials between blood vessels and brain tissue
What is the blood brain barrier
A semipermeable barrier
Lipid soluble substances can pass through. Substances with large molecules (e.g., glucose) must be actively transported through walls.
Purpose of the blood brain barrier
Maintain stable environment
Protection from potentially disruptive/damaging chemicals
What is the cerebral cortex
Outer surface cerebrum
3mm thich
Folded to allow a bigger surface area
Clefts/cracks/grooves = sulci
Major grooves = fissures
Folds/bulges = gyri
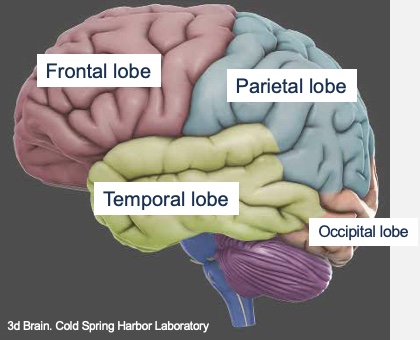
Lobes of the cerebral cortex
Frontal
Parietal
Occipital
Temporal
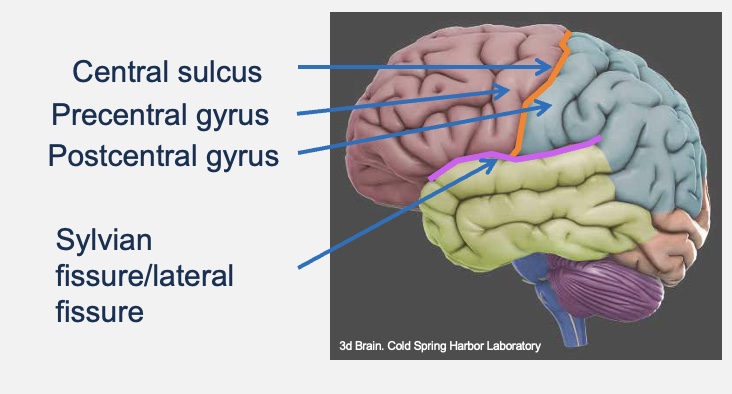
Major sulci and Gyri
Central sulcus
Precentral gyrus
Postcentral gyrus
Sylvian
Fissure / lateral
Fissure
What is the frontal lobe
The anterior area of the cortex, rostral to parietal lobe, dorsal to temporal lobe
Divided from parietal lobe by the central sulcus
Functions: motor and cognition
What is the parietal lobe
Caudal to frontal lobe, dorsal to temporal lobe
Function- somatosensory
What is the occipital lobe
Caudal to parietal and temporal lobes
Function: vision
What is the temporal lobe
Rostral to occipital lobe and ventral to parietal and frontal lobes
Functions: hearing, vision, cognition, emotion
Primary areas
Primary somatosensory cortex
Primary visual cortex
Primary auditory cortex
Primary motor cortex- connected to muscles in body
All contralateral (except olfaction and taste)
Primary association areas
Sensory association areas- receive and analyse info from primary regions