08.A BIO, C1 Cell Reproduction (PART A)
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Reproduction (Description)
A process that occurs that allows organisms to grow and replace damaged cells as well as to produce offspring; also known as cell division
Growth (Description)
Means to get bigger; to get bigger cells undergo cell division to add cells

Development (Description)
Means to change into an adult form (mature)
Growth (Examples)
Examples include a plant getting bigger or you growing taller

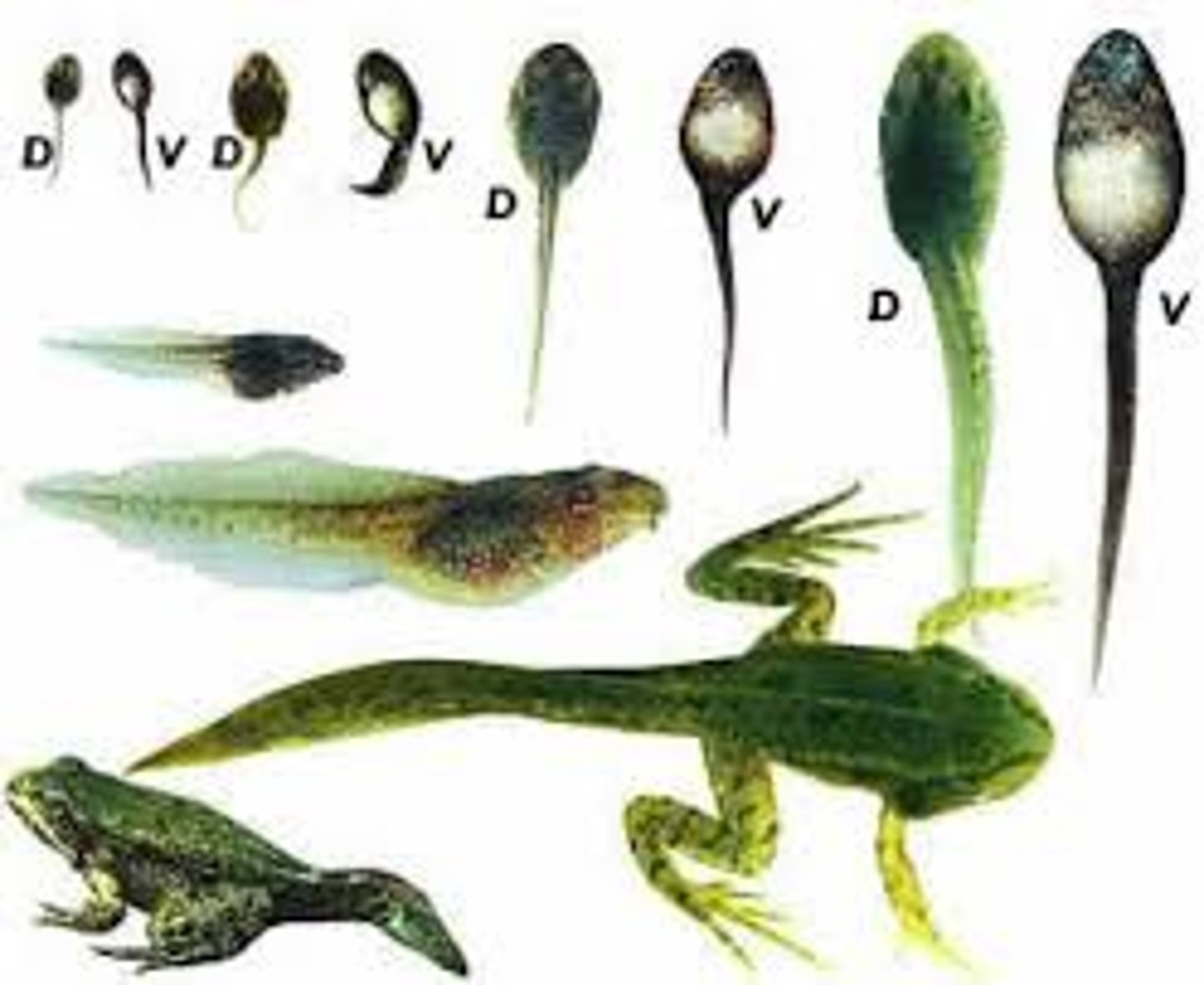
Development (Examples)
Examples include a tadpole becoming a frog or a human embryo becoming a fetus, child, and then adult

Reproduction (Types)
Asexual & Sexual
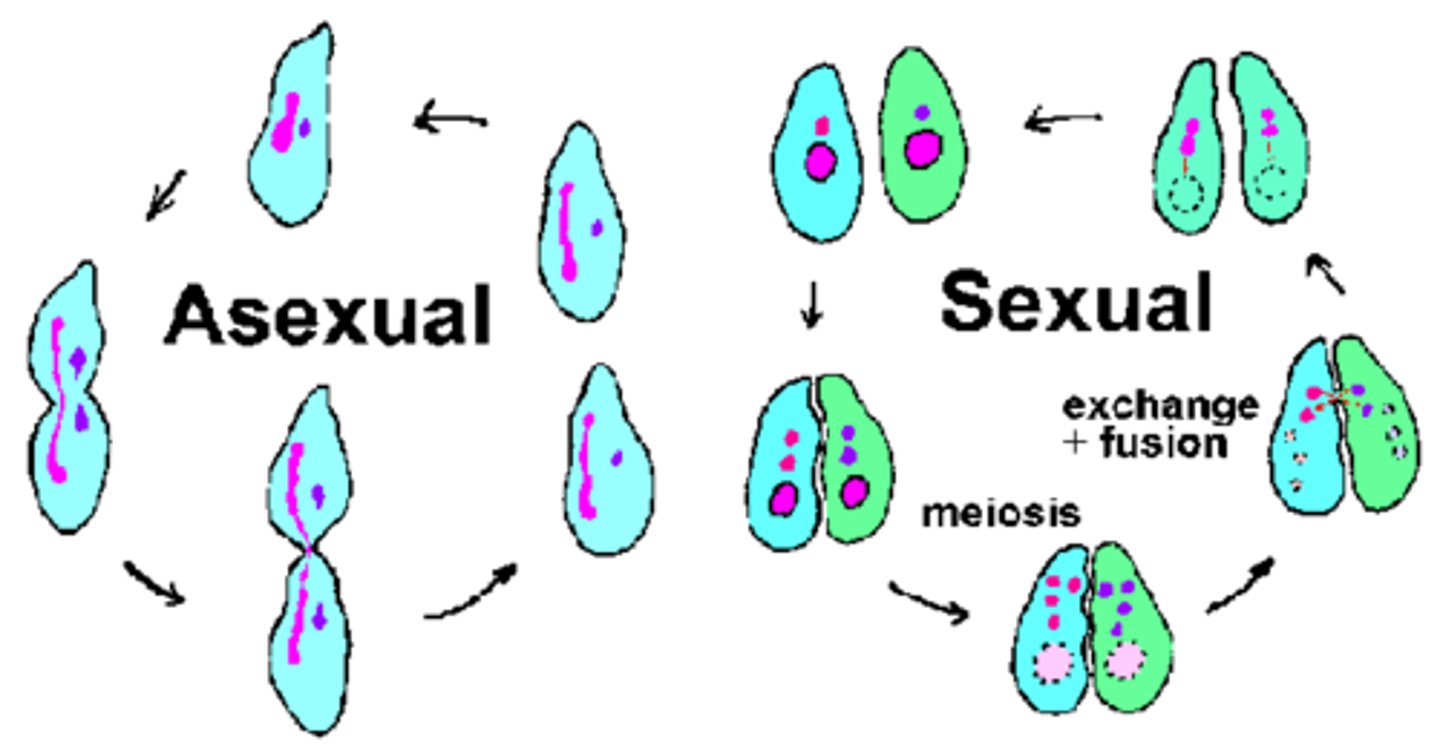
Asexual reproduction (Description)
A type reproduction in which DNA is replicated and two genetically identical daughter cells are reproduced from one parent cell

Sexual reproduction (Description)
A type of reproduction in which DNA from two different gamete cells is recombined to form a genetically different cell
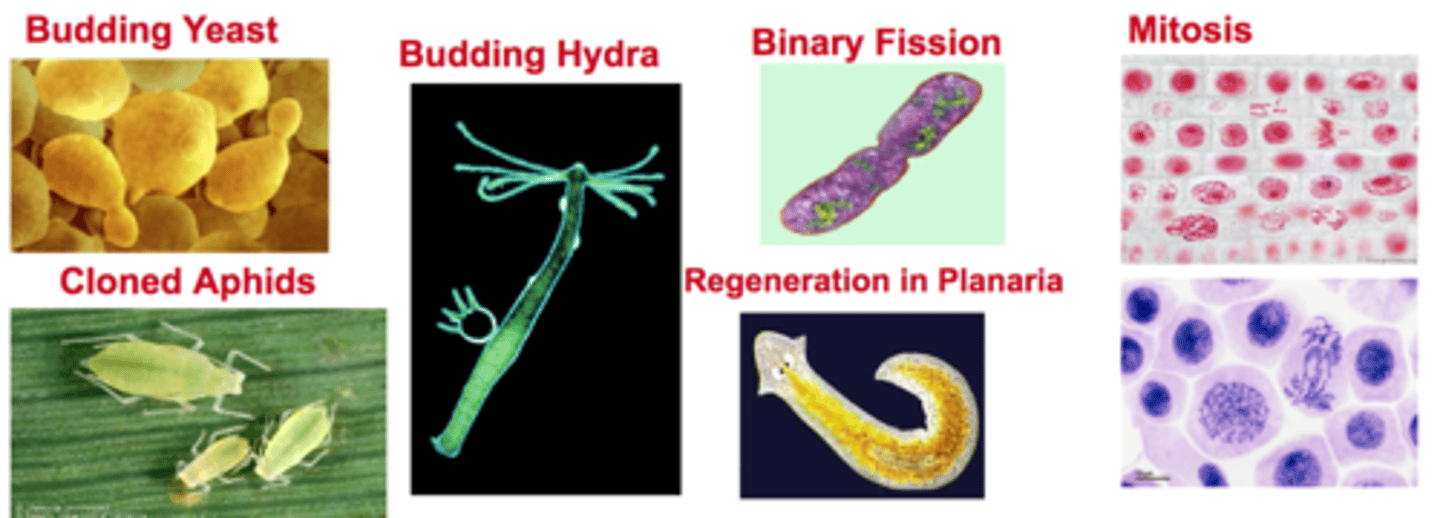
Asexual reproduction (Examples)
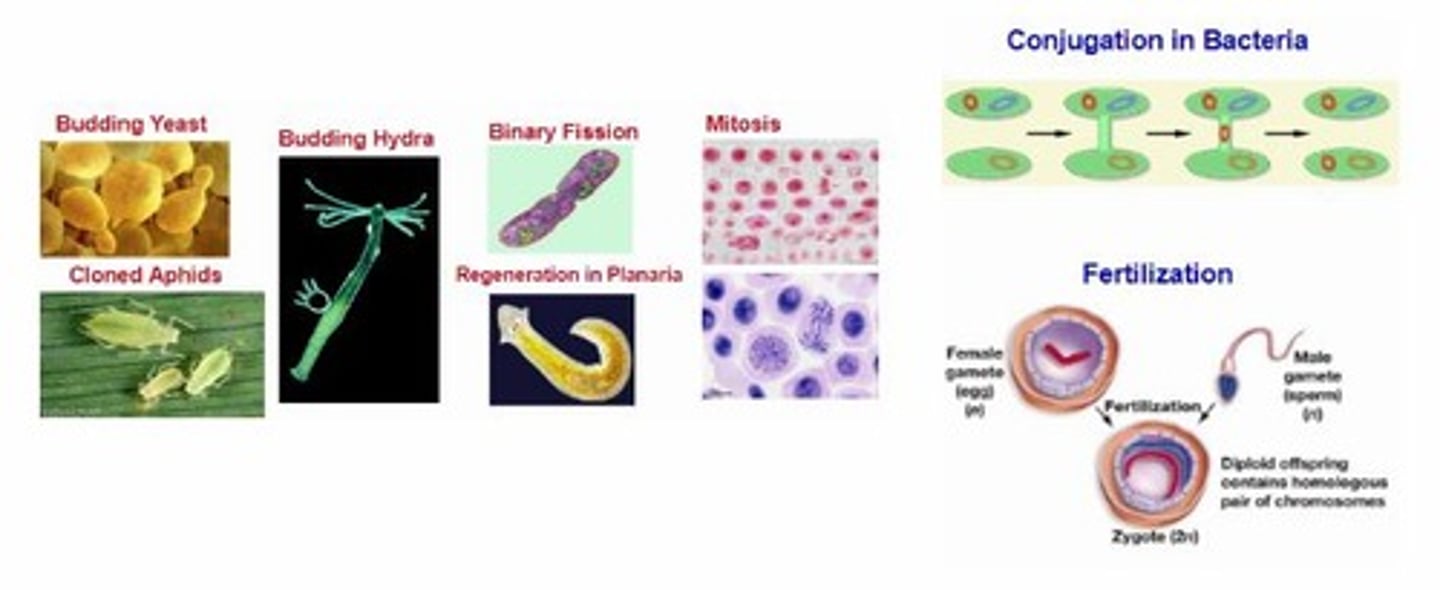
Examples of this type of reproduction include binary fission, budding, regeneration, cloning and mitosis
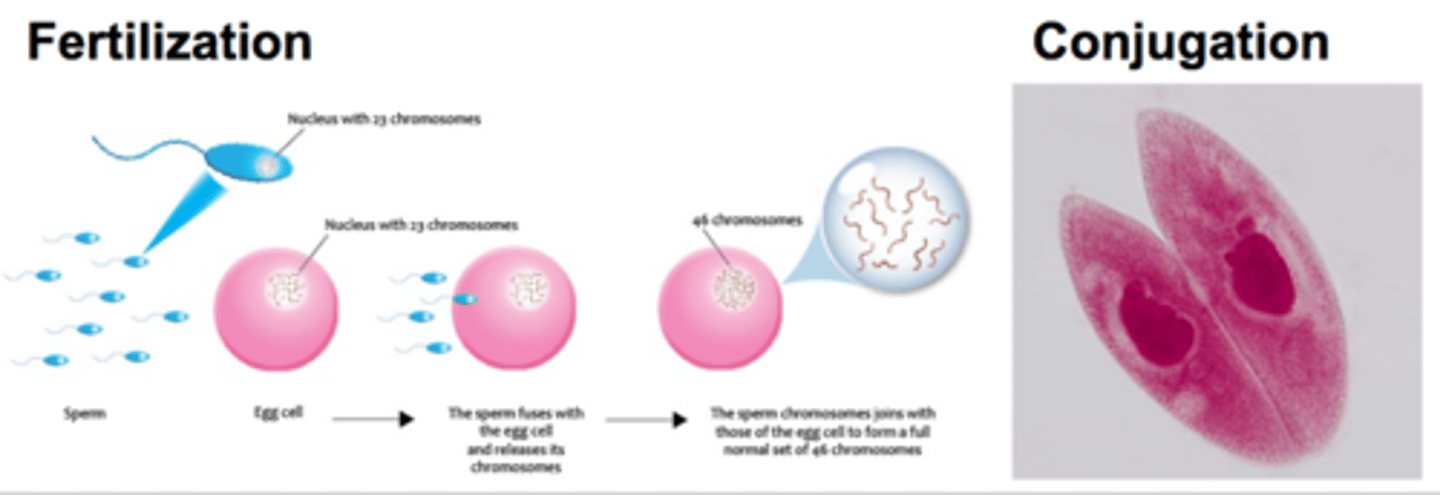
Sexual reproduction (Examples)
Examples of this type of reproduction include conjugation, meiosis, fertilization, and pollination
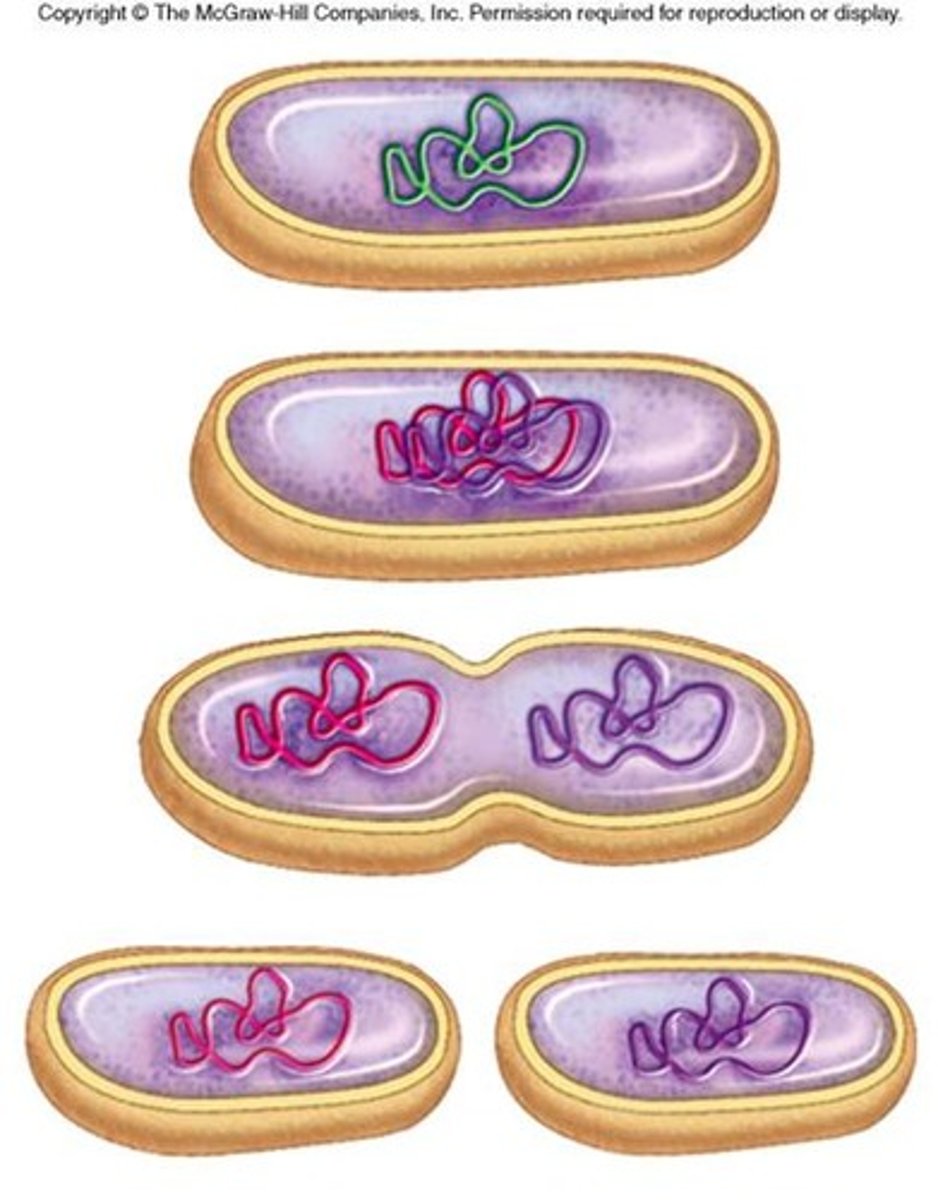
Binary fission
A type of asexual reproduction in which one prokaryotic cell divides to form two identical cells; occurs in bacteria
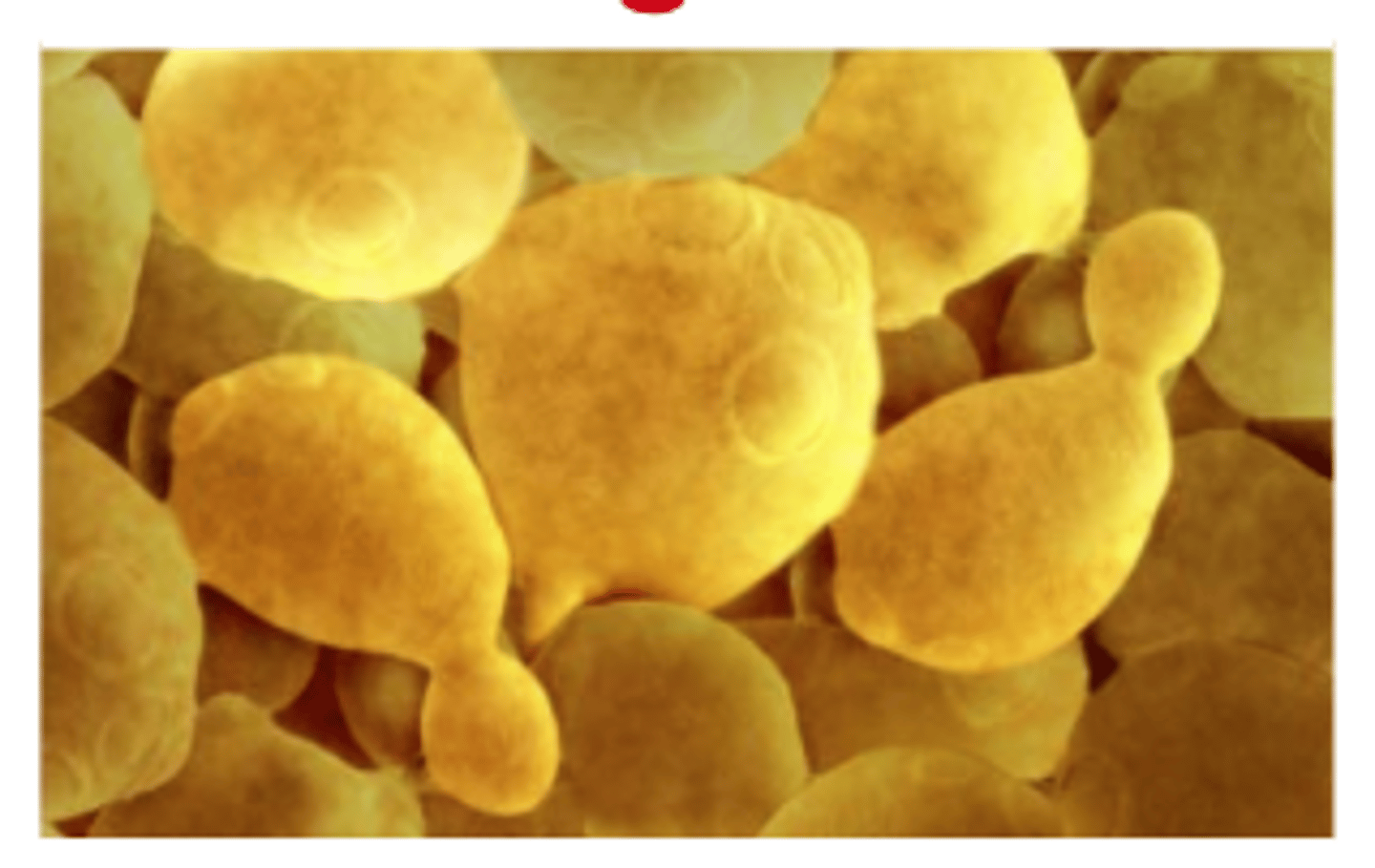
Budding
A type of asexual reproduction in which a part of the parent organism pinches off and forms a new organism; occurs in yeast, hydra and many other organism
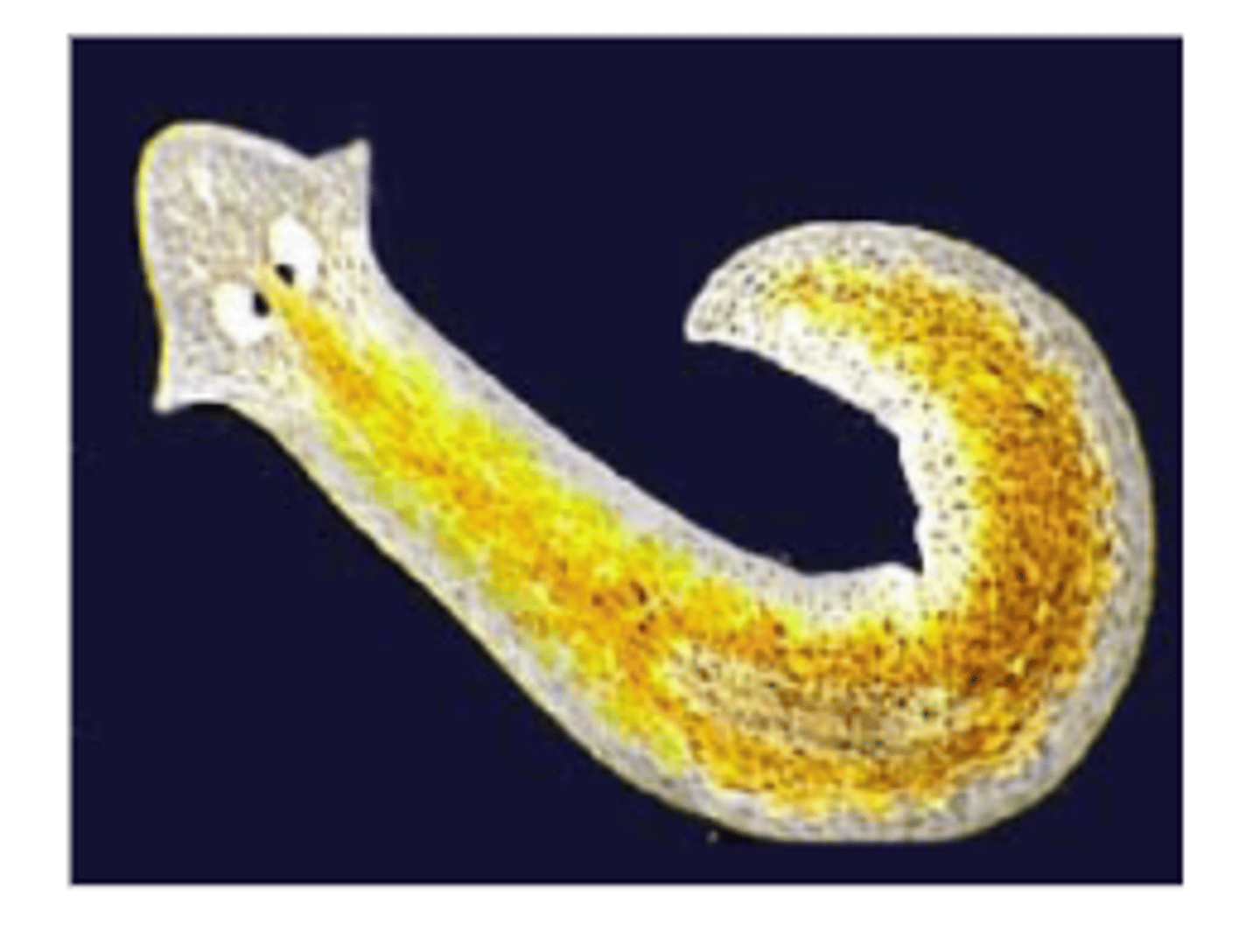
Regeneration
A type of asexual reproduction in which certain organisms regrow missing body parts; occurs in planaria, starfish and many other organisms
Cloning
A type of asexual reproduction in which a cell or organism is copied from an original source; i.e. aphids

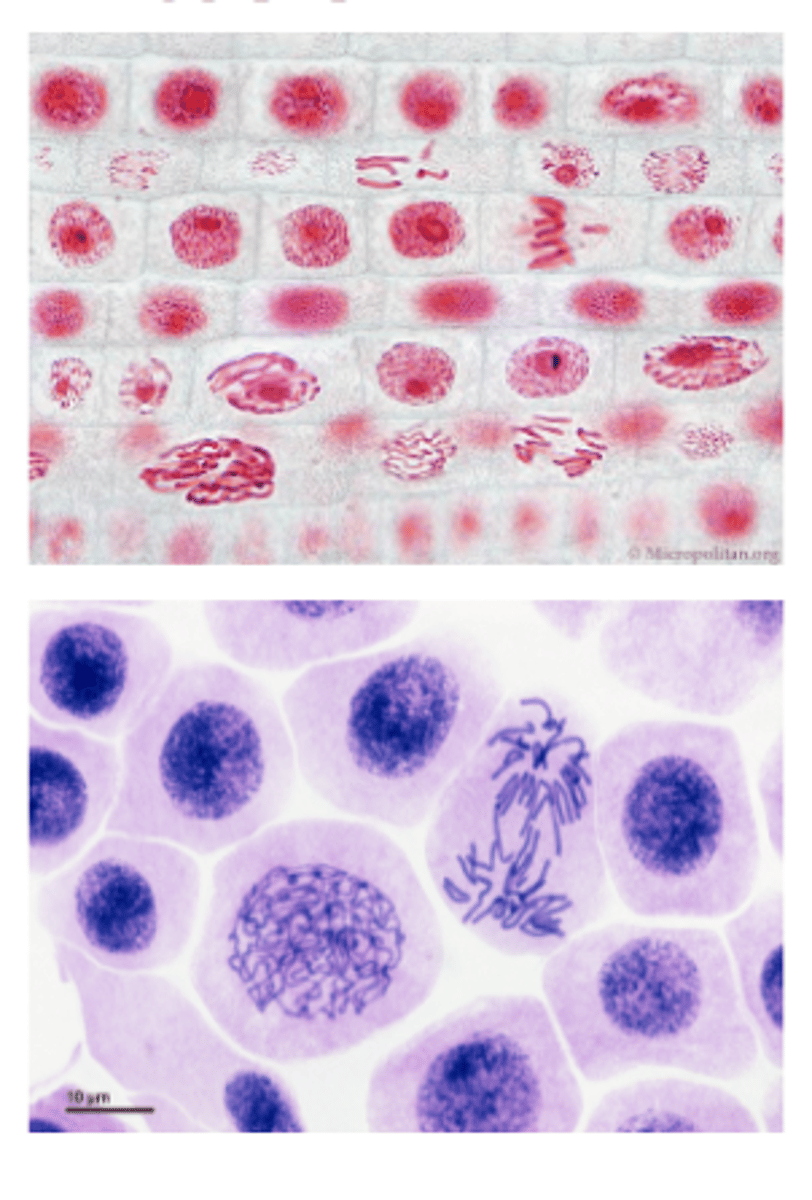
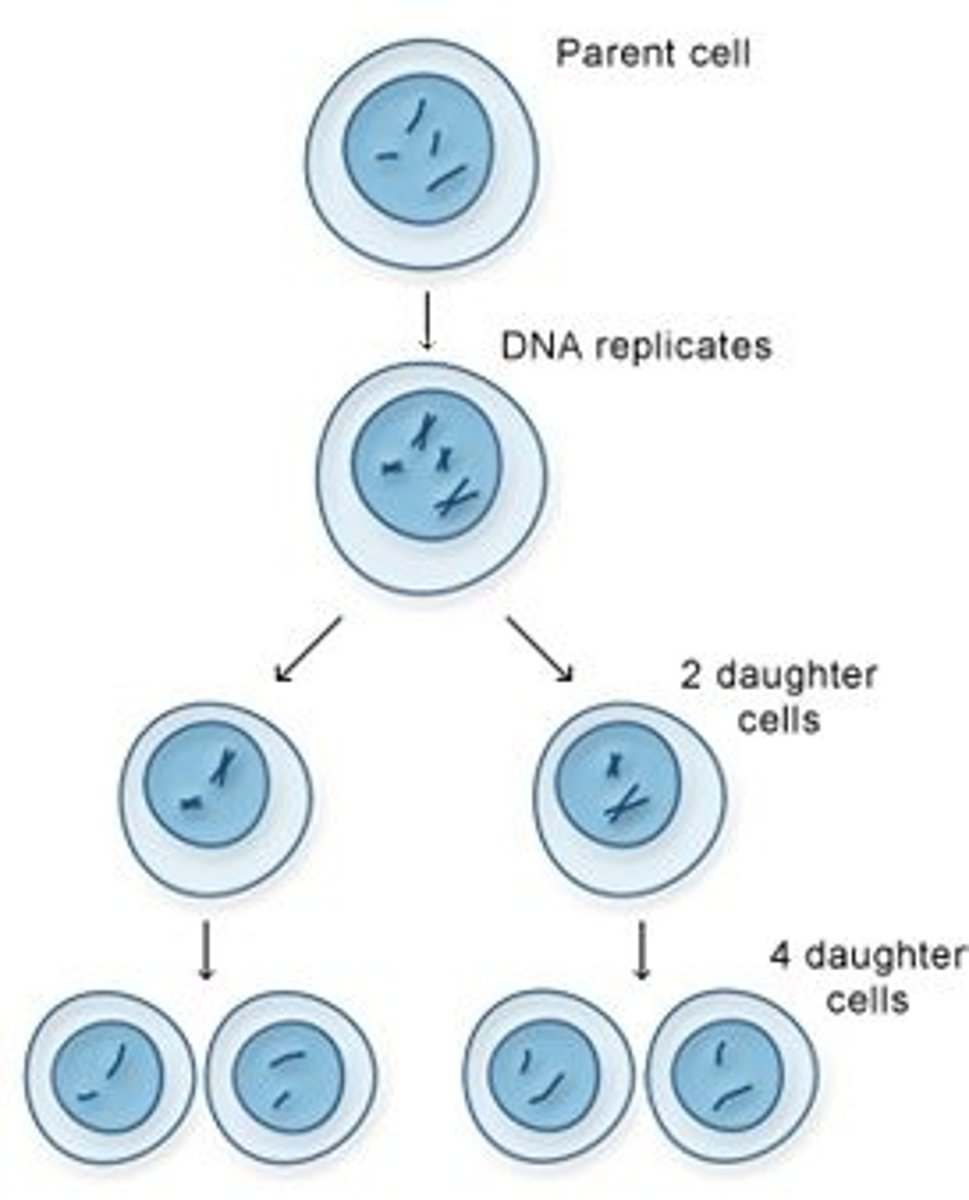
Mitosis
A type of asexual reproduction that occurs in eukaryotes when a parent cell copies the DNA and divides to produce two identical daughter cells typical of ordinary tissue growth and repair
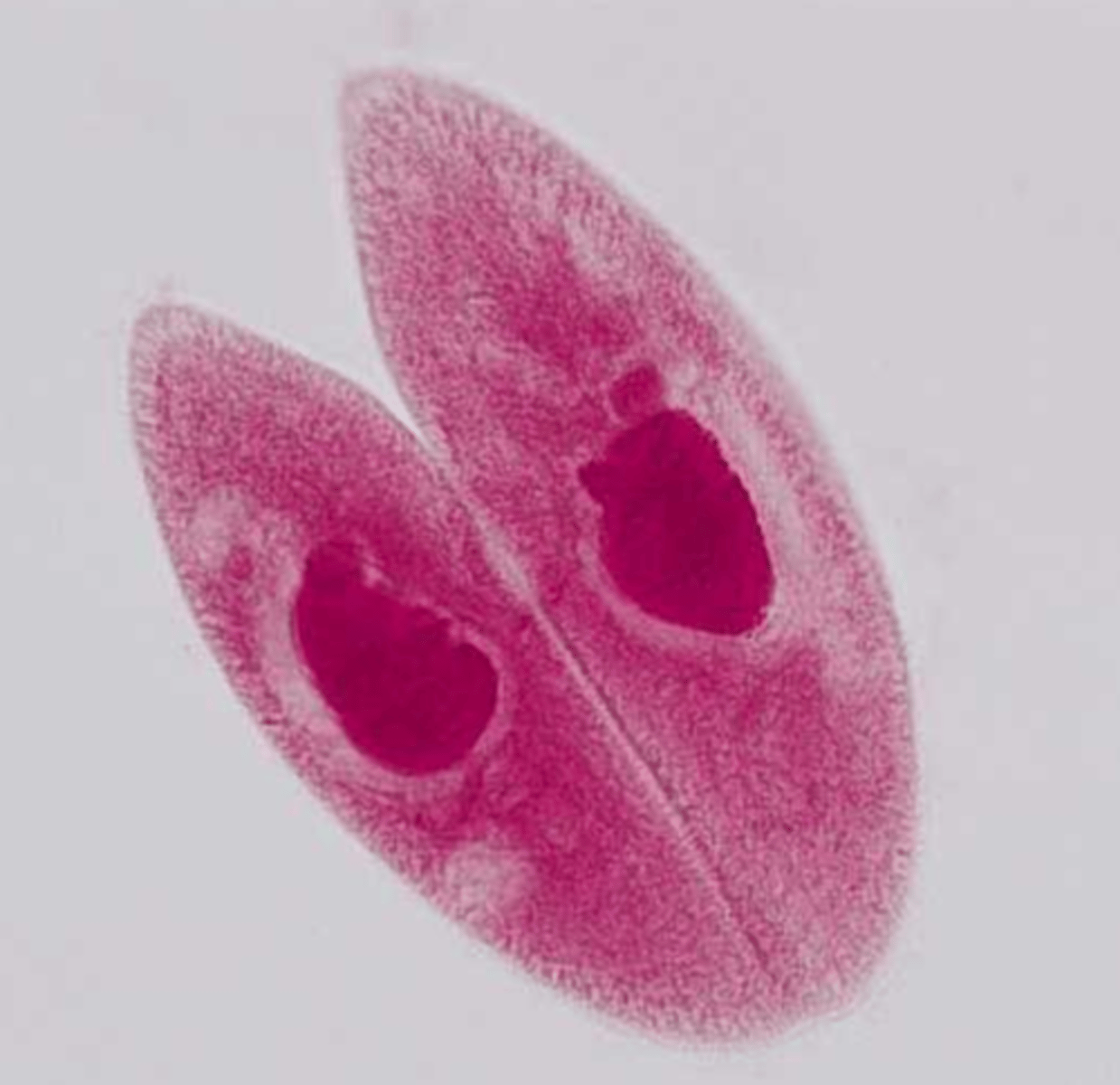
Conjugation (Eukaryotes)
A type of sexual reproduction that occurs when unicellular eukaryotic cells like paramecium join and exchange DNA
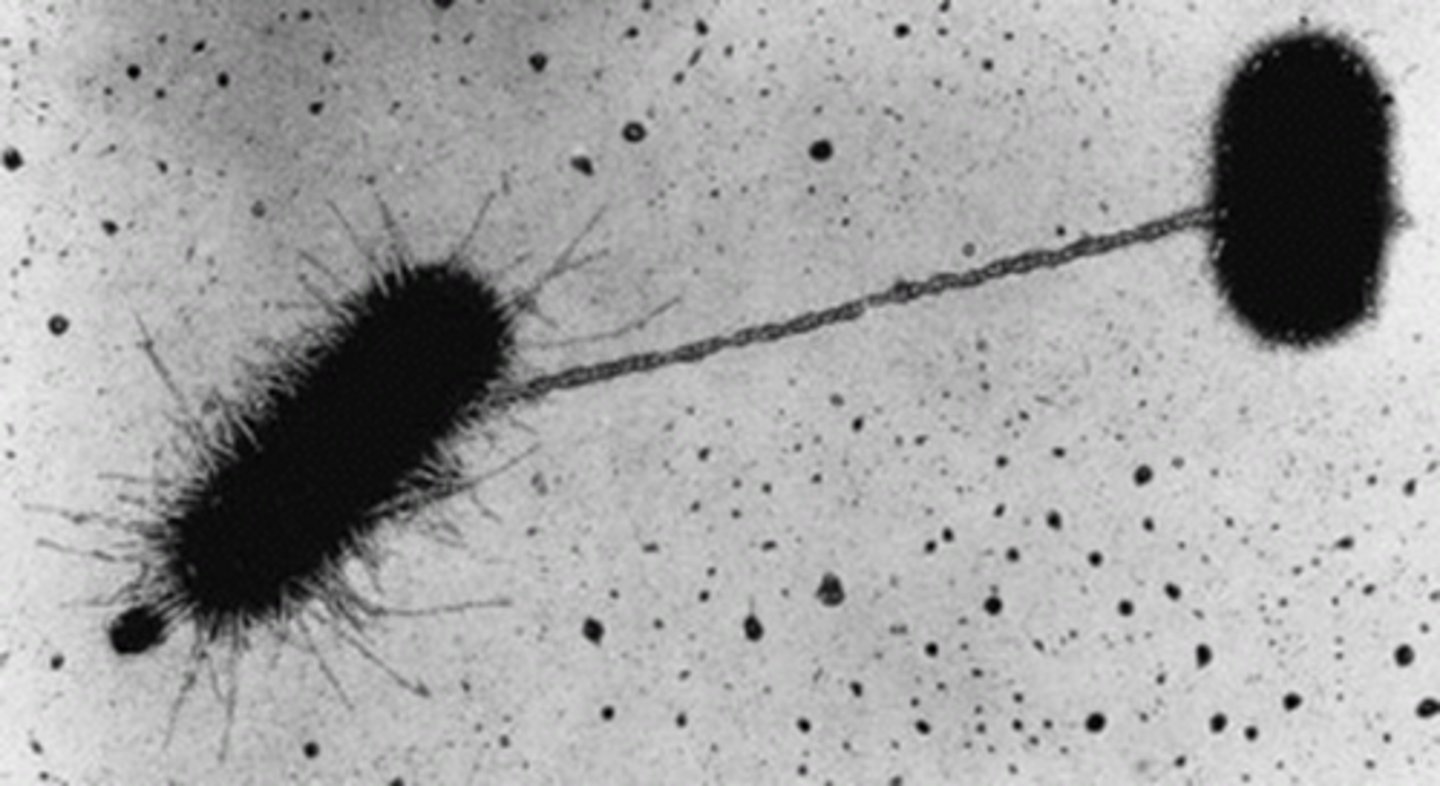
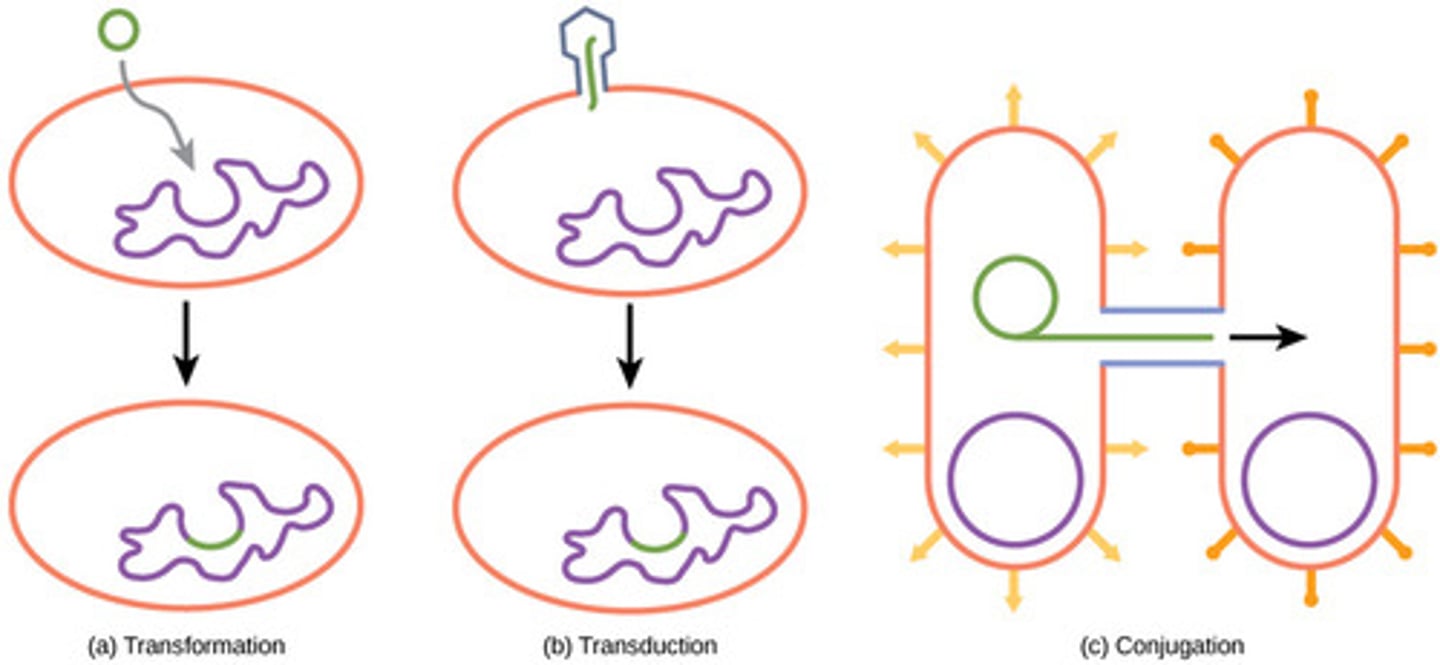
Conjugation (Prokaryotes)
A type of sexual reproduction that occurs when two bacteria join via pili and exchange DNA
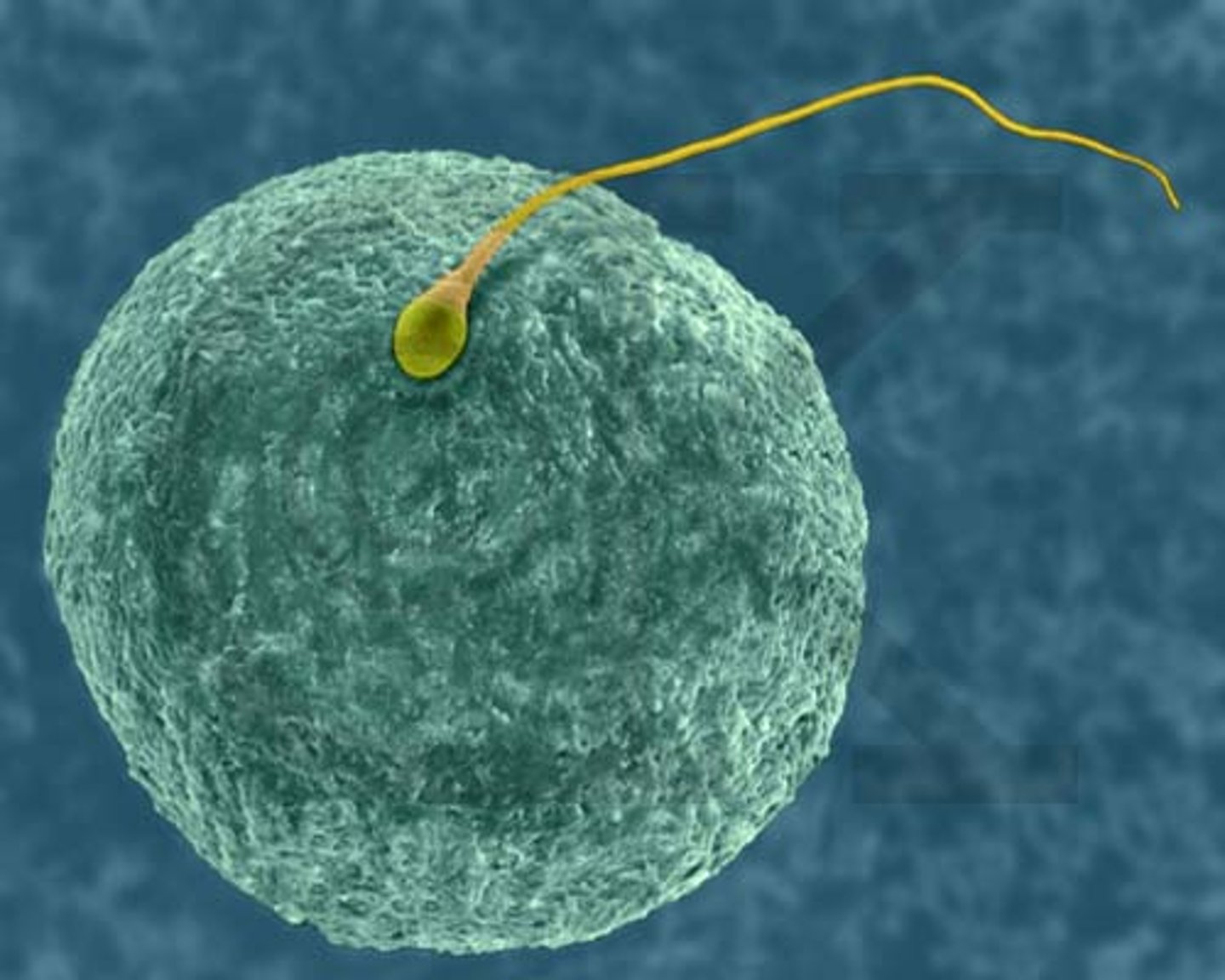
Fertilization
A process in sexual reproduction in which male and female reproductive cells (gametes) join to form a new cell called a zygote
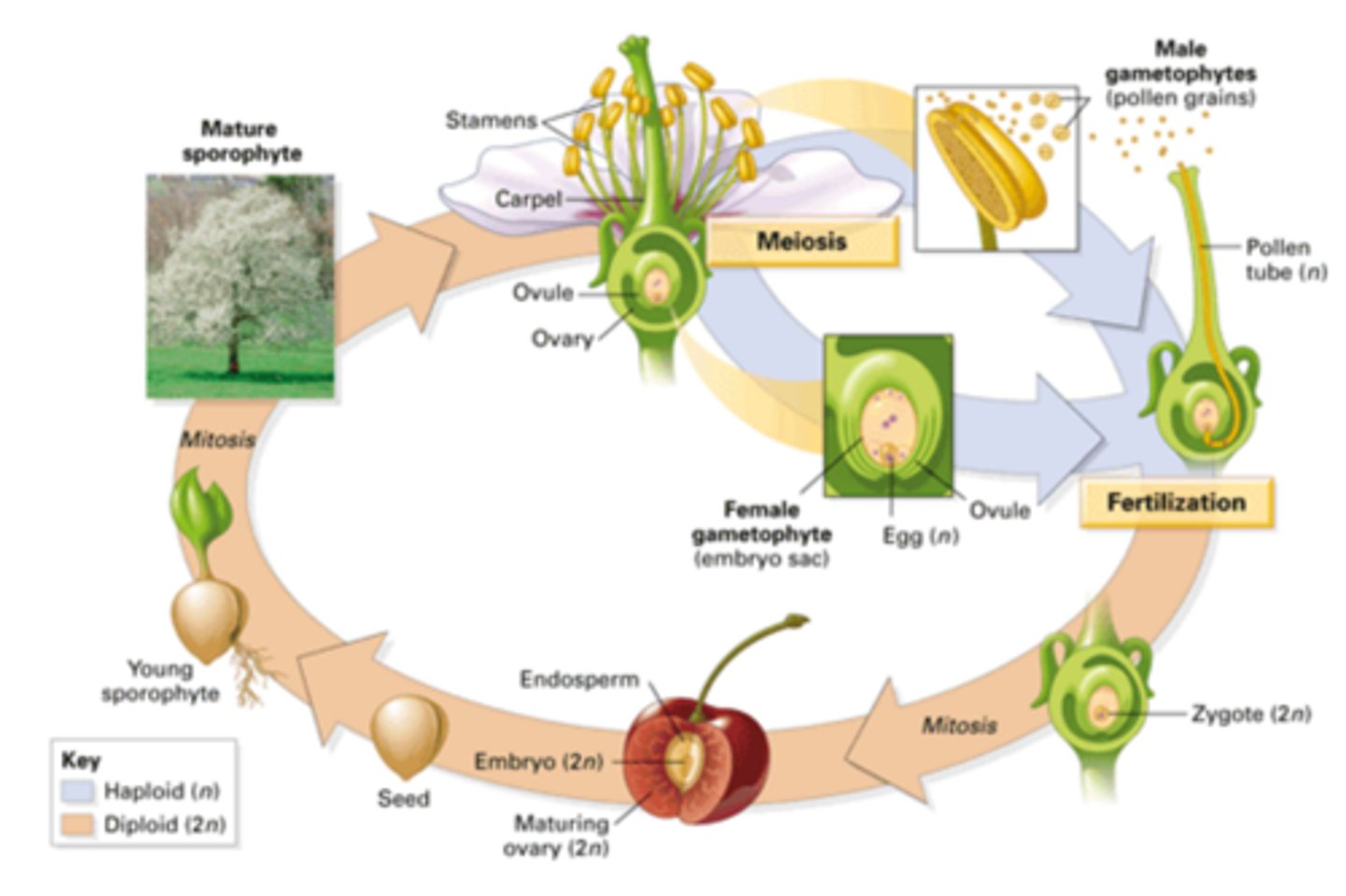
Fertilization in Plants
A type of sexual reproduction in plants in which the sperm (pollen) and egg fuse to form a genetically unique zygote (also called pollination)
Zygote
The cell formed when a sperm fertilizes an egg
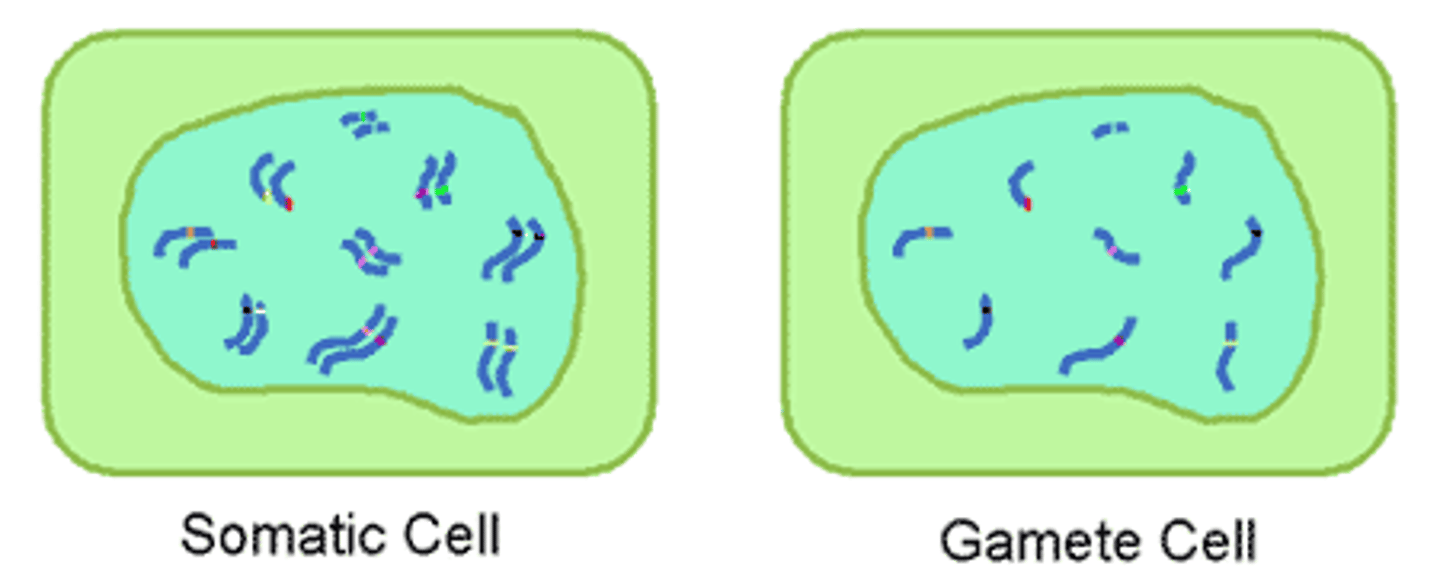
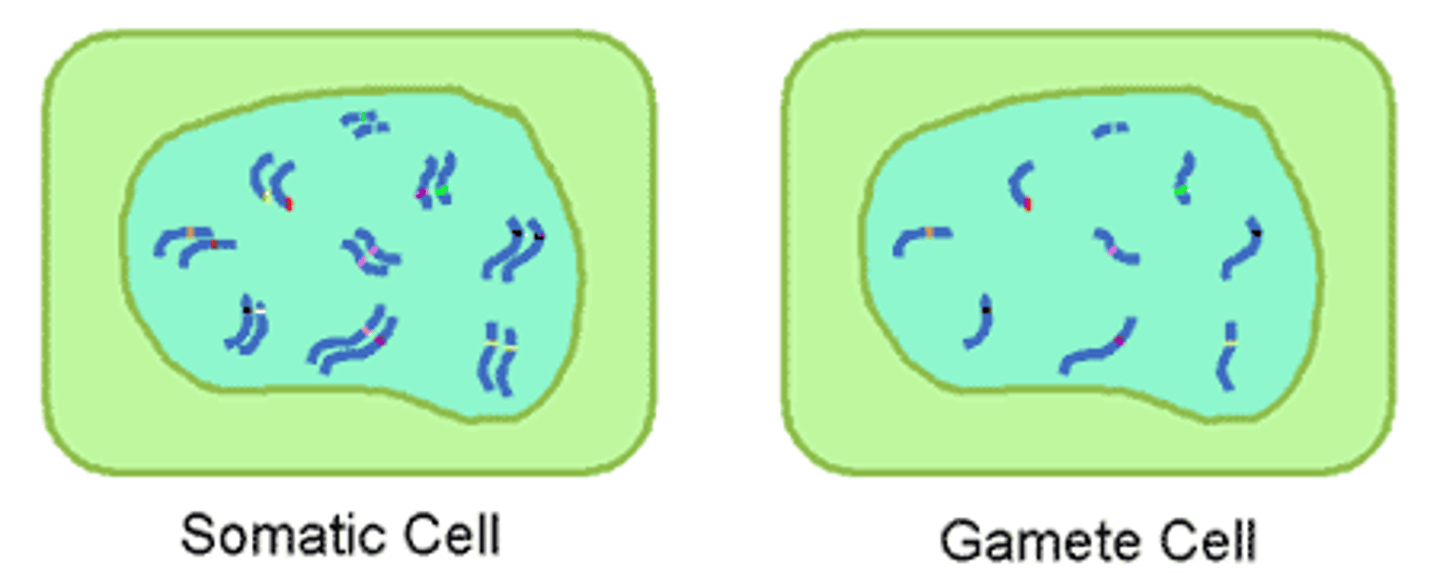
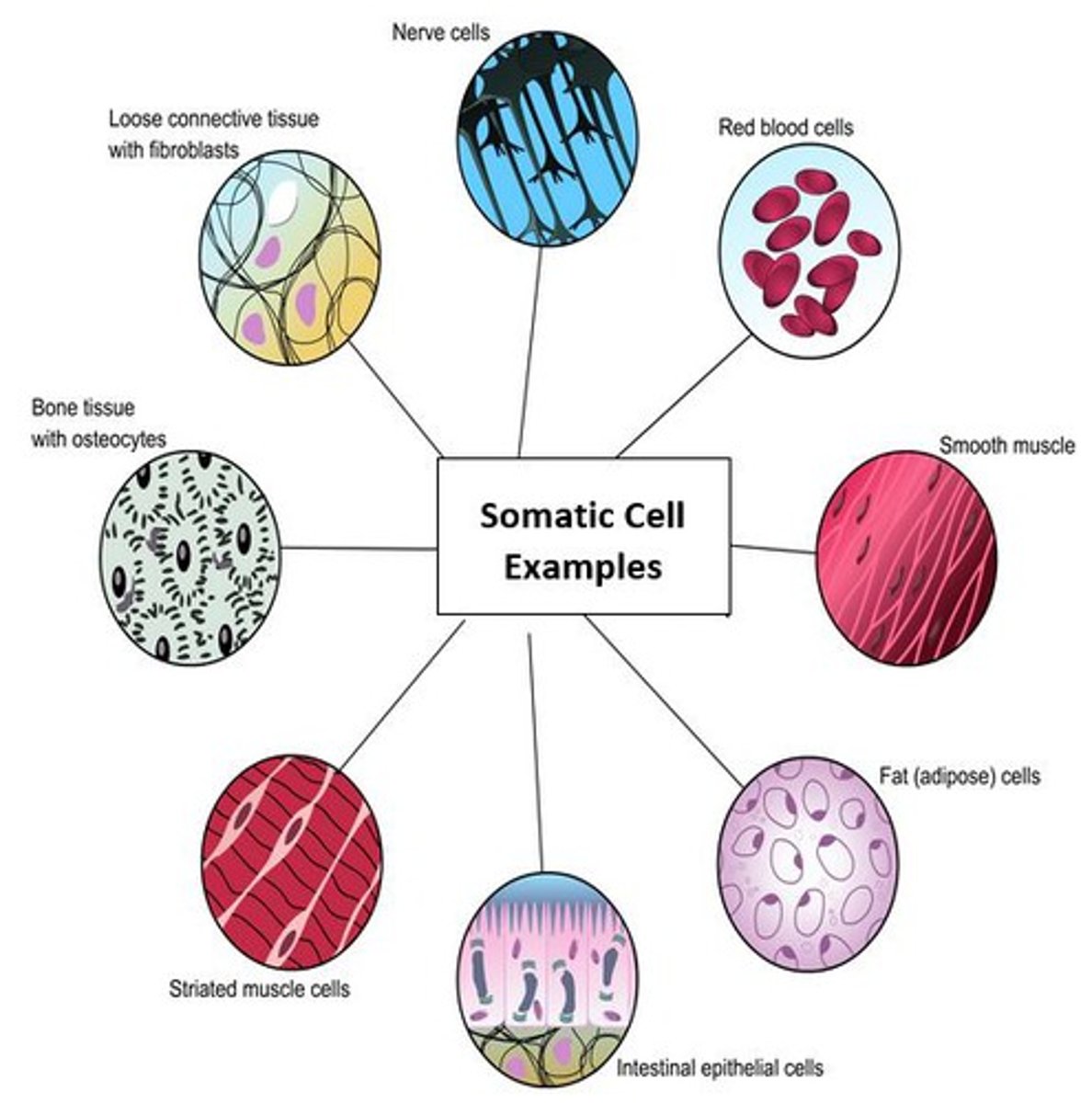
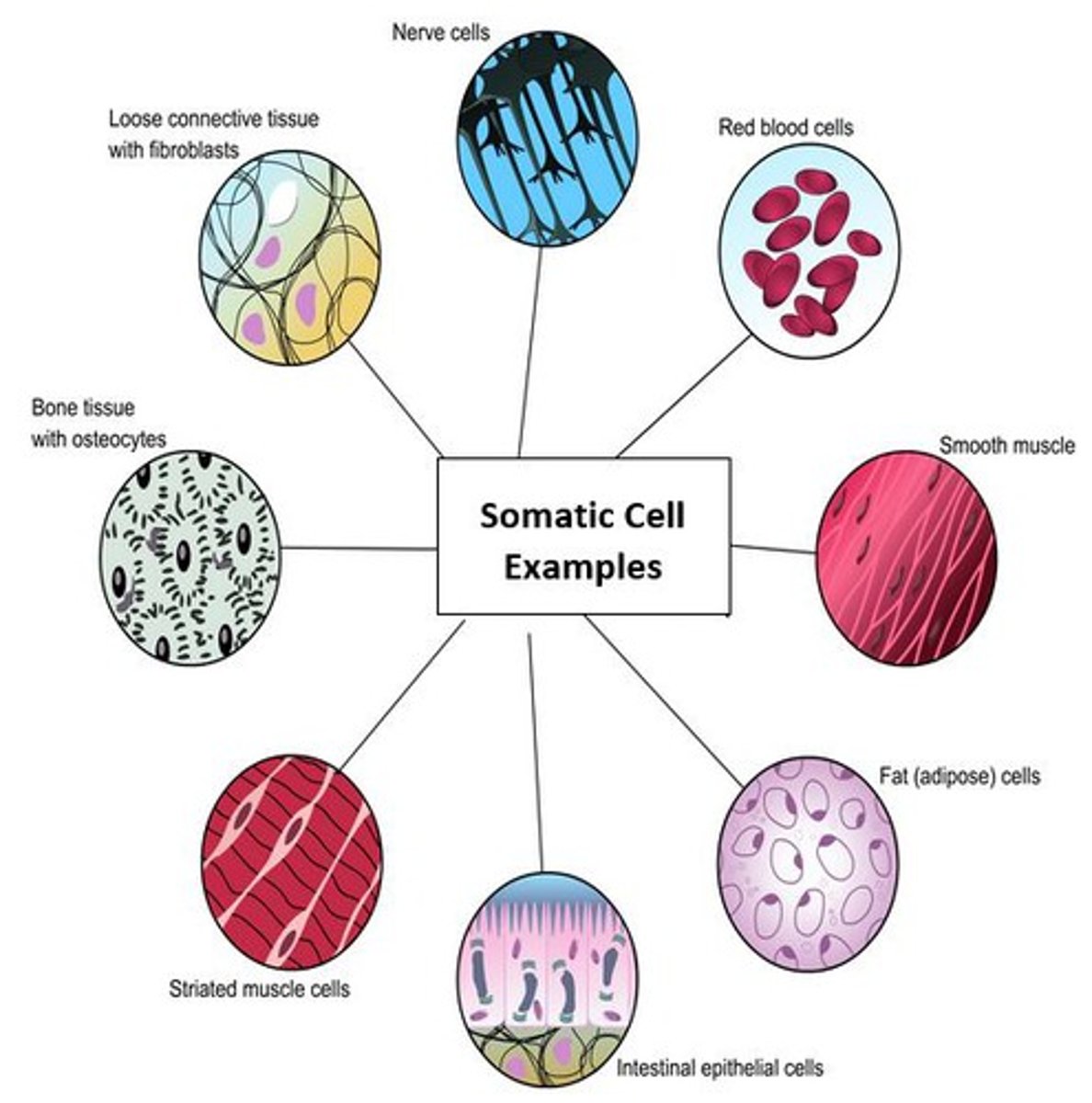
Somatic Cells (Description)
"Non-sex" body cells that contain 2 copies of every chromosome (one from mom and one from dad); cells are referred to as "diploid" (2n)
Germ Cells (Description)
Cells that undergo meiosis to produce gametes
Somatic Cell (Ploidy)
Diploid cells (2n)

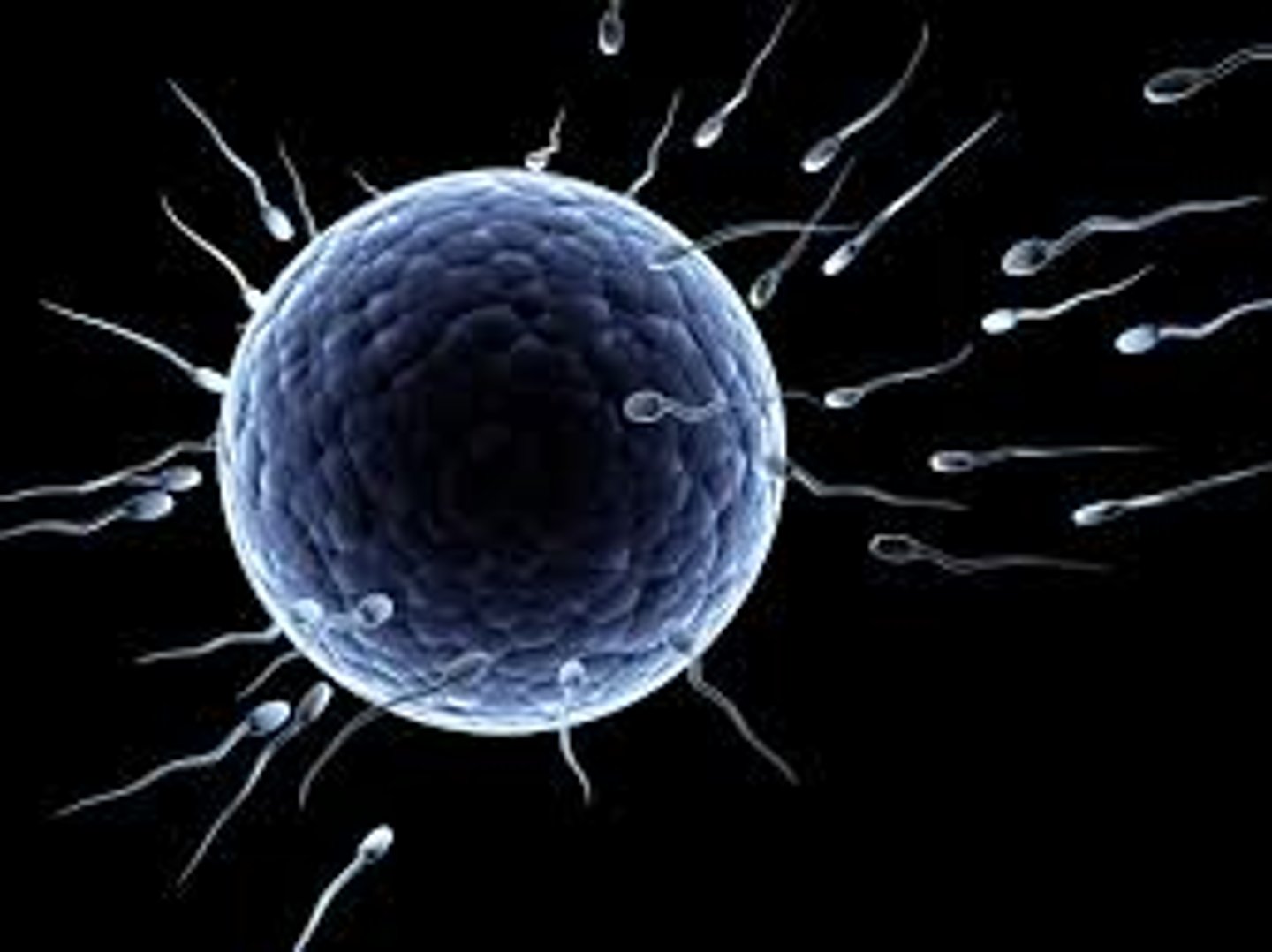
Gamete (Description)
Specialized sex cells that contain only ½ the normal number of chromosomes; referred to as "haploid" (n)
Somatic cells (Examples)
Examples include cells found in the skin liver, stomach, brain, muscle
Gametes (Examples)
Examples include sperm cells and ova/eggs
Gametes (Ploidy)
Haploid cells (n)
Reproduction in Prokaryotes (Examples)
Asexual = binary fission
Sexual = conjugation
Reproduction in Eukaryotes (Examples)
Asexual = budding, regeneration, cloning, fragmentation, mitosis
Sexual = conjugation, meiosis, fertilization, pollination
Meiosis (Description)
A type of cell reproduction in eukaryotes in which diploid germ cells (2n) become haploid (n) gametes that are genetically unique; occurs in germ cells during the production of gametes
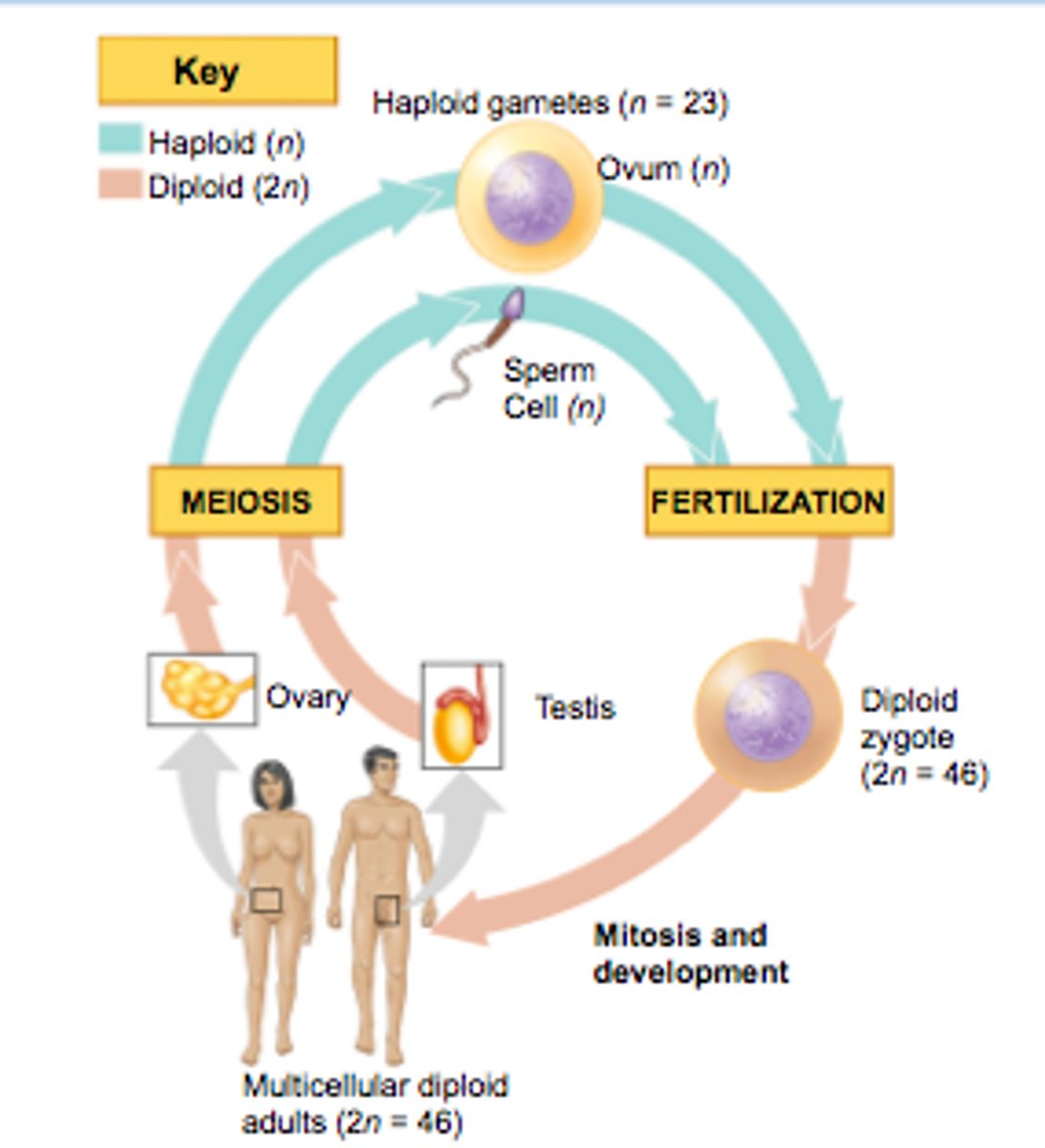
Meiosis in Humans
Germ cells (2n) within the testes and ovaries undergo a special type of cell division to produce haploid cells called gametes (n) (egg/sperm)
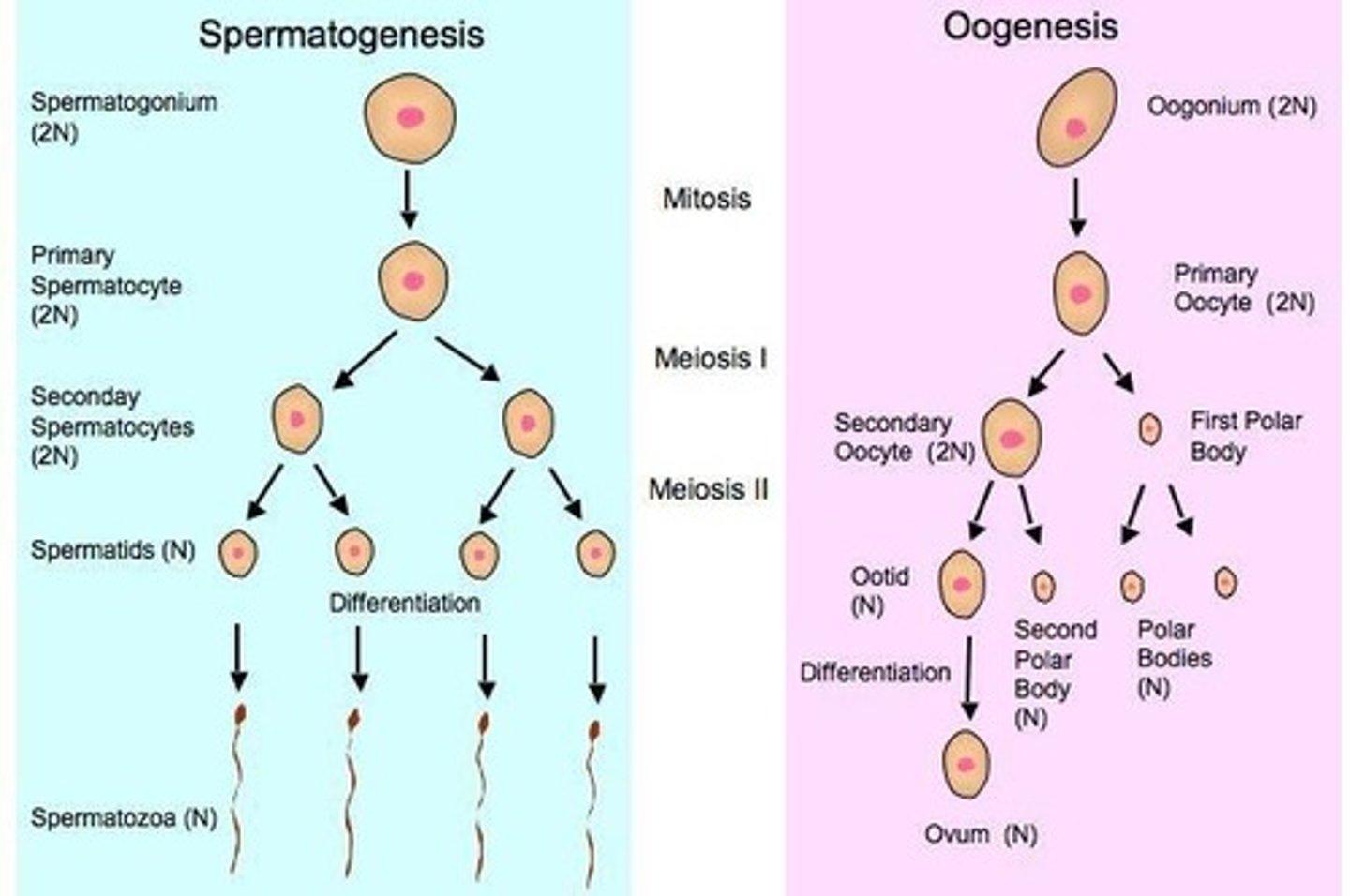
Gametes in Humans
Haploid sex cells (sperm/ova) that contain 23 chromosomes; produced during meiosis from diploid germ cells found in the testes and ovaries
Somatic Cells in Humans
Diploid "non-sex" cells found in the body that contain 46 chromosomes; replaced during mitosis
Germ Cells in Humans
Specialized diploid cells found in the testes and ovaries that undergo meiosis to produce gametes (sperm/ova)
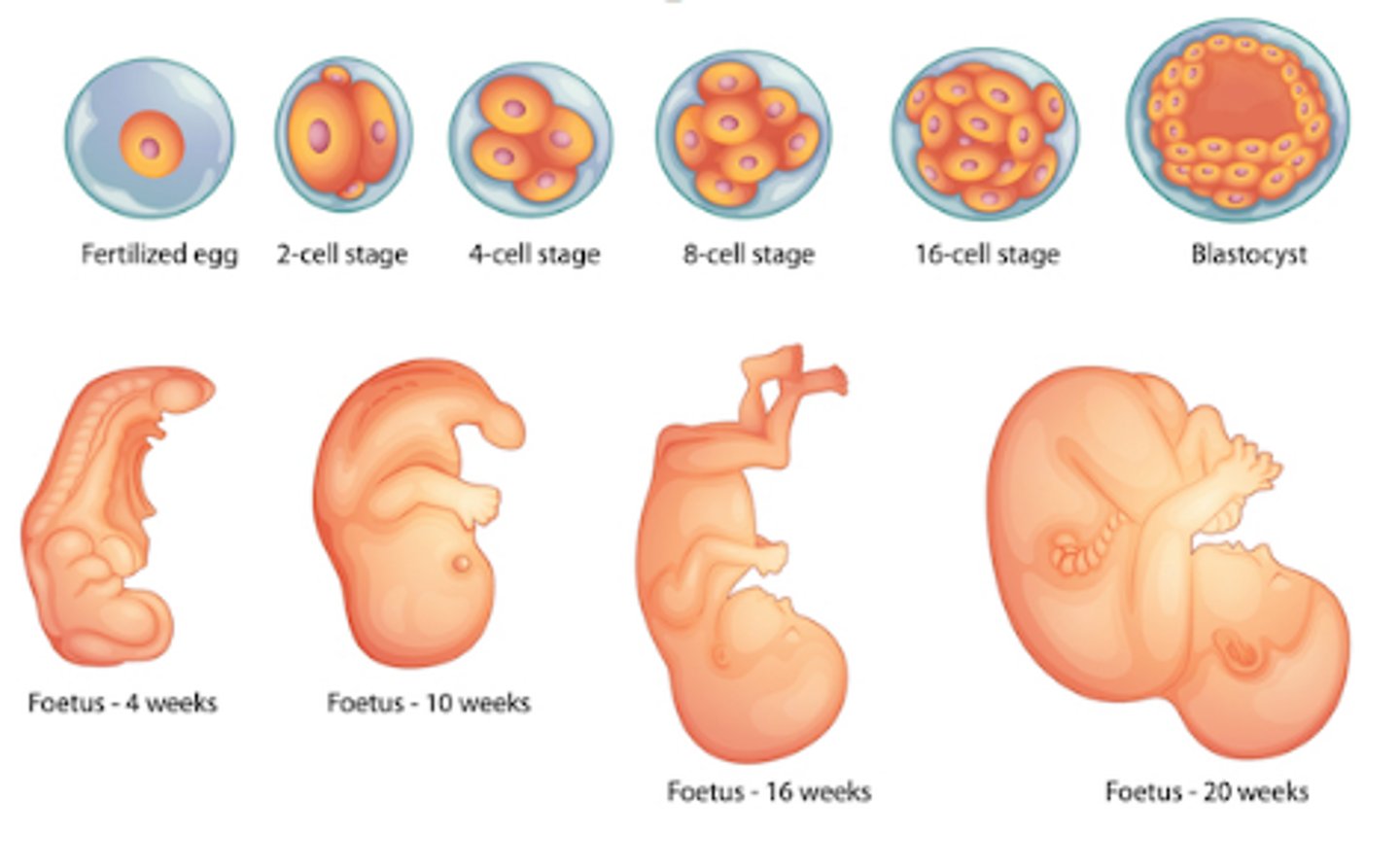
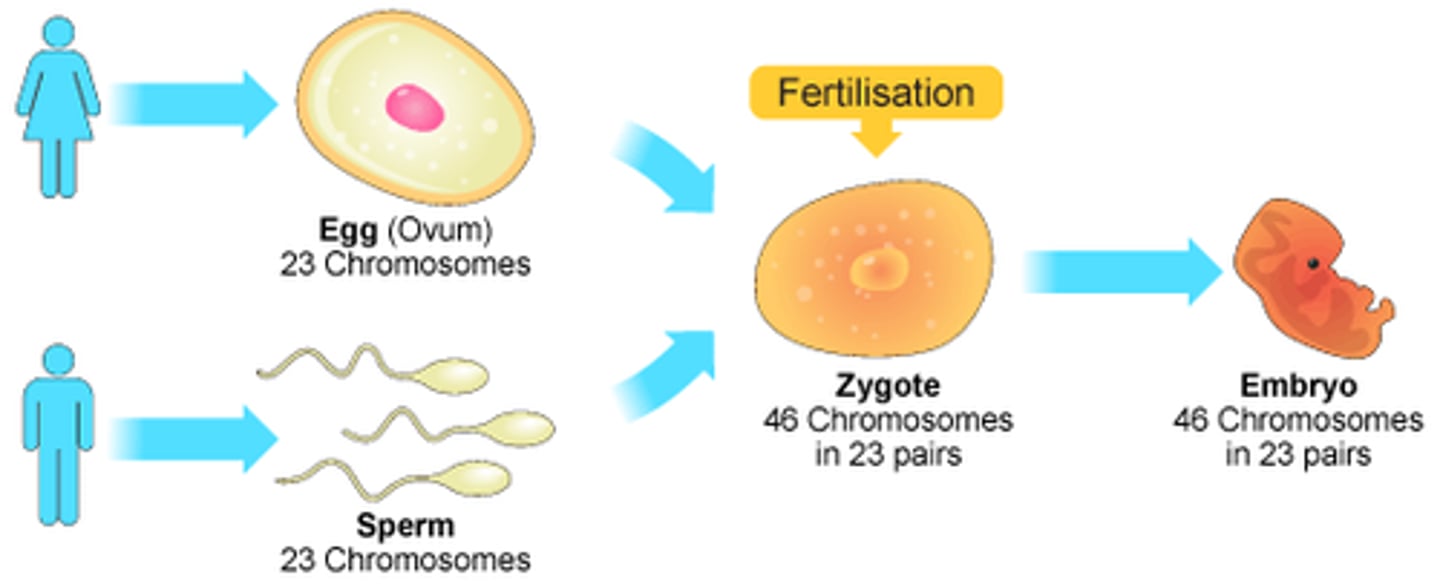
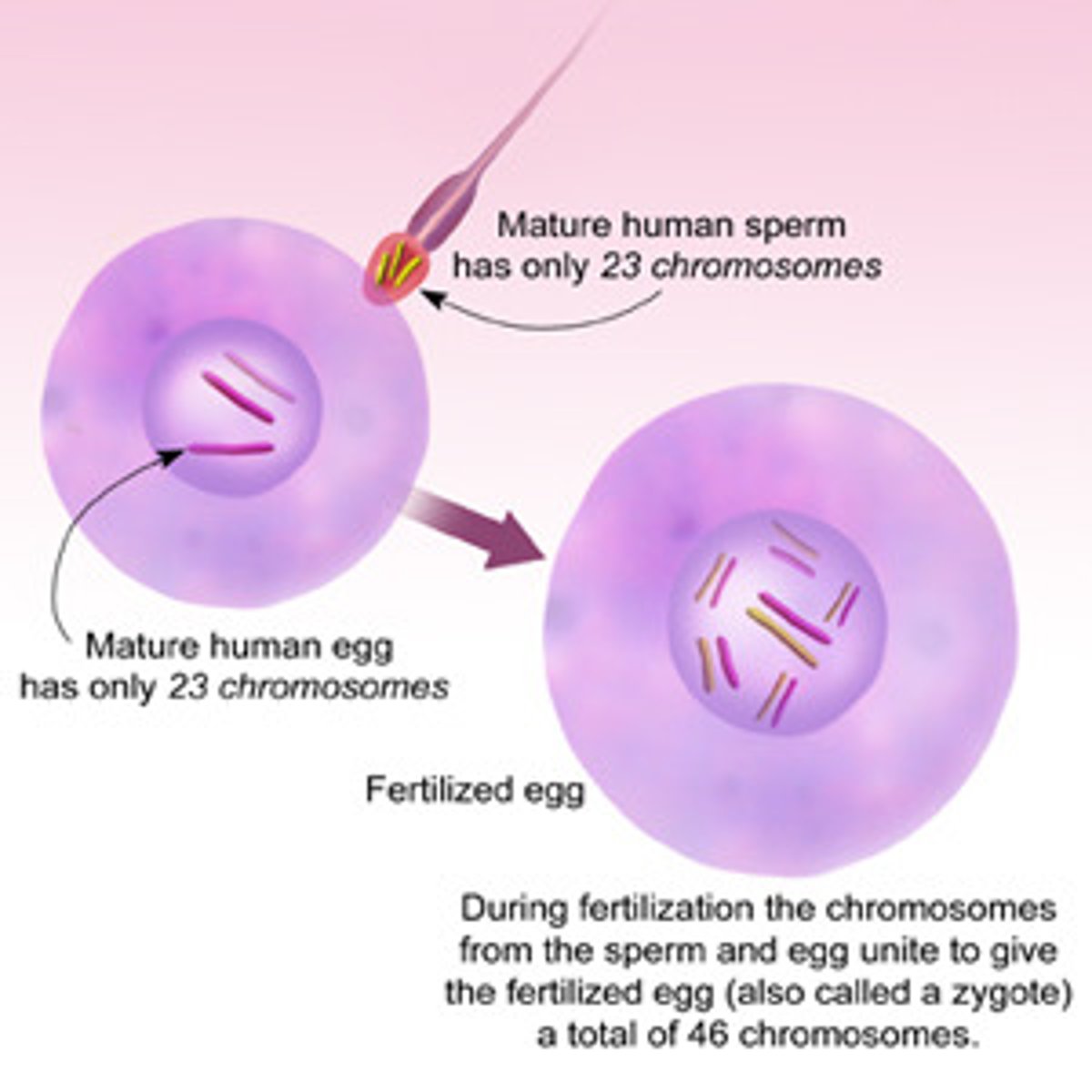
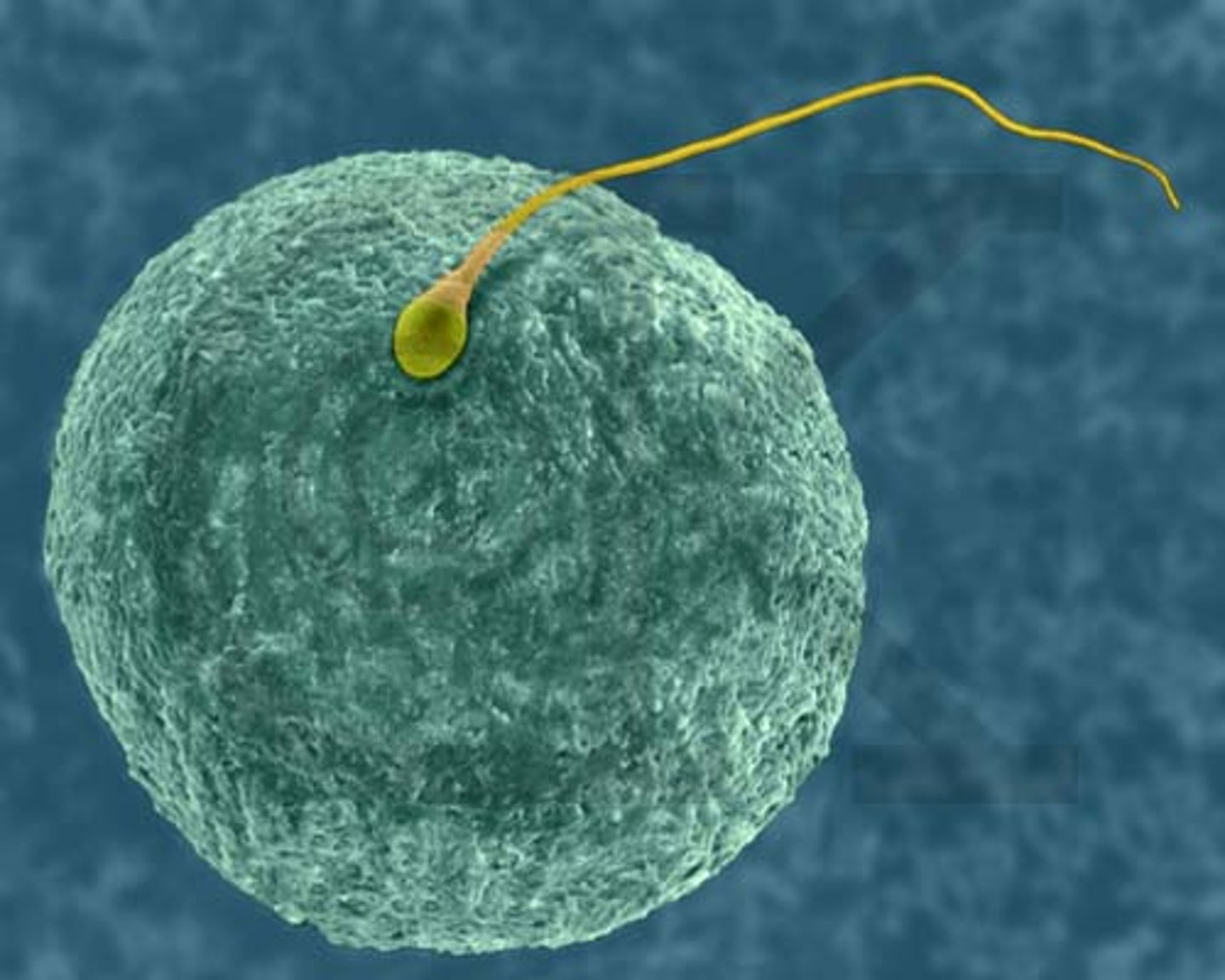
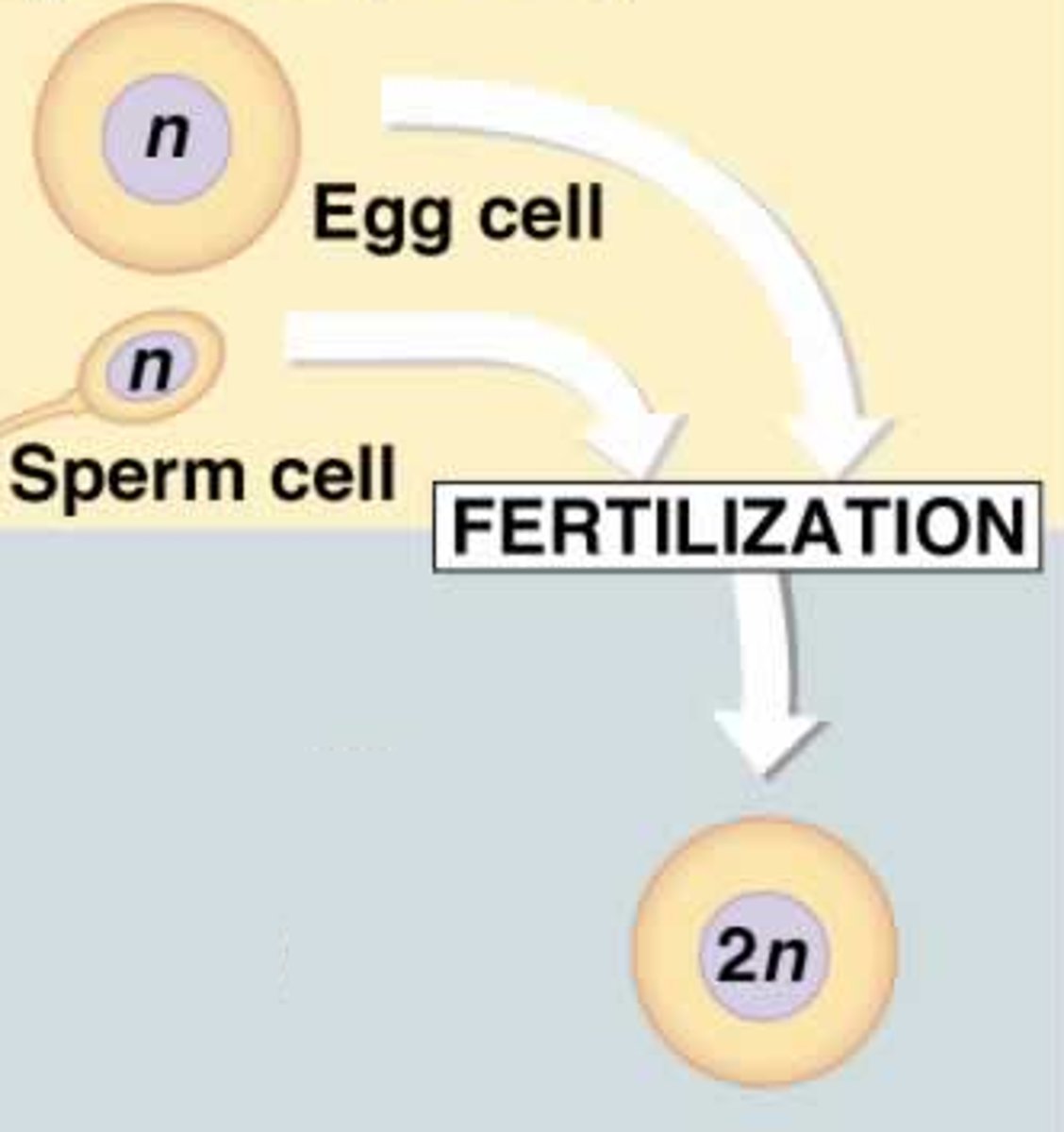
Fertilization in Humans
A process that occurs when two haploid cells, a sperm and ovum (egg), combine to form a zygote; each parent donates 23 chromosomes and the resulting zygote has 46 chromosomes
Blastula
A small ball of cells produced after fertilization that contains specialized cell called stem cells that can differentiate into all the cells in your body
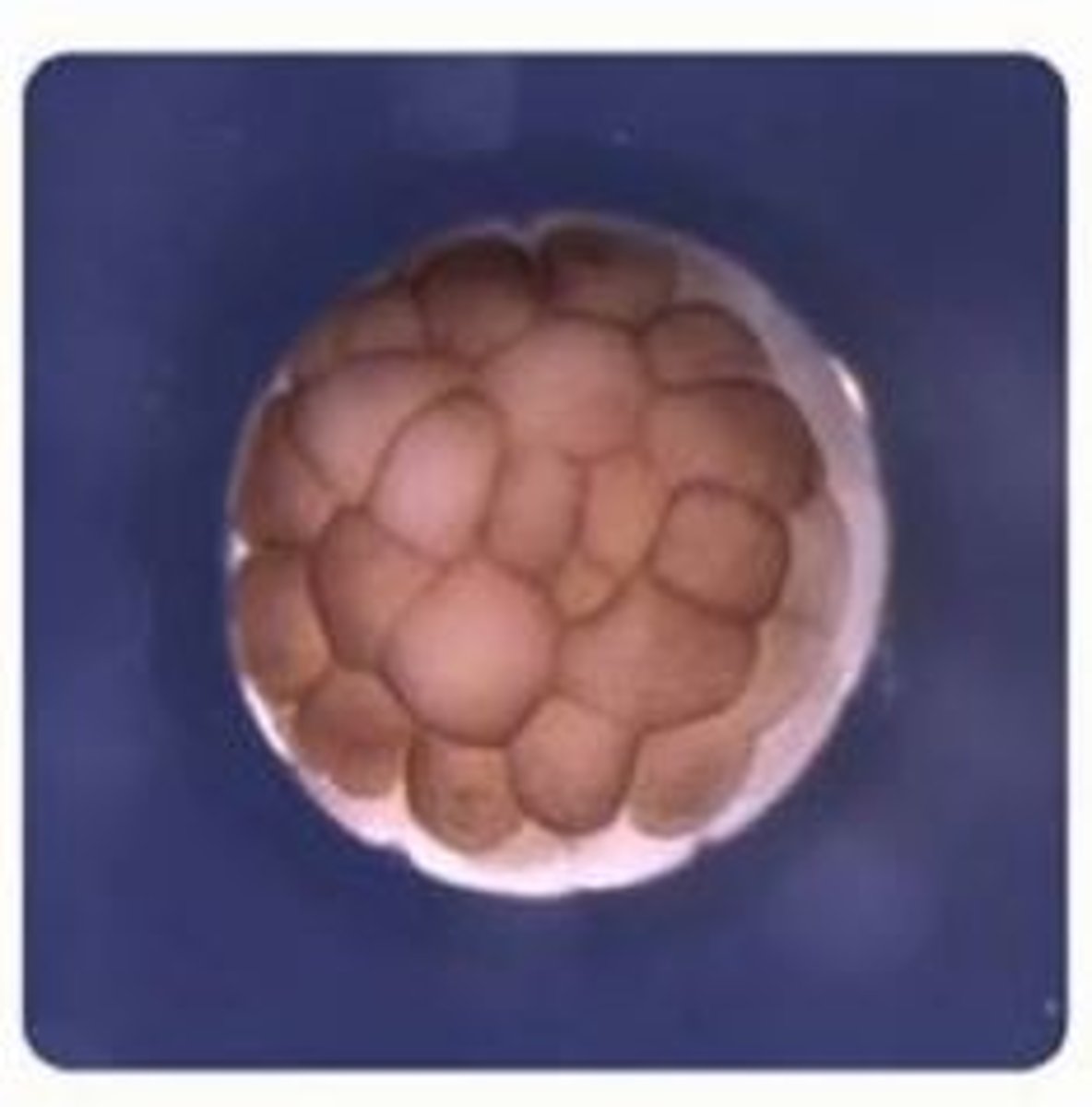
Stem cells
Unspecialized cells in the embryo that have the ability to differentiate into the different cells in your body; as stem cells differentiate most of them lose the ability to become any type of cell
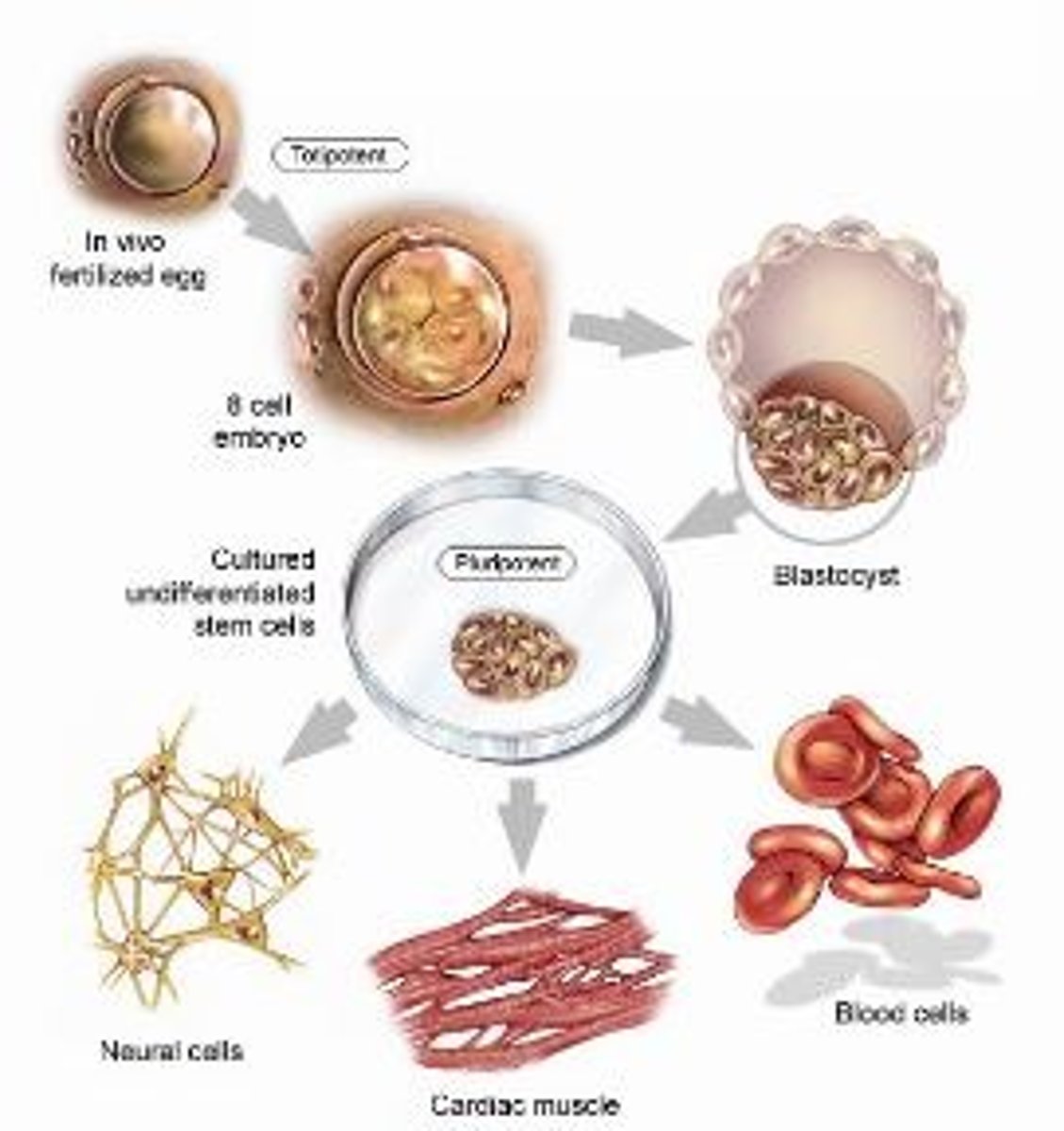
Cell Differentiation in Humans
The process by which cells develop specialized functions; occurs when different genes are turned on and off, allowing only some genes to be expressed; by birth there are 200 different cells
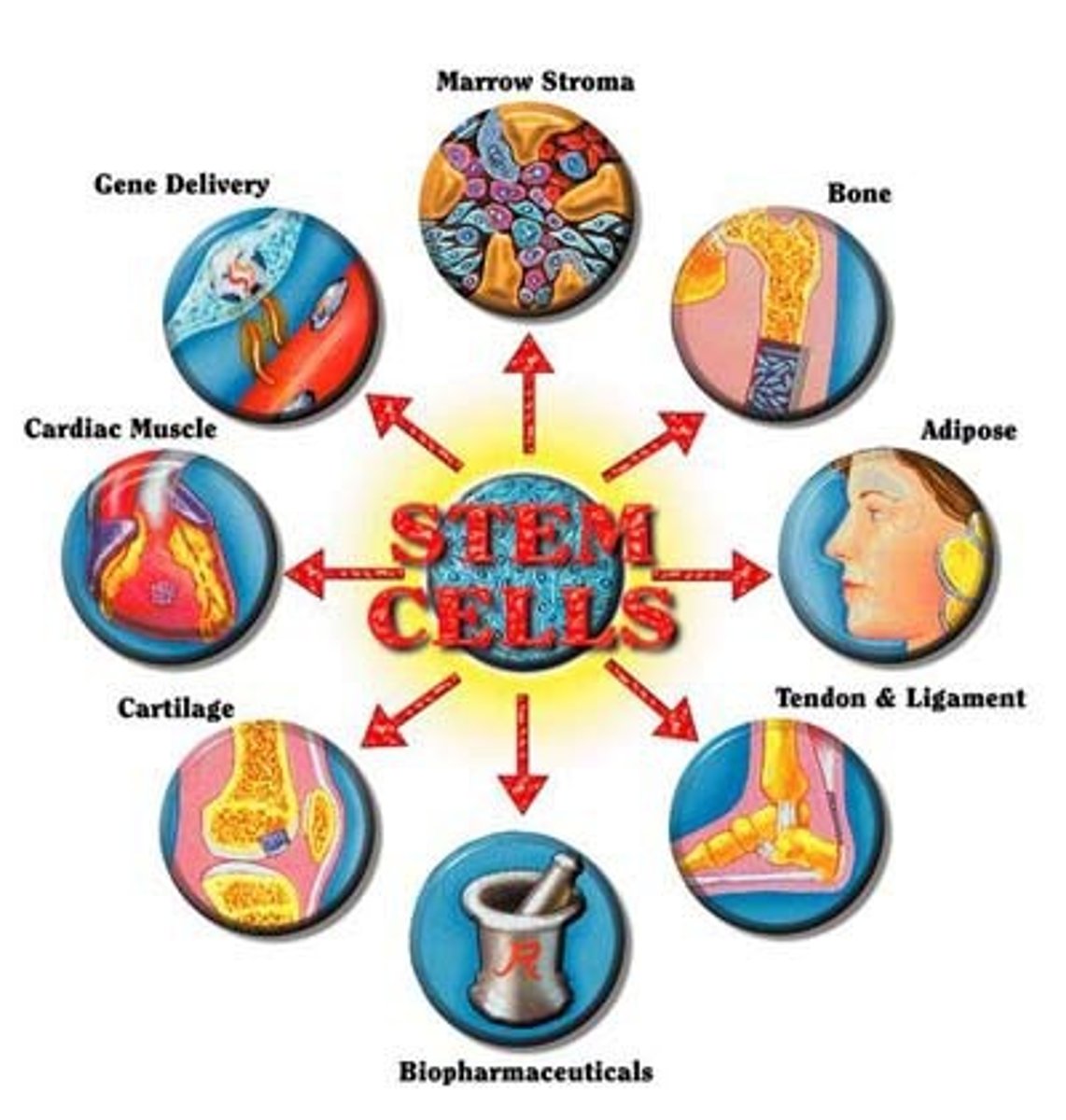
Reproductive Cycle in Humans
Growth and reproduction of an individual