Different Types of Intermolecular forces
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
What is intermolecular force ?
Is a type of forces that hold molecules together, ie : between molecules
The further away from the nucleus the intermolecular force are stronger
What are the 3 types of intermolecular forces ?
Van Der Waals ( weakest IM force )
Permanent dipole - permanent dipole
Hydrogen Bonding ( Strongest IM force )
What are the types of forces between ionic / covalent bonding ?
Ionic compound / molecules attract through electrostatic force of attraction
Covalent bonding / simple molecular … attract through the 3 types of IM forces
Van Der Waals
weakest bond held between molecules/ last the shortest —> exist between all molecules
No of electrons increased → VDW forces get stringer —> increase the boiling points —→ more eggy needed to overcome the VDW forces
electrons are moved quickly —> likely to move from one to another to create a temporal dipole —. Causes another temporary dipole in the opposite direction. —» Causes a 3rd temporary dipole.
→ Causes an effect of atom / molecule to be attracted to another
If the molecule are branched → VDW forces get weaker as there’s smaller contact space for the IM forces
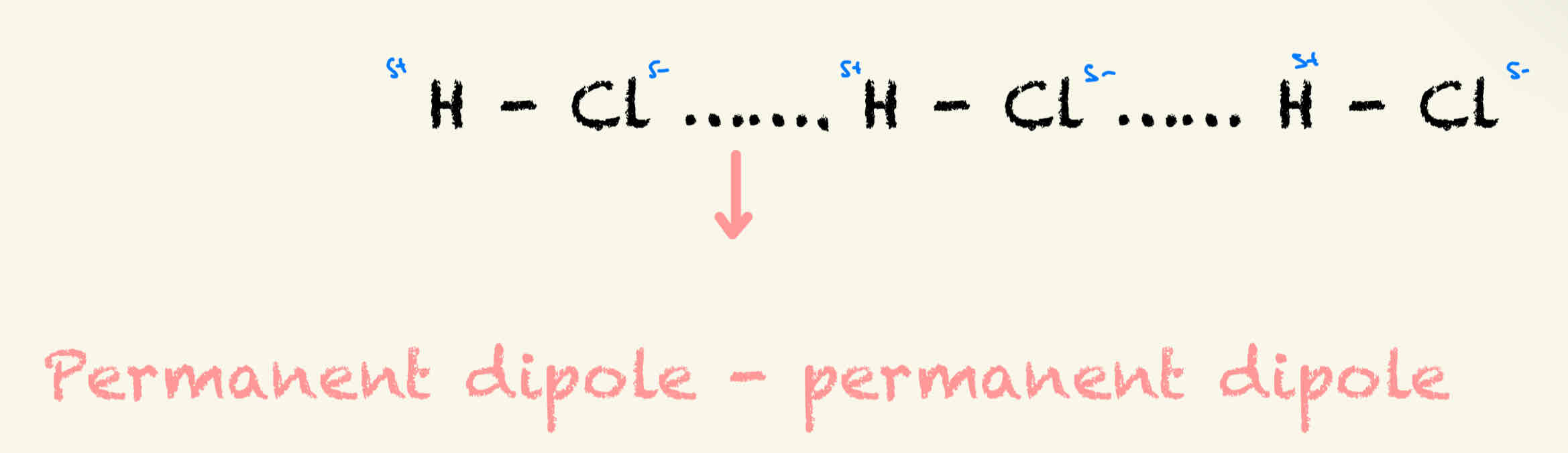
Permanent Dipole - Permanent Dipole
Permanent intermolecular force between 2 dipoles
Theses are in addition to VDW forces
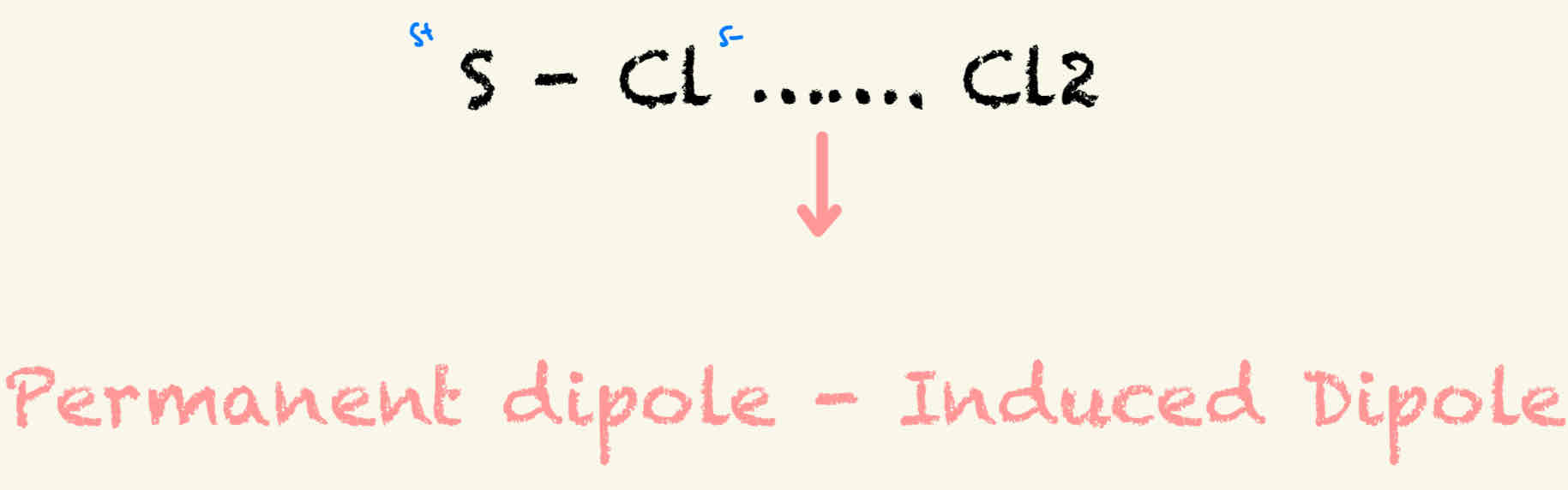
Permanent dipole - induced dipole
need 2 molecules, each with a polar bond. ( 2 elects with a large enough difference in electronegativity)
Stronger than VDW forces / Weaker then PD - PD
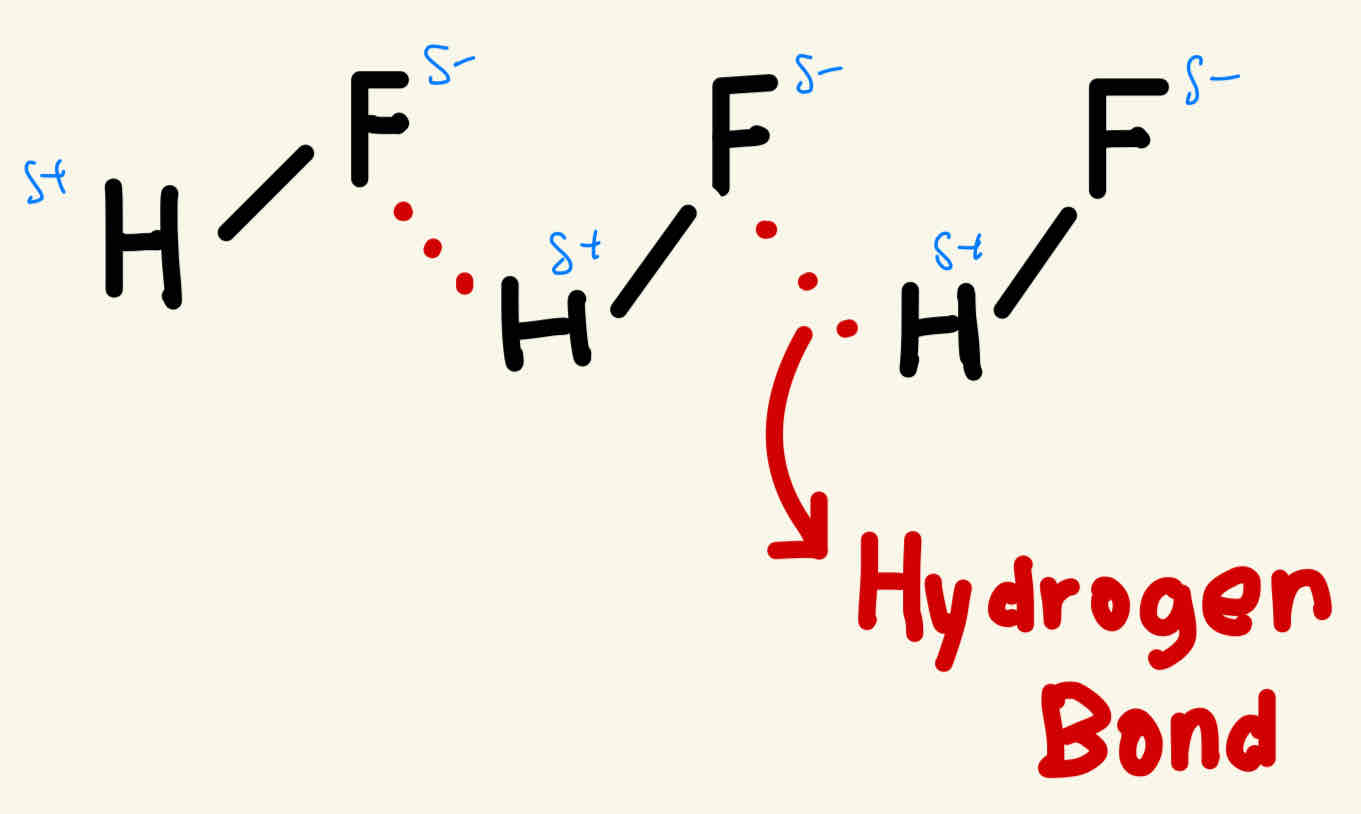
Hydrogen Bonding
HF / H2O / NH3 —> always have a hydrogen bond
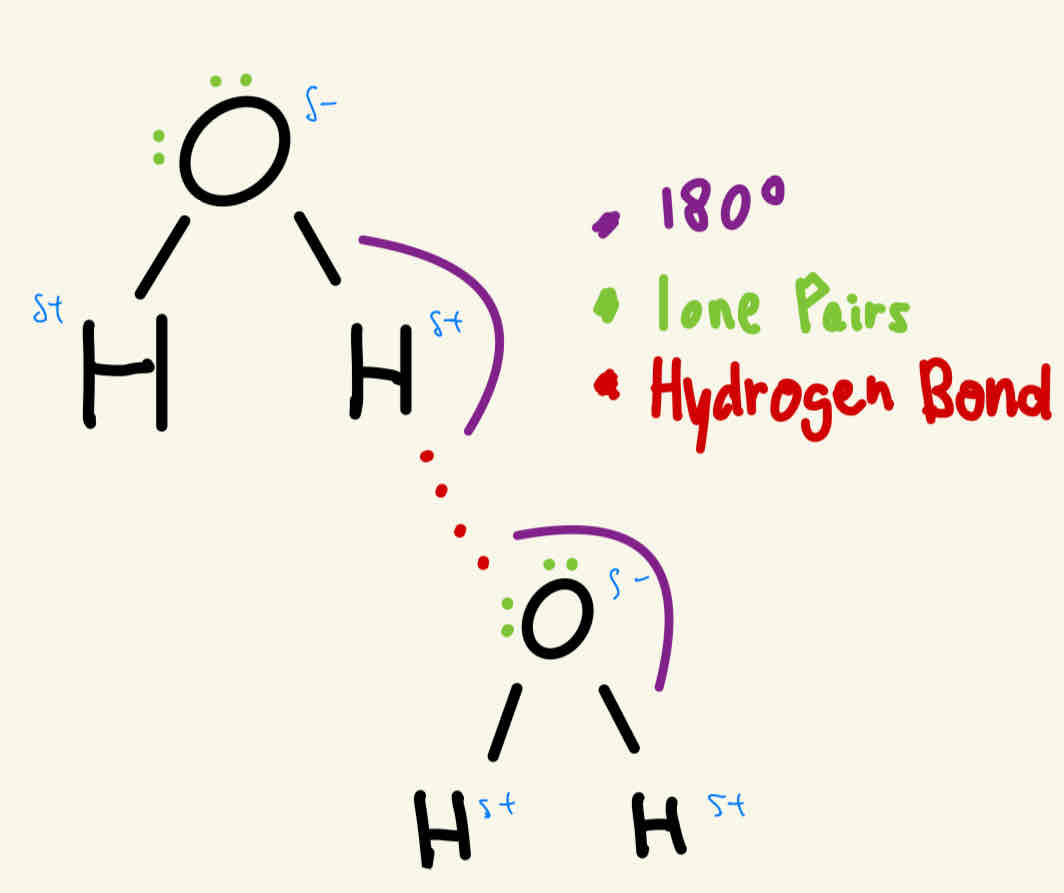
How do we know if it is hydrogen bonds ?
When the hydrogen reacts with nitrogen, oxygen or fluorine
Why is hydrogen bond the strongest
strong electrostatic attraction between a hydrogen atom bonded to a highly electronegative atom (like O, N, or F) and the partial negative charge on another electronegative atom.
Why does iodine have a higher melting point than fluorine?
Cuz as u go down the group the nuclear charge increase , more electrons, stronger VDE forces holding the electrons together