05.F BIO, C1 The Calvin Cycle (PART F)
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
Light Independent Reaction
Reactions that do not require light that occur in the stroma of the chloroplast; also referred to as the Calvin cycle after the scientists who identified the reactions
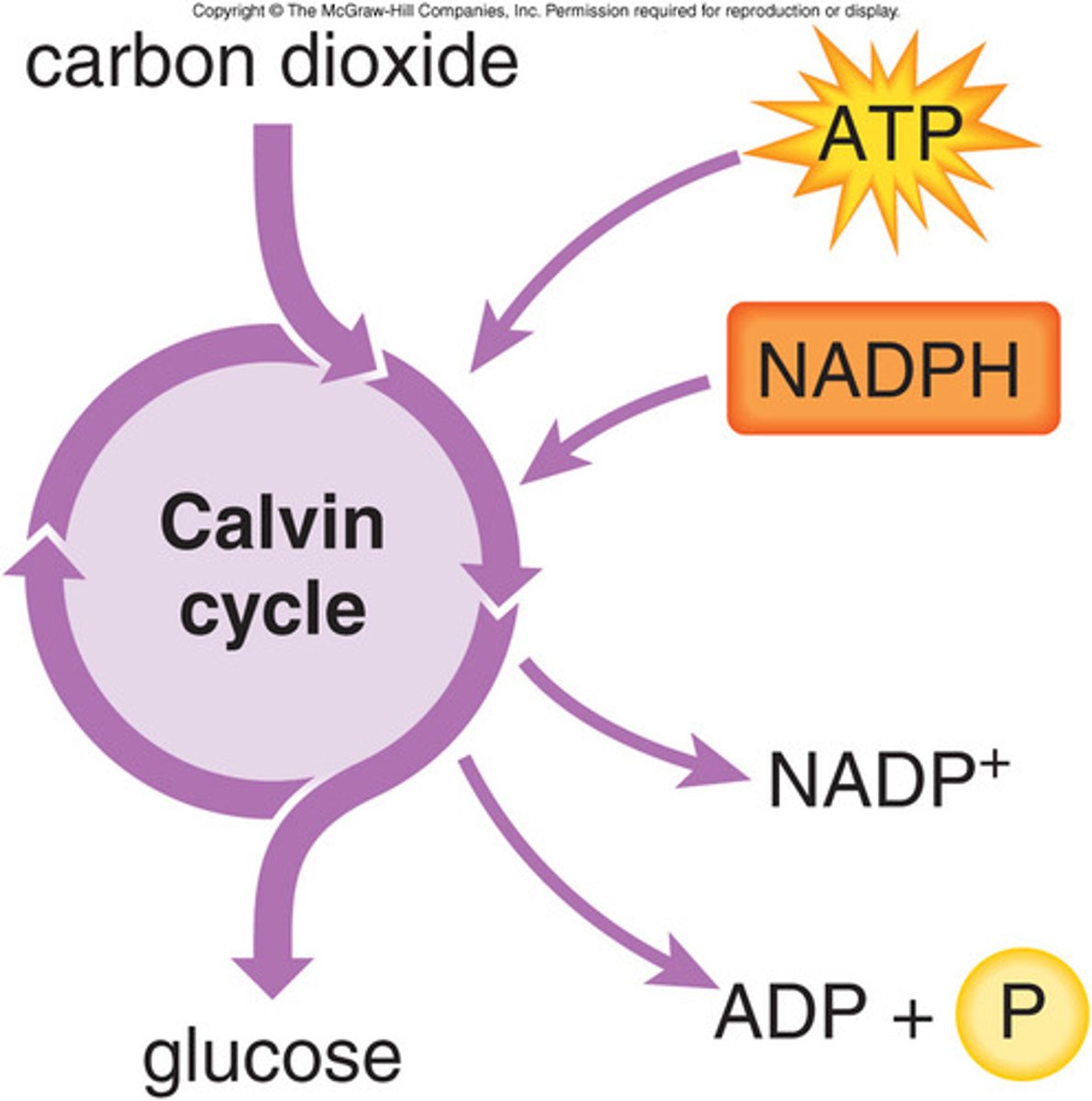
Calvin Cycle
Also known as the light independent reactions; occurs in the stroma of the chloroplast; the cycle builds sugar from CO2 and a five carbon sugar called RuBP by using ATP and NADPH; this is a cycle because the starting material (RuBP) is regenerated
The Calvin Cycle (Reactants)
5-carbon sugar, CO2, ATP and NADPH
The Calvin Cycle (Products)
Glucose, ADP, phosphate, NADP+ and 5-carbon sugar
5-Carbon Sugar (starting the cycle)
The starting material in the Calvin Cycle; combines with carbon dioxide to produce an unstable 6-carbon molecule
5-Carbon Sugar (regenerated at end of cycle)
Produced when ATP is used to rearrange a 3-carbon molecule to regenerate the same 5-carbon molecule that starts the cycle
Carbon dioxide (CO2)
Atmospheric gas that is taken up by plants through the stomata and used to make sugars during photosynthesis
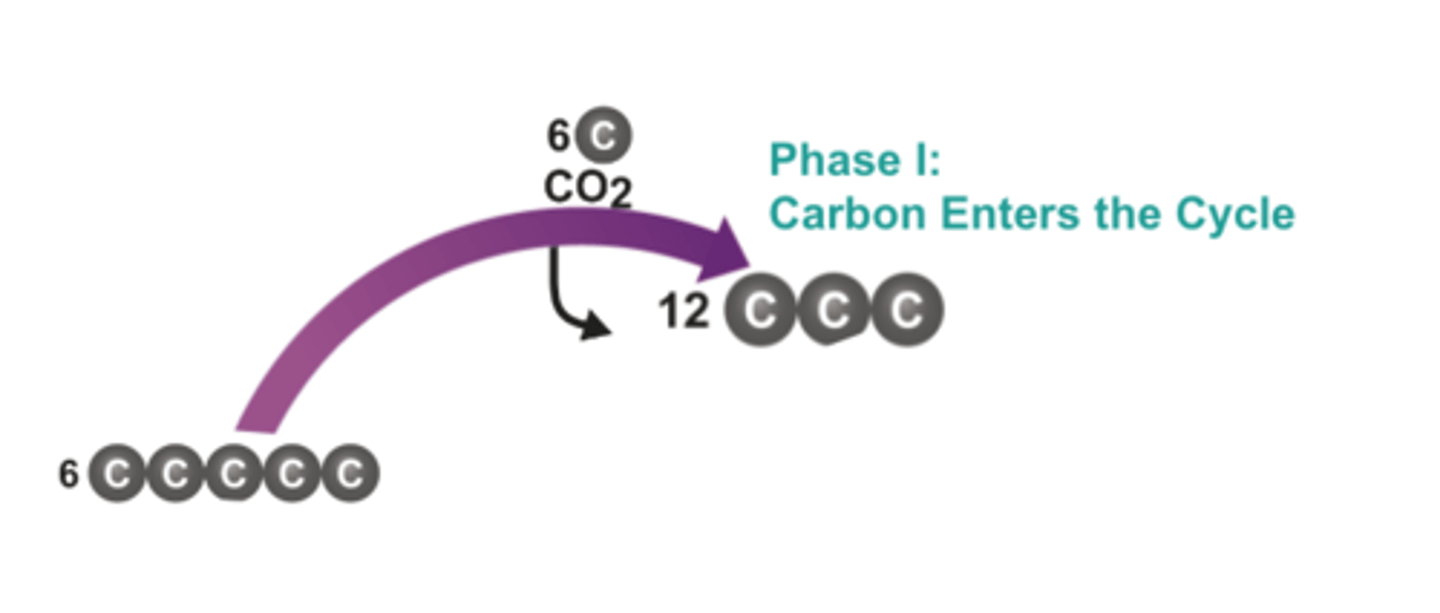
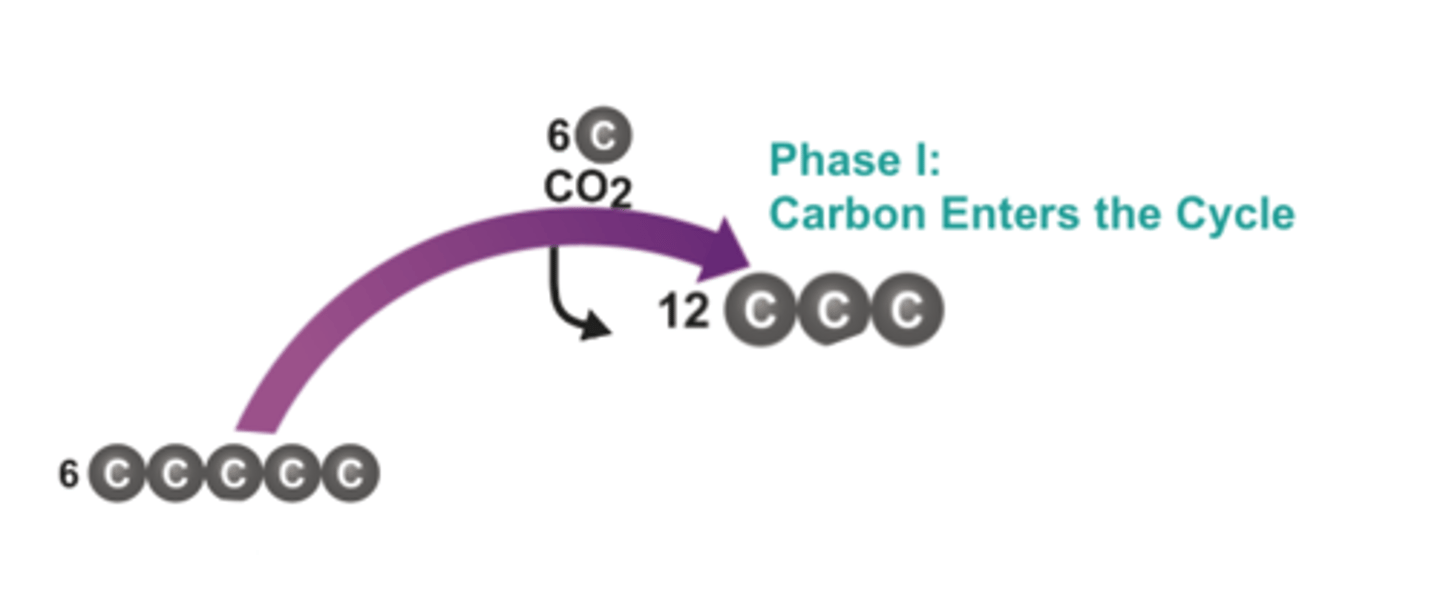
3-Carbon Sugar
Formed in the second phase of the Calvin cycle; can leave the cycle and be used to make glucose and other organic compounds
Calvin Cycle (Four Phases)
Carbon Fixation
Energy Input
6-Carbon Sugar Produced
5-Carbon Molecule Regenerated
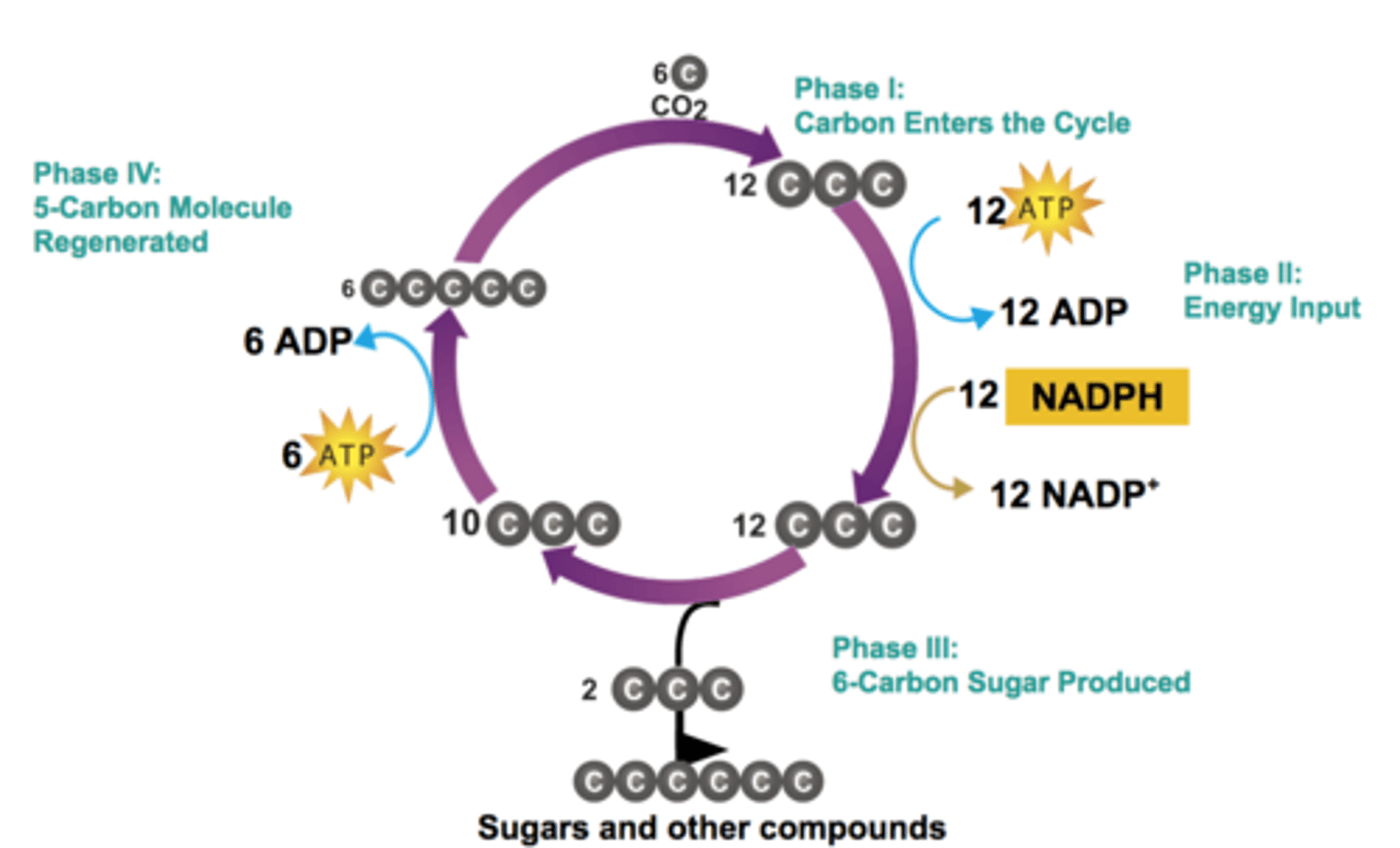
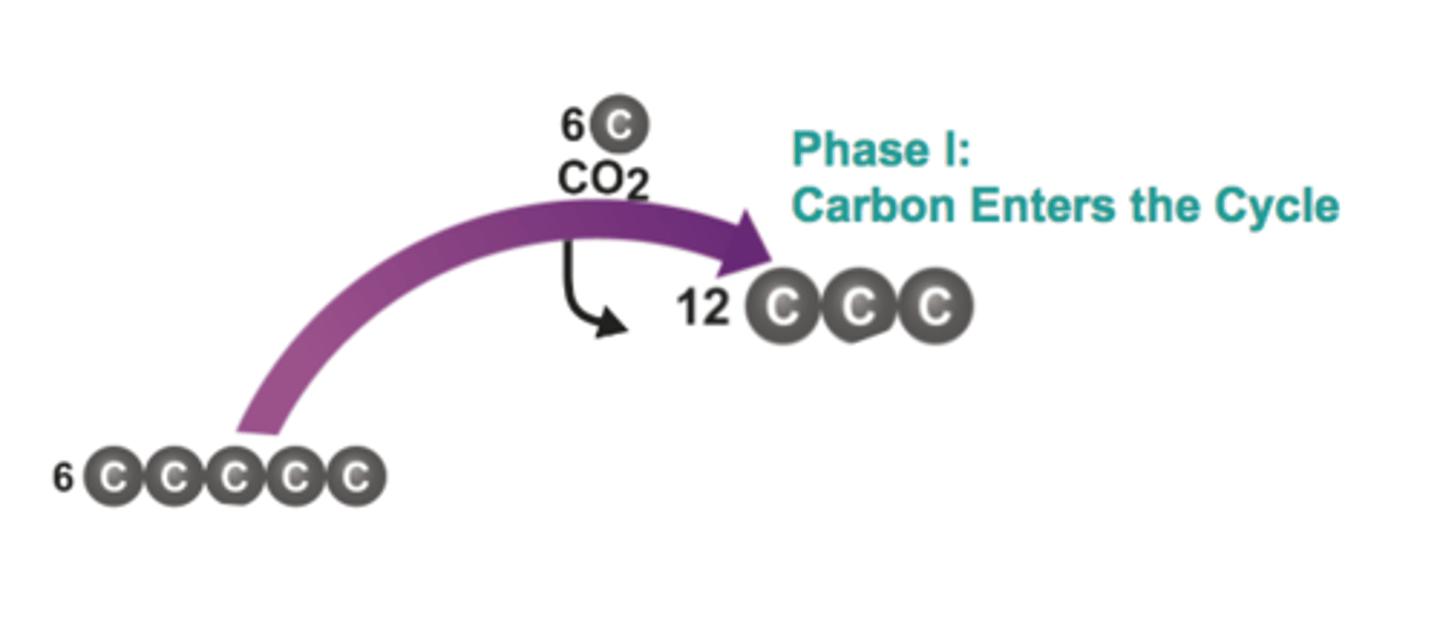
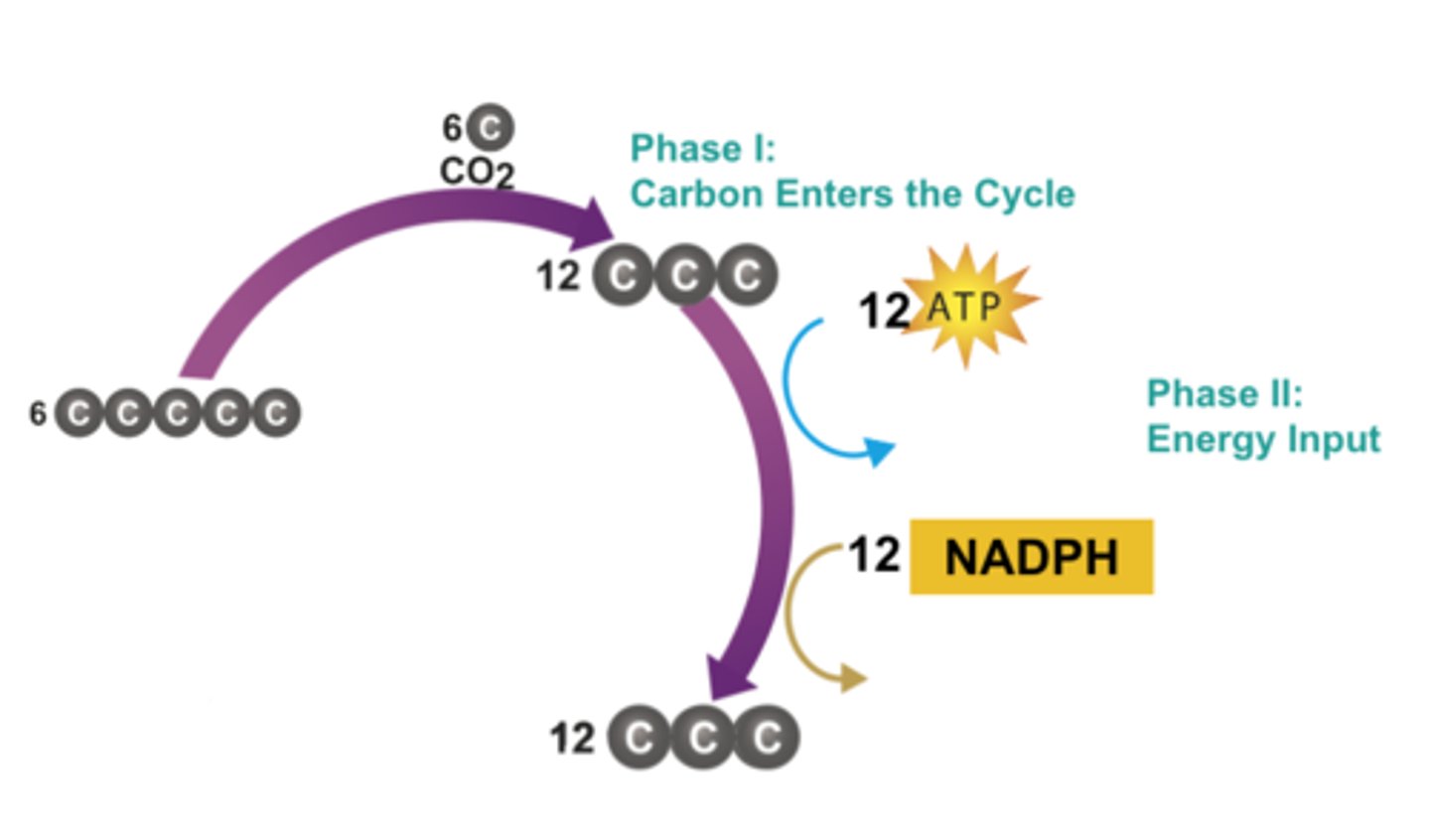
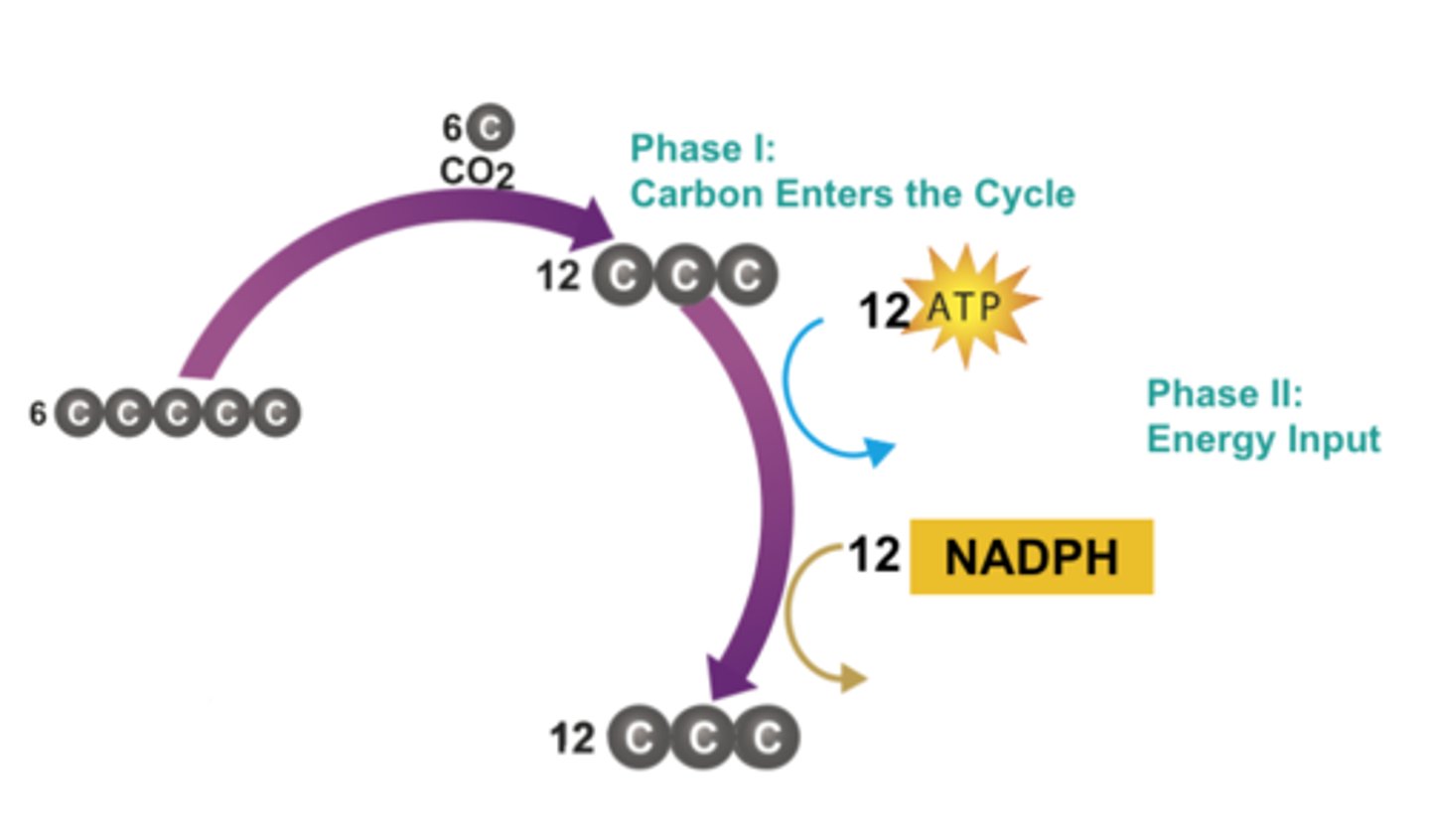
Phase I - Carbon Fixation
The process by which CO2 is used to produce organic compounds
Phase II - Energy Input
During this phase of the Calvin cycle ATP and NADPH are used to produce a 3-carbon sugar that can be used to make glucose
Phase III - 6-Carbon Sugar Produced
3-carbon sugars are combined to form glucose
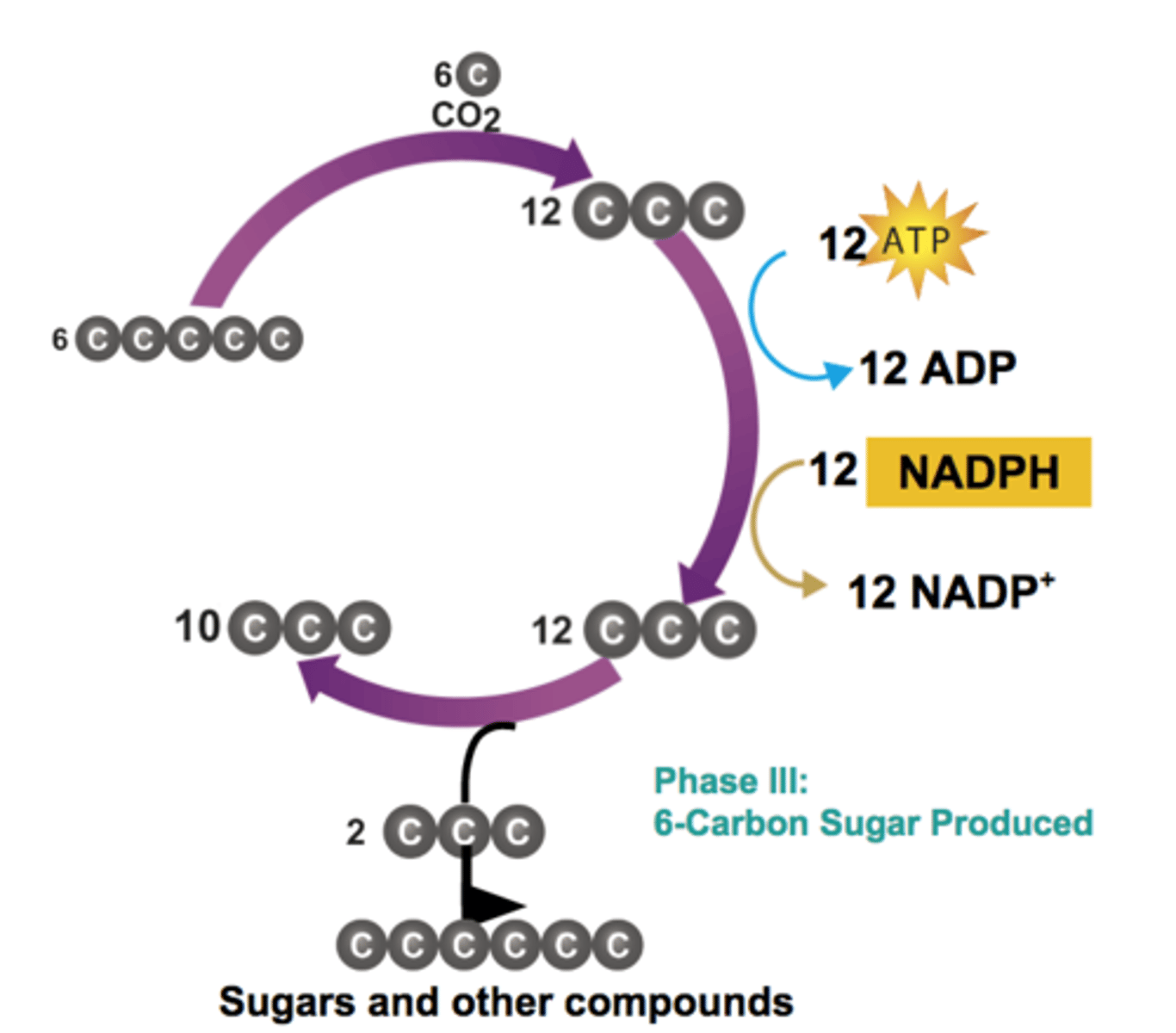
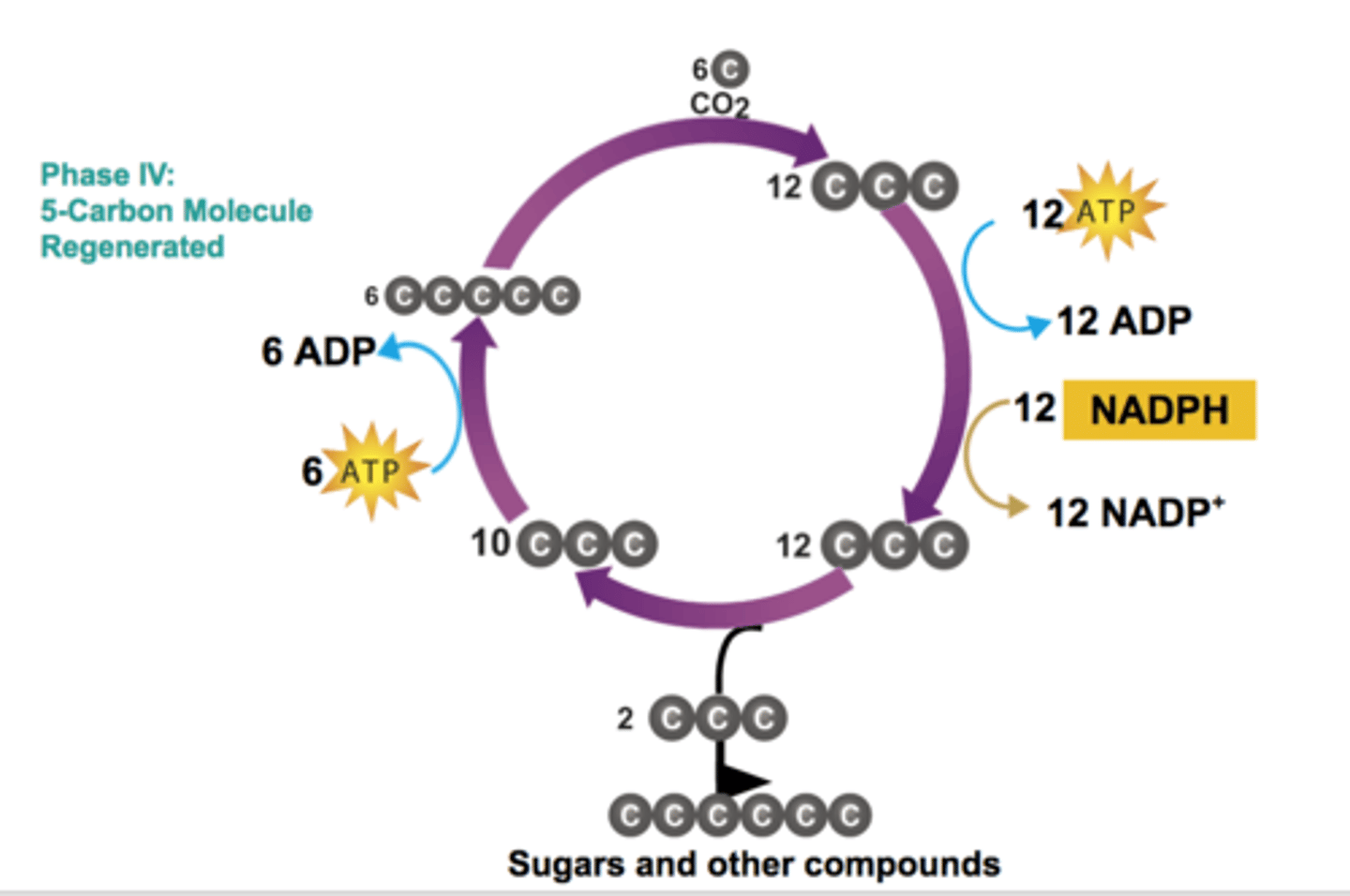
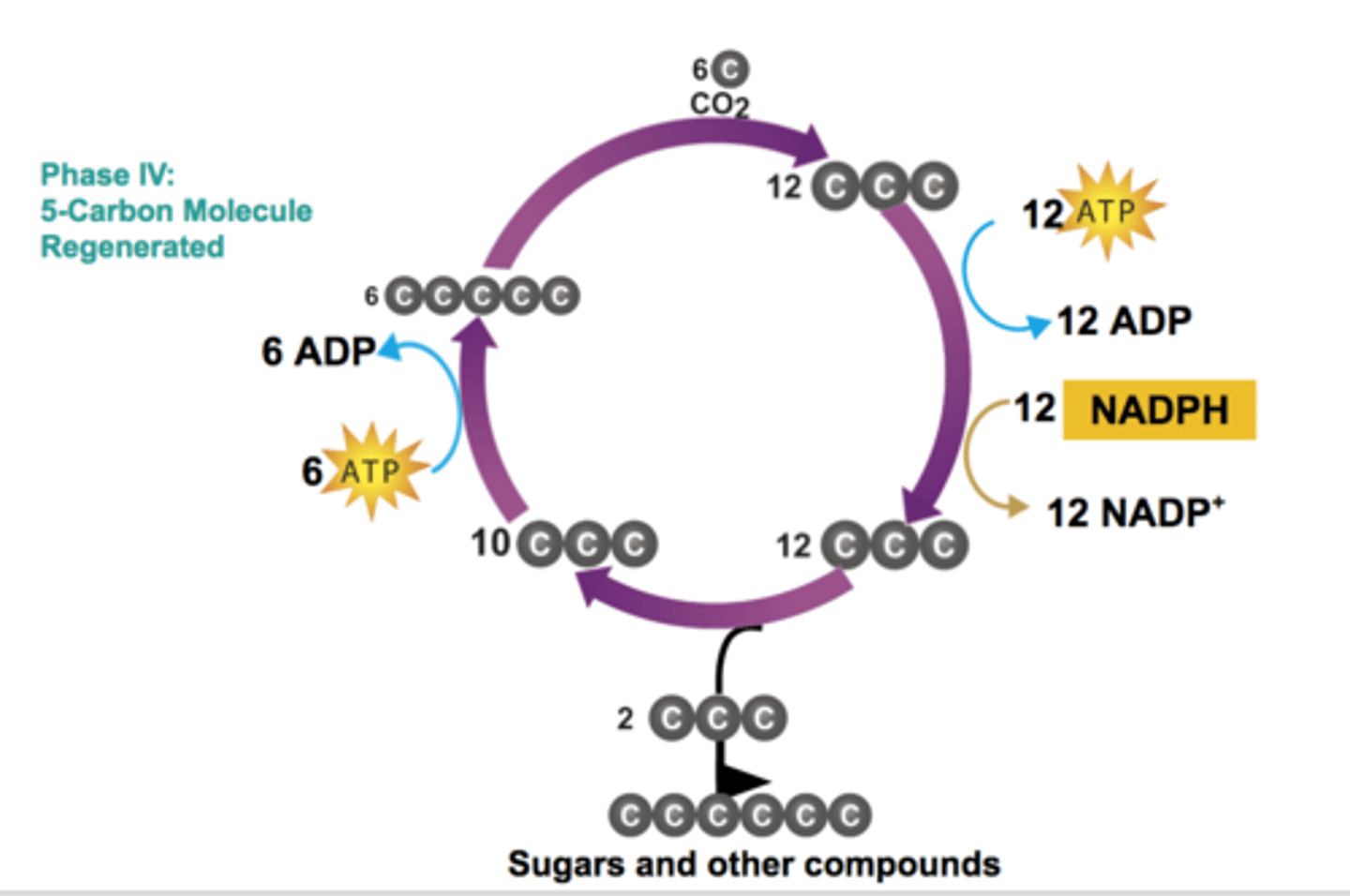
Phase IV - 5-Carbon Molecule Regenerated
3-carbon sugars are recombined using energy from ATP to produce 5-carbon molecule