Bio Chapter 3 Study Guide
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Organic compound
Molecules that primarily contain carbon atoms and usually hydrogen atoms, forming the basis of all known life forms.
Functional group
Groups attached to the carbon and hydrogen framework that give molecules their chemical properties and are involved in chemical reactions.
Monomer
A small molecule that can bind chemically to other similar molecules to form a larger molecule known as a polymer.
Polymer
A large molecule composed of repeating structural units called monomers; examples include carbohydrates, proteins, and nucleic acids.
Carbohydrate
Compounds that serve as fuel and building material, including monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides.
Monosaccharide
The simplest form of carbohydrates that serve as fuel and building material in biological systems; they are simple sugars.
Glycogen
A polysaccharide that serves as the nutrient storage form of carbohydrates in animals. It is composed of many monosaccharides joined together.
Disaccharide
A type of carbohydrate formed when two monosaccharides are joined together by a glycosidic linkage.
Polysaccharide
Complex carbohydrates formed by the linkage of multiple monosaccharides, serving functions like energy storage and structural support. They serve various functions in living organisms, including energy storage and structural support.
Complex carbohydrate
Polysaccharides, which are long chains of monosaccharides linked together, such as starch, glycogen, cellulose, and chitin.
Give an example of a sugar.
Consists of monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides.
Relationship between sugar, obesity, and type II diabetes
Excessive consumption of sugars, particularly high-fructose corn syrup, can lead to obesity, which is a significant risk factor for developing type II diabetes. The body's ability to manage blood sugar levels becomes impaired, leading to insulin resistance and diabetes.
Monosaccharides as sugars
Monosaccharides are considered sugars and are the simplest form of carbohydrates consisting of single sugar molecules. They consist of single sugar molecules and have molecular formulas that are multiples of the unit CH2O.
Are polysaccharides considered sugars, or complex carbohydrates?
Polysaccharides are complex carbohydrates, not simple sugars, composed of many monosaccharides linked together.
Starch
A carbohydrate that serves as the nutrient storage form in plants, composed of many monosaccharides (forming a polysaccharide).
Chitin
A tough carbohydrate that forms the external skeleton of arthropods.
Cellulose
A rigid, structural carbohydrate found in the cell walls of plants, also known as fiber.
Lipid
A group of hydrophobic compounds that do not mix with water, generally considered not large enough to be macromolecules.
Fat
Constructed from glycerol and three fatty acid molecules, formed by a dehydration reaction creating an ester linkage.
Saturated fats
Fats with no double bonds between carbon atoms in their hydrocarbon chains, which means they are "saturated" with hydrogen atoms. They are solid at room temperature. Examples: Butter, bacon, cheese, milk, and coconut oil.
Unsaturated fats
Unsaturated fats have one or more double bonds in their hydrocarbon chains, which creates "kinks" in the molecule. These are liquid at room temperature. Examples: Olive oil, canola oil, and fish oil. These fats are healthier than saturated fats and can improve cholesterol levels.
Trans fats
A type of unsaturated fat that is created industrially by adding hydrogen to liquid vegetable oils, making them more solid.
Hydrogenation
A chemical reaction where hydrogen is added to an unsaturated compound, typically involving double or triple bonds, to make it saturated. This process is commonly used to create trans fats.
Steroids
A class of lipids with a carbon skeleton made of four fused rings; function as hormones and are crucial for physiological processes.
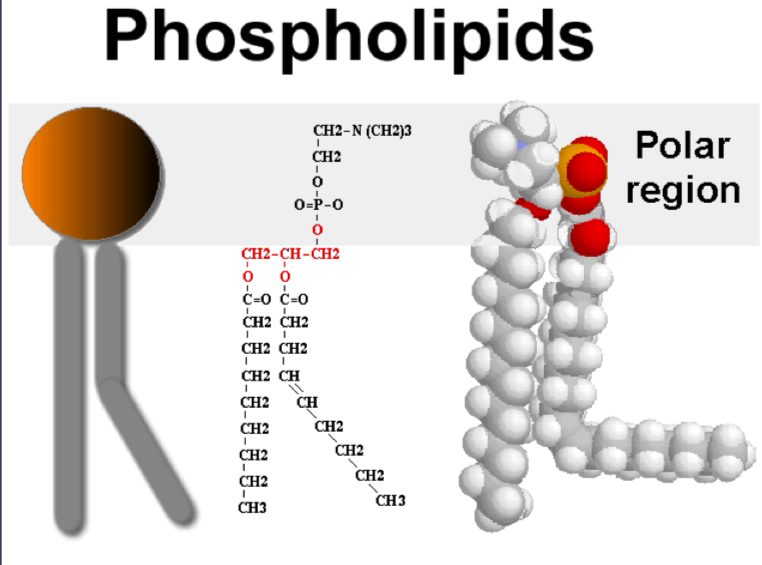
Phospholipid
A major component of cell membranes, consisting of two fatty acids, a glycerol unit, and a phosphate group. They make up cell membranes.
Protein
A biological molecule composed of one or more polypeptides made from 20 different amino acids.
Amino acid
Molecules containing both an amino group and a carboxyl group, linked to form polypeptide chains.
Nucleic acid
Polymers of nucleotides essential for all known forms of life.
Nucleotide
The fundamental building block of nucleic acids, such as DNA and RNA.
Types of nucleic acids
Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA): consists of two strands of nucleotides linked by hydrogen bonds. The rungs consist of bases hydrogen-bonded together, and the outer "rails" of the double helix are composed of sugar and phosphate components of the molecule.
Ribonucleic Acid (RNA): composed of nucleotides that include a nitrogenous base, a sugar, and a phosphate group. RNA uses ribose as its sugar, whereas DNA uses deoxyribose.
Waxes
A type of lipid composed of a single fatty acid linked to a long-chain alcohol, important for sealing functions in living organisms.