photosynthesis
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
what is energy used for in animals?
. muscle contractions
. cell division
. DNA replication
. maintenance of body temperature
. active transport
what is energy used for in plants?
. photosynthesis
. cell division
. DNA replication
. opening and closing of stomata
. active transport
what are the essential properties of ATP
. stores/ releases manageable energy amounts only (no heat is wasted)
. small and soluble
. easily broken down
.quick to remake
. make other molecules more reactive (phosphorylation)
. cannot leave the cell
what is the ATP cycle
. During respiration ATP is made for use as an energy source
. Respiration released energy from glucose in stages and uses to join ADP and Pi to make ATP in a condensation reaction using ATP synthase
.when energy is required the ATP is hydrolysed releasing energy
what the photosynthesis eqaution
Water + carbon dioxide > oxygen + glucose
what is the respiration equation
glucose + oxygen > carbon dioxide + water
what is the role of photosynthesis
. converts light energy from sun light to chemical energy stored in carbon compounds including carbohydrates, proteins and lipids
. provides energy for most food chains
what is photolysis
the use of energy to split water
how does photolysis use energy to split water
. frees up H+ ions which reduces carbon dioxide into glucose
. electrons used to provide energy in the reaction
. oxygen diffuses out of cell as a waste product from high concentration to low in the atmosphere
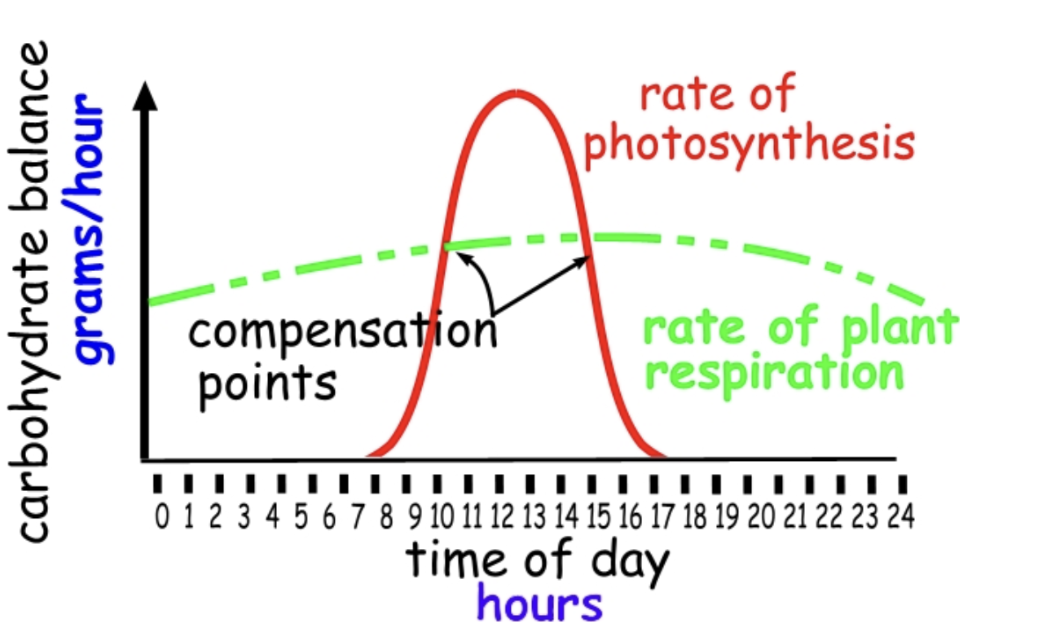
what is a compensation point
. its where the rate of respiration and photosynthesis proceed at the same rate
. no net gain or loss of oxygen
. no net gain or loss of carbohydrates
key notes for compensation points on graphs
. x-axis is light intensity or time, y-axis is carbon dioxide exchange
. crossing point is at 0
. negative number means carbon dioxide release and low light intensity
. positive number means carbon dioxide uptake and high light intensity
structure of chloroplast DNA
a small, circular double stranded molecule found in the stroma
structure of the inner and outer membrane
they make up the chloroplast envelope, both membranes have a phospholipid bilayer
structure of the inter membrane space
this is the fluid filled pace between the two membranes, it is extremely small 10-20nm thick in chloroplasts
structure of the chloroplast ribosomes
these are small 70s ribosomes which make the chloroplast protein, smaller than the ribosomes in the chloroplast
structure of the stroma
its a dense gel like matrix containing rubisco, DNA, ribosomes and starch granules
role of the stroma
. where light independent reactions occur
. within the stroma there are enzymes, sugars, proteins and lipids to fuel the calvin cycle
starch grain structure and role
they are storage structures composed of polymerised glucose (amylose and amylopectin) formed in the stroma for photosynthesis
structure of granum
its a stack of thylakoid membranes, which can be two or more
structure of lamella
they are thylakoids organised into stacked grana connected by the stroma lamellae
structure and role of the thylakoid
they are flattened disc-like membranous sacs within chloroplasts that serve as the site for light dependent reactions of photosynthesis
photosynthetic pigments
. they are coloured substances that absorb the light energy needed for photosynthesis
. found in the thylakoid membranes and attached to proteins
. this is called a photosystem
pigments
. chloroplasts contain several different photosynthetic pigment within the thylakoids, which absorb different wavelengths of light
. in higher plants for example flowers and trees photosynthetic pigments are split into two groups chlorophylls and carotene
. plants have different pigments to absorb light at different wavelengths
. chlorophyll pigments mainly absorb light in the red and blue-violet regions of the light spectrum reflecting green
photosystems
arrangement of pigments
the origin of chloroplasts