Chemical bonding and language
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
what is covalent bonding
electrostatic attraction between the protons in the nucleus and the shared pair of electrons
what is ionic bonding
electrostatic attraction between the cation and anion formed by the transfer of electrons from a metal to a non-metal
what is metallic bonding
the electrostatic attraction between metal ions, arranged in a lattice structure and the free-floating electrons around them
why can ionic compounds only conduct electricity in molten form
as a solid —> ions are bonded in a lattice
electrons aren’t free to move
why are metals malleable and ductile
layers of metals ions can easily slide over each other without breaking the bonds —> the electrostatic attraction is strong
why can metals conduct electricity
sea of delocalized electrons that are free to move when a voltage is applied
structure of silica (SiO2)
each silicon atom is bonded to four oxygen atoms
forms similar shape as diamond
properties of metalloids
solids at room temp
some have metallic luster
brittle
intermediate electrical conductivity
moderate densities
examples of metalloids
boron
silicon
what is an alloy
mixture of a metal with other metals or carbon designed to improve its properties e.g. strength or resistance to corrosion
how are an alloy’s properties different to the parent metal
harder
different elements in the alloys = different size therefore regular lattice arrangement broken
this makes it more difficult for the ions to slide over each other
uses for copper and suitability
electrical wires - very good conductor of electricity and ductile
pots + pans - very good conductor of heat, very unreactive, malleable
water pipes - unreactive to hot or cold water and malleable
surfaces in hospitals - antimicrobial properties
different types of steel
mild steel - iron + 0.25% carbon
high-carbon steel - iron + 0.6-1.2% carbon + small amount of manganese
stainless steel - iron + chromium + nickel
uses of mild steel and suitability
machinery - increased hardness and strength
car bodies - malleable and ductile
define malleable
can be easily hammered into various shapes
define ductile
can be easily drawn into wires
uses of high-carbon steel
cutting tools
harder
more resistant to wear than mild steel
BUT more brittle
define brittle
breaks or shatters more easily when a force is applied and doesn’t bend and stretch
uses of stainless steel
sinks
saucepans
knives
forks
gardening tools
chemical industries e.g. brewing and dairy where corrosive resistant is essential - chromium = strong layer of oxide + protects iron
what is volatility
how easily a substance evaporates
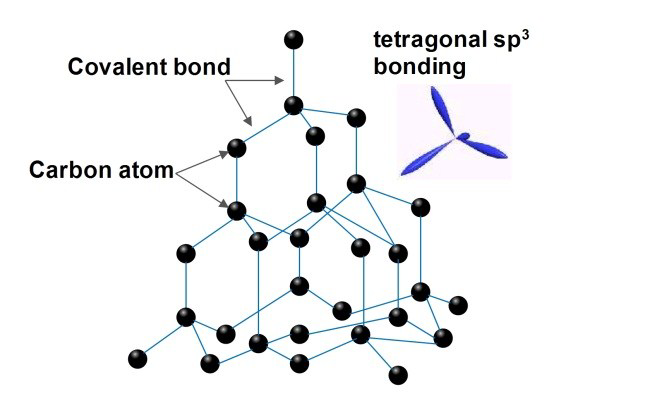
structure of diamond
each carbon atom bonds with 4 atoms
max number of bonds made
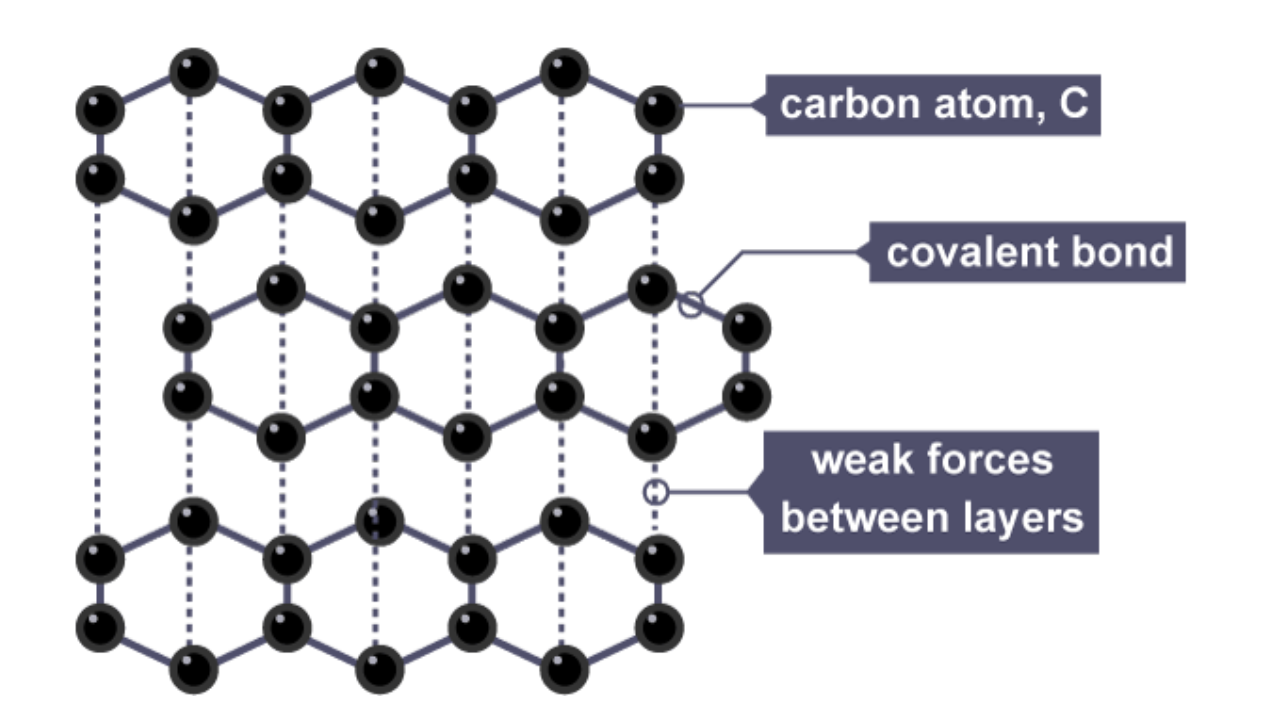
structure of graphite
each carbon atom bonds with 3 carbon atoms
layers slide over each other
sea of delocalised electrons
fullerene (C60)
made of 60 carbon atoms (or more)
carbon atoms for pentagons and hexagons

what are the three allotropes of carbon
diamond
graphite
fullerene
what are allotropes
a different form of the same element in the same physical state where atoms are arranged in a different structure
properties of diamond and why
very hard
high melting point
not a conductor
strong covalent bonds throughout and NO free electrons
properties of graphite and why
soft/slippery
conducts electricity
high melting point
layers slide over each other + sea of delocalised electrons are free to move when voltage is applied
properties of fullerene and why
soft
low melting point (comparably)
conducts SOME electricity
molecules held by weak forces + electrons move WITHIN molecules but not BETWEEN
properties of silica (silicon dioxide) and why
very high MP - lots of strong covalent bonds that need energy to break
hard
insoluble - covalent bonds are too strong to be taken over by water
doesn’t conduct electricity - no free moving electrons or ions