3rd chapter: stars
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
the only star in the solar system
has own source of energy, radiated in all directions throughout the solar system
massive sphere of gases that emit their own light and provide hear (star)
Sun
age of the sun
4.5 billion yrs old
milky way contains more than ______ billion, including our sun
100 billion
The universe could contain up to __________ stars
1 septillion
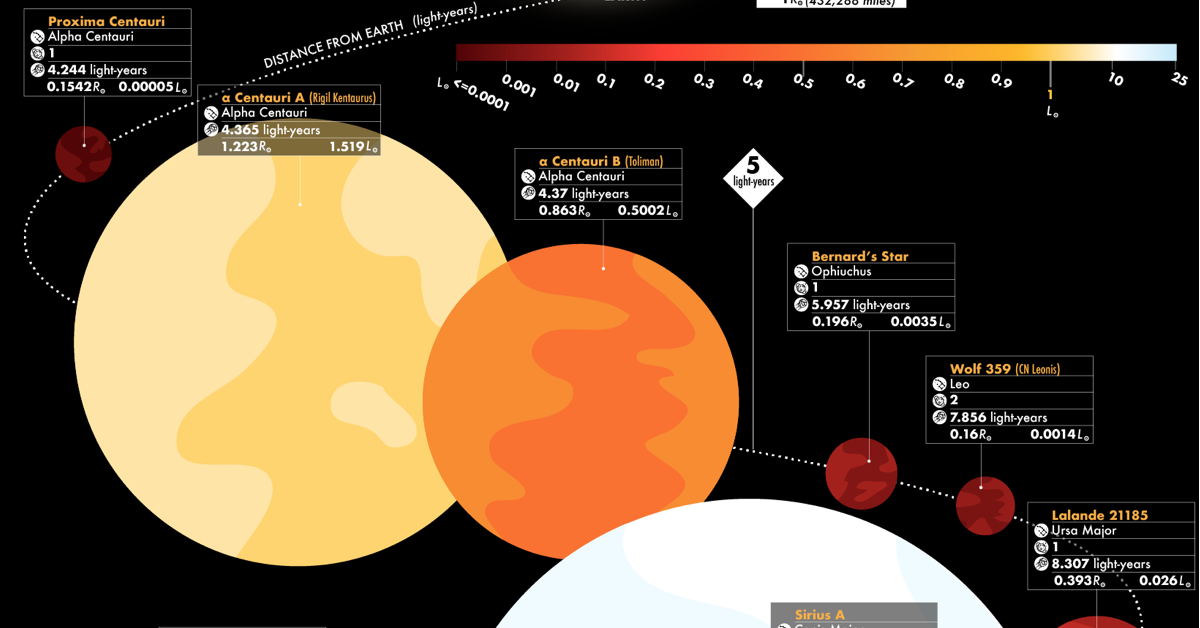
Stars near the sun
alpha centauri A
proxima centauri (the closest)
alpha centauri B
sun/stars are mainly composed of?
91% H (hydrogen) and 8.9% He (helium)
stars emit their own light through process called
Nuclear Fusion
combination of the atomic nuclei from the same element to form another element
nuclear fusion
what size (star) is the sun?
a medium sized star
there are stars with much more mass and are larger than the sun like Betelgeuse
standard unit of mass in astronomy
Solar Mass
Sun = 1 solar mass
Red Dwarf = 0.08 solar mass
Red Giant = < 5 solar masses
Rigel = 3.5 solar masses
the more massive a star is, the greater the gravity,
the hotter and denser a star must be
approximate mass of the sun
1.98892 × 10 ^ 30 kg
the heaviest star is known as
R136a1 (300 times the suns mass)
What color of the star shines with the hottest temp and coolest temp
Blue stars = hotter
Red stars = cooler
because of of wavelength and frequency
R M I V U X G (order of emag spectrum)
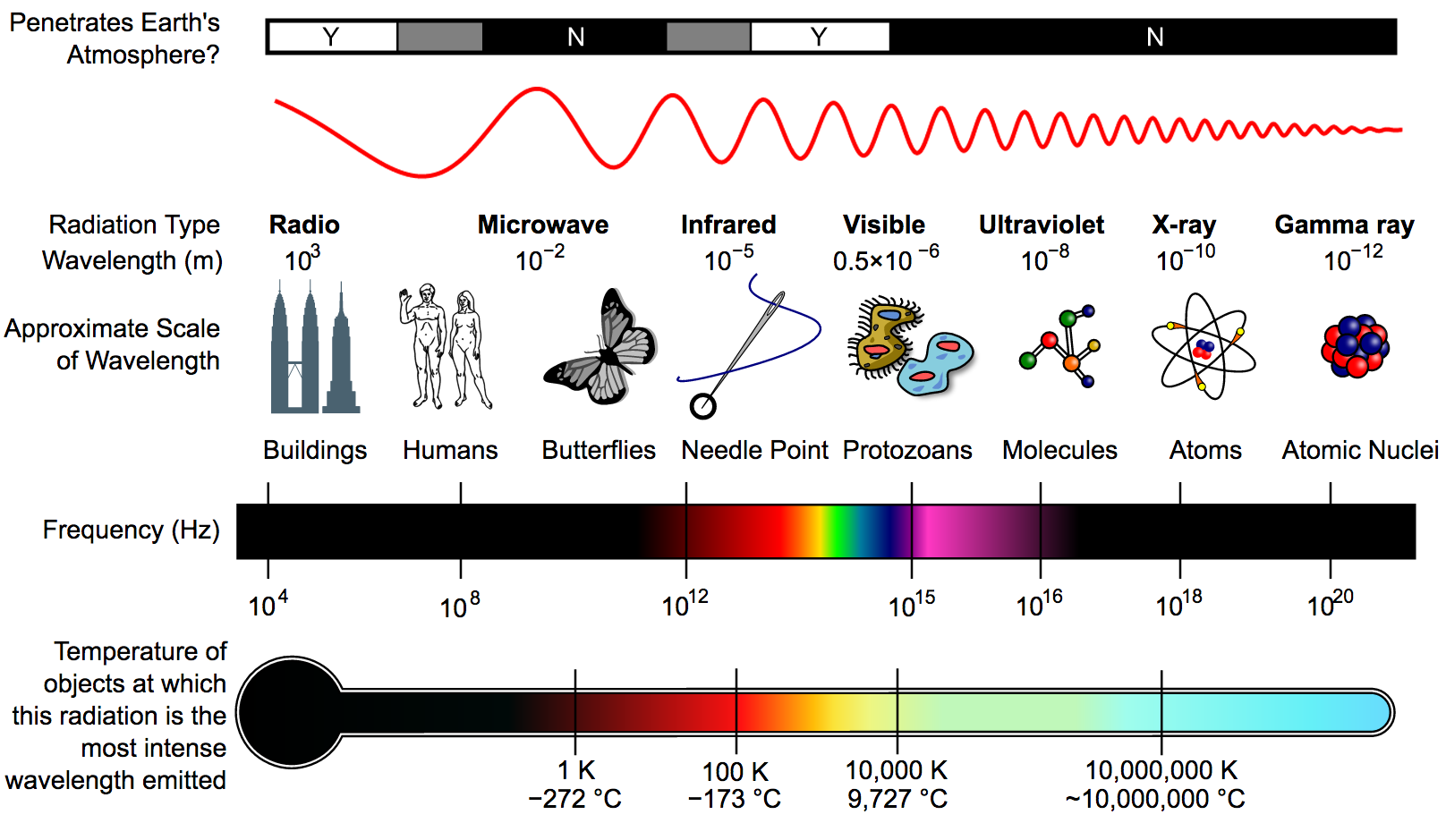
uses the letters O, B, A, F, G, K, and M to designate a star's spectral type, by subdividing the range of possible stellar temperatures, from the coolest, M, to the hottest, O
Morgan - Keenan System
Oh Be A Fine Guy, Kiss Me

surface temp of the sun and its color
Sun is
yellow
surface temp of 5,000 K
astronomers place stars in spectral colors class categories based on their surface temp
the energy output from the surface of a star per second measured in _____
the brightness of a star depends upon the ______ and its ______
watts
distance and luminosity
ways of observing the brightness of the sun
Absolute Magnitude
true brightness of a star
in comparison to sun
Apparent Magnitude
how bright a star appears to be on earth
Rigel is _______ times larger than our sun
Sun and Rigel is approximately _____ light yrs away from each other
60,000
900 light yrs away (the distance light travels in one earth year)
why do stars twinkle?
also called STELLAR SCINTILLATION
light of the star is bent (refracted) many times in diff. directions (layers of the atmosphere)
diagram that describes the relationship between the absolute magnitude, color and temp of stars
Hertzsprung-Russel Diagram
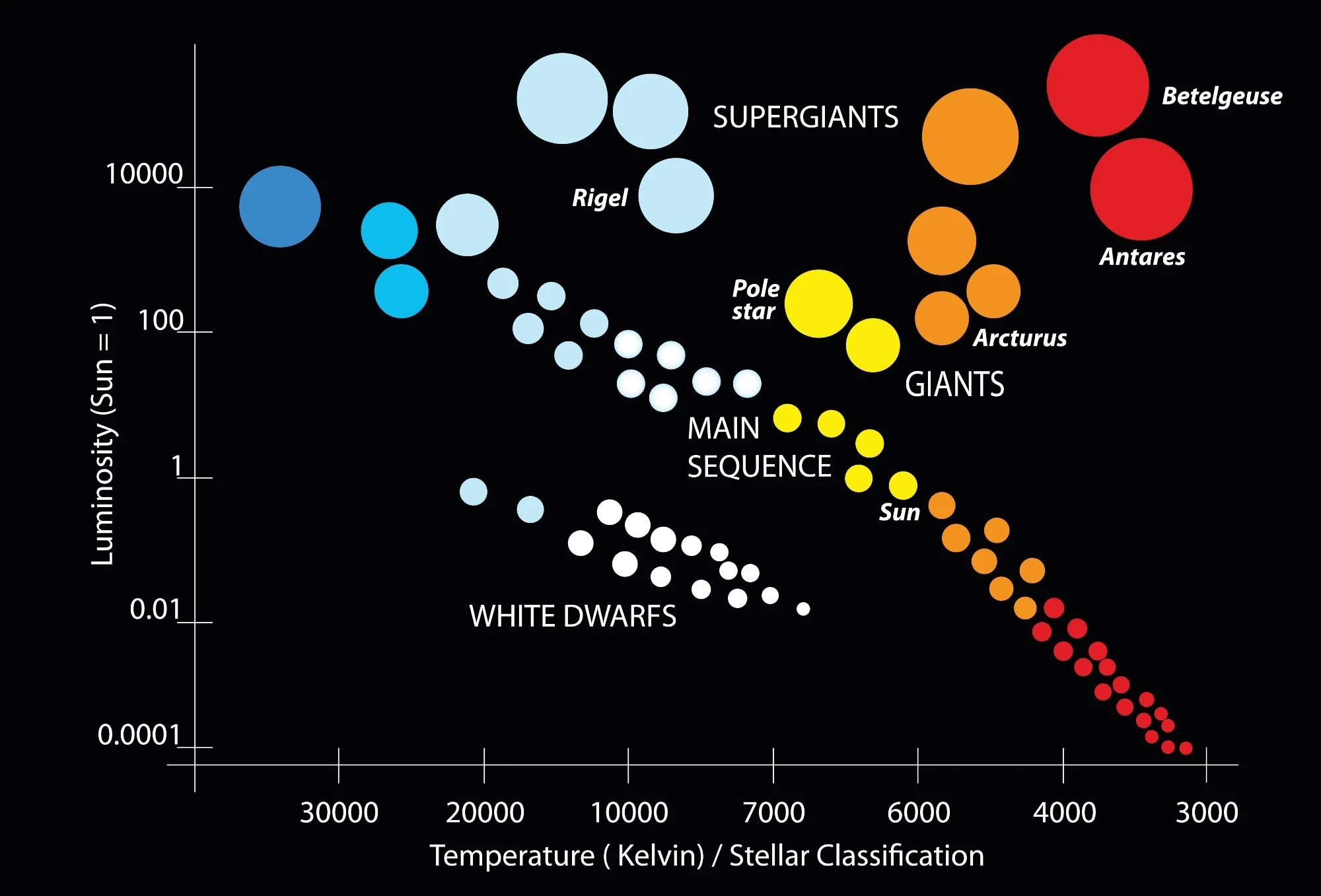
designates the color of the stars
depends on temp
from hot to coolest
Spectral Class (morgan keenan system)
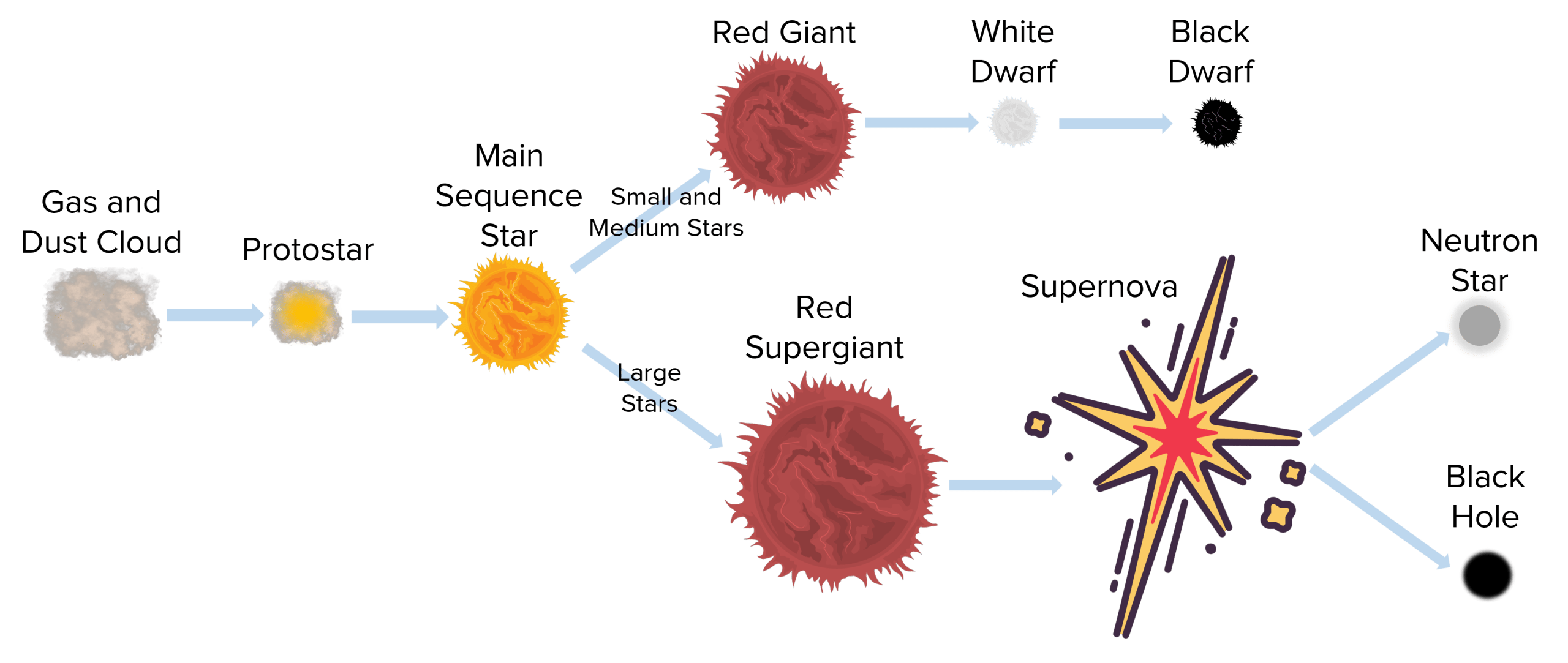
Life Cycle of a Star
Nebula (dust + gas)
Protostar
Main Sequence Star
Super Red Giant
Supernova
Neutron Star
Blackhole (massive)
Red Giant
White Dwarf
Black Dwarf
refers to a group of stars that forms a particular pattern in the sky
Constellations
a distinctive pattern formed by a group of stars which belongs to one or more constellation
Asterism
Big Dipper (Big Bear) is an asterism of the constellation ursa major
IAU
International Astronomical Union
How many recognized constellations are there
88
why are stars are not related to one another
because they have different distances (light years)
in the course of the night, constellations shange positions (east to west) in the night sky
rotation of the earth on its axis
causes diff. constellations to be observed at diff times of the year
revolution of earth around the sun
Types of constellations
Circumpolar Constellations
Non-Circumpolar Constellations
Zodiacal Constellations
never fully set below the horizon
can be seen all year long near NORTH CELESTIAL POLE (NCP)
caused by earths rotation
moves counterclockwise around polaris
usually seen in the northern hemisphere, where PH is located
Circumpolar Constellations
Major Circumpolar Constellation
Ursa Major - big dipper is an asterism of ursa major
Ursa Minor - tail represents polaris
Cassiopeia - Queen of ethiopia, W or M, forms a crown, northern sky (seen)
Draco - dragon named ladon, guards golden apple tree of Goddess Hera
Cepheus - King of ethiopia, kingdom (mukang house)
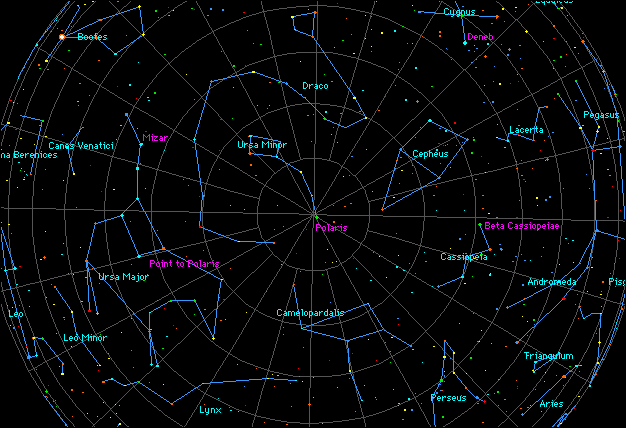
constellations appear in the sky only in a particular season
also known as SEASONAL CONSTELLATIONS
Non-circumpolar Constellations
WINTER CONSTELLATIONS (DEC - FEB)
winter in northern hemisphere and summer in southern hemisphere
ORION
Cancer
Gemini
Monaceros
Taurus
and friends
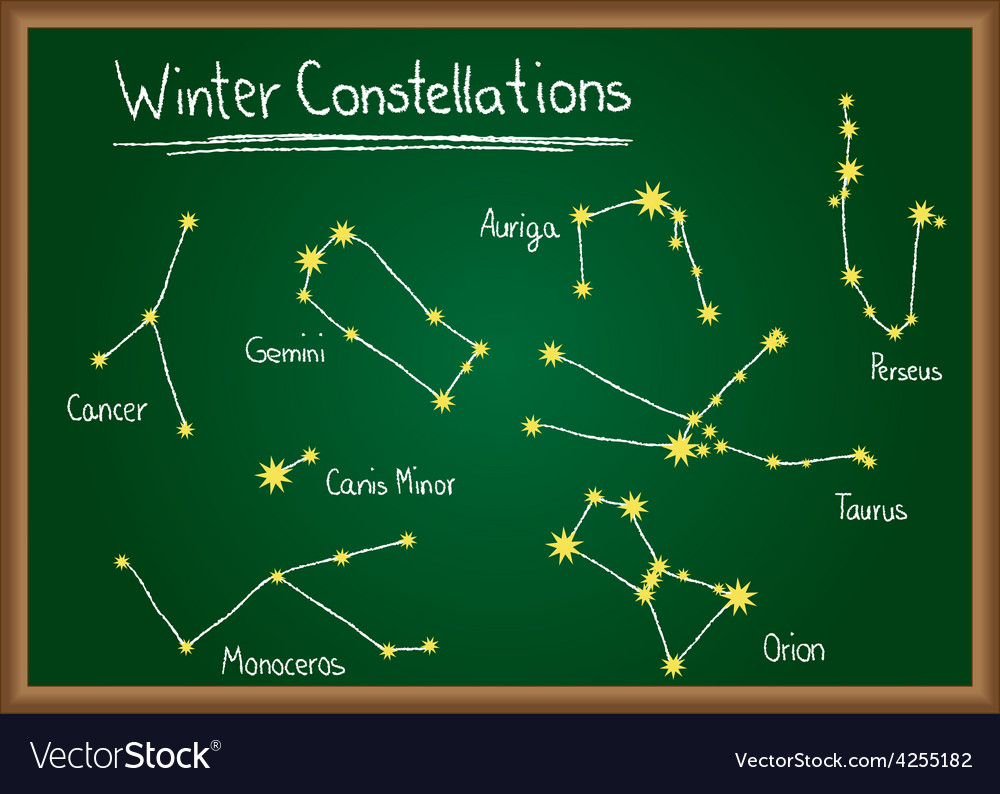
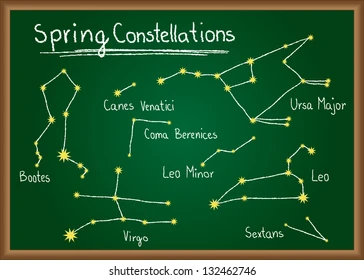
SPRING CONSTELLATIONS (MAR - MAY)
spring in northern hemisphere, autumn in southern hemisphere
LEO (yeahhhhhhh)
Bootes (hahahah)
Leo Minor
Ursa Major
Virgo
and friends
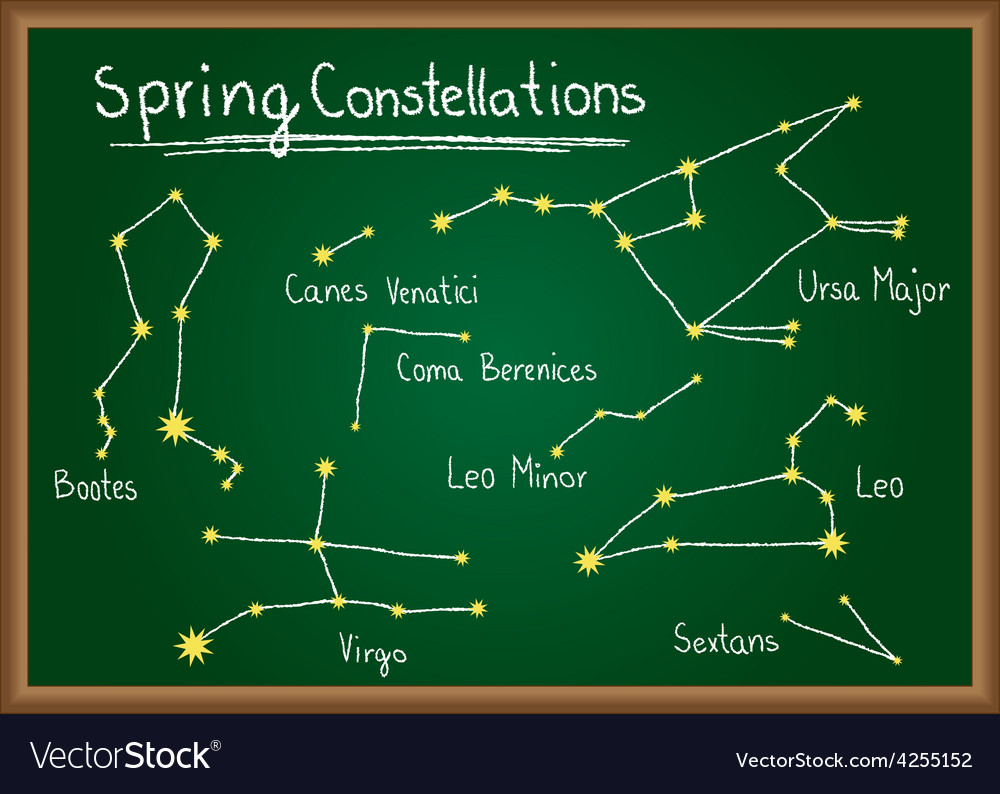
SUMMER CONSTELLATIONS (JUNE - AUG)
summer in northern, winter in southern
LYRA
Hercules (ngik)
Corona Borealis
Ophiuchus
Sagittarius
Delphinus (YEZZZZZ)
and friends
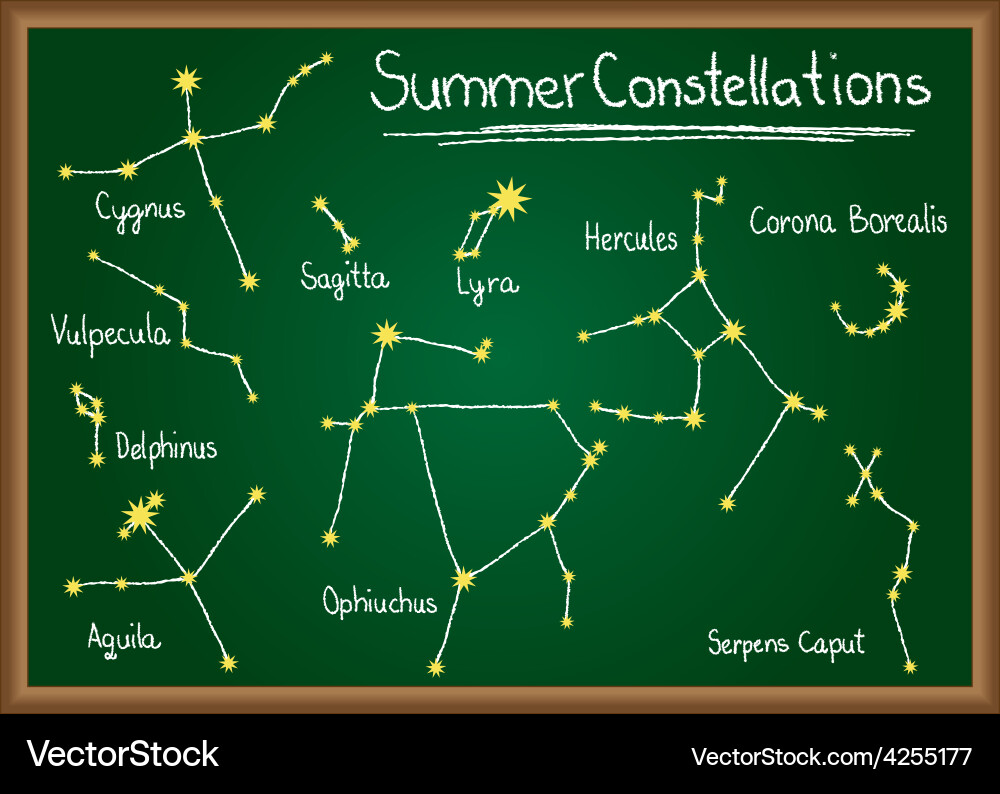
AUTUMN CONSTELLATIONS (Sept to Nov)
visible during clear atumn nights, if u point at it u see andromeda galaxy
spring in southern
ANDROMEDA
Pegasus (bida bida)
Pisces
Aries
Triangulum (bat kaya no)
Cassiopeia
and friends
Handy way to measure distance
pinky - 1 deg
girl scout fingers - 5 deg
fist - 10 deg
rockstar na walang thumb - 15 deg
rockstar na walang pointer - 25 deg
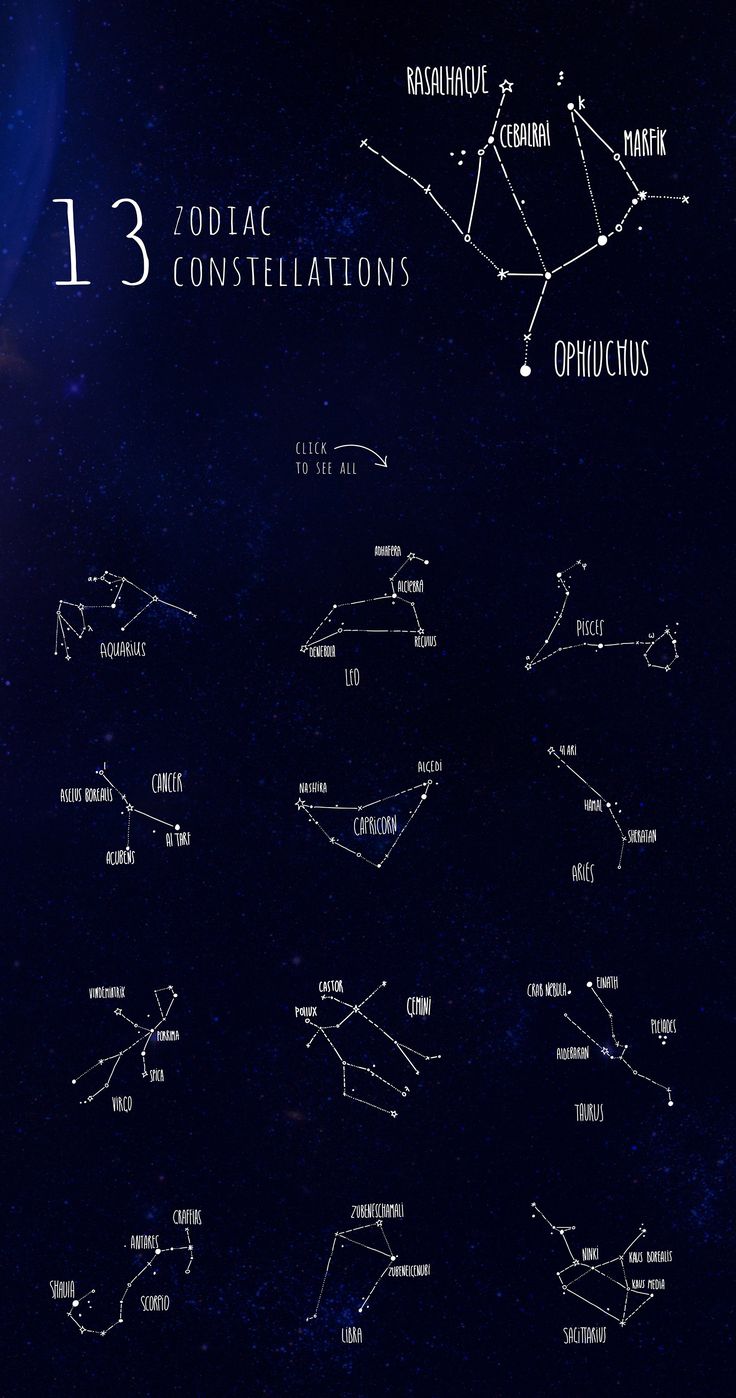
constellations that lie along the plane of the ecliptic
the ecliptic (apparent path) of the sun is the circular path of the sun across the sky as seen from earth
ecliptic passes through 13 constellations - astronomy
12 only - astrology
Zodiacal Constellations
circular path of the sun across the sky as seen from the earth
apparent path
Ecliptic
the zodiacal that is april 19-may 13
ARIES
Zodiacal may 14 - june 19
TAURUS
zodiacal june 20 - july 20
gemini
july 21 - aug 9
cancer (hala!)
aug 10 - sept 15
LEO YESSSSS
sept 16 - oct 30
virgo
oct 31 - nov 22
libra
nov 23 - nov 29
scorpius
nov 30 - dec 17
OPHIUCHUS YESSS
dec 18 - jan 18
sagittarius
jan 19 - feb 15
capricornus
feb 16 - mar 11
aquarius
march 12 - april 18
pisces
SUNOD SUNOD NA ZODIACAL CONSTE
ARIES - april 19 - may 13
TAURUS - may 14 - june 19
GEMINI - june 20 - july 20
CANCER - july 21 - aug 9
LEO - aug 10 - sept 15
VIRGO - sept 16 - oct 30
LIBRA - oct 31 - nov 22
SCORPIUS - nov 23 - nov 29
OPHIUCHUS - nov 30 - dec 17
SAGITTARIUS dec 18 - jan 18
CAPRICORNUS - jan 19 - feb 15
AQUARIUS - feb 16 - mar 11
PISCES - march 12 - april 18
Uses of constellation
find location
farming
navigation (sea)