Quiz 7: Biomedical Sciences
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
What is the definition of heart failure?
a clinical syndrome resulting from any structural or functional cardiac disorder that impairs the ability of the ventricle to fill or eject blood
What are the 3 major etiologies of HF?
CAD, long-standing hypertension, and cardiomyopathies
What are examples of cardiomyopathy causes?
familial/genetic, diabetic, or infectious myocarditis
What are some drug-related causes of heart failure?
- direct cardiotoxic anti-cancer drugs
- negative inotropes (non-DHP CCBs, beta-blockers, some anti-arrhythmics)
- drugs that cause Na⁺/water retention (NSAIDs, corticosteroids)
Preload
venous return that fills the left ventricle, stretching the muscle prior to contraction
What does the Frank-Starling law state?
within physiological limits, increased LV filling increases stroke volume
How does preload-stroke volume response differ in compensated HF vs normal?
Reduced strove volume with same given preload compared to normal.
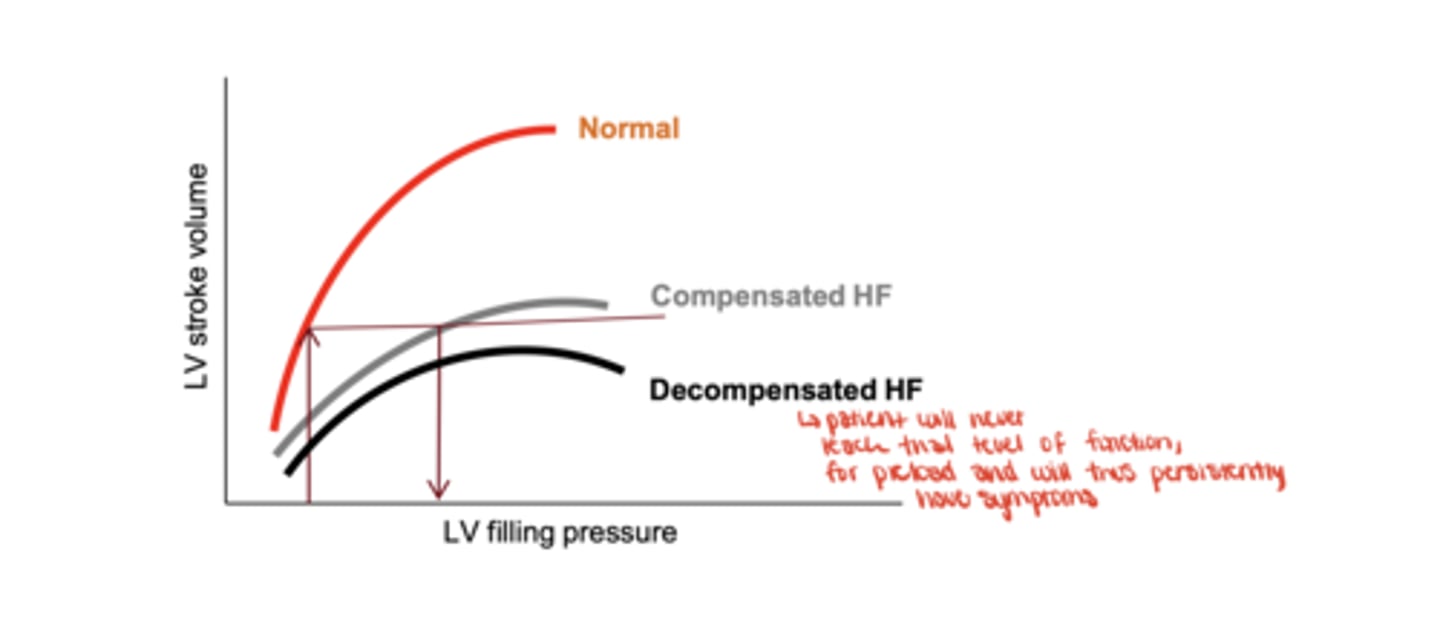
What happens in decompensated heart failure regarding preload?
increasing LV filling no longer increases stroke volume; symptoms persist
Afterload
the resistance the heart must pump against, represented by systemic vascular resistance
What is cardiac output?
stroke volume × heart rate
Why is extremely high heart rate harmful in HF?
it reduces diastolic filling time, decreasing stroke volume
Contractility
the intrinsic strength of the cardiac muscle
What two major consequences occur when the heart pump fails?
increased venous congestion and decreased cardiac output
What symptoms result from venous congestion?
pulmonary edema and peripheral edema
What symptoms result from decreased cardiac output?
fatigue, weakness, reduced organ perfusion
What neurohormonal systems activate in response to low cardiac output?
RAAS and the sympathetic nervous system
What are key mediators released due to RAAS/SNS activation in HF?
angiotensin II, aldosterone, norepinephrine, epinephrine
How does Ang II and aldosterone worsen HF?
increase afterload, preload, sodium/water retention, and direct myocardial remodeling
Why is HF described as a "vicious cycle"?
compensatory responses worsen cardiac workload and structural damage over time
All the following are maladaptive responses to heart failure,
EXCEPT:
improved renal blood flow
3 multiple choice options
What are the four primary drug therapy pillars for HFrEF?
Beta-blockers, RAAS inhibitors (ARNi > ACEI > ARB), SGLT2 inhibitors, MRAs
Which beta-blockers reduce mortality in HF?
bisoprolol, carvedilol, metoprolol succinate (SR)
How do beta-blockers benefit HF?
reduce catecholamine toxicity, decrease remodeling, reduce workload
How do ACE inhibitors benefit HF?
reduce preload, afterload, and long-term cardiac remodeling; improve survival
When are ARBs used in HF?
when ACE inhibitors are not tolerated (e.g., cough, angioedema)
Why is combining NSAIDs with ACEI/ARB dangerous in HF?
loss of afferent vasodilation + efferent vasoconstriction → ↓ GFR → acute kidney injury
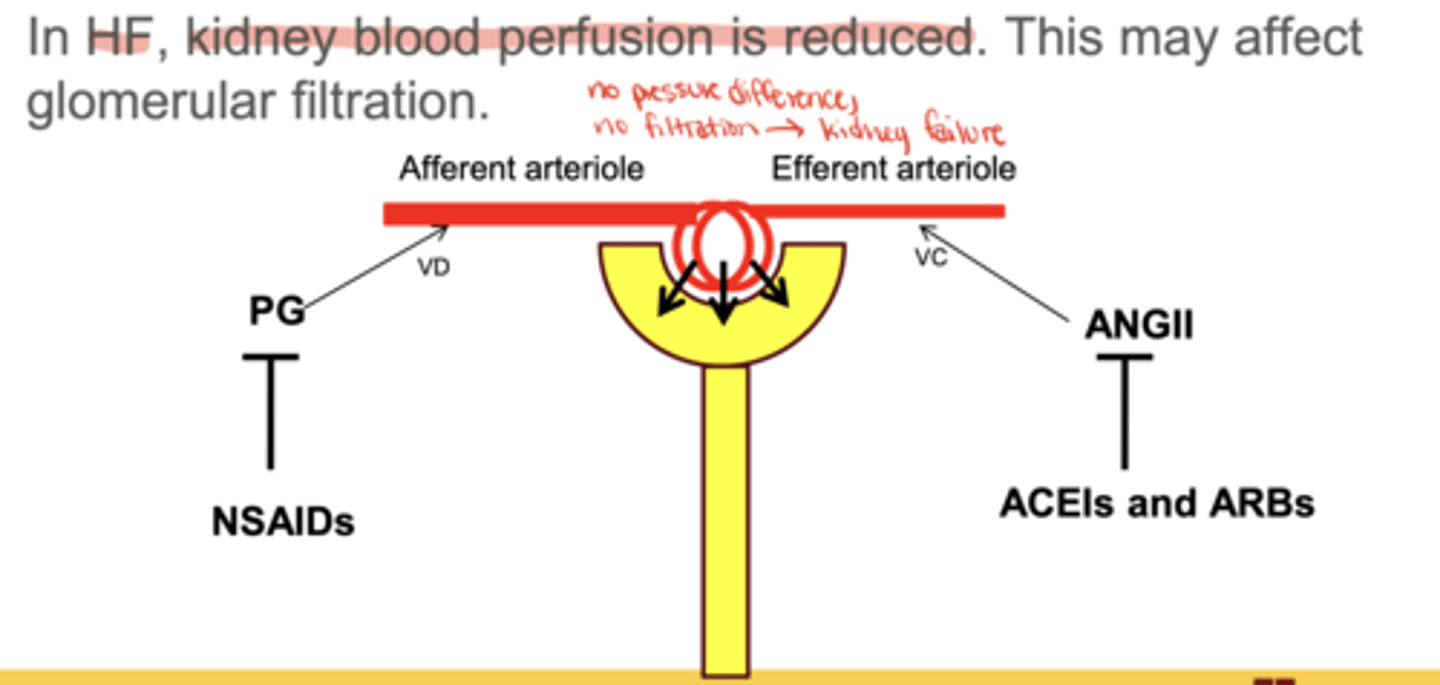
What is the major benefit of SGLT2 inhibitors in HF?
reduce HF worsening and CV death regardless of diabetes status
What is the primary role of loop diuretics in HF?
reduce fluid (water and salt) overload and improve symptoms
What extra benefit do MRAs (spironolactone/eplerenone) provide in HF?
reduce morbidity and mortality by blocking aldosterone-mediated remodeling
Venodilators
long-acting nitrates (ISDN, ISMN, nitroglycerin)
Arteriodilators
hydralazine
Which vasodilator combination reduces mortality in African Americans with HF?
isosorbide dinitrate + hydralazine
When is the nitrate/hydralazine combo used instead of ACEI/ARB?
pregnancy, intolerance, or renal insufficiency.
What is ejection fraction (EF)?
stroke volume ÷ end-diastolic volume
HFrEF
systolic dysfunction (reduced contraction)
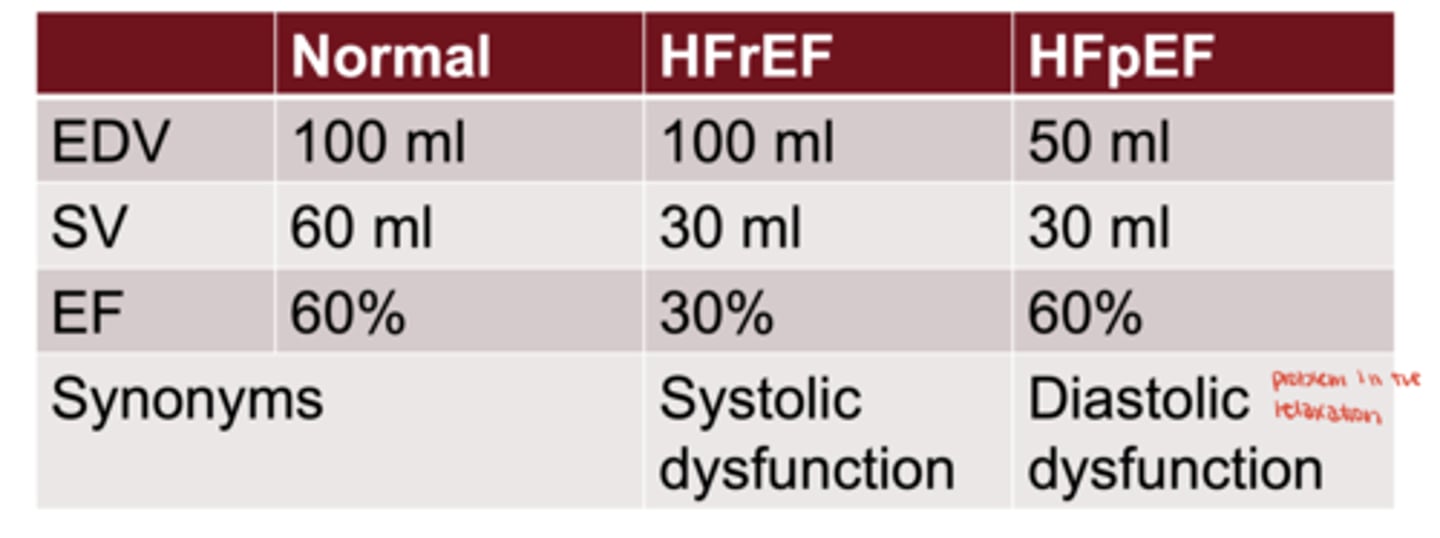
HFpEF
diastolic dysfunction (impaired filling)
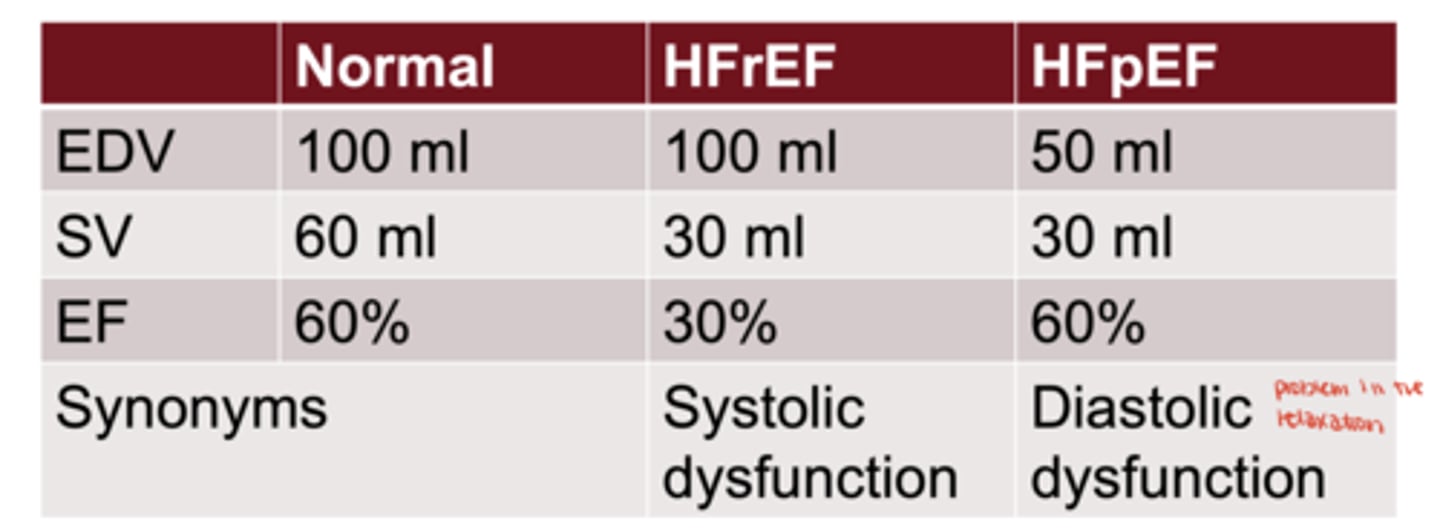
Are positive inotropes used in HFpEF?
No, because contractility is not the primary problem
Mr. A.A. is a 58-year-old patient who is recently diagnosed with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF).
His past medical history includes hypertension, IHD, dyslipidemia, and
bronchial asthma. His medication list includes HCTZ, verapamil, atorvastatin,
aspirin, clopidogrel, and occasional terbutaline inhaler for his mild asthma.
Which of these medications should be
discontinued after the recent diagnosis
of HFrEF?
Verapamil
3 multiple choice options
Which of these medications should be
prescribed to Mr. A.A.?
Ramipril
3 multiple choice options
If the cardiologist prescribes bisoprolol to Mr. A.A., you should educate the patient that
bisoprolol may worsen his asthma
3 multiple choice options