B7.2 Transport in Mammals | Quizlet
1/20
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
cardiovascular system
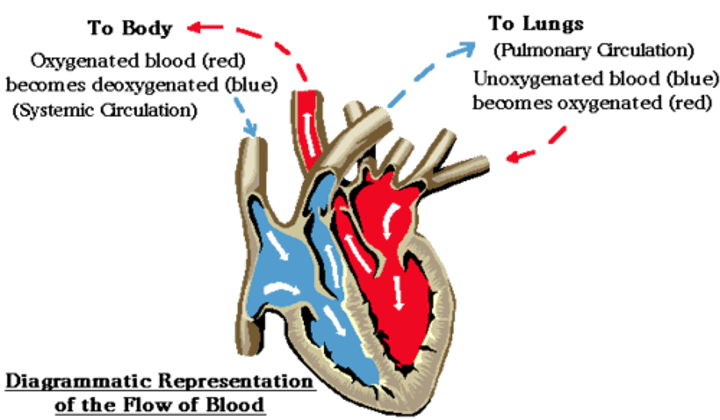
Blood vessels transport blood, which carries oxygen, carbon dioxide, nutrients, wastes, etc. The heart pumps blood.
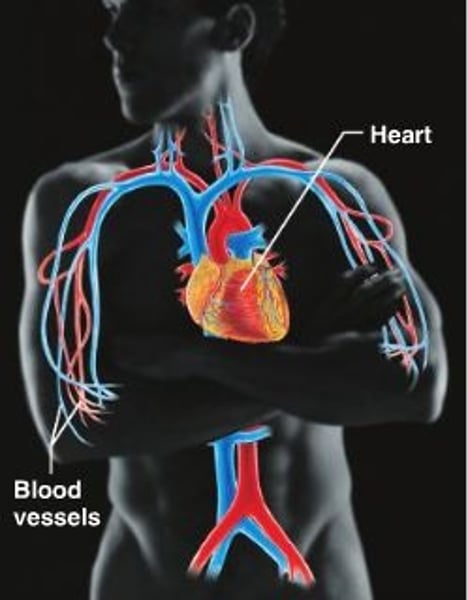
Double circulatory system
Blood passes through the heart twice in one complete circuit of the body e.g. in a human
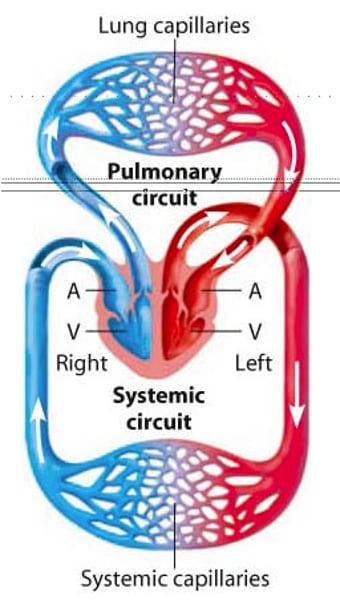
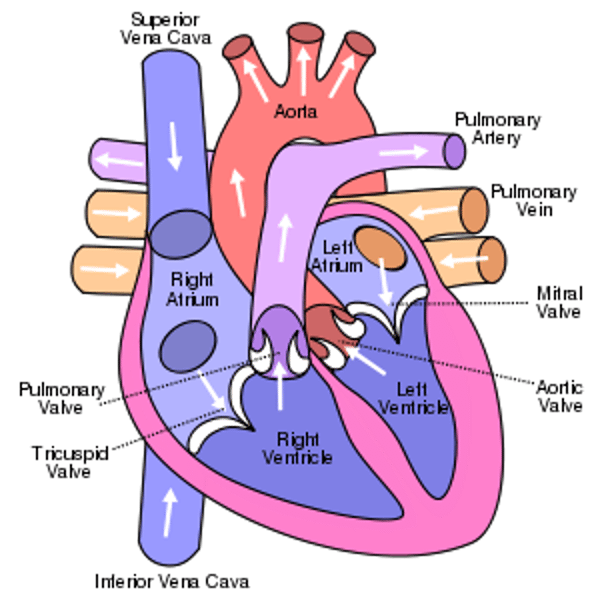
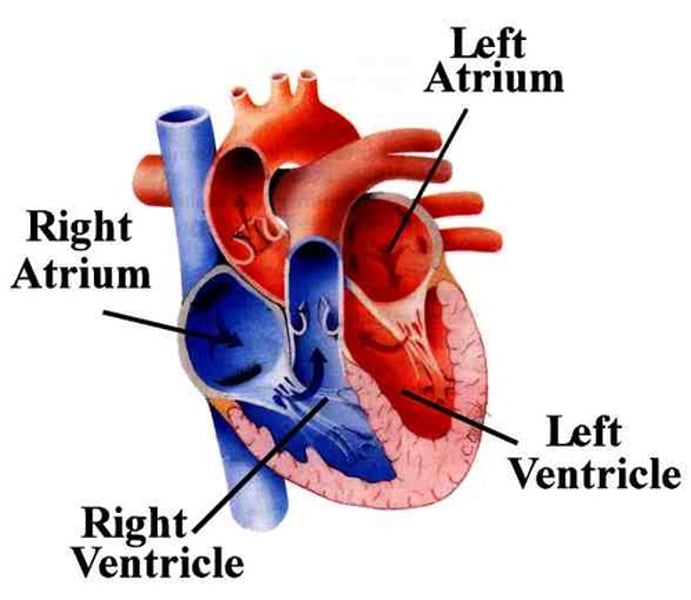
left vs right side of the heart
Left ventricle and left atrium are oxygen rich blood and right ventricle and right atrium and ventricle have oxygen poor blood
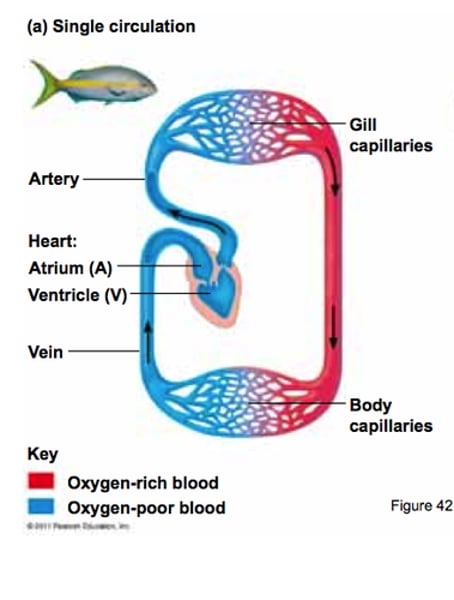
Single circulatory system
Blood passes through the heart once only in a complete circuit of the body e.g. in a fish
Pulmonary
pertaining to the lungs
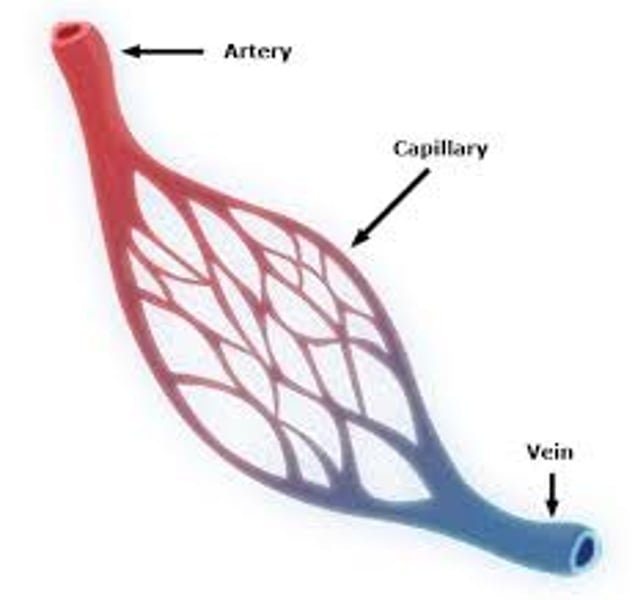
Capillaries
Microscopic vessel through which exchanges take place between the blood and cells of the body
atria function
receive blood returning to the heart
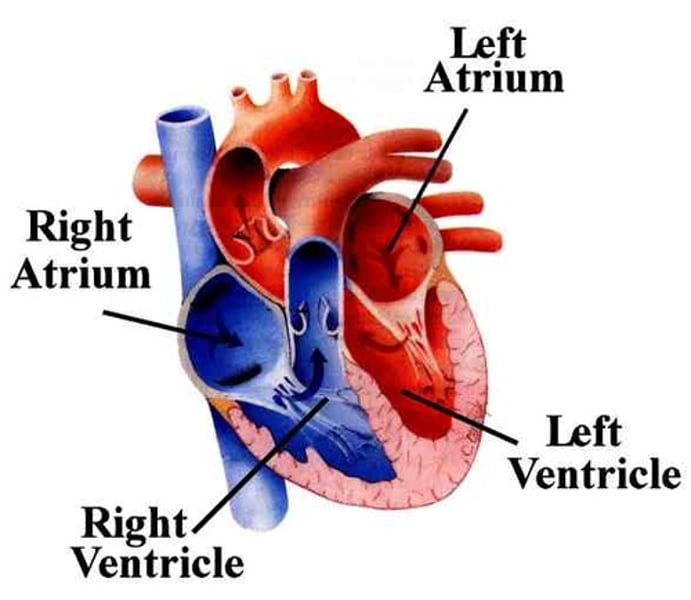
ventricles function
pumps blood out of the heart
function of pulmonary veins
carry oxygenated blood from the lungs to the left atrium
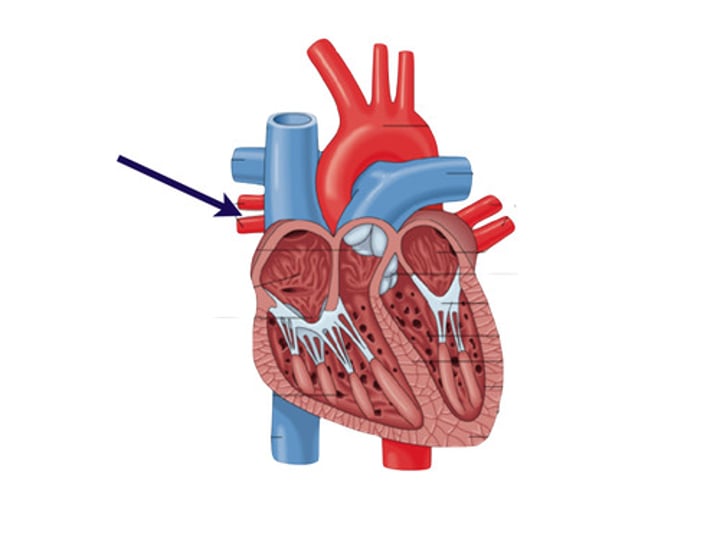
Function of pulmonary artery
carries deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle to the lungs.
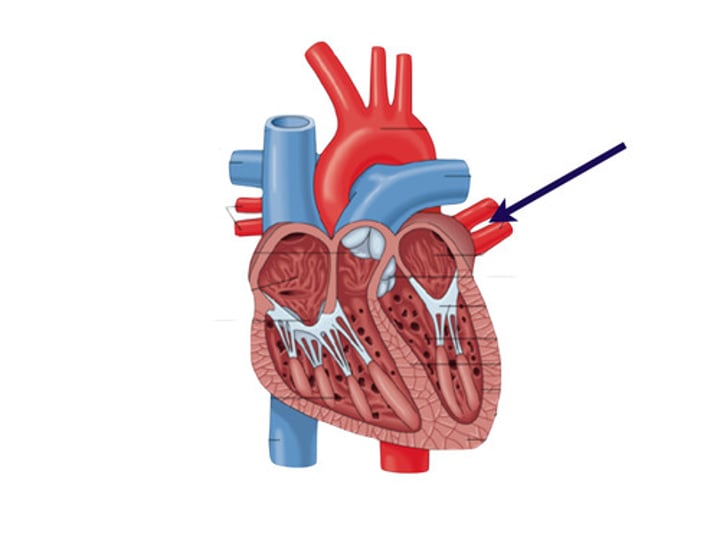
function of aorta
carries blood from the left ventricle to the arteries serving all the parts of the body
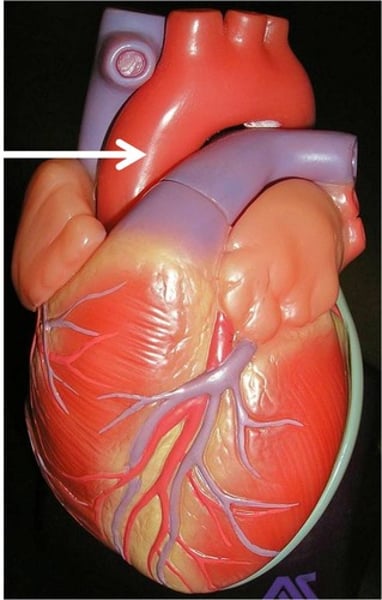
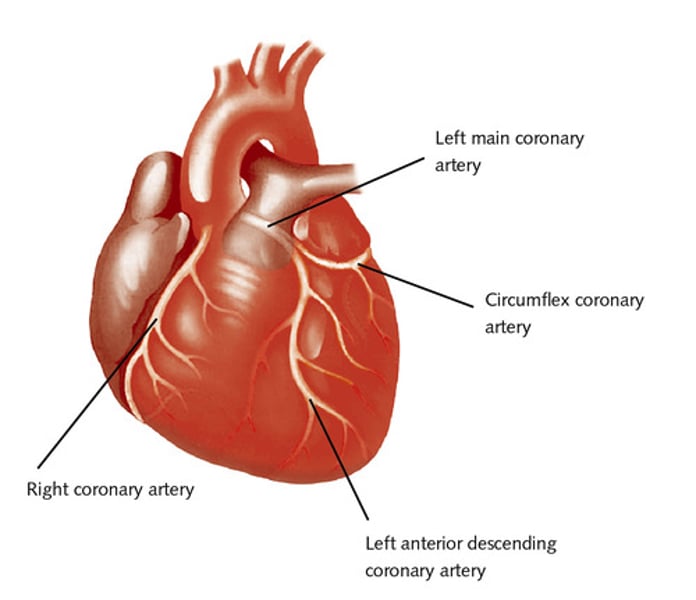
coronary arteries function
supply blood to the heart muscle
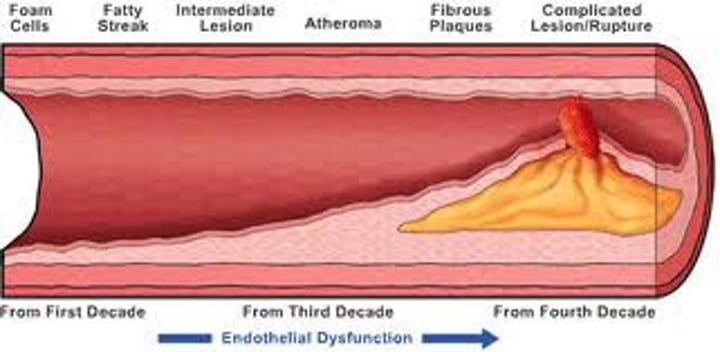
Artherosclerosis
Hardening and narrowing of the arteries due to buildup of cholesterol plaques
pulse
The rhythmic expansion and recoil of arteries resulting from heart contraction; can be felt from the outside of the body.
pacemaker
A device that delivers electrical impulses to the heart to regulate the heartbeat
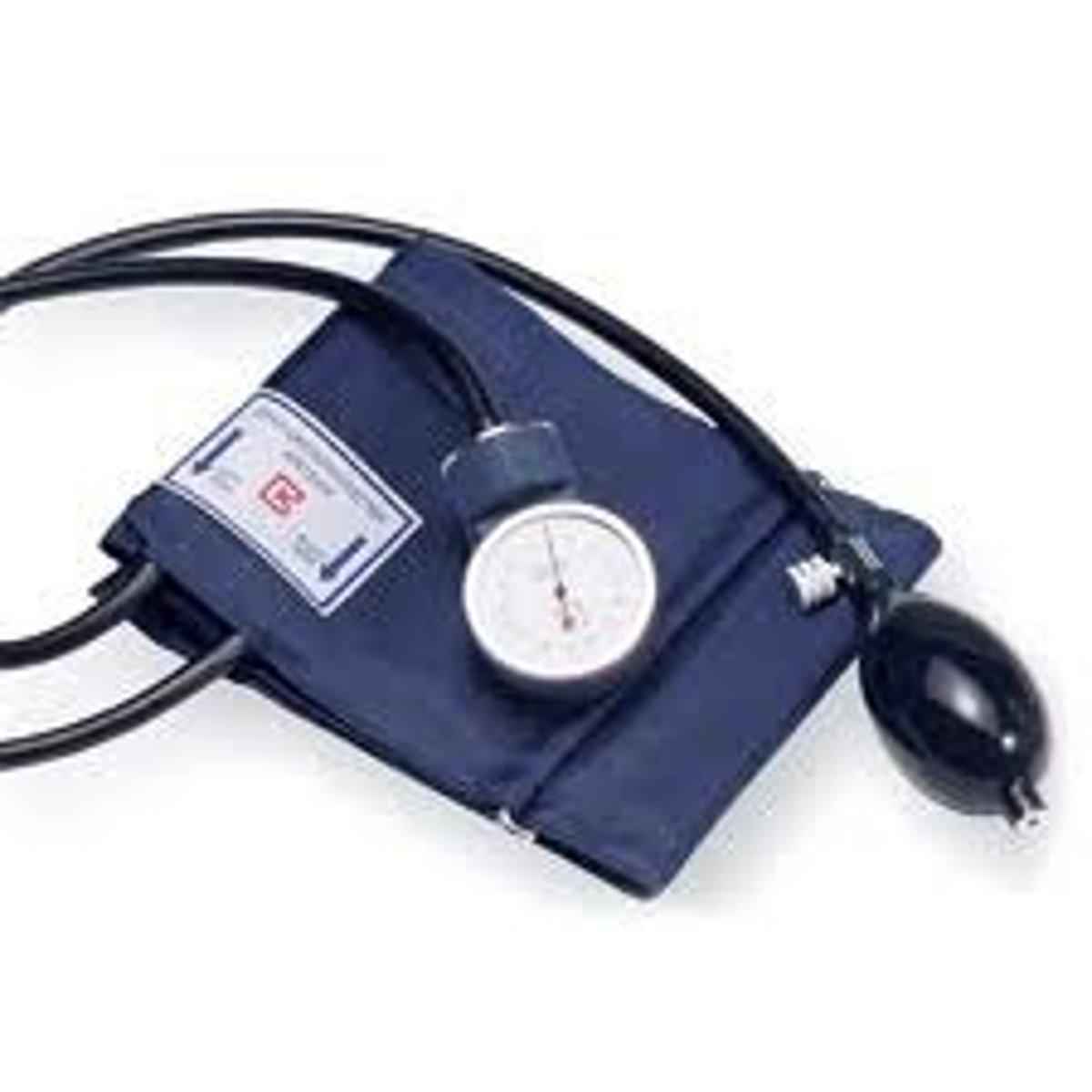
sphygmomanometer
instrument to measure blood pressure
platelets function
blood clotting
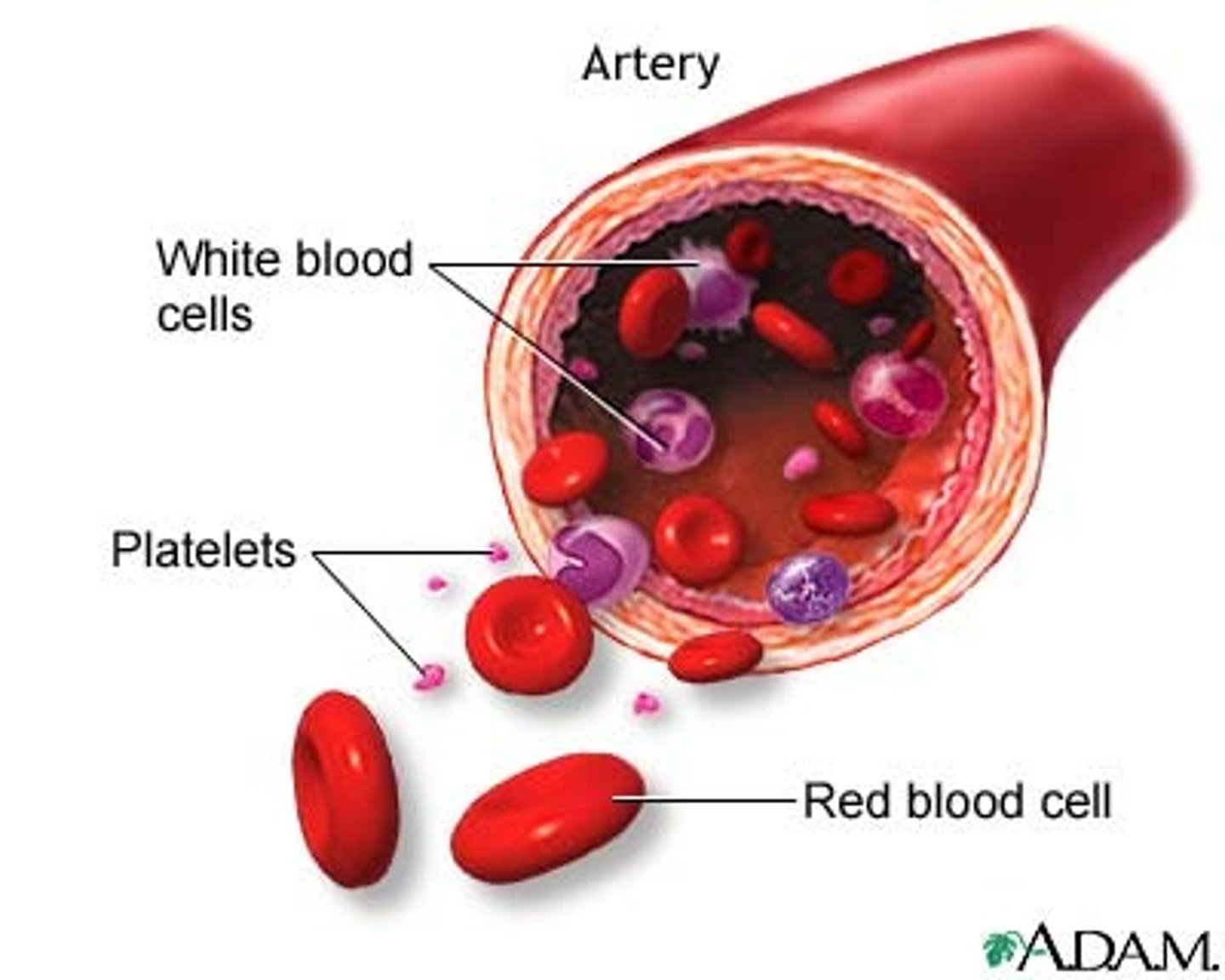
white blood cells (leukocytes)
innate capacity to recognize and differentiate any foreign material
Plasma
Liquid part of blood
red blood cells (erythrocytes)
transport oxygen and carbon dioxide
Phagocytes
a type of cell within the body capable of engulfing and absorbing bacteria and other small cells and particles.
