Autonomic Nerv Sys + Brain development + Grey/White matter
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
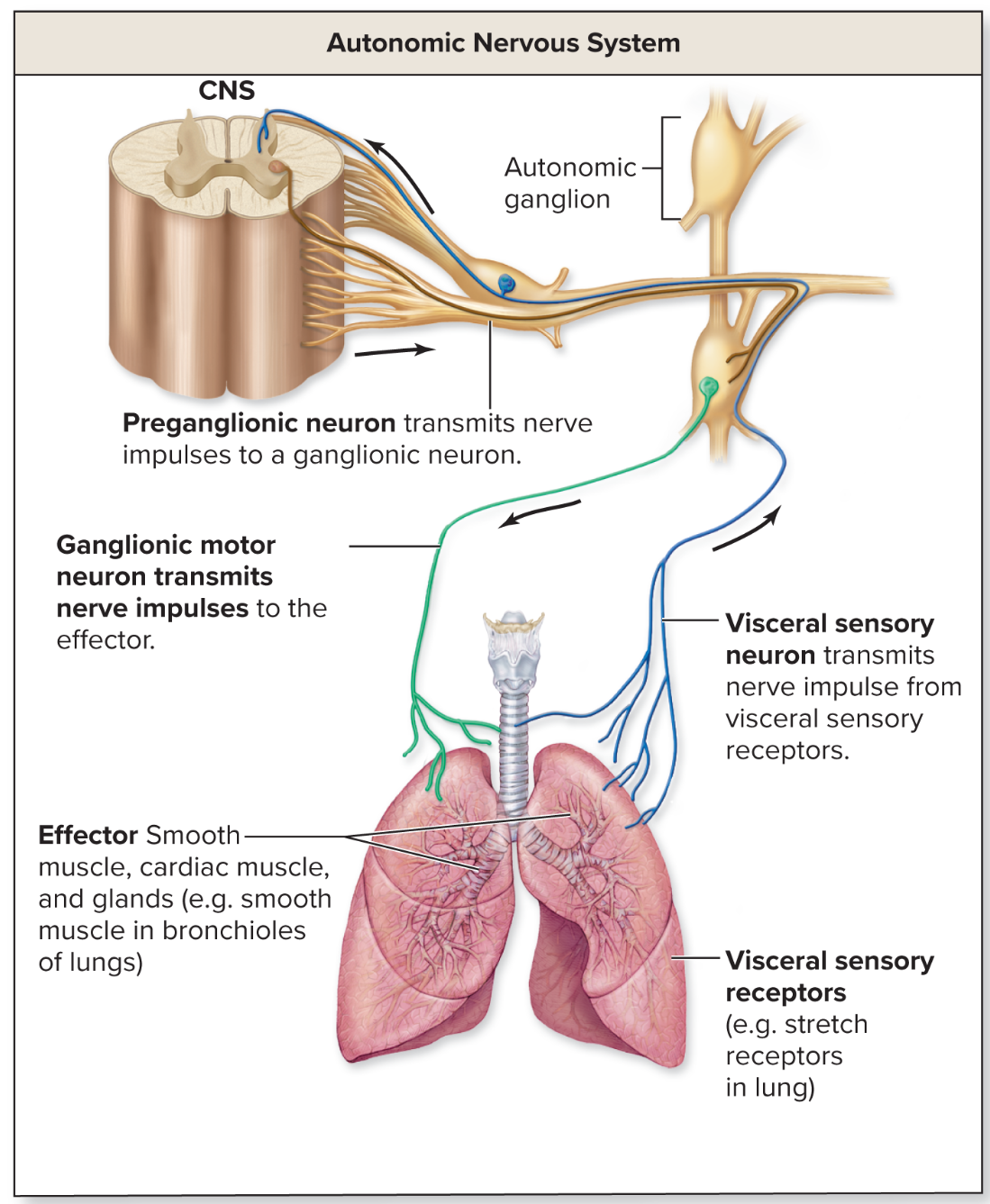
Autonomic nervous system
also called the visceral nervous system
processes regulated below the conscious level → motor system
initiates and transmits nerve impulses along autonomic motor neurons from the CNS to effectors → including cardiac muscle, smooth muscle, and glands
maintaining homeostasis!!
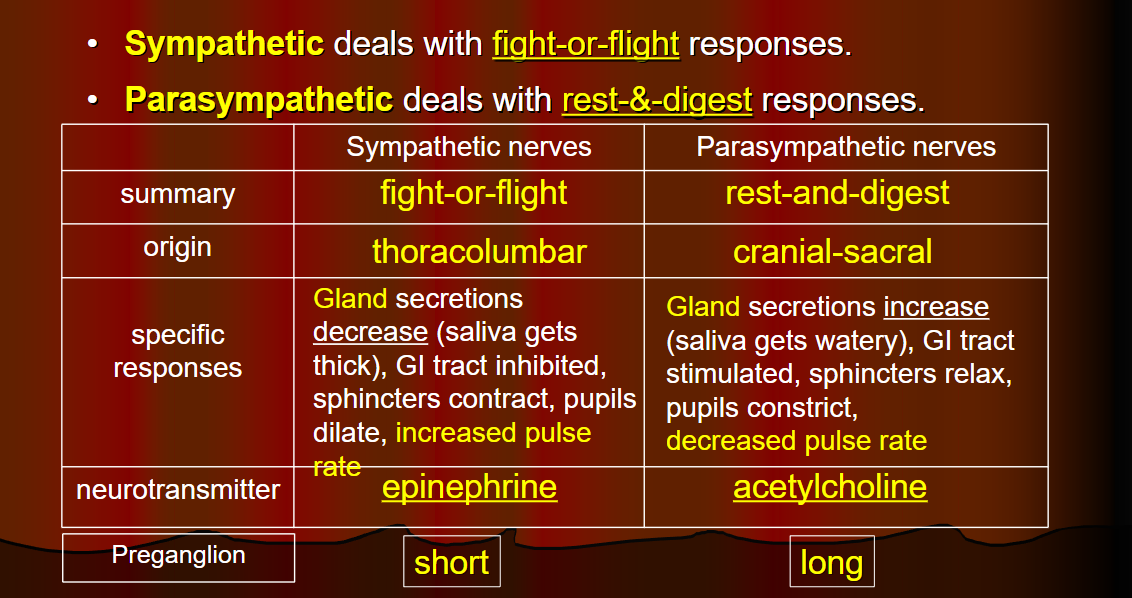
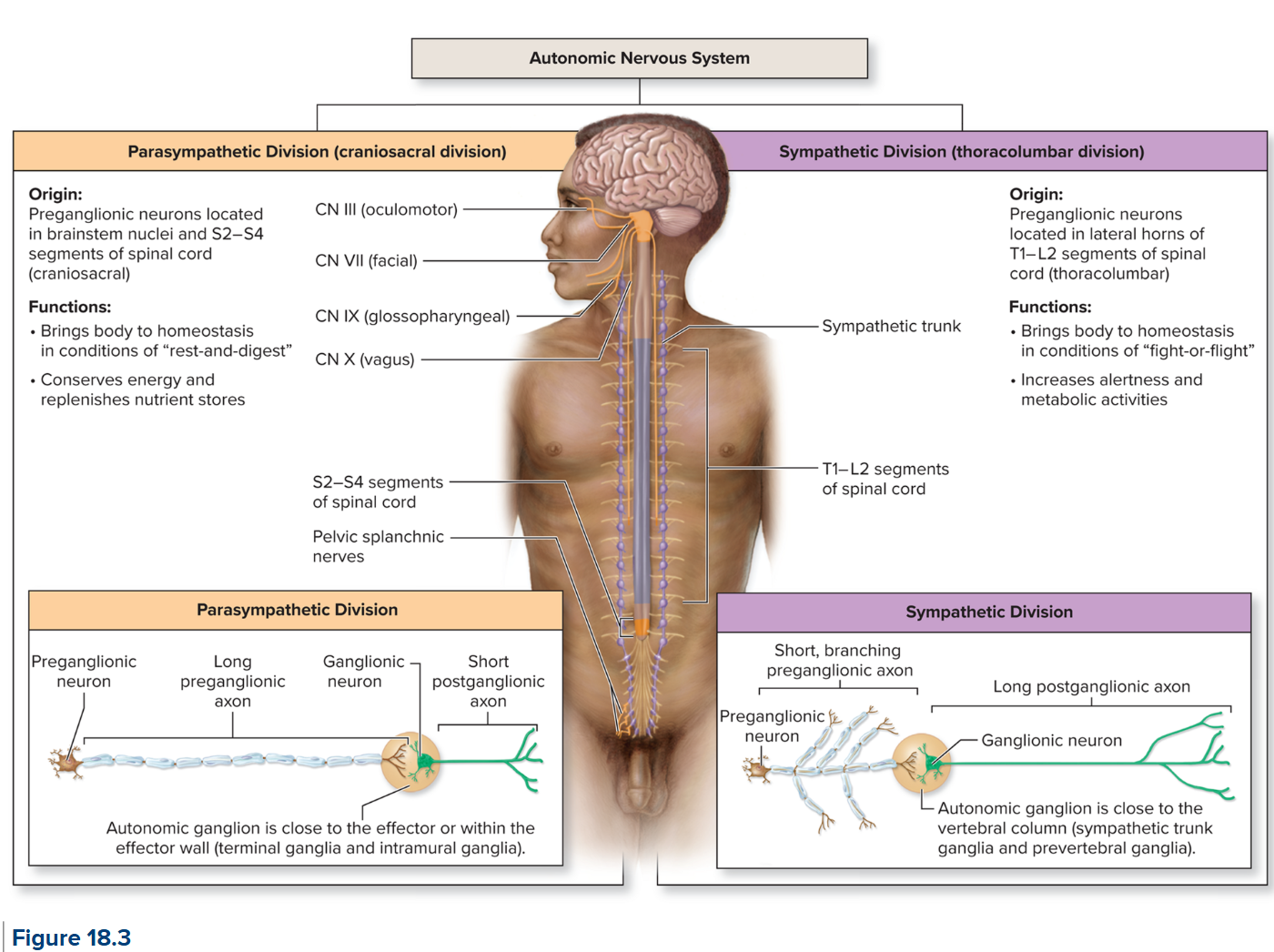
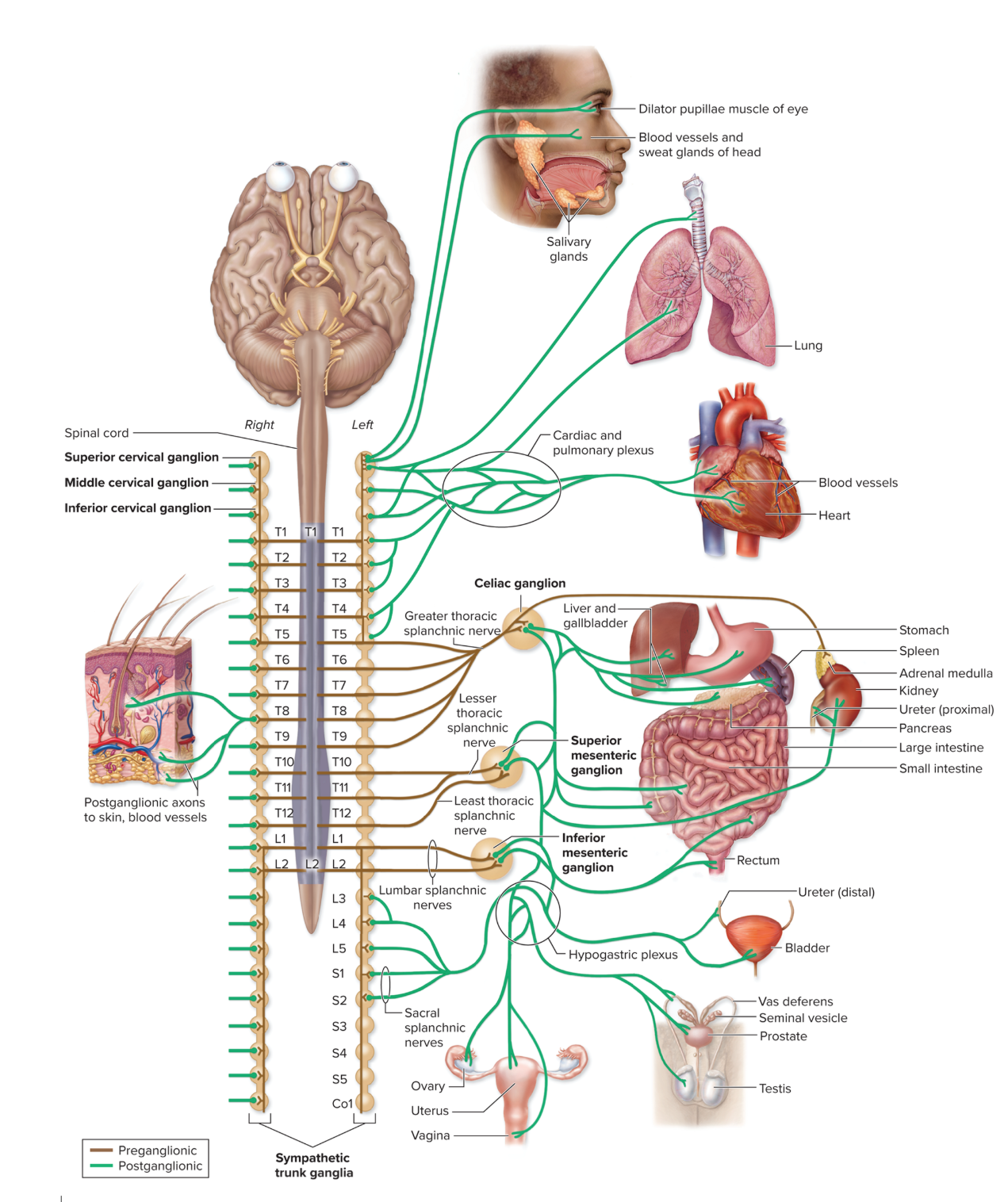
Sympathetic vs Parasympathetic comparison
that
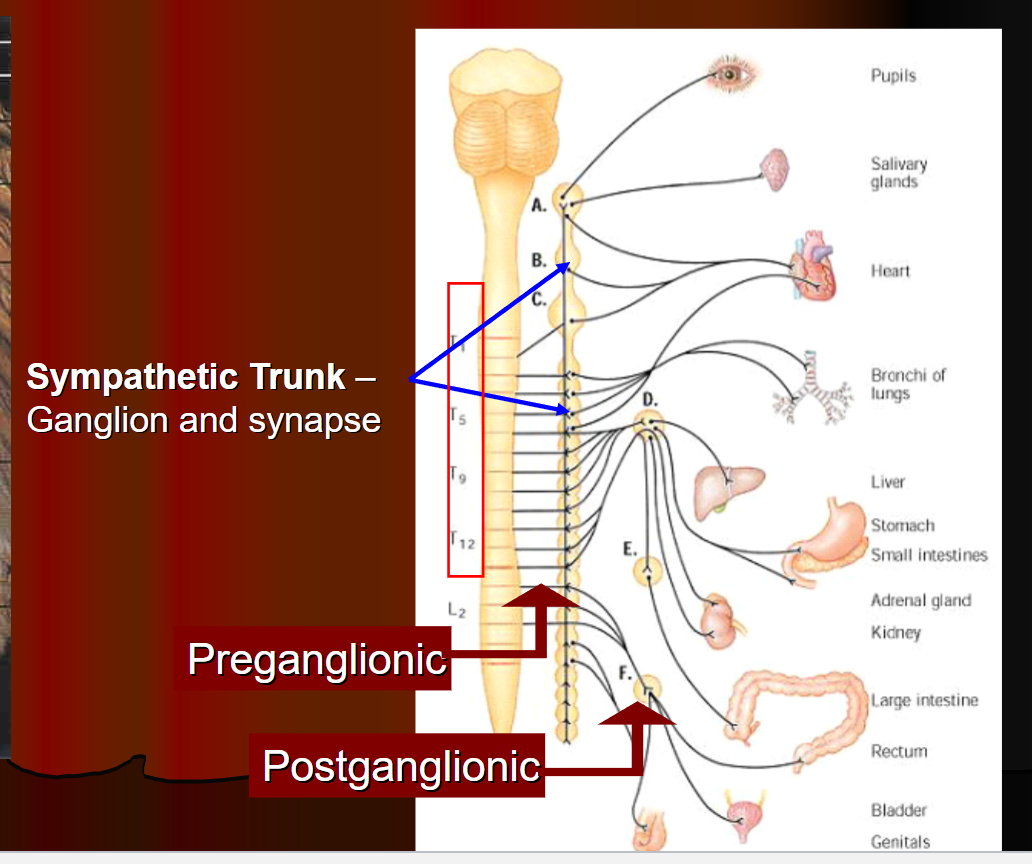
Sympathetic
for fight or flight responses!
maintains homeostasis during exercise or times of stress or emergency → release of nutrients from stores
Ex: glucose released from the liver
exhibiting mass activation response
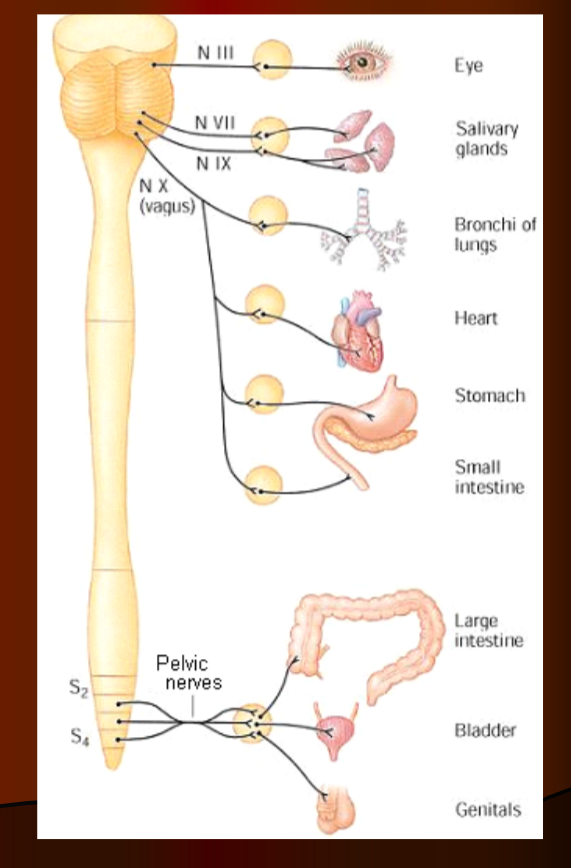
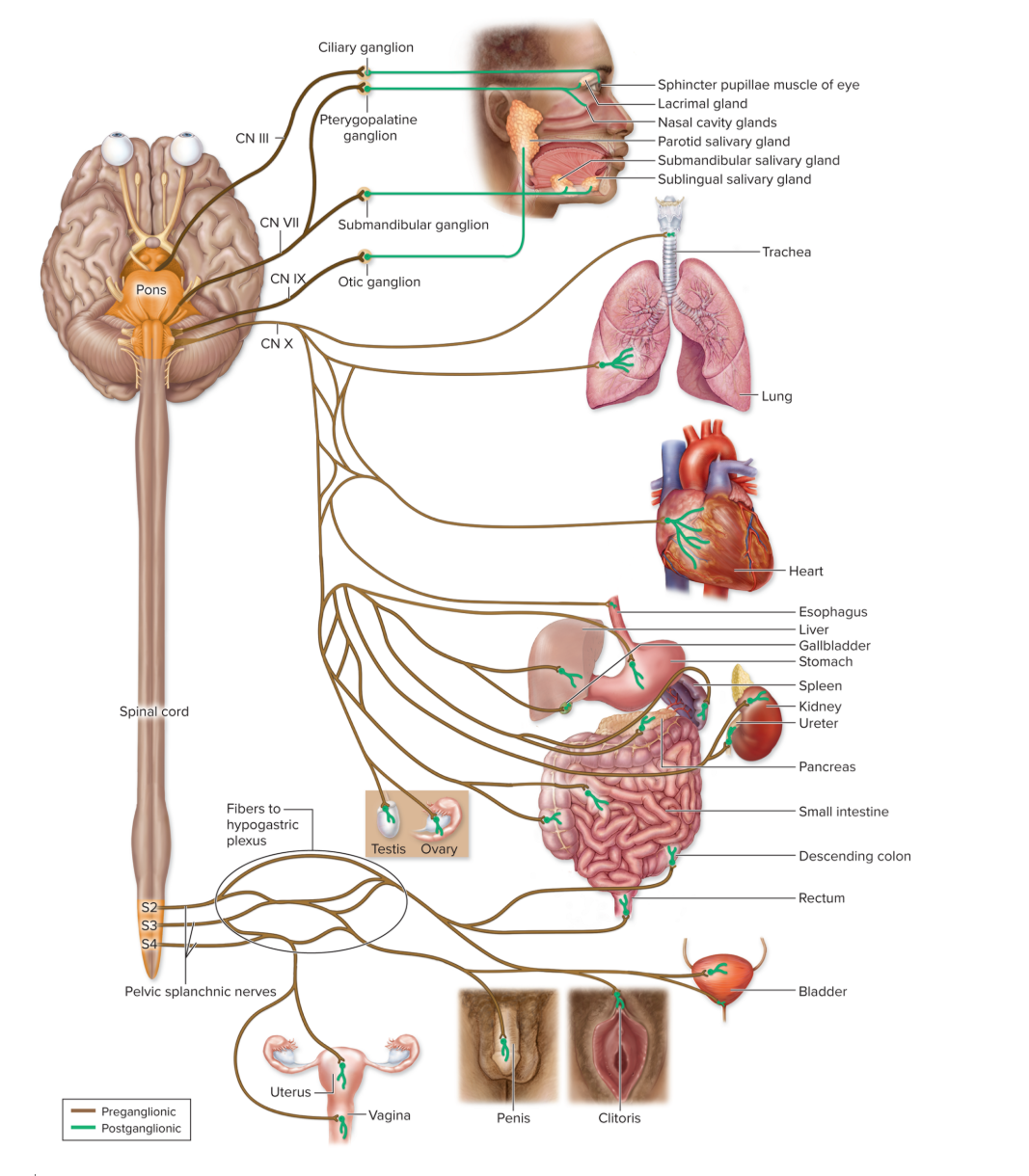
Parasympathetic
rest and digest
conserving energy and replenishing nutrient stores
ganglia are closer to organs
long preganglionic neurons and short postganglionic neurons
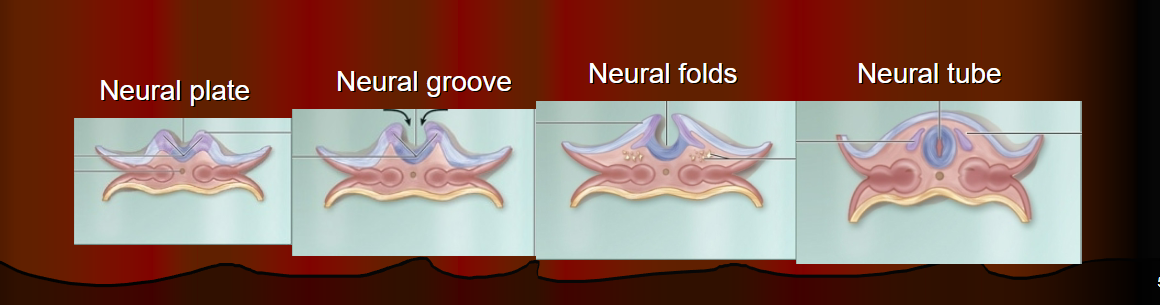
Brain development comes from…
The neural tube!
Which is from the germ layer: ectoderm (neurulation)
→ starts at the cephalic end and continues to caudal
What happens if it doesn’t close at the caudal end?
→ Spina bifida (poor baby :(
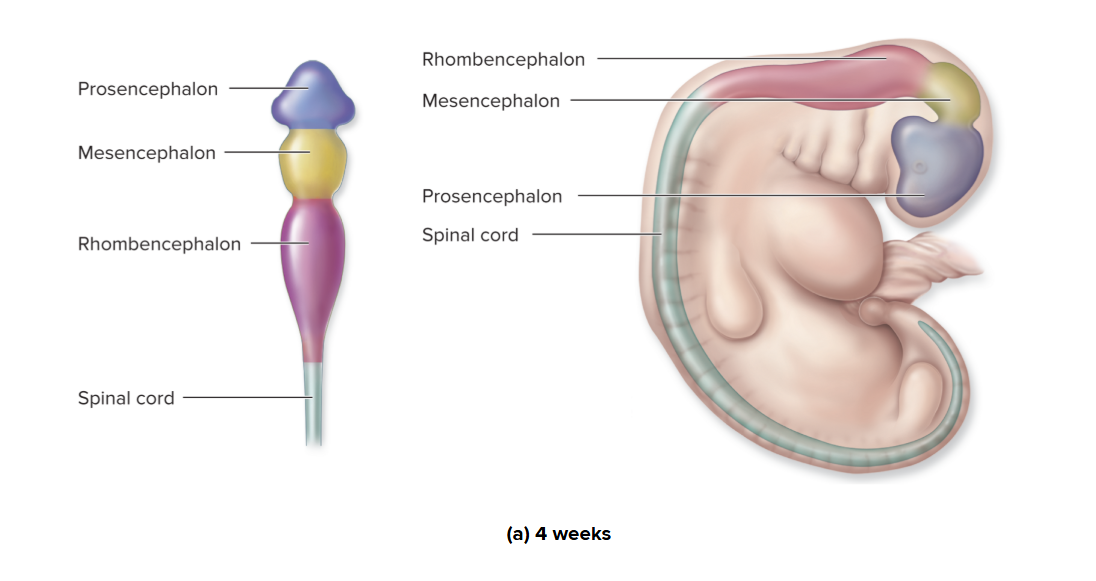
Brain development: 4 weeks
In the human embryo, the brain forms from the cranial (superior) part of the neural tube, which undergoes disproportionate growth rates in diff regions
late 4th week of development, growth has formed 3 primary brain vesicles
→ forebrain: prosencephalon
→ midbrain: mesencephalon
→ hindbrain: rhombencephalon
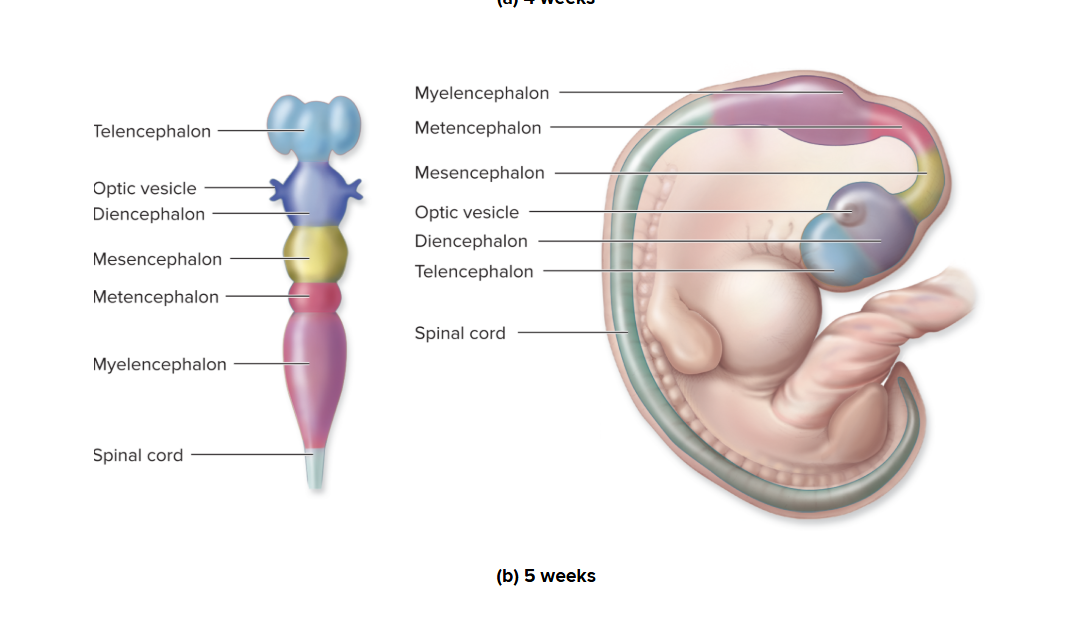
Brain development: 5 weeks
Telencephalon: Cerebrum
Diencephalon: Thalamus and Hypothalamus
Mesencephalon: Peduncles and Colliculi
Metencephalon: Pons and Cerebellum
Myelencephalon: Medulla oblongata
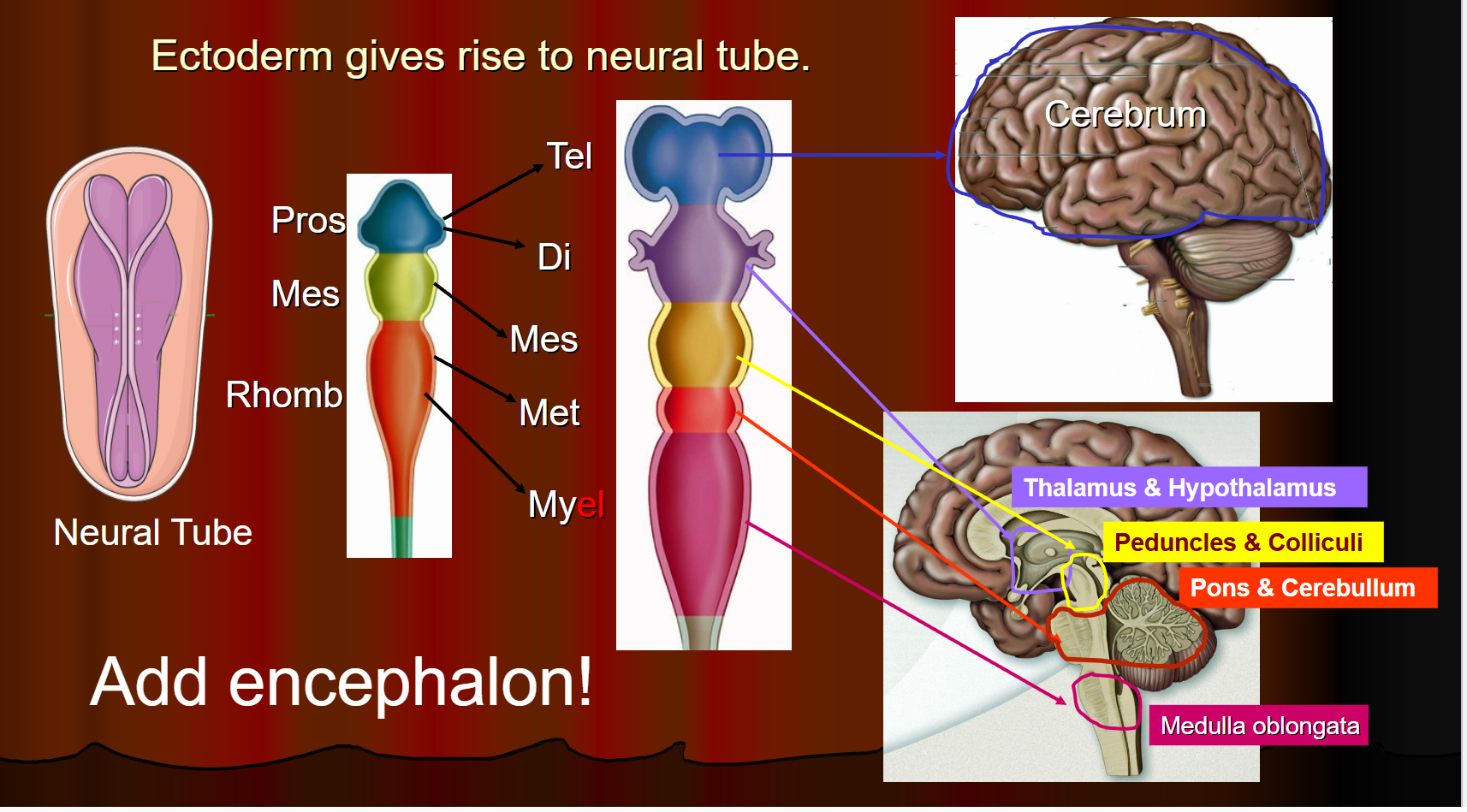
Organization of Neural Tissue Areas in the brain
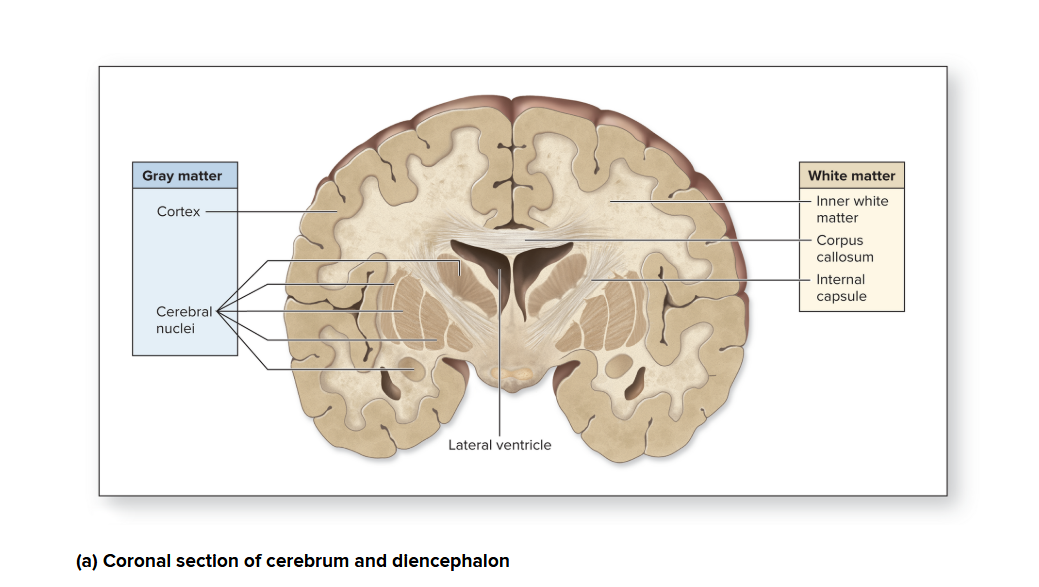
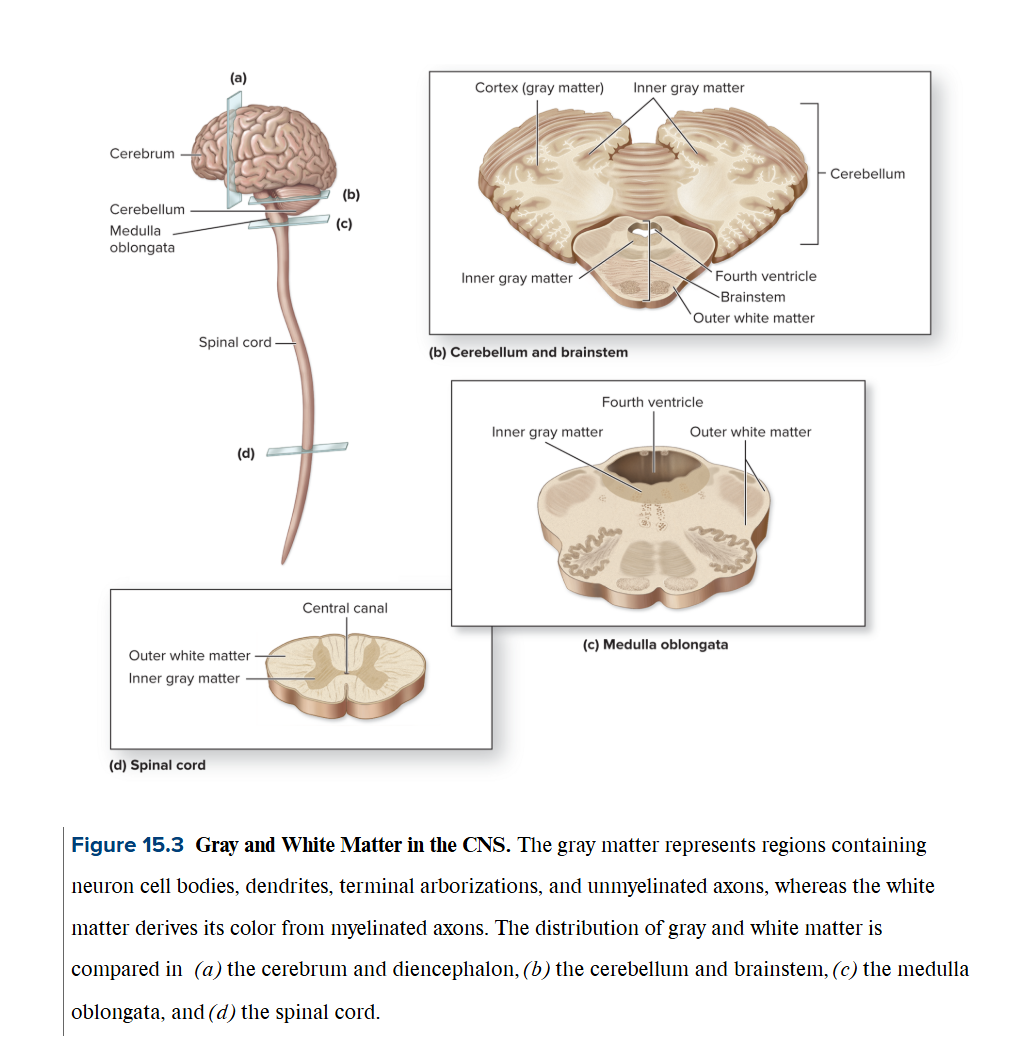
Gray and White matter
Gray matter
houses motor neuron and interneuron cell bodies, dendrites, terminal arborizations, + unmyelinated axons
outer layer: cortex → covering most of the surface of an adult brain
White matter
derives its color from the myelin in the myelinated axons
deep into the gray matter of cortex
within masses of white matter in the cerebrum contains discrete internal clusters of gray matter called cerebral nuclei (oval, spherical, sometimes irregularly shapes clusters of neuron cell bodies)
Where are ganglia and nuclei located? What do they contain?
Ganglia are clusters of nerve cell bodies located primarily in the peripheral nervous system (PNS).
→ relay points for neural signals and are involved in the processing of sensory information and coordination of motor responses.
Nuclei are collections of nerve cell bodies found within the central nervous system (CNS), including the brain and spinal cord.
→ play a crucial role in relaying and processing information, coordinating higher-order functions such as cognition and motor control.
In summary, ganglia are located in the PNS and are involved in sensory processing, while nuclei are located in the CNS and are involved in higher-order functions.