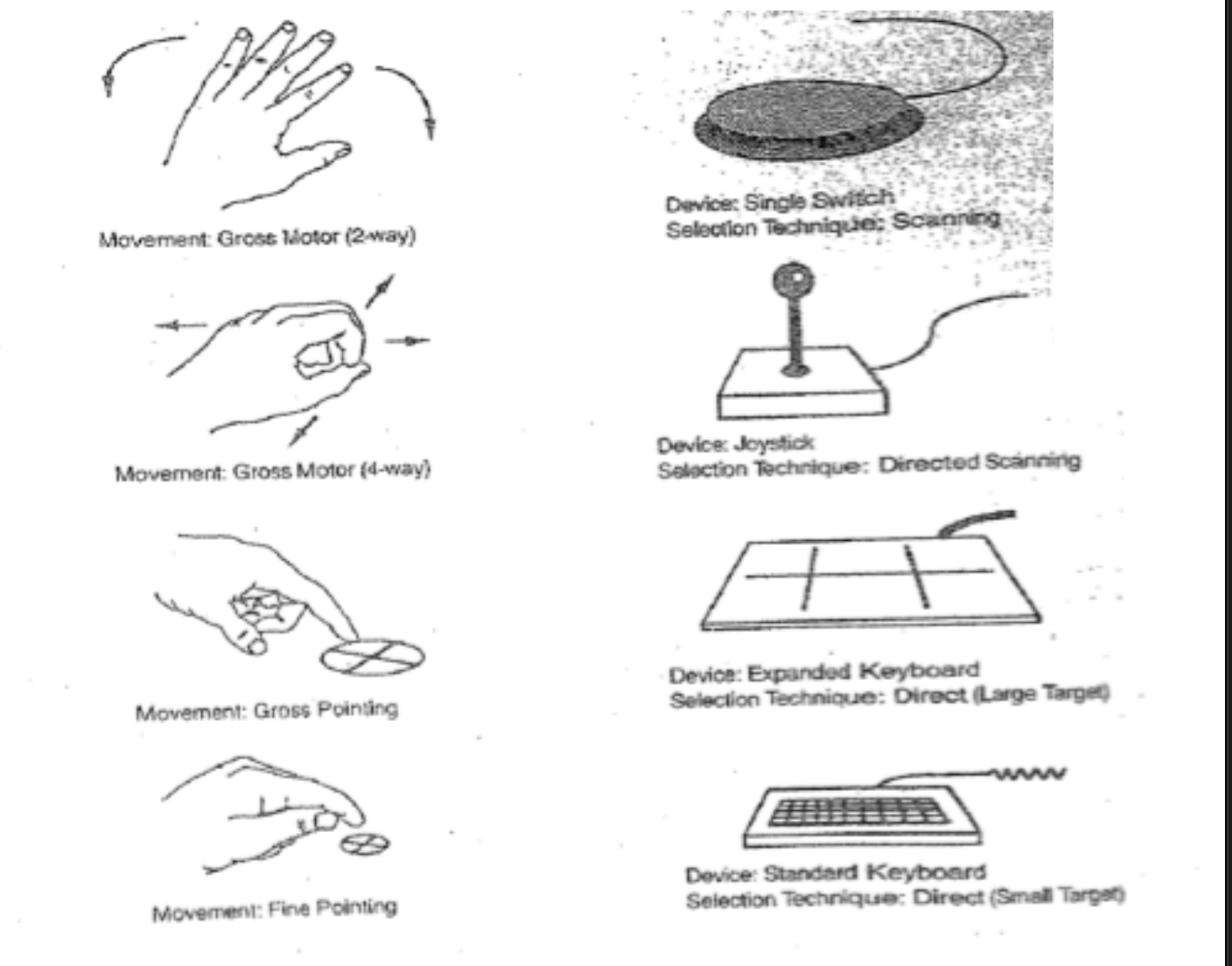
Theoretical Perspectives On Assistive Technology
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
AT System
Consists of…
an AT device,
a human operator who has a disability, and
an environment in which the activity is to be carried out
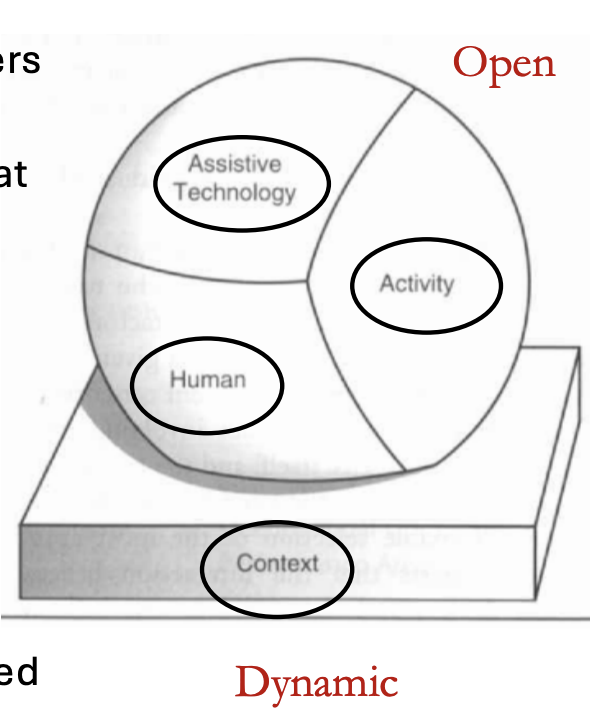
Human Activity Assistive Technology (HAAT) Model
Human:
Potential Users and Stakeholders (e.g., competencies, abilities)
Activity:
The desired functional tasks that the user wants to do but cannot do without the device
Context:
All environments in which the activities will be completed, and the device will be used
Assistive Technology:
Device used to improve activity or functional performance
Interfaces:
Analyze how interactions need to be handled
HAAT: Human
Human:
“Someone doing something some place”
Human performance
“the result of a pattern of actions learned to satisfy an objective according to some standard”
Human ability:
“the person’s capacity and limitations to learn a skill”
what ability does the client bring to the situation
Must be assessed:
Physical skills
Cognitive Skills
Insight and Awareness
if a patient doesn’t have this, the type of technology recommended highly changes (give them a caregiver-controlled AT, not something they’d have to operate independently; they won’t have the discipline to use the AT)
Emotional status
Expert v. Novice:
Level of Proficiency (Ability vs. Skill)
having skill —> having speed, comfortability, efficiency
“Intrinsic enablers”
in this case, the human
Structured Interviews
Objective assessment tools
HAAT: Activity
An individual person preference: life roles, position in society
The tasks that enable one to complete life roles
Depends on the environment
Mediated by performance and skill
Need to identify key activities
How often do they need to perform the activity
Activity analysis
Consider the perspective of the user
HAAT: Setting/Context
Physical Context
Social Context
Cultural Context
e.g., where do they go on vacation? what is their sense of personal space?
Institutional Context
e.g., how accessible is class at school (e.g., specifically Columbia University)?
Micro
the closest people in your own personal context
e.g., family, friends
Meso
people you aren’t the most close with, but still see often
e.g., people you work with, go to school with, see at the grocery store
Macro
people who you will never meet but impact your life significantly
e.g., the president
HAAT: Assistive Technology
Interface between the human and the activity (extrinsic enabler)
May become a part of oneself
Operation may be shared with a caregiver or aide
Level of independence
that the person needs vs wants
Tied to the environment it is used in
e.g., what kind of wheelchair do you need if you go to the beach often? —> one that can run on sand!
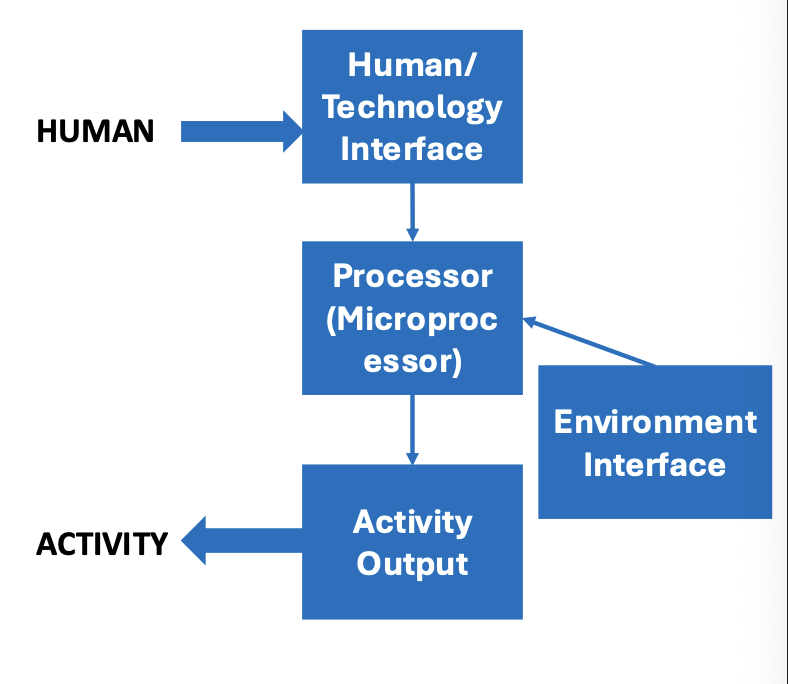
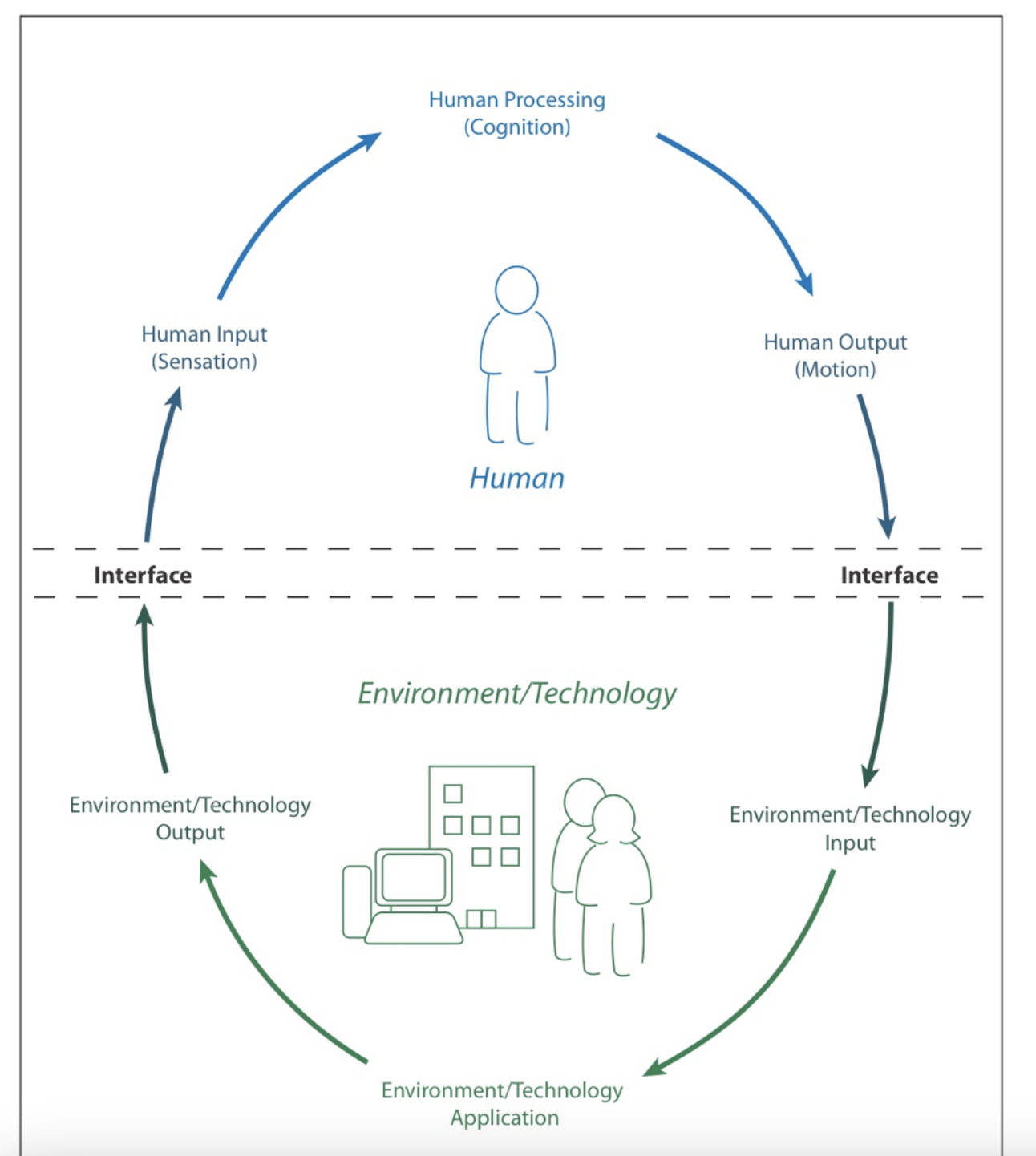
HETI: Human-Environment-Technology Interface
what is the best way for a human to interact with their technology to produce their desired outcomes?
what will be most beneficial? (e.g., type of wheelchair wheels? whether the person is pushing the wheelchair themself vs they have a caregiver pushing them?)
SETT
Student –
abilities, special needs, and requirements
Environment –
materials available in the environment (physical arrangement, special concerns, instructional arrangement, expected changes, support, and resources available)
Tasks –
activities taking place in the environment, supporting curriculum, critical elements of the activities, and modifying activities
Tools –
technology options
the AT in this model
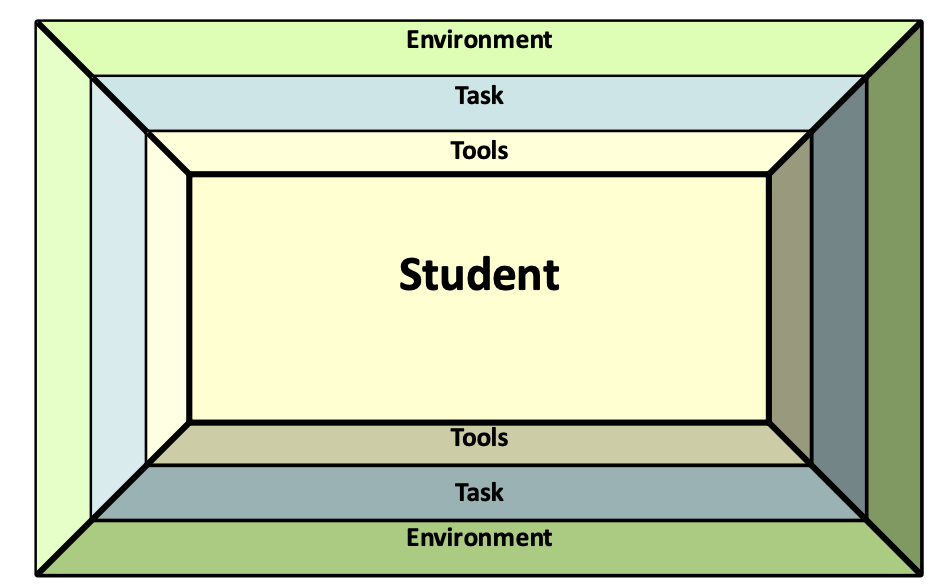
IMPACT2 Model
model created for AT
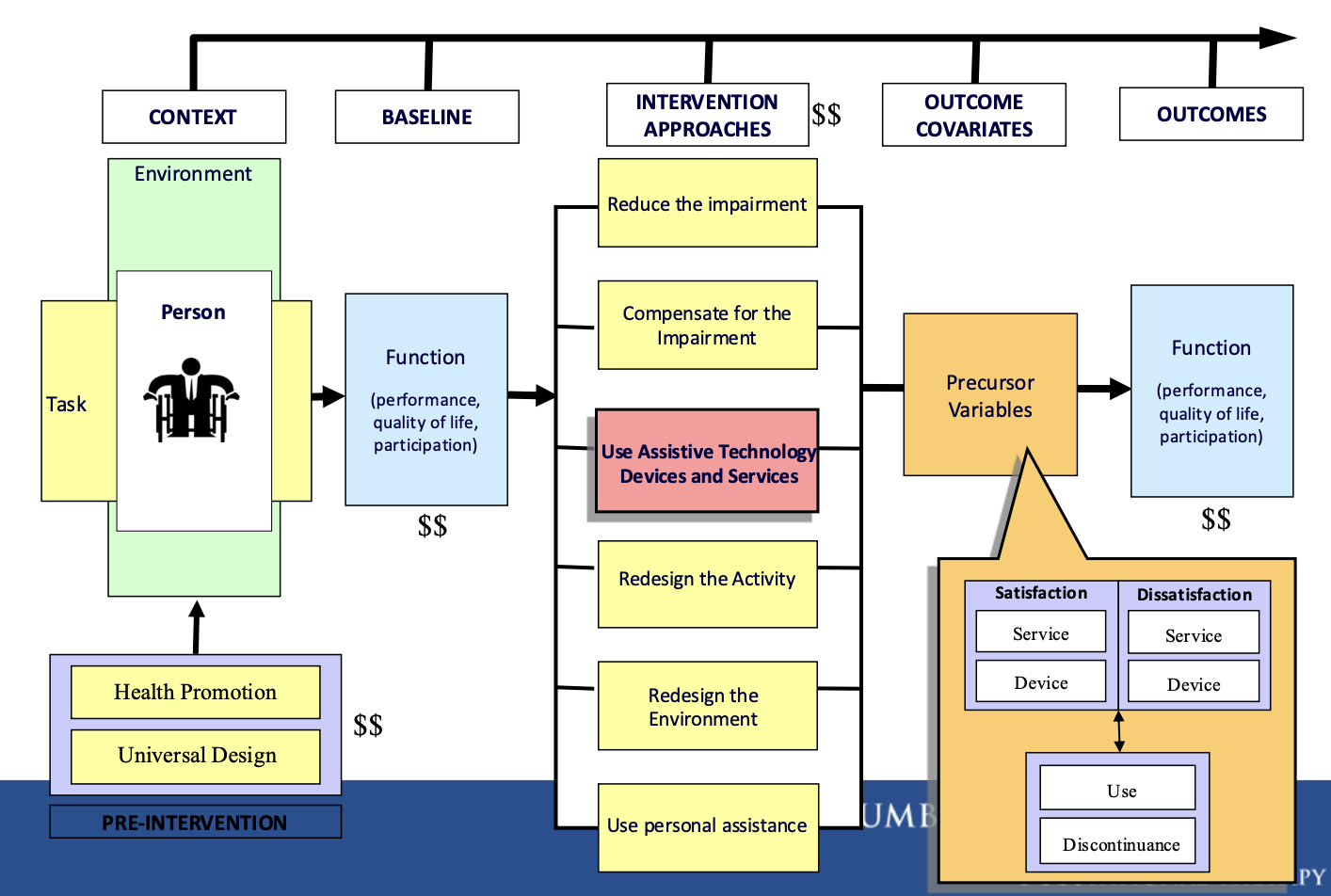
Parallel Interventions Model
provides solutions that can change over time to become more advanced; parallel interventions for today, but also tomorrow