CH 7 gen chem
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
Thermochemistry
The study of energy changes that occur during chemical reactions and changes in state
System
The matter that is being observed.
The total amount of reactants and products in a chemical reaction.
Surroundings or environment
Everything outside of the system
Isolated system
The system cannot exchange energy (heat or work) or matter with the surroundings; for example, and insulated bomb calorimeter.
isolated—- as in by yourself— as in with no one and nothing— so this one cannot exchange both
Open system
The system can exchange energy (heat and work) and matter with the surroundings
Closed system
The system can exchange energy (heat and work) but not matter with the surroundings
Process (system)
A change in one or more of its properties (such as concentrations of reactants or products, temperature, or pressure).
First law of thermodynamics and related equation
Energy can be transferred and transformed, but it cannot be created or destroyed.
U-internal energy of the system
Q-heat added to system
W-work done by system
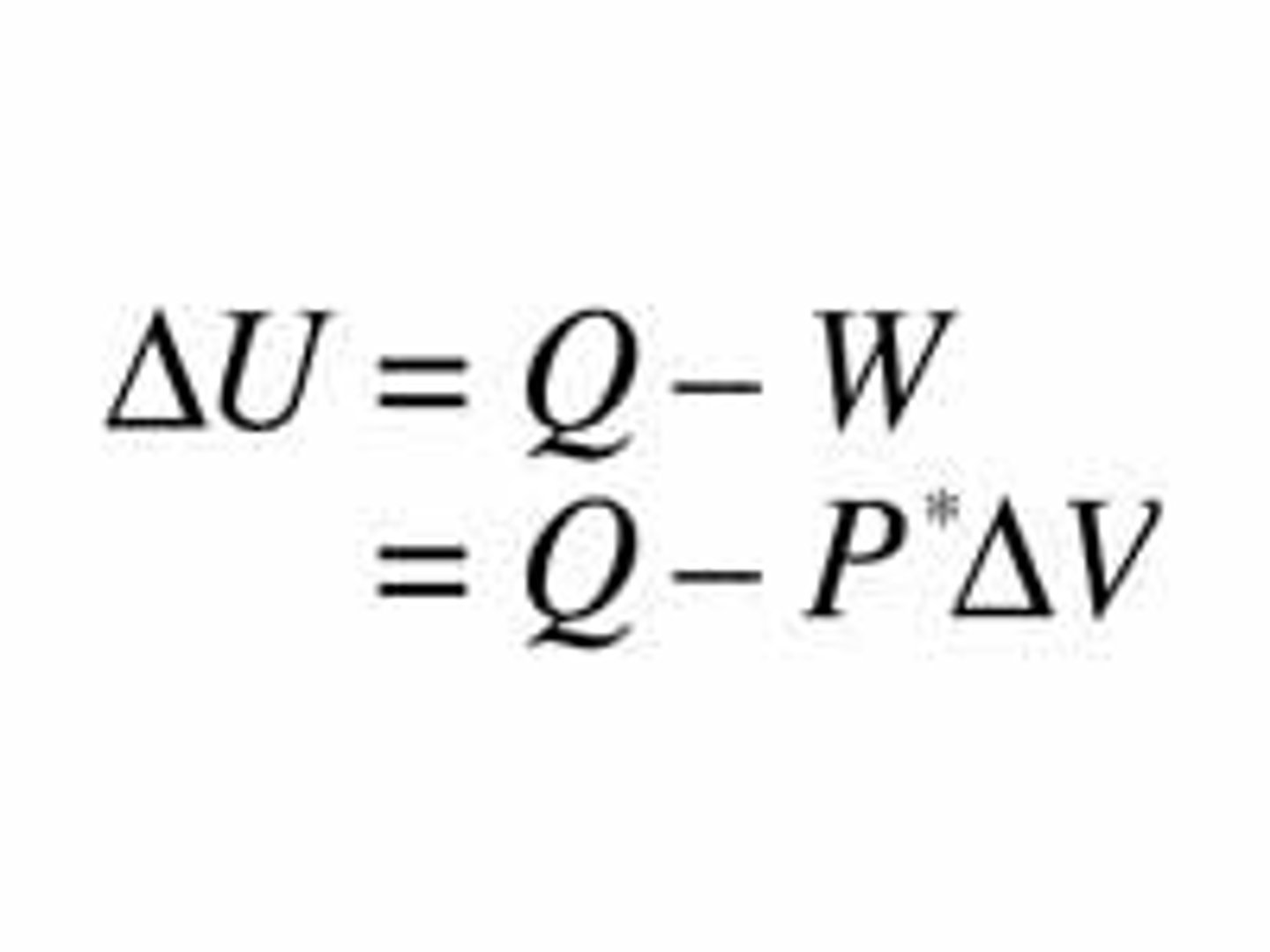
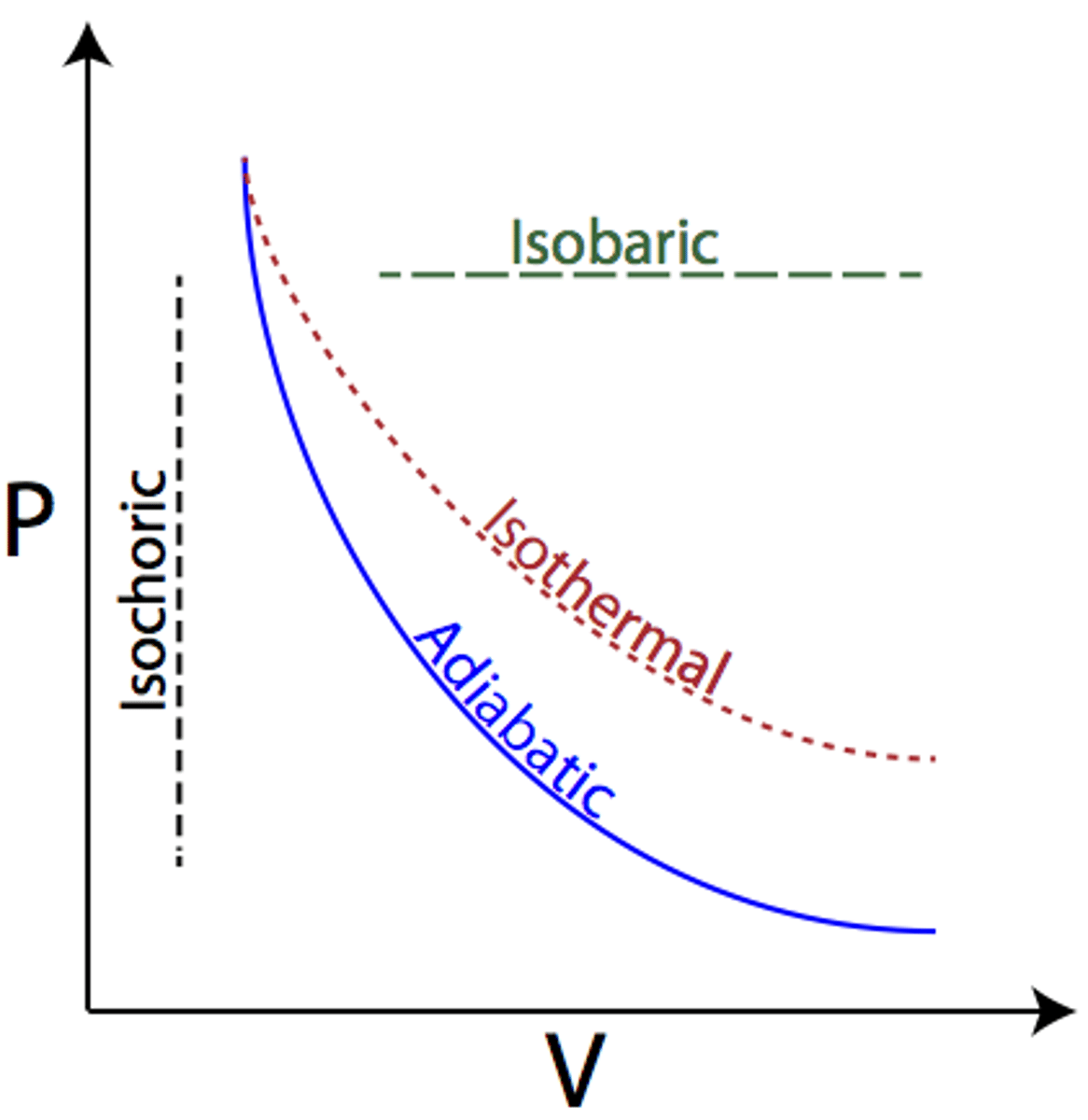
Isothermal process
Constant temp. implies that the total internal energy of the system (U) is constant
no change in temp.; change in ΔU=0; Q=W (heat added to the system equals work done by the system)
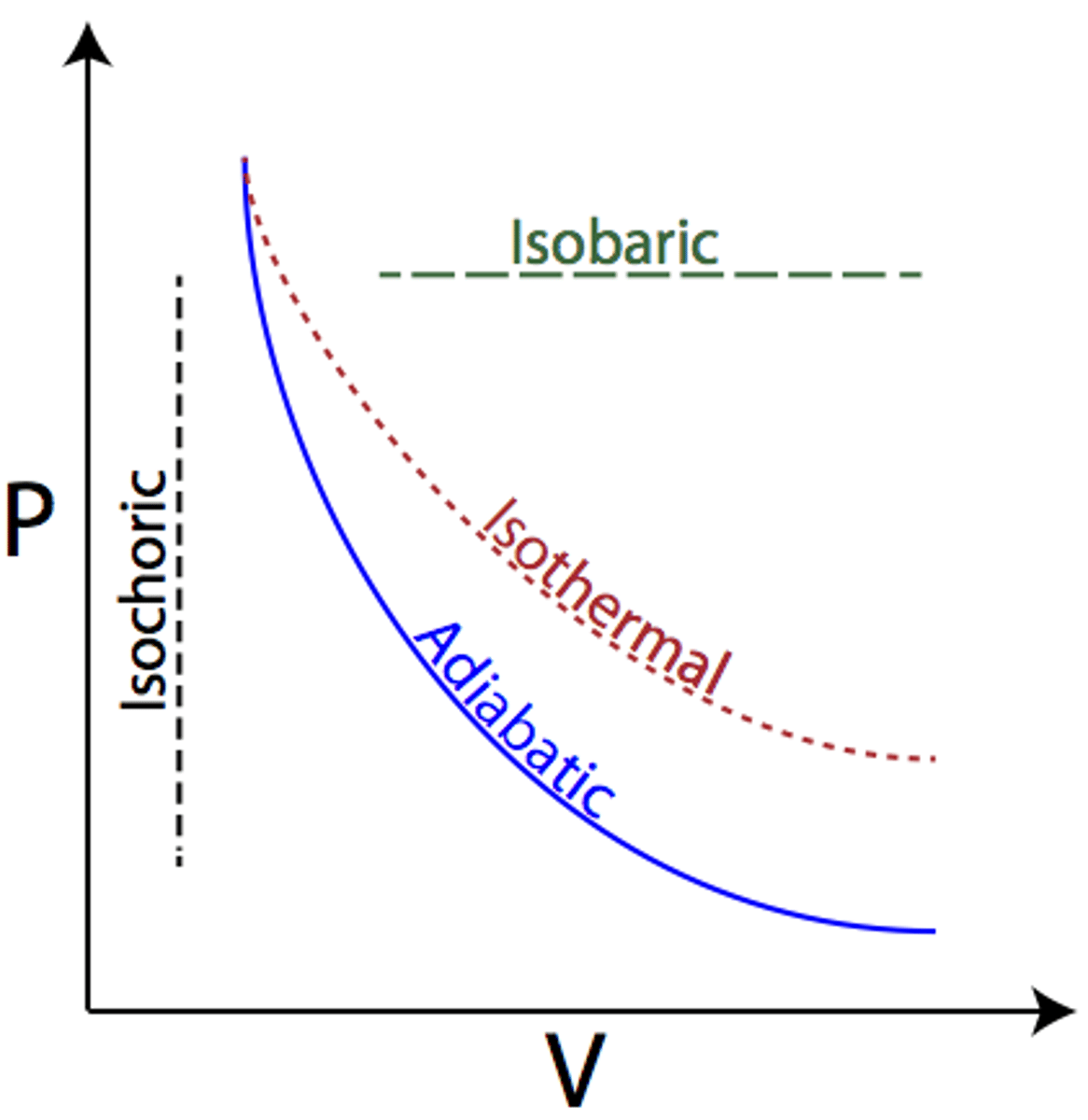
Adiabatic process
A process in which no heat is transferred to or from the system by its surroundings
When Q = 0, the first law simplifies to ΔU = -W (the change in internal energy of the system is equal to work done on the system)
Isobaric process
Occur when pressure of the system is constant. Does not alter the first law of thermodynamics.
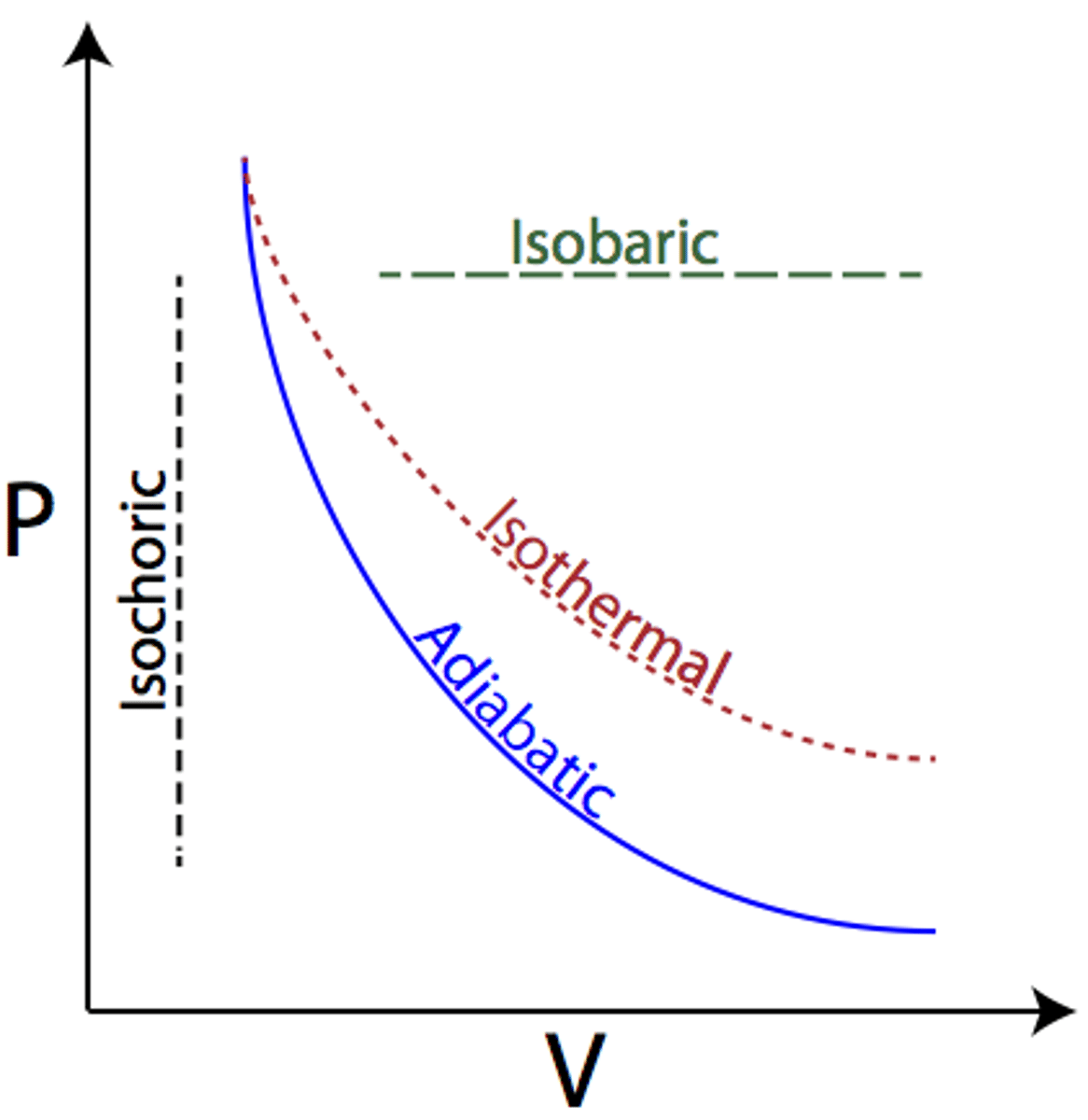
Isochoric (isovolumetric)
A process in which there is no change in volume.
W=0, ΔU=Q
no work done
Spontaneous process
One that can occur without having to be driven by energy from outside source.
coupling
A common method for supplying energy for nonspontaneous reactions is by ___________ nonspontaneous reactions to spontaneous ones
State functions
Describe the system in an equilibrium state.
Path independent- depend only on the current state of the system not how it got there
When I am under Pressure and feeling Dense, all I want to do is watch TV and get HUGS.
Pressure (P), density (p), temperature (T), volume (V), enthalpy (H), internal energy (U), Gibbs free energy (G), and entropy (S).
Entropy Equation
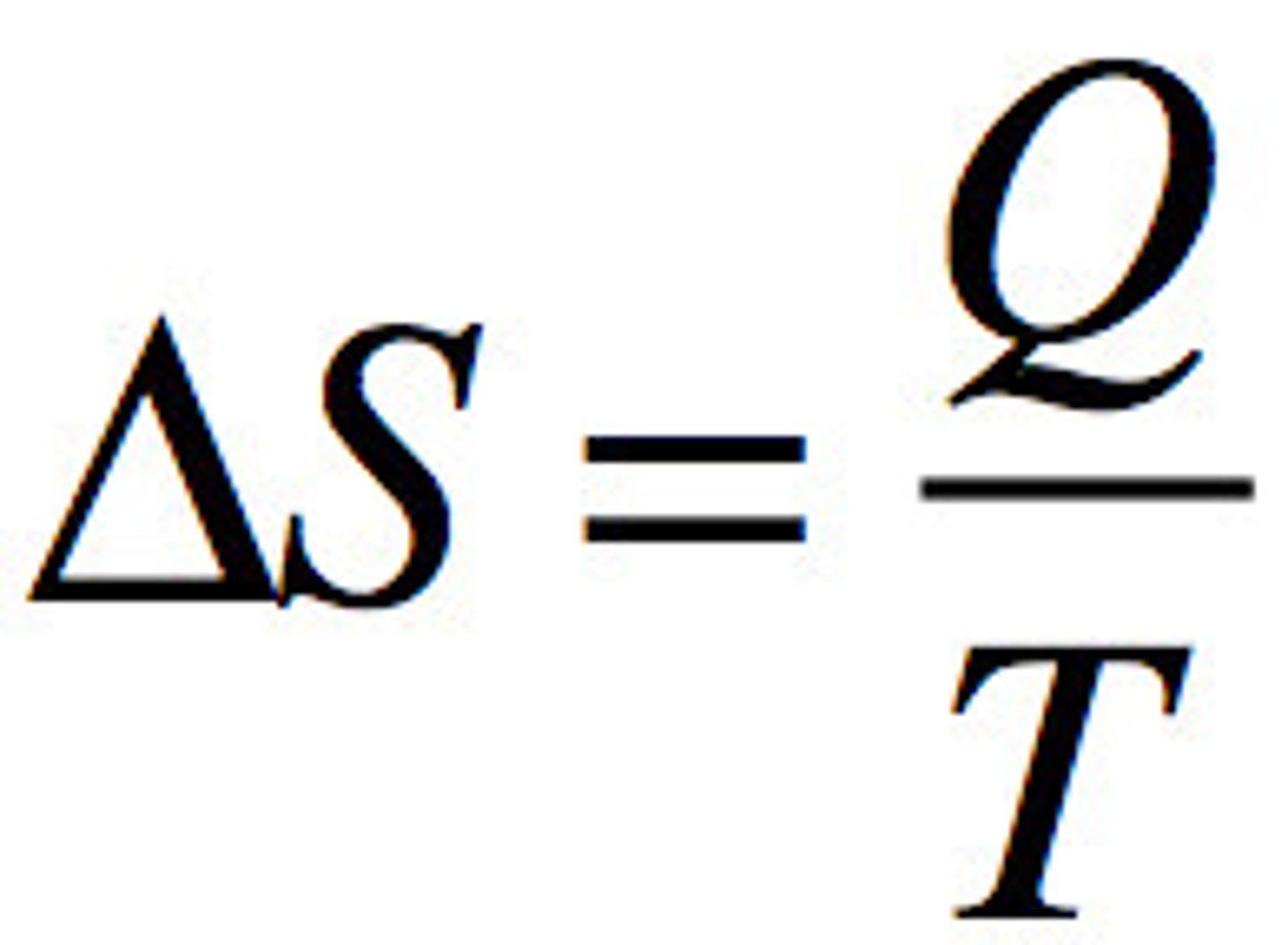
What are standard conditions? and what should it not be confused with
Standard conditions are simply a set of agreed-upon reference values for temperature, pressure, and concentration.
The standard conditions defined for measuring the enthalpy, entropy, and Gibbs free energy of a reaction.
25 C (298 K), 1 atm pressure, and 1 M concentration.
don't confuse this with STP which is used in gas law calculations: at STP temp is 273k and pressure is 1atm
Standard state of a substance
The most stable state a substance can exist in at standard conditions.
For example, H2 (g), H20 (l), O2 (g), NaCl (s), C(s)
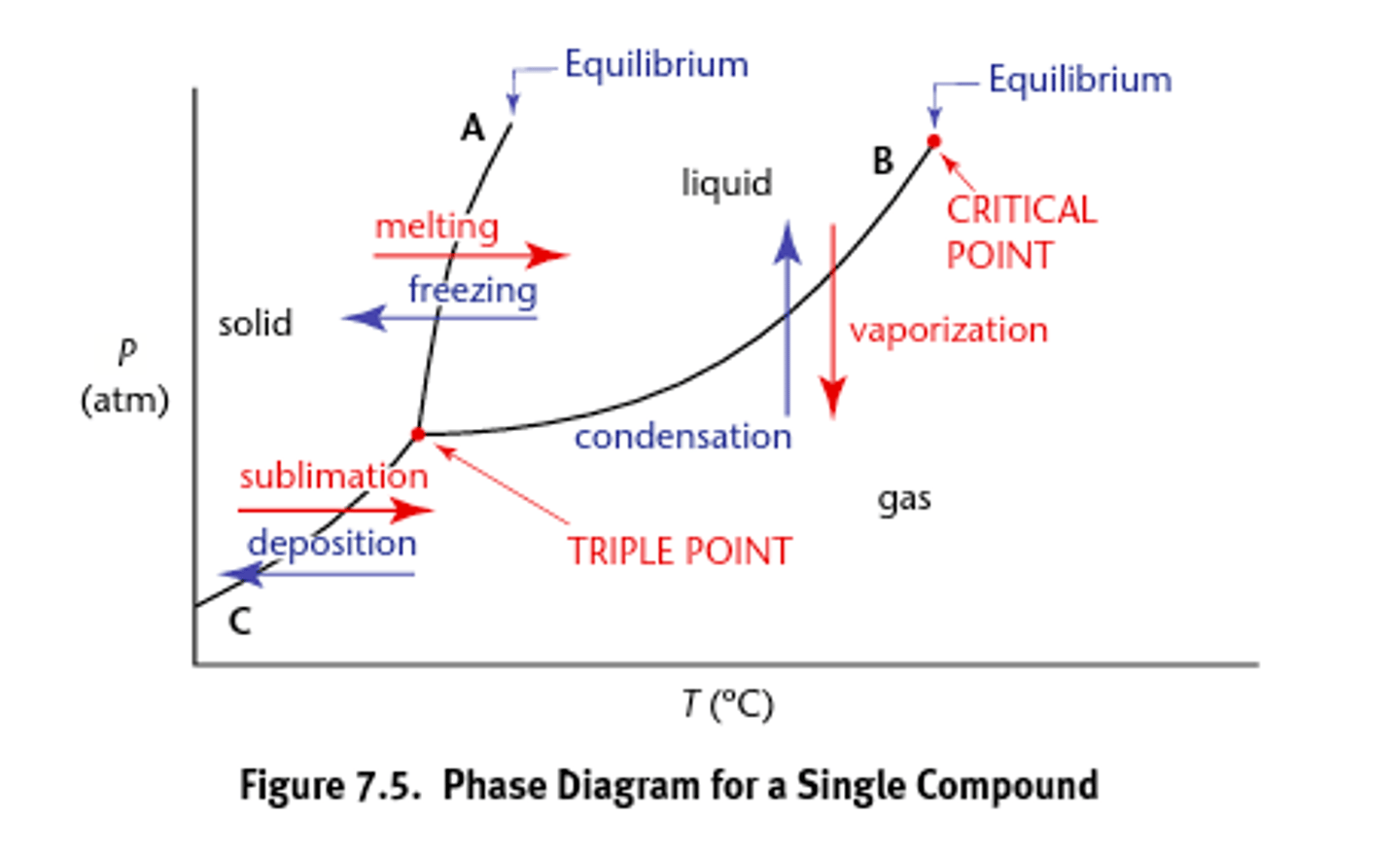
Phase diagrams
draw and label each phase and each point of importance
Graphs the phase equilibria as a function of temperature and pressure for a system.
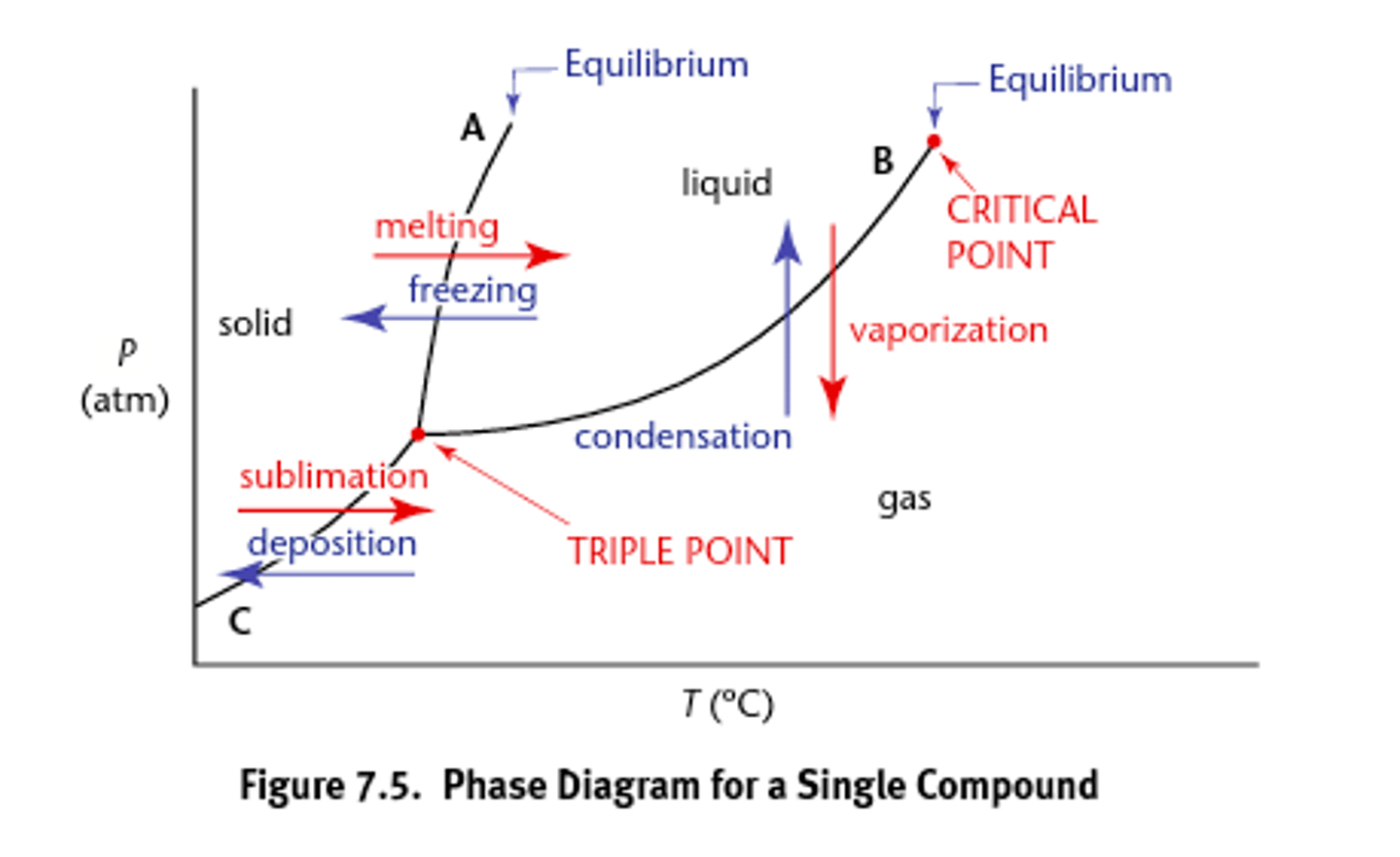
Phase changes (types)
Exist as characteristic temperature and pressures (they are reversible):
1) Fusion (melting) and freezing (crystallization and solidification)
2) Vaporization (evaporation or boiling) and condensation
3) Sublimation or deposition occur at the boundary between the solid and gas phase.
evaporation (vaporization)
A transformation from a liquid to a gas
-ex: boiling (happens when a liquid is heated to become a gas at its boiling point)
condensation
Gas to liquid
- lower temperature and higher pressure
melting (fusion)
solid to liquid
freezing (crystallization or solidification)
liquid to solid
sublimation
solid to gas
depositon
gas to solid
Critical point
what to note about it
what is it called here
draw phase diagram labeling x and y axis
The temperature and pressure at which the gas and liquid states of a substance become identical and form one phase
supercritical fluid
- heat of vaporization at this point and all temps and pressures above this point is zero
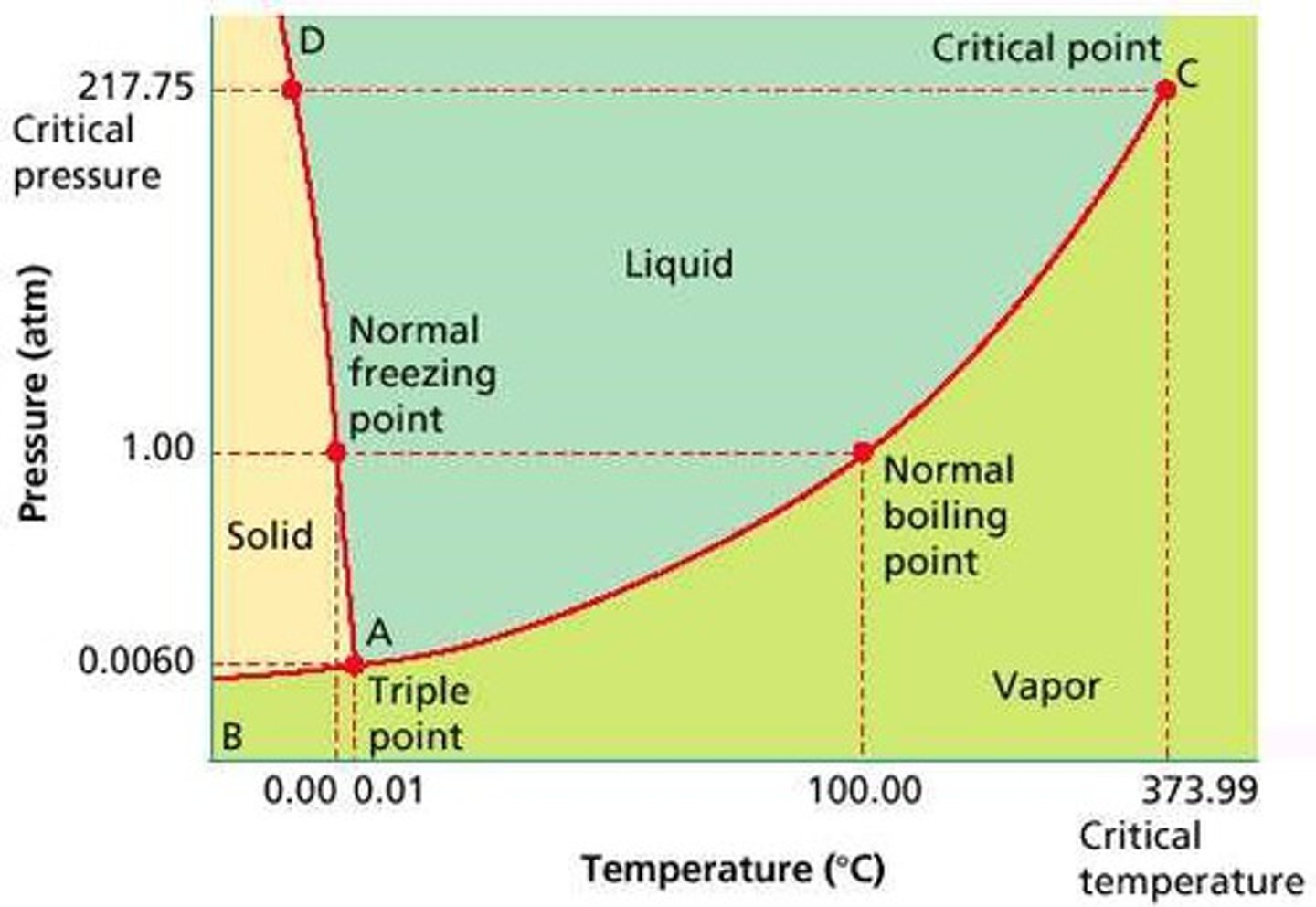
Triple point
The point where all three phases of matter exist in equilibrium.
Heat
The transfer of energy that results from differences of temperature between two substances.
Temperature
The scaled measure of the average kinetic energy of a substance. (how hot or cold something is)
Heat vs Temperature
Heat is a specific form of energy that can enter or leave a system. (process function)
Temperature is a measure of the kinetic energy of the particles in a system.
Zeroth law of thermodynamics- 2 definitions
objects are in thermal equilibrium only when their temperatures are equal
if two thermodynamic systems are both in thermal equilibrium with a third system, then the two systems are in thermal equilibrium with each other
endothermic
Absorbs heat (ΔQ>0)
exothermic
Releases heat (ΔQ<0)
what is the unit of heat
Enthalpy (ΔH)
what happens when substances of different temperatures are brought into thermal contact- meaning that there is a physical arrangement allowing for heat transfer
unit of energy called the joule. one joule us equal to 4.184 cal
The heat content, Q, of a system at constant pressure
energy will move from warmer to cooler substance

Calorimetry
The precise measurement transferred heat
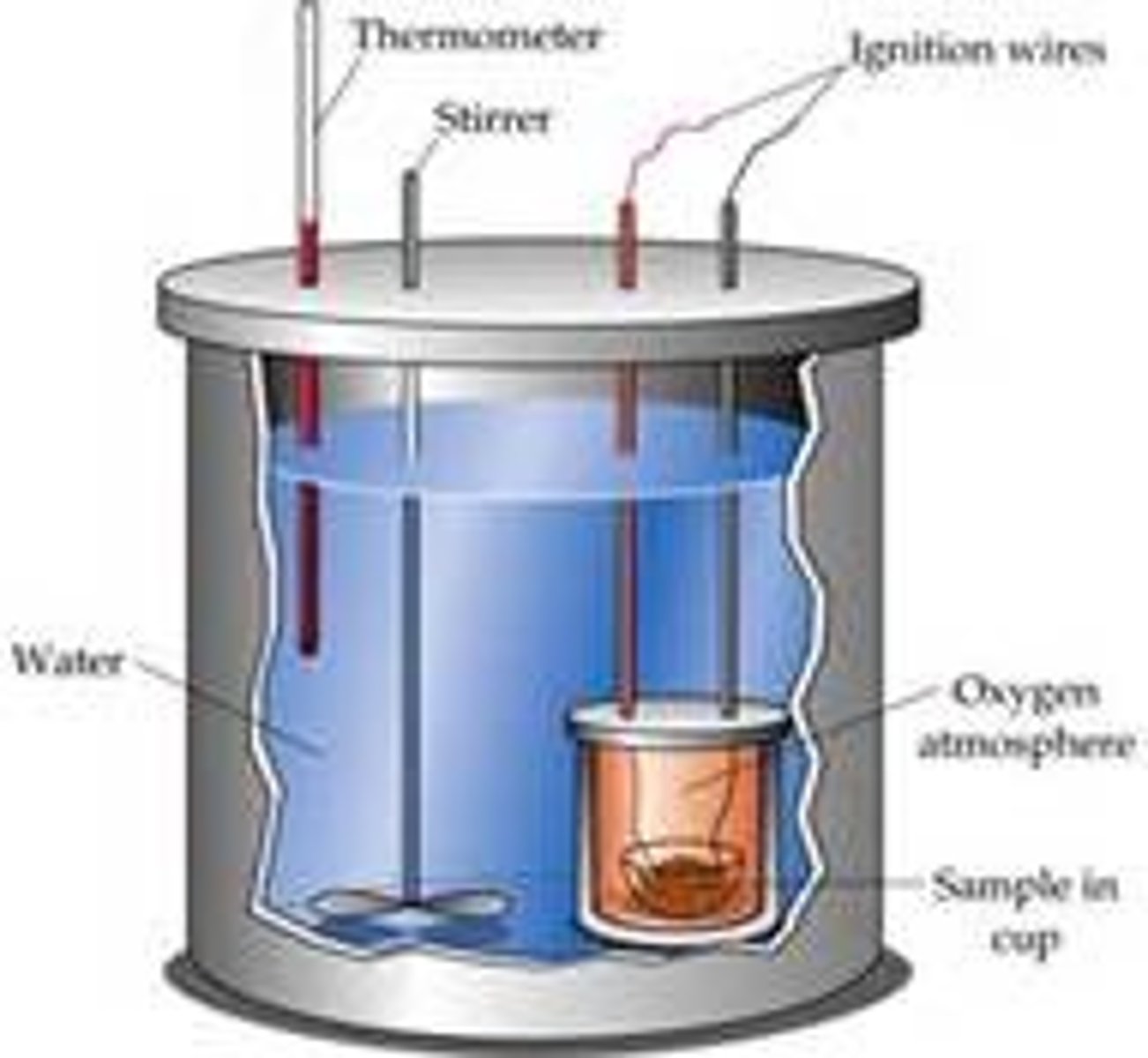
constant pressure calorimeter
Insulated container covered with a lid and filled up with a solution in which a reaction or some physical process (such as dissolving) is occurring.
Equation of heat transfer-no phase change
q=mcAT, where m=mass, c=specific heat, T = change in temp.
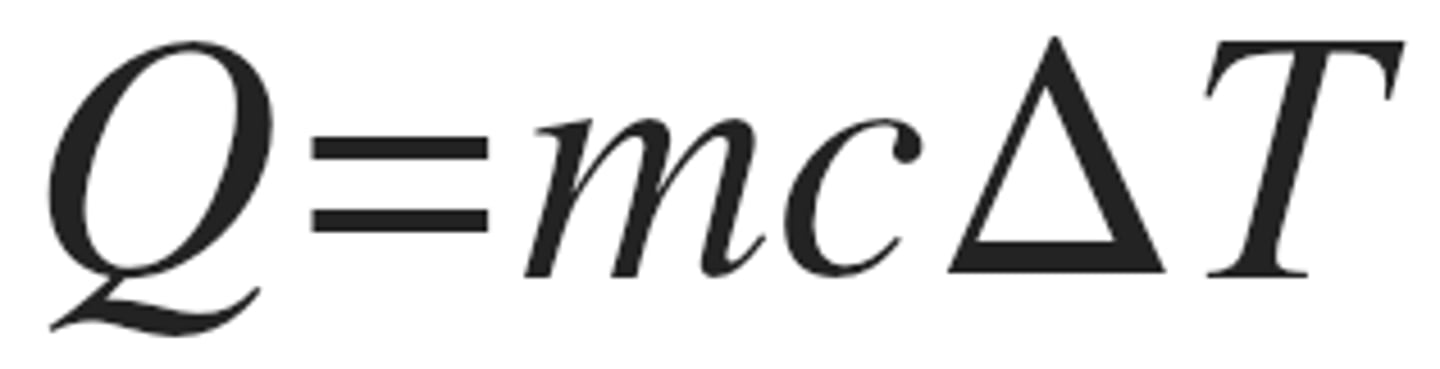
Specific heat and heat capacity
what does heat capacity mean
the amount of energy required to raise the temperature of one gram of a substance by one degree Celsius (or one degree kelvin).
heat capacity=mc

bomb calorimeter
a device for measuring the heat evolved in the combustion of a substance under constant-volume conditions
constant volume calorimetry
the measurement of heat at a constant volume to find the change in internal energy of the system; requires the use of a "bomb" calorimeter
Draw a heating curve graph
make note about phase change regions
change regions do not undergo changes in temp— at constant temp
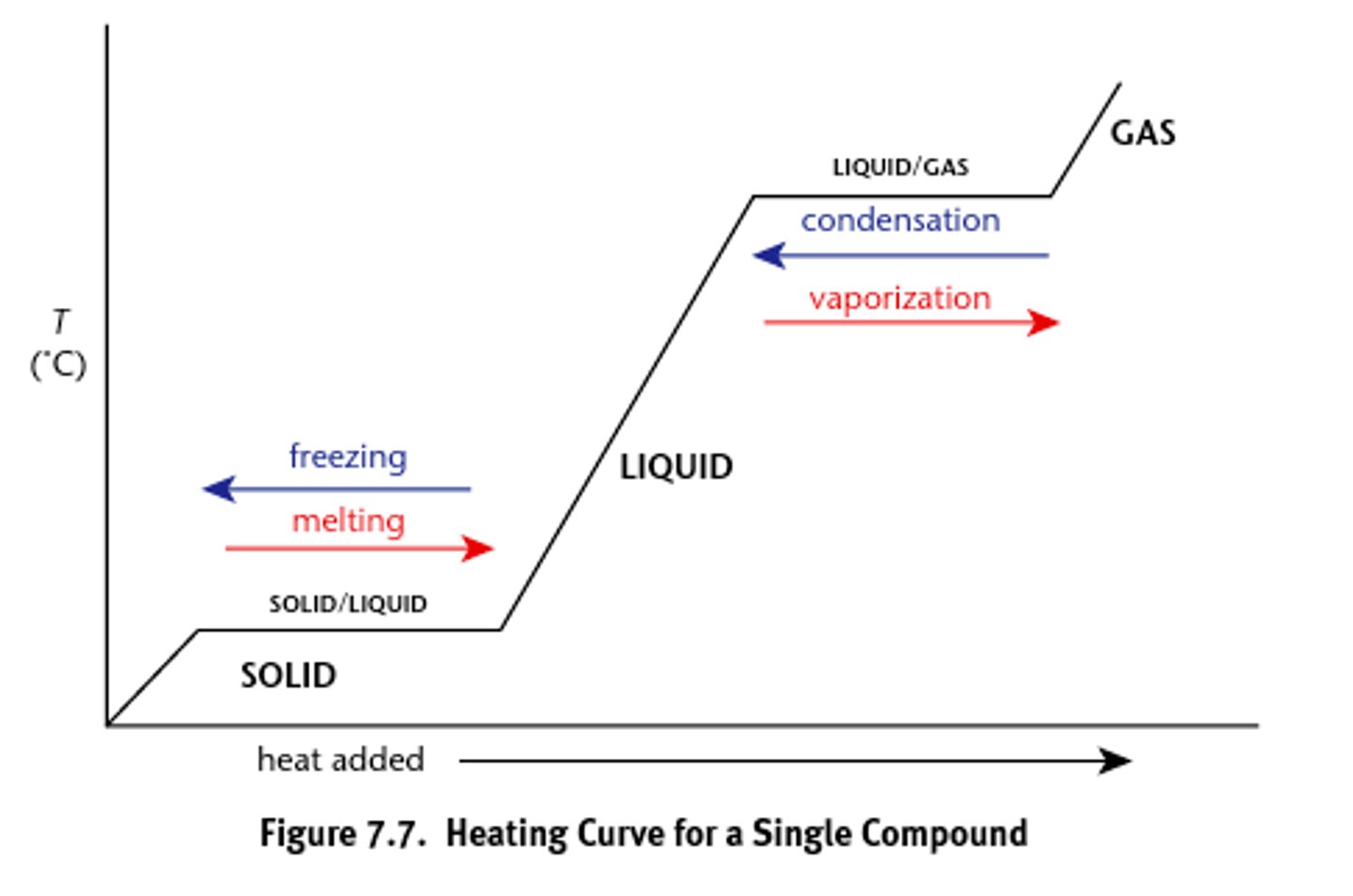
ΔHfus
enthalpy of fusion
- must be used when transitioning at the solid-liquid boundary
ΔHvap
enthalpy of vaporization
-must be used when transitioning at the liquid-gas boundary
Calculating heat transfer (q) during phase changes?
Energy is still required but the change in temperature is 0.
q= internal energy
L = latent heat (enthalpy of isothermal process)
m = mass
cannot use mcdeltaT equation because temperature is constant during a phase chnage— would be erroneous to assume q would be zero
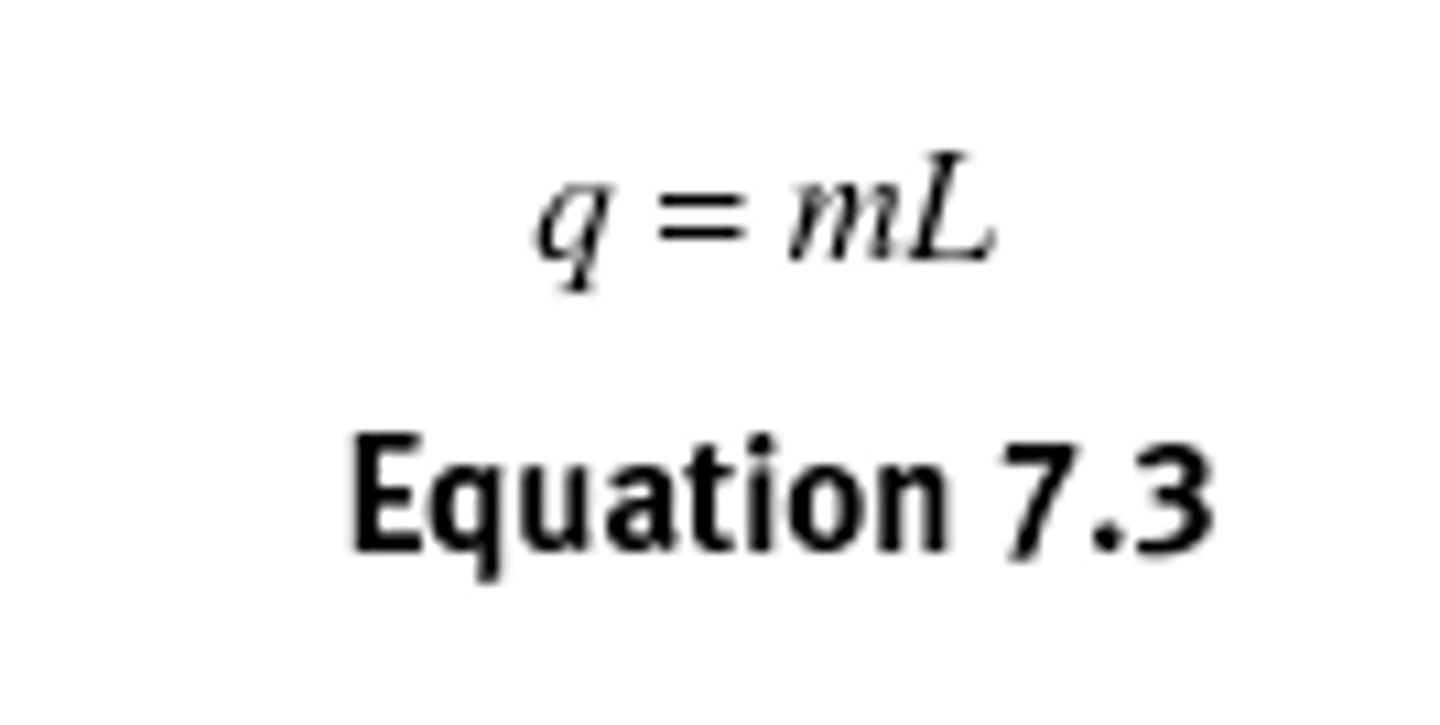
enthalpy
The heat content of a system at constant pressure
Enthalpy change of reaction, ΔHrxn for Endo thermic and exothermic
+ ΔH = endothermic
-ΔH= exothermic
Hess's Law

Standard enthalpy of formation— whats the symbol and definition
enthalpy required to produce one mole of a compound from its elements in their standard states
by definition, ΔHf of an element in its standard state is 0
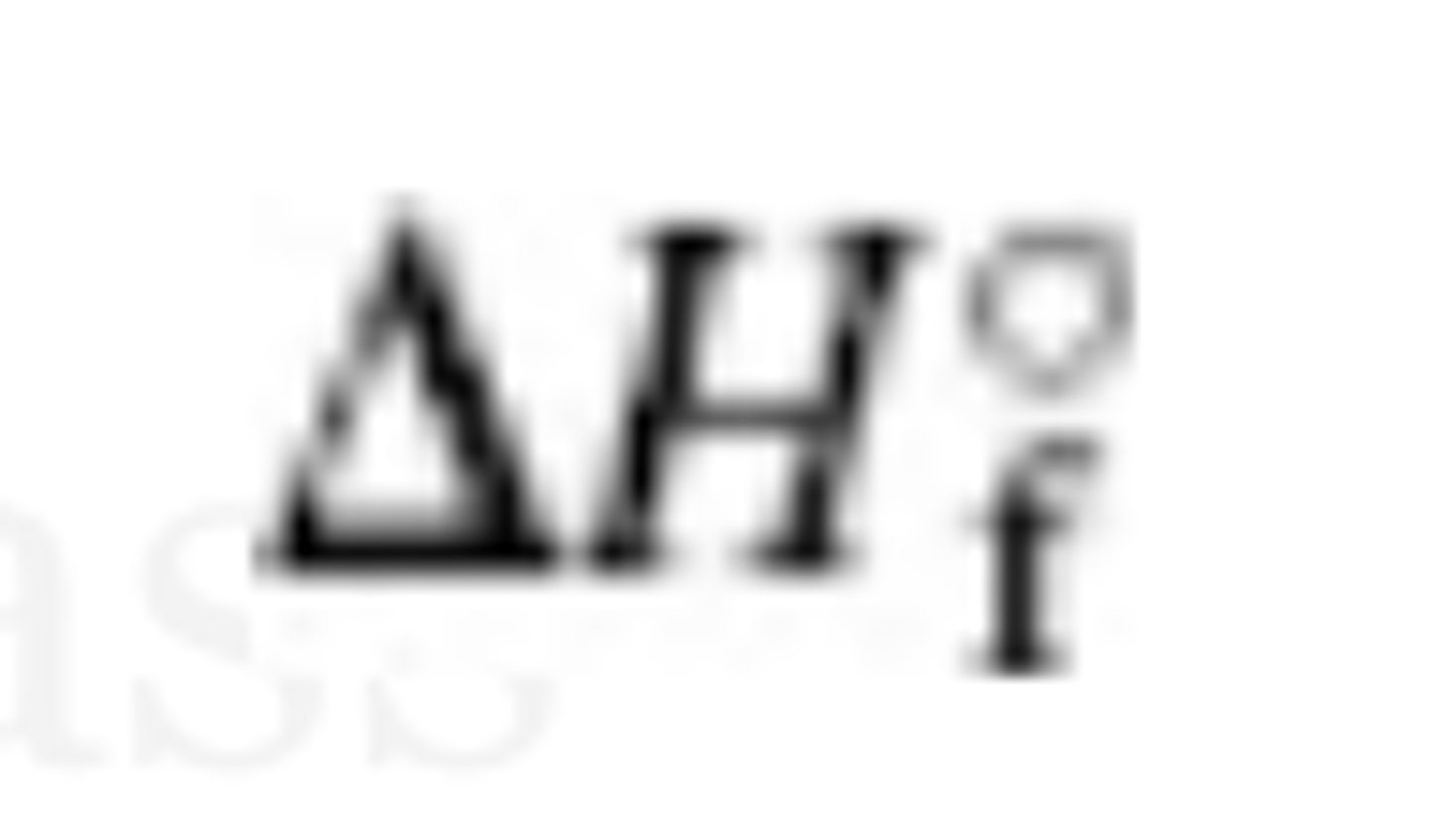
standard heat of a reaction (ΔHrxn) definition and equation
The change in enthalpy of a reaction under standard conditions
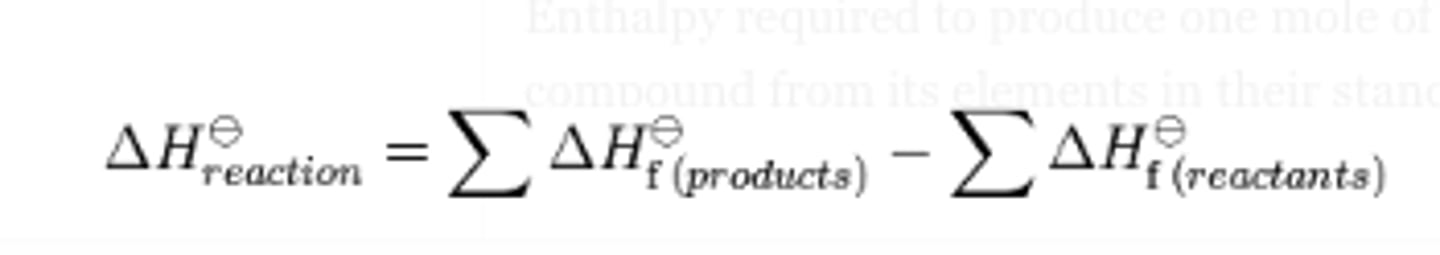
Hess's law
what is it and what does it apply to (practice equations for Hess’s law— how to find overall heat of reaction given multiple equations)
states that enthalpy changes of rxn are additive—- applies to any state function including entropy and Gibb’s free energy
When doing problems, make sure to switch signs when you reverse the equation
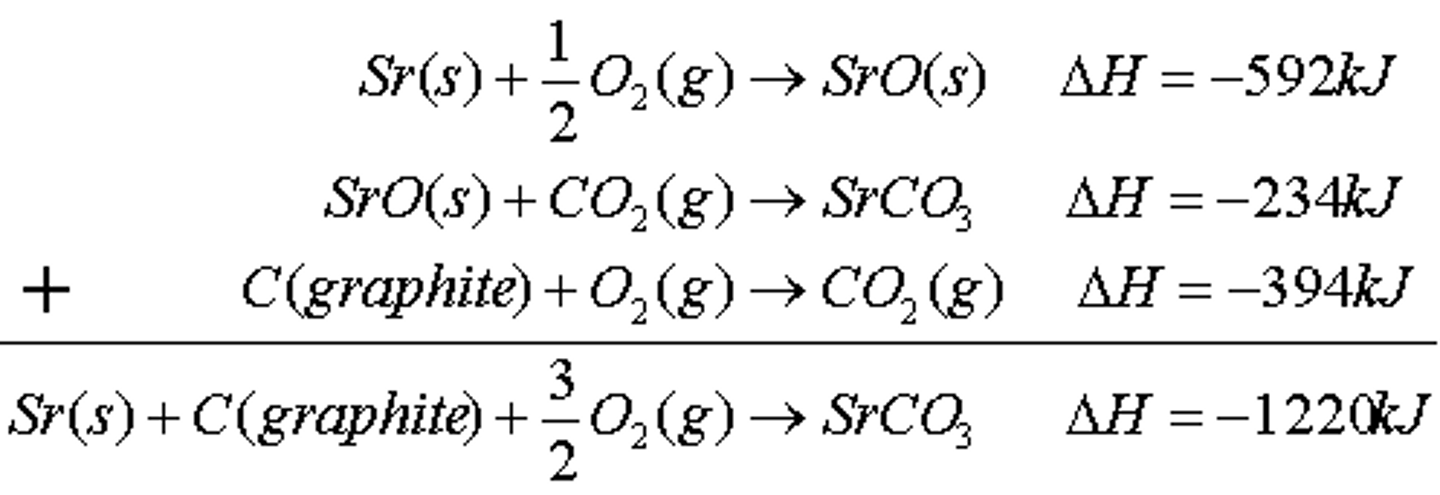
Bond Enthalpy Equation— once again practice using these equations
Energy absorbed-energy released

Bond dissociation energy
what is important to note and use mnenomic device
BARF- broken absorbed, released formed in relation to bond energies
The average energy required to break a particular type of bond between atoms in a gas phase.
formation exothermic, energy release (-)
dissociation endothermic
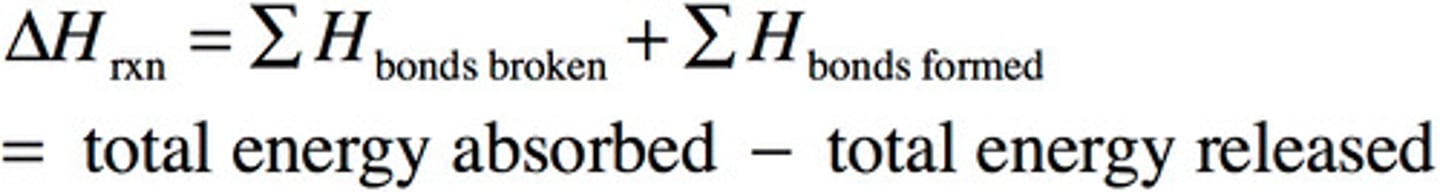
standard heat of combustion— once again, practice using this in equation
ΔH°(comb) is the enthalpy change associated with the combustion of a fuel
most combustion appears in presence of O2 in atmosphere
2nd law of thermodynamics
energy spontaneously disperses from being localized to becoming spread out if it is not hindered
Entropy
definition and equation
a measure of the disorder of a system, measures at a specific temperature
qrev/T where Qrev is the heat that is gained or lost in a reversible process
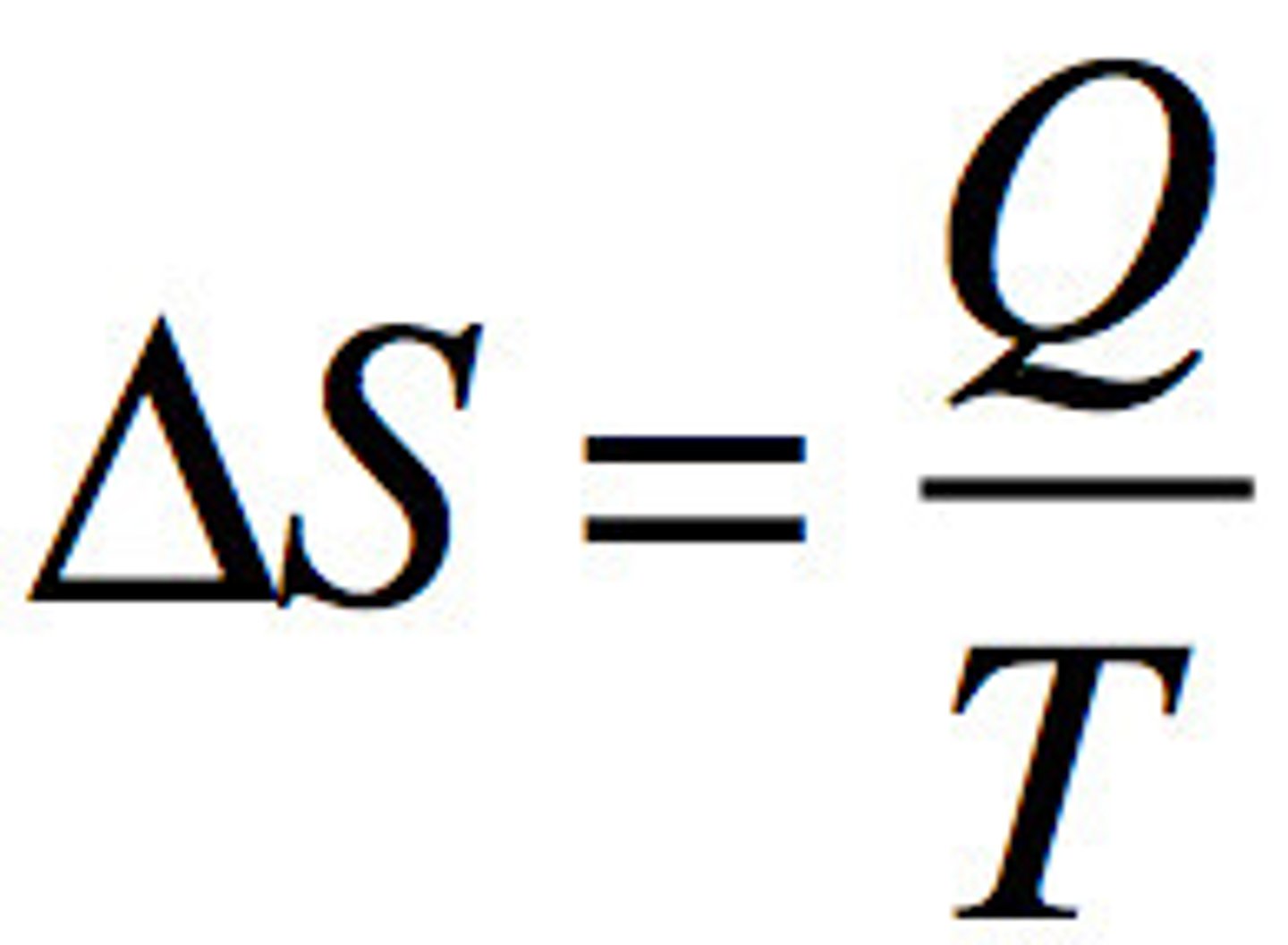
entropy of the universe
meaning and equation
entropy of the universe is always increasing
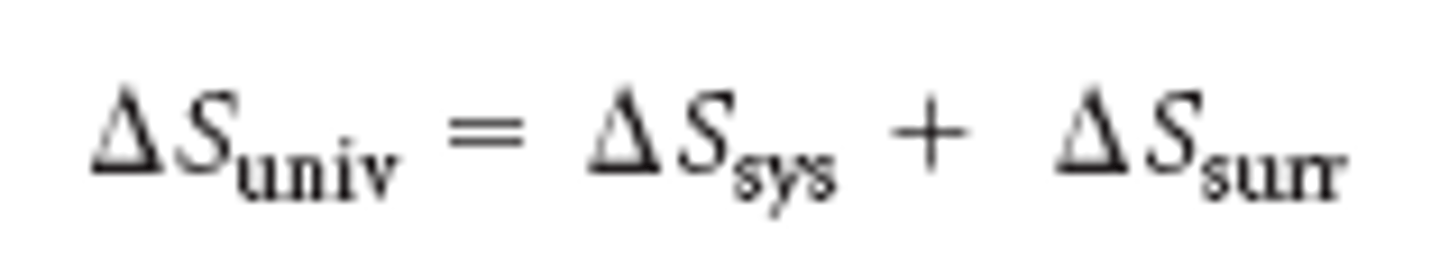
standard entropy change
use Hess’s law

entropy in phases in order from least to most
the amount of entropy increases from solid--> liquid---> gas
Change in Gibbs free energy
Goldfish are Horrible (minus sign) without tarter sauce
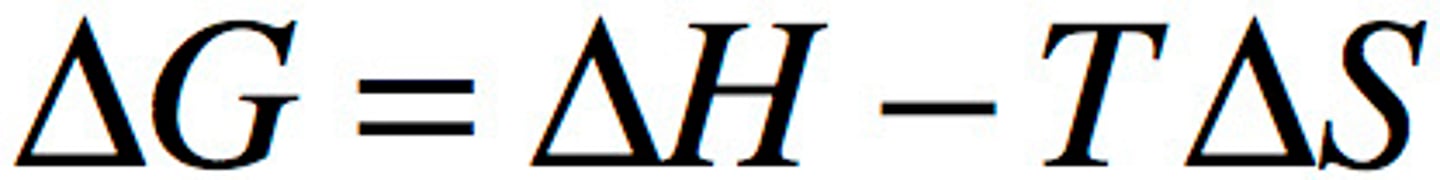
gibbs free energy chart
ΔG is temperature dependent when ΔH and ΔS have the same sign
remember order like HS G— his girlfriend
when the signs are opposite, the third and first sign match, example” -+-
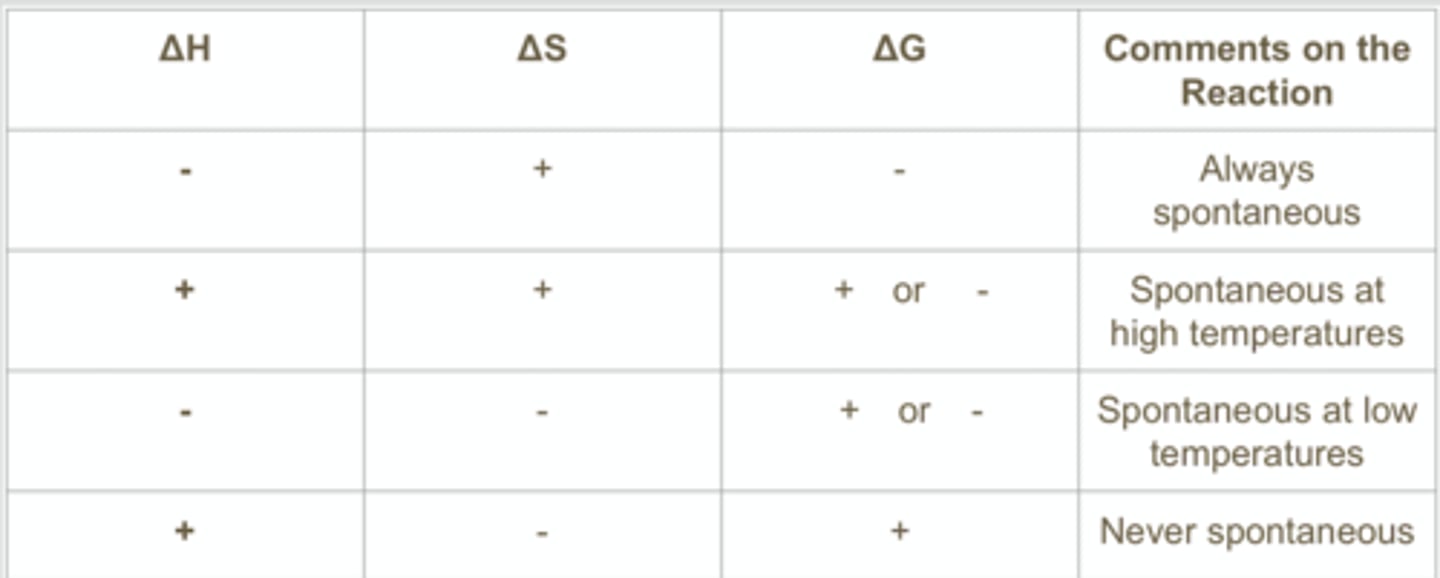
Standard Gibbs free E from eq const
the greater the value of Keq, the more negative the standard free energy change (the more spontaneous the reaction)
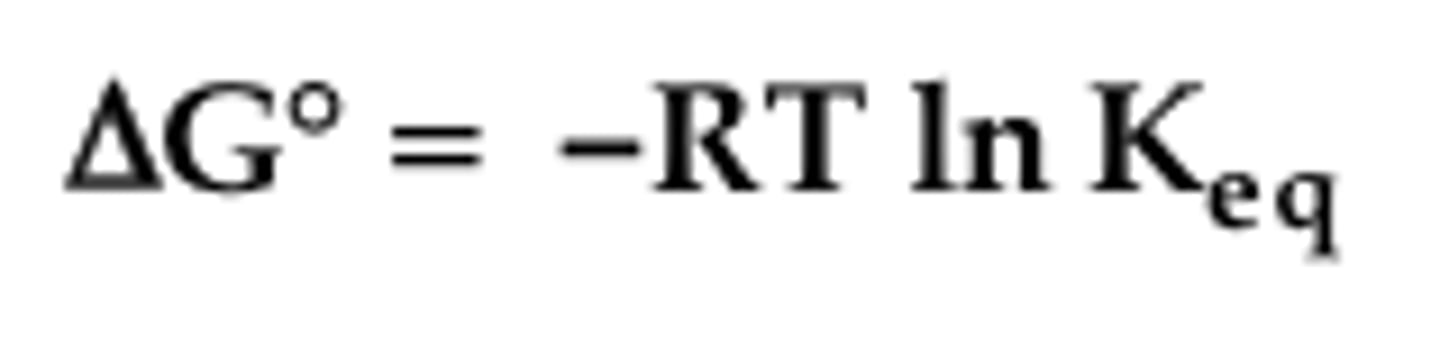
exergonic reaction
A spontaneous chemical reaction in which there is a net release of free energy.
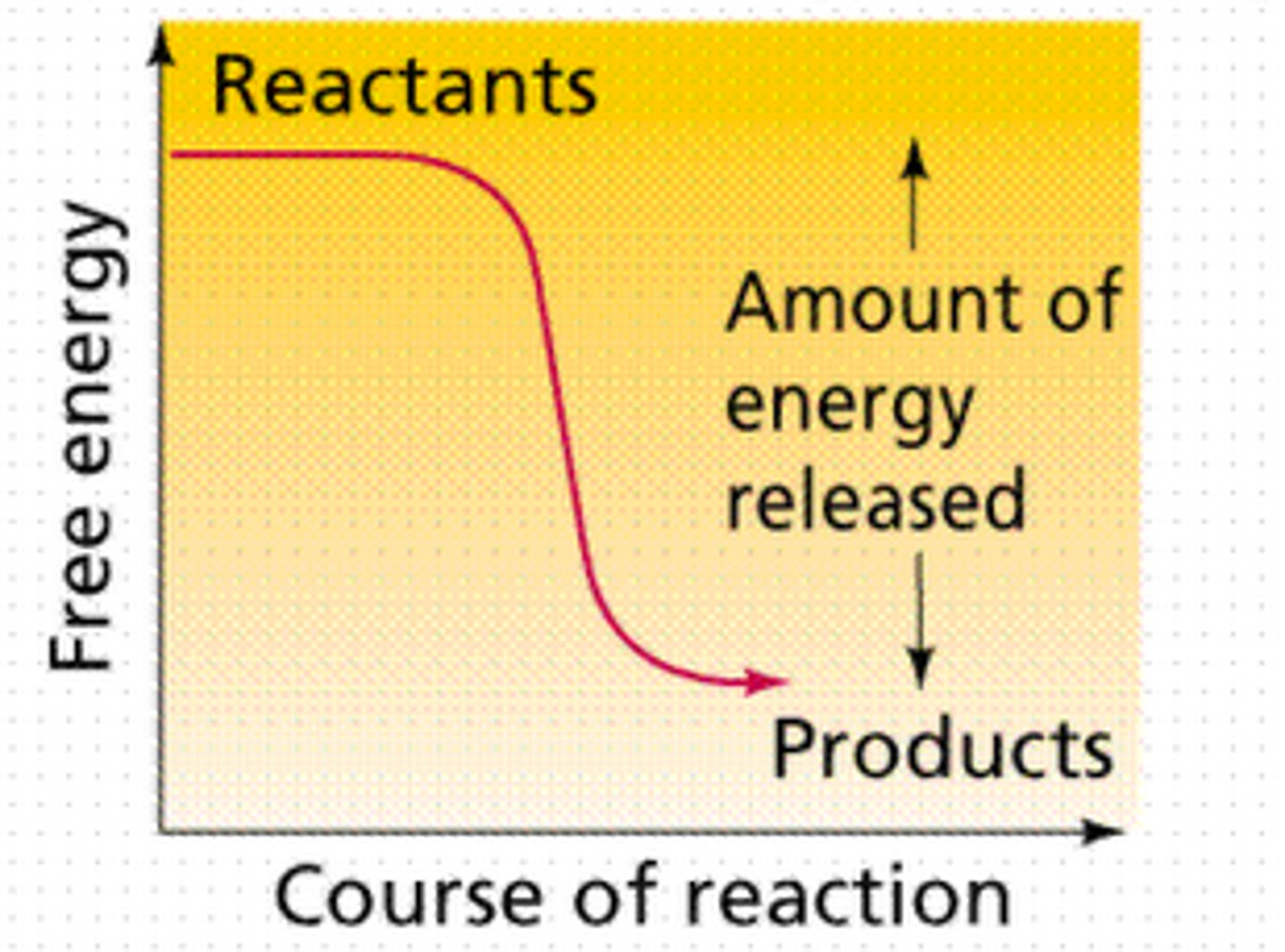
endergonic reaction
Reaction that absorbs free energy from its surroundings. (nonspontaneous)
endergonic/exergonic
endothermic/exothermic
endergonic/exergonic - Gibbs free energy
endothermic/exothermic - enthalpy
Standard Gibbs free energy of reaction
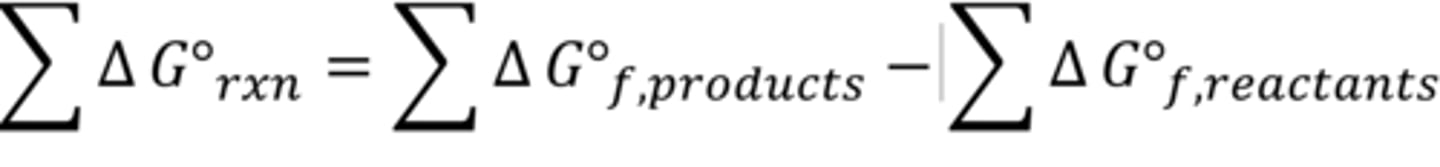
Standard Enthalpy of Reaction

Gibbs free energy from reaction quoteint
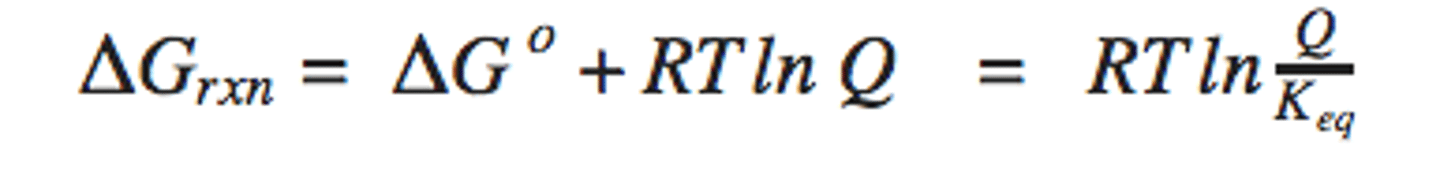
Generalized Enthalpy of Reaction

the _______ the alkane the more numerous the combustion product
the __larger__ the alkane the more numerous the combustion product
thermodynamics vs. kinetics
thermodynamics and kinetics are separate. when a reaction is thermodynamically spontaneous, it has no bearing on how fast it goes. it only means that it will proceed eventually