Basic Organic and Water Chemistry Biology Quiz
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/119
Last updated 3:33 PM on 11/13/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
120 Terms
1
New cards
organic chemistry
the chemistry of organisms
2
New cards
inorganic chemistry
the chemistry of the nonliving world
3
New cards
Chemists of the nineteenth century belief
molecules of cells must contain a vital force
4
New cards
organic molecules
contain both carbon and hydrogen atoms (can be synthesized in the lab)
5
New cards
four classes of organic compounds
carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids
6
New cards
How many electrons does carbon have?
6 electrons
7
New cards
How many electrons are in carbon's first shell?
2 electrons
8
New cards
How many electrons are in carbon's outer shell/valence?
4 electrons
9
New cards
What are the elements that make up most of the weight of living things?
CHNOPS
10
New cards
How many electrons does carbon need to complete its valence?
4
11
New cards
What are hydrocarbons?
chains of carbon atoms bonded exclusively to hydrogen atoms
12
New cards
What do double bonds do?
they restrict the movement of attached atoms and contribute to the shape of the molecule
13
New cards
What bonds can carbon form?
single, double, triple
14
New cards
What is the carbon chain of an organic molecule?
its skeleton or backbone
15
New cards
What is a functional group?
a specific combination of bonded atoms that always reacts in the same way, regardless of the particular carbon skeleton
16
New cards
Hydrophobic
not soluble in water
17
New cards
hydrophilic
soluble in water
18
New cards
What are isomers?
organic molecules that have identical molecular formulas but a different arrangement of atoms
19
New cards
isomers are variations in the _________ ____________ of a molecule
molecular architecture
20
New cards
Organic molecules are _______ and _______
diverse; complex
21
New cards
Carbon _________ vary in shape and size
skeletons
22
New cards
__________ ______ have various chemical characteristics
functional groups
23
New cards
Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids are called?
macromolecules because of their large size
24
New cards
Polymers
the largest of macromolecules that are constructed by linking together a large number of monomers
25
New cards
Monomers
same type of subunits in polymers
26
New cards
How can polymers get so large?
Cells use the modular approach when constructing polymers; they get longer as monomers bond to one another
27
New cards
dehydration reaction
when cells use the same type of condensation reaction to synthesize any type of macromolecule because the equivalent of a water molecule is removed as the reaction occurs
28
New cards
hydrolysis reaction
when water is used to break the bond holding subunits together
29
New cards
all types of reactions in cells need ______ present
enzymes
30
New cards
What do enzymes do?
molecules that bring reactants together to speed up reactions
31
New cards
________ usually have to be activated to react
monomers
32
New cards
_______ _________ are routinely built up in cells by the removal of water during a dehydration reaction
organic molecules
33
New cards
Organic molecules are degraded in cells by the addition of water during a __________ ________
hydrolysis reaction
34
New cards
What do chemicals make up?
our bodies, the bodies of other organisms, and the physical environment
35
New cards
What is life's chemistry tied to?
water
36
New cards
Life first evolved in _____
water
37
New cards
All ______ _____ require water
living things
38
New cards
The chemical reactions of your body occur in cells consisting of how much water?
70-90%
39
New cards
What are living organisms composed of?
matter
40
New cards
matter
anything that has mass and occupies space
41
New cards
What is matter composed of?
chemical elements
42
New cards
element
a substance that cannot be broken own by other substances
43
New cards
How many types of atoms are in an element?
one
44
New cards
What are the most common elements?
Carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen, calcium, phosphorus, potassium, sulfur, sodium, chlorine, magnesium
45
New cards
What elements make up 96% of living matter?
carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen
46
New cards
Why are trace elements important?
Crucial to many body functions, including metabolic pathways and some are required to prevent disease
47
New cards
Nonpolar bonds
bonds that share electrons equally
48
New cards
What type of bond is a nonpolar bond?
covalent
49
New cards
What type of bonds can nonpolar covalent bonds have?
single, double, and triple bonds
50
New cards
hydrogen structural formula
H * H
51
New cards
hydrogen molecular formula
H2
52
New cards
polar bond
bonds that share electron unequally
53
New cards
What type of bond is a polar bond?
covalent
54
New cards
What type of bond is more likely to be found around one atom?
polar covalent bonds
55
New cards
In what bond do molecules develop slight changes or poles?
polar covalent bonds
56
New cards
Can polar covalent bonds be represented in molecular or structural formulas?
yes
57
New cards
Water atomic structure
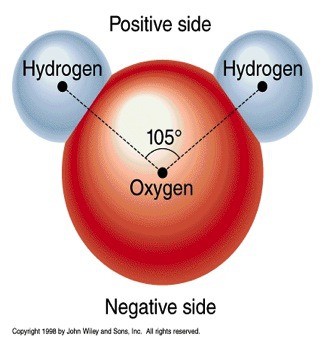
58
New cards
Ionic bond
occurs when electrons are taken from one atom by another atom
59
New cards
___ ____ are very important in biological structures
free ions
60
New cards
What breaks down water into ions?
salt
61
New cards
What are strong bonds?
covalent (polar and nonpolar) and ionic bonds
62
New cards
What are weak bonds?
hydrogen bonds
63
New cards
hydrogen bonds
weak attractions between a hydrogen ion and a polar molecule
64
New cards
In living systems the polar molecule in hydrogen bonds are usually what?
oxygen or nitrogen
65
New cards
What do hydrogen atoms bond to in a water molecule?
oxygen
66
New cards
Cohesion
holds water molecules together
67
New cards
adhesion
holds water molecules to other polar substances
68
New cards
surface tension
caused by cohesion of water to itself and lack of adhesion to air
69
New cards
Water has an extremely ___________ specific heat.
high
70
New cards
It takes a lot of ______ to raise water's temperature
energy
71
New cards
It takes energy to break ________ _____ between water molecules
hydrogen bonds
72
New cards
Water helps moderate ___________
temperature
73
New cards
Water is most dense at what temperature?
4°C
74
New cards
What holds molecules apart in solid structure?
hydrogen bonds
75
New cards
What insulates bodies of water?
ice
76
New cards
Water _________ a huge range of compounds (H-bonds)
dissolves
77
New cards
solution
evenly distributed mixture of 2 or more substances
78
New cards
solvent
substance that is dissolving another substance
79
New cards
solute
substance being dissolved
80
New cards
hydrophobic sustances...
do not form H-bonds with water
81
New cards
hydrophobic examples
oil, membranes, some proteins
82
New cards
hydrophilic substance...
form H-bonds with water
83
New cards
hydrophilic examples
ions, sugars, cellulose, some proteins
84
New cards
How many hydrogen atoms are in a molecule of water?
2 hydrogen atoms
85
New cards
How many oxygen atoms are in a molecule of water?
1 oxygen atom
86
New cards
What holds the hydrogen atoms to the oxygen atom?
covalent bond
87
New cards
Where is the majority of negative charge on a water molecule?
around the oxygen atom
88
New cards
What is the bond between a hydrogen atom and an oxygen atom in the same water molecule?
covelant bond
89
New cards
What is the bond between a hydrogen atom in one molecule and an oxygen atom in another molecule?
hydrogen bond
90
New cards
What causes the attractions between molecules of water?
the positive charge of a hydrogen atom attracts to the negative charge of an oxygen atom from another molecule
91
New cards
Suspensions
a mixture of water and a non-dissolved material
92
New cards
Suspension examples
blood (also a solution) and mud
93
New cards
pH 0
strong acid
94
New cards
pH 14
strong base
95
New cards
acids
have extra H+ ions, have a pH less than 7, ex. hydrochloric acid and vinegar
96
New cards
bases
have more OH- ions, have a pH greater than 7, also called Alkalines, ex. soap and ammonia
97
New cards
Neutral
solutions have exactly the same number of H+ and OH- ions, pure water... has one H+ for every OH-, ex. tap water usually has a pH just above 7
98
New cards
Buffers
weak acids or bases that react with strong acids or bases to prevent sudden changes in pH (help maintain homeostasis in the body)
99
New cards
Polar substances can dissolve _____ _____ _________
other polar substances
100
New cards
Non-polar substances dissolve ______ ______ ________
other non-polar substances