Audiology Exam 2
1/95
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Central Auditory System Vestibular System Acoustics What is Sound The Audiogram
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
96 Terms
How Sound Travels Through The Ear
Acoustic energy > Mechanical energy > Hydraulic energy > Chemical signal > Electrical signal
Acoustic energy
sound waves enter the ear from the pinna and the sound hits the TM causing it to vibrate (changing it into mechanical energy)
Mechanical energy
the malleus (attached to TM) moves the ossicular chain and the stapes pushes in and out of the oval window and sound travels to the round window (creating a fluid motion/hydralic energy)
Hydraulic energy
the fluid movement causes the hair cells to shear the tectorial membrane in the organ of Corti (creating a chemical signal)
Chemical signal
chemical signal in inner hair cells that has chemical energy traveling down the hair cell to the synaptic junction (creating electric signal)
Electrical signal
electrical signal is sent up the auditory nerve to the brain
Functions of Central Auditory System
sound localization
speech recognition
take sounds from two different areas to make into one sound
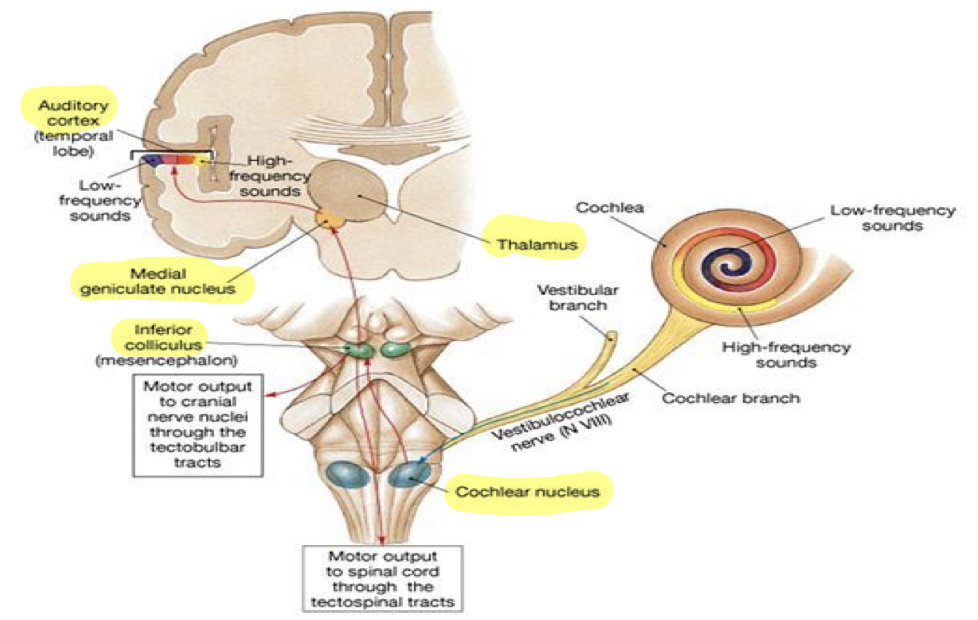
Afferent Pathway
auditory nerve
brainstem pathway
cochlear nucleus (medulla oblongata)
superior olivary complex (pons)
lateral lemniscus (midbrain)
inferior colliculus (midbrain)
thalamus
medial geniculate body
auditory cortex (in cerebral cortex)
Efferent Pathway
might send a signal to OHC to relax
Contralateral processing of sound
the information ascends through the contralateral side of the brainstem and brain to the cortex (sound crosses over pathways)
Cochlear nucleus
in the auditory portion of medulla oblongata
tonotopically organized
Decussations
cross-over points
helps up figure out which side sound comes from
localization and lateralization
Superior Olivary Complex
first place along hearing highway where neurons receive and input from both ears (from both sides of the body)
key player in binaural integration (being able to focus on a target sound)
located in pons
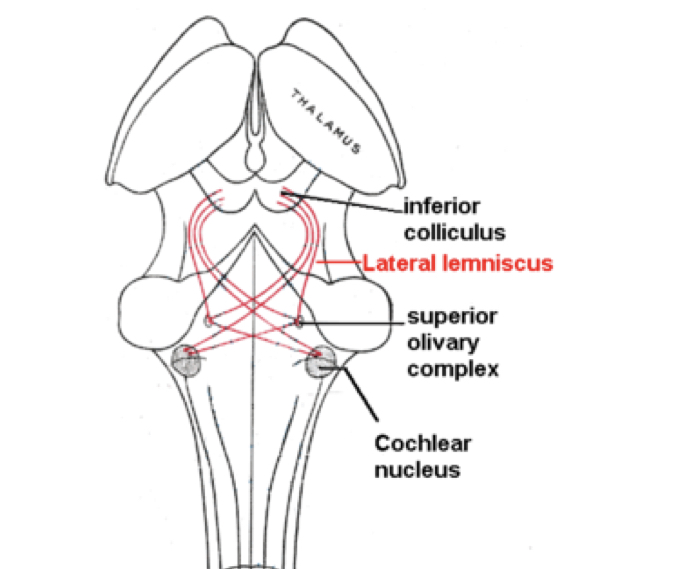
Lateral Lemniscus
tract of nerve fibers
connects superior olivary complex to inferior colliculus
sensitive to timing/amplitude changes in sound
located in midbrain (crossing to opposite side of brain)
Inferior Colliculus
responsible for the startle reflex and vestibulo-ocular reflex
sensitive to changes in intensity and frequency
responsible for detection of pitch
located in midbrain
Medial Geniculate Body
all sounds must stop at the medial geniculate body
helps us direct and focus attention on target sound (high order processing of bineural inagration)
located in thalamus
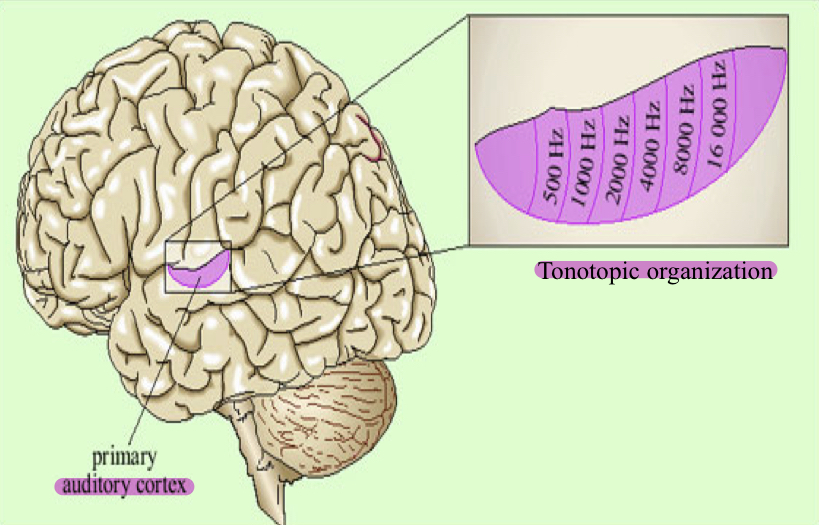
Auditory Cortex
assigns meaning and value to sounds
has tonotopic organization
Sound must travel through each portion of the _________ for hearing to occur
ear and to the brain
Outer hair cells are the…
amplifier that refines sensitivty and frequency from the vibrations in the cochlea
Tonotopicity occurs from..
the cochlea to the cortex
Detection and localiztion occur at..
the level of lower order neurons
Sound may be detected, but it is still processed at…
the level of auditory cortex
One can have severe cortical damage (in auditory cortex) but…
can still have “normal” hearing
What happens in the temporal bone?
peripheral system
Where is the central system?
in the brainstem
Vestibular pathways lead to…
large muscles in head, neck, torso, arms, legs, and feet
Vestibular ocular reflex
keeps images on our retina stable with our head movement
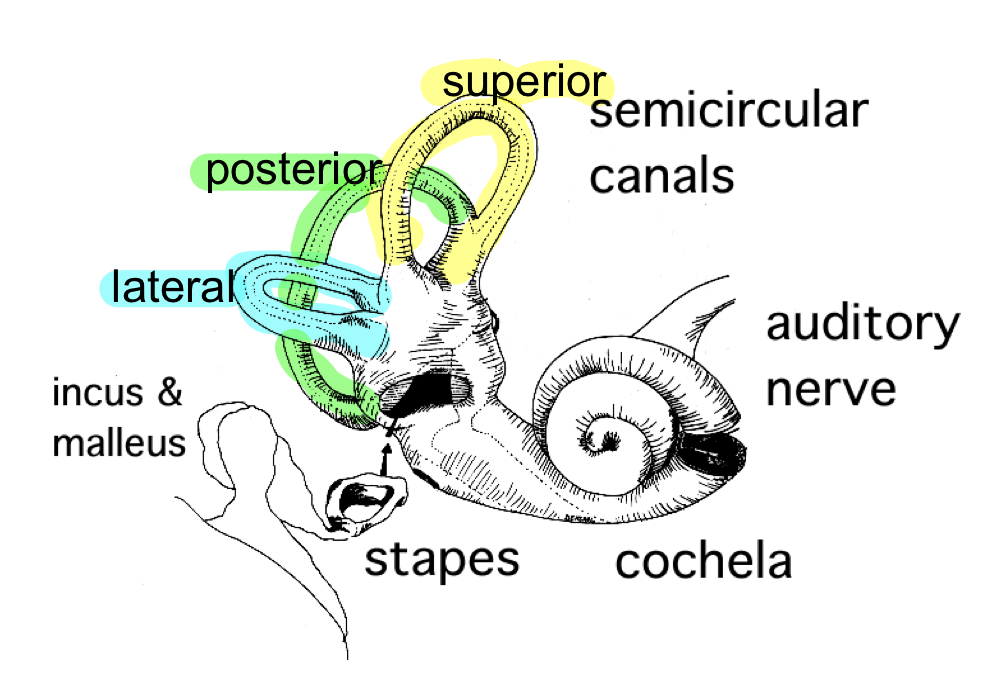
Three semi-circular canals
superior/anterior
posterior
lateral
The semi-circular canals share which fluid with the cochlea?
endolymph
The semi-circular canals contain hair cells with cilia that are sensitive to…
movement of fluid (gravity and acceleration)
Vestibular system (functions)
monitors the position of the head in space
controls balance
provides sensation of movement/acceleration
sends signals to eyes for visual stablilization
sends signals to muscles to keep us upright
The 8th nerve innervates the…
cochlea and vestibular part of the ear
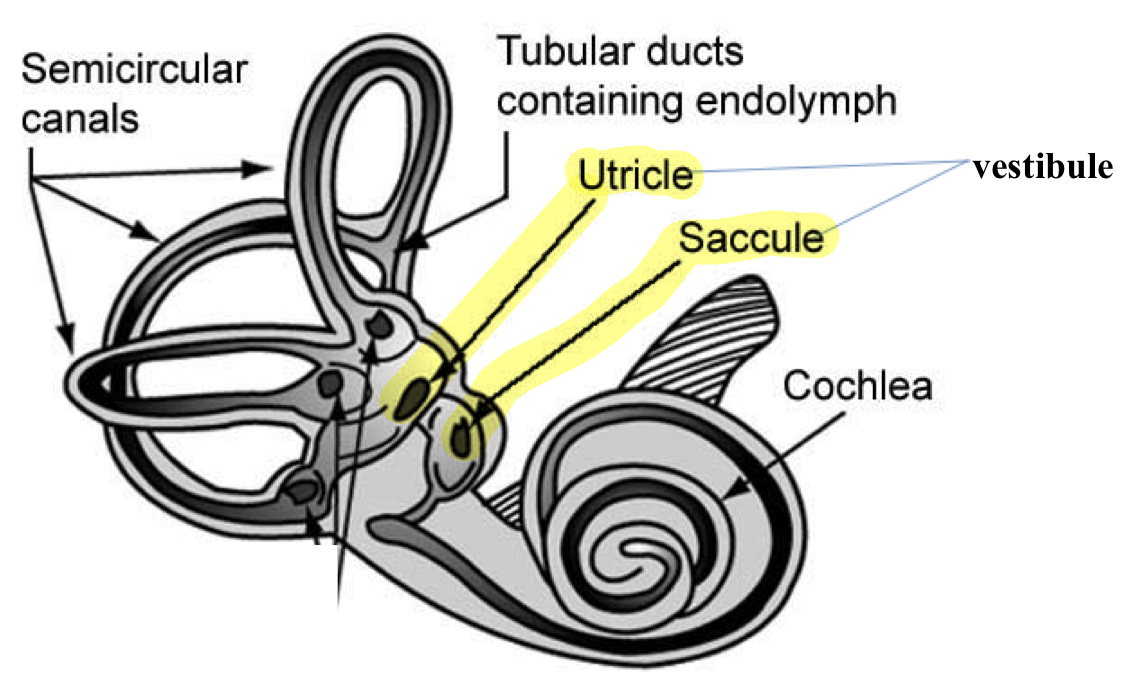
Saccule and Utricule
two otolith organs of the membranous labyrinth located within the vestibule
use small stones (otoconia) and viscous fluid to stimulate hair cells to detect motion in a straight line
Acoustic filters
selective device that allows some sounds to pass through and obstructs others
gain - applying emphais to certain sounds (presented to listener)
attenuation - obstructing certain sounds (not presented to listener)
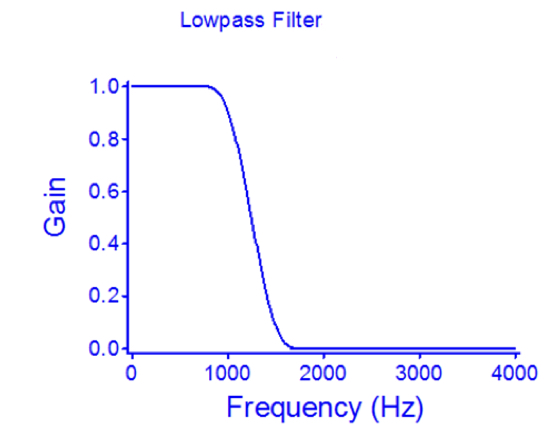
Low Pass Filter
below point is given gain, above point is attenuated
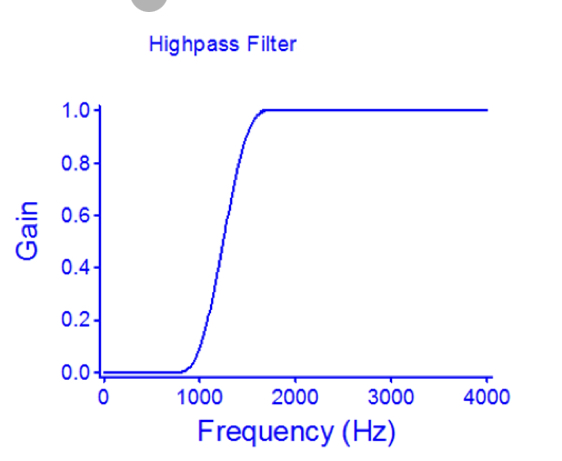
High Pass Filter
below point is attenuated, above point is given gain
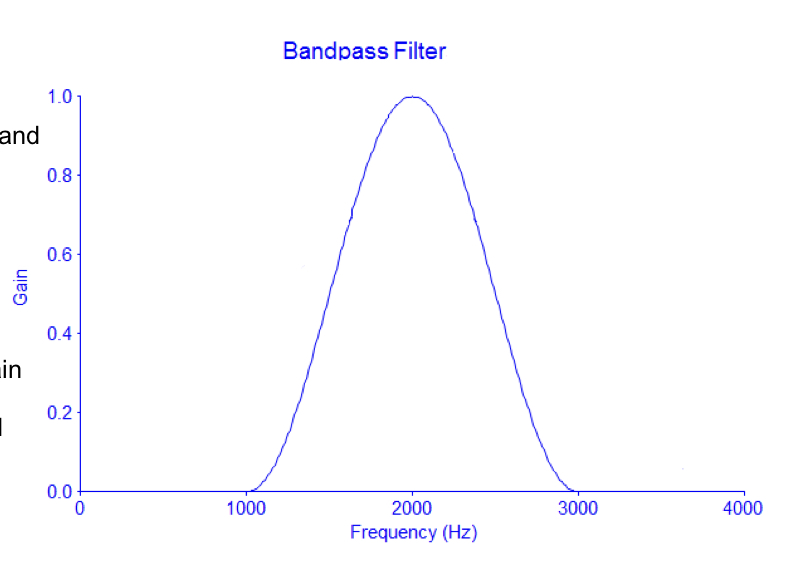
Band Pass Filter
two knee points
Hz between band are given gain, outside of the band are attenuated
Acoustic filters are determined by…
frequencies
Amplitude can be measured as…
sound pressure or sound power
Amplitude is the…
intensity & height of a waveform; loudness; reflection of power/pressure acoustic waveform is generating
Logarithic
all units of measurement are larger than the preceding
compresses large range of sounds into a smaller scale
0 db is not the absence of sound, it is…
the starting point with reference to human hearing ability
10dB Rule
every 10 dB increase in intensity is a doubling in loudness
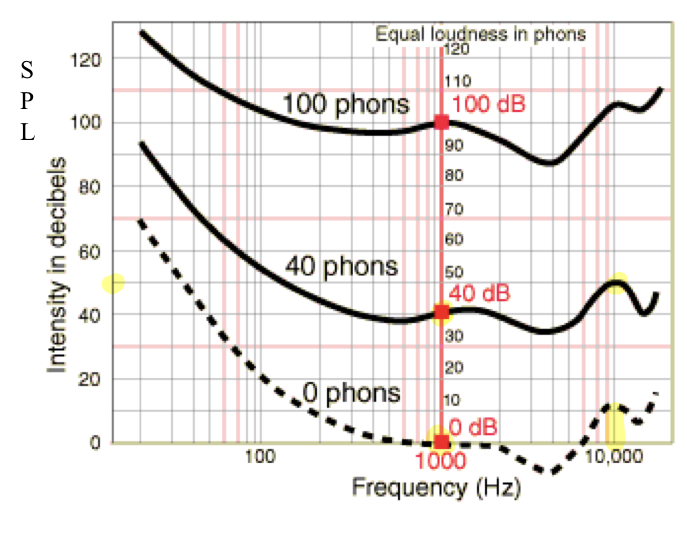
Equal Loudness Contour
comparing to be equally as loud
loudness curves for the human ear
Intensity is described in units called…
decibels (dB)
Loudness is described in units called…
phons
Pitch is decribed in units called…
mel
The human ear is most sensitive to…
mid-frequencies (2000-5000 Hz)
Minimum Audibility/Threshold
the smalled amount of sound pressure required to produce a sound that is audible to a listener
Reference
the threshold of audibility for a particular listener at a particular frequency
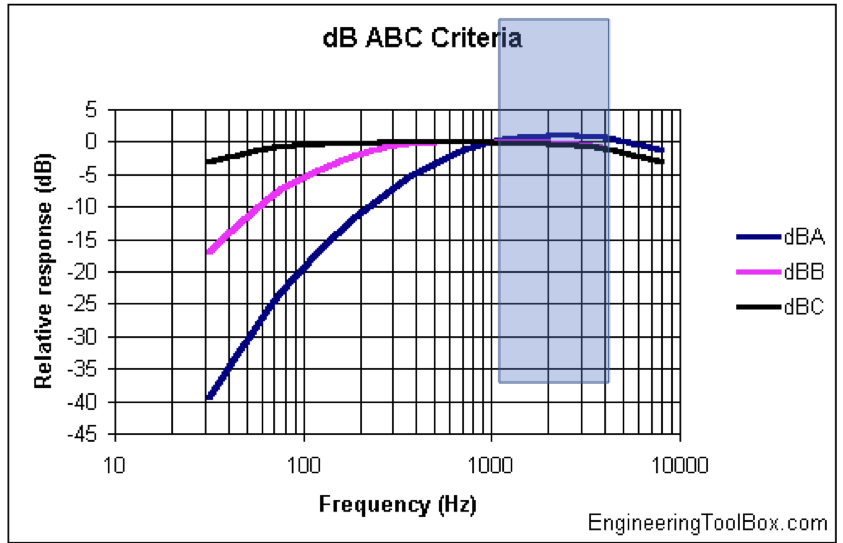
dB (A)
this filter is widely used
makes sound level meter less sensitive to very high and very low freq.
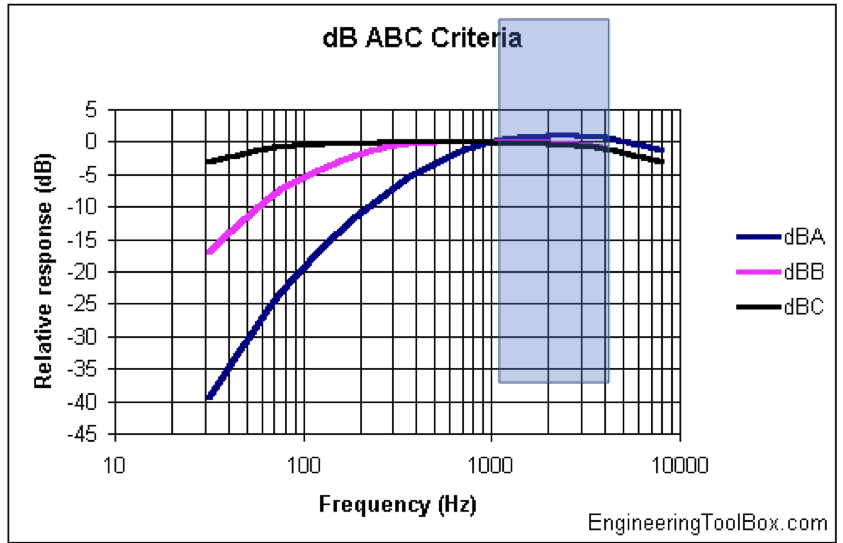
dB (B)
rarely used
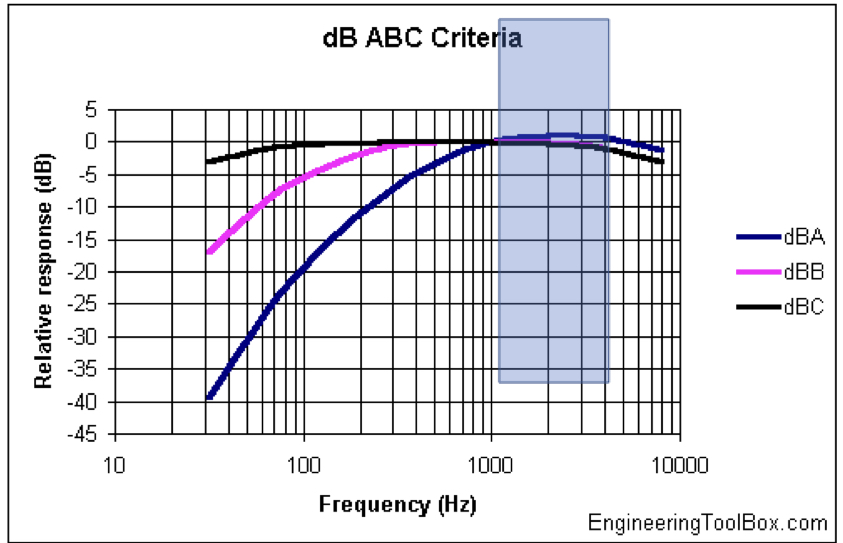
db (C)
used for subjective measurements at high sound pressure levels
almost linear at several octaves
Inverse Square Law
the intensity of sound decreases as sound waves travel further from the source of sound
What is sound?
a tool to assess hearing
Complex sounds
speech and noise sounds (energy at more than one frequency)
Pure tones
tones at specific frequenices (all of the energy at one frequency)
Physics
vibration of air particles produced by the vibration of an object
Psychological
the perception of those waves and the enterpretation of the waves by the brain
Psychoacoustics
our perception of the physical attributes of sound
Pitch
subjective perception of frequency
Loudness
subjective perception of intensity
Sound is a result of…
back and forth motion of air particles
Longitudinal wave or compression wave
air particles move parallel to the direction of the wave motion
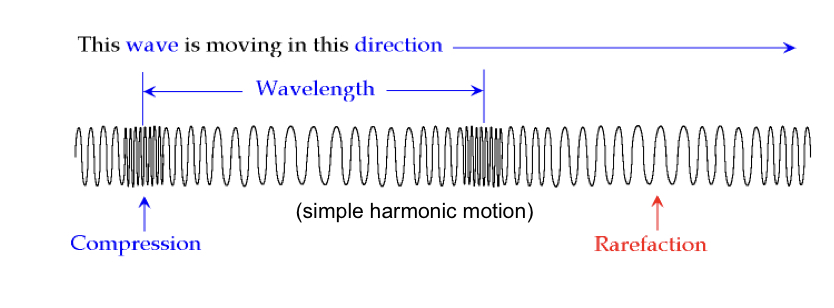
Condensation and rarefaction
increase and decrease regions of air pressure in a repeating manner
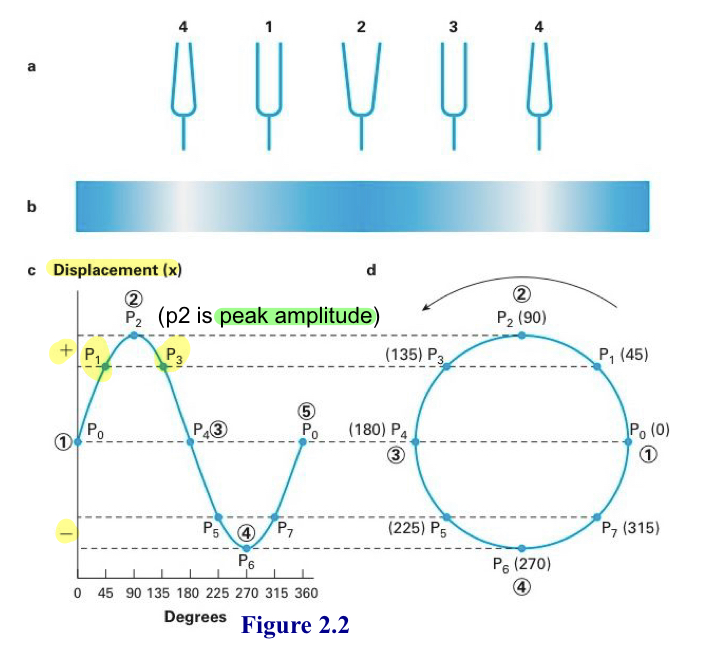
Simple harmonic motion
constant back and forth motion of sound
Amplitude
displacement in a wave form
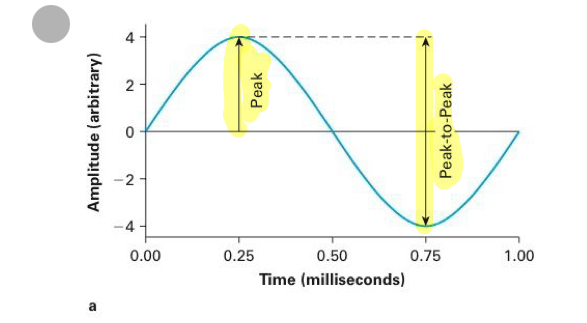
Peak
maximum postive or negative displacment from baseline
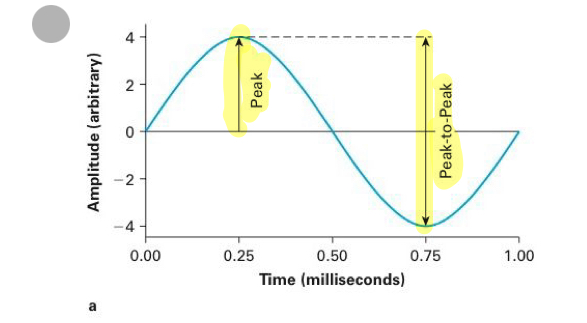
Peak to peak
difference in displacement from the positive to the negative peaks
Root-mean-square
square all instantaneous amplitudes, then averaged
Damping
decrease of vibration due to resistance (amplitude fades or decreases)
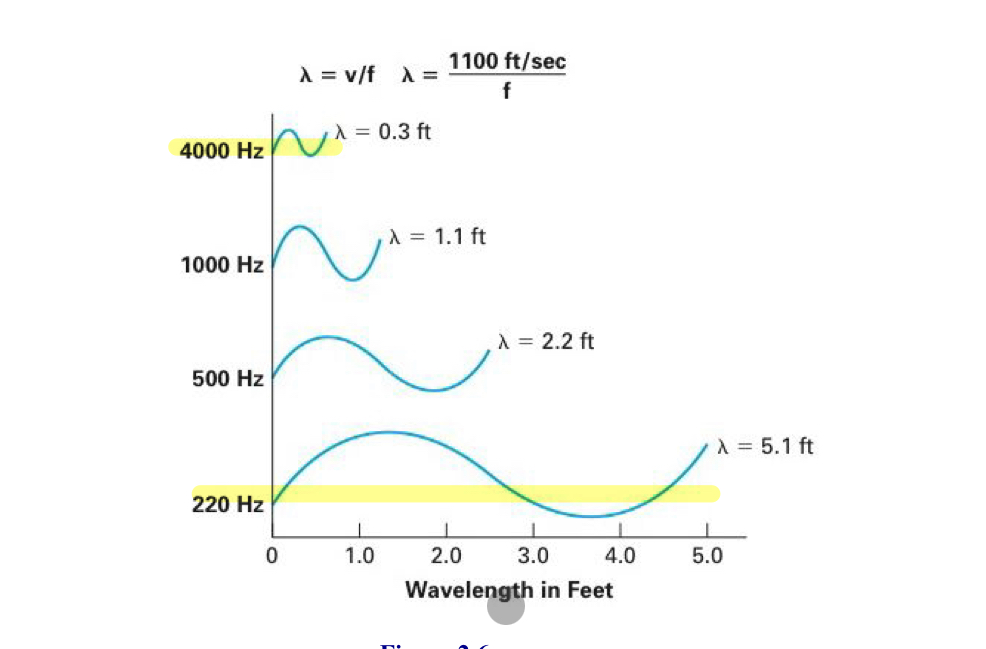
Wavelength
wavelength (length of the wave) = velocity(the speed of sound)/frequency

Speed of sound
distance a sound travels in a space of time (1100 ft/sec or 345 m/s)
Low frequency sounds have a…
longer wavelength
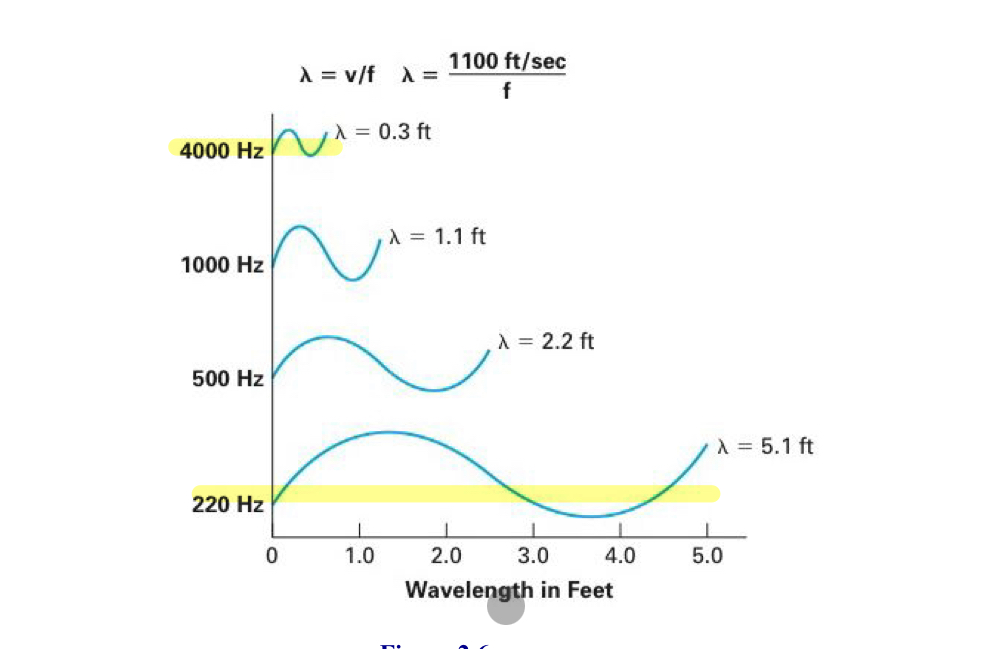
High frequency sounds have a…
shorter wavelength
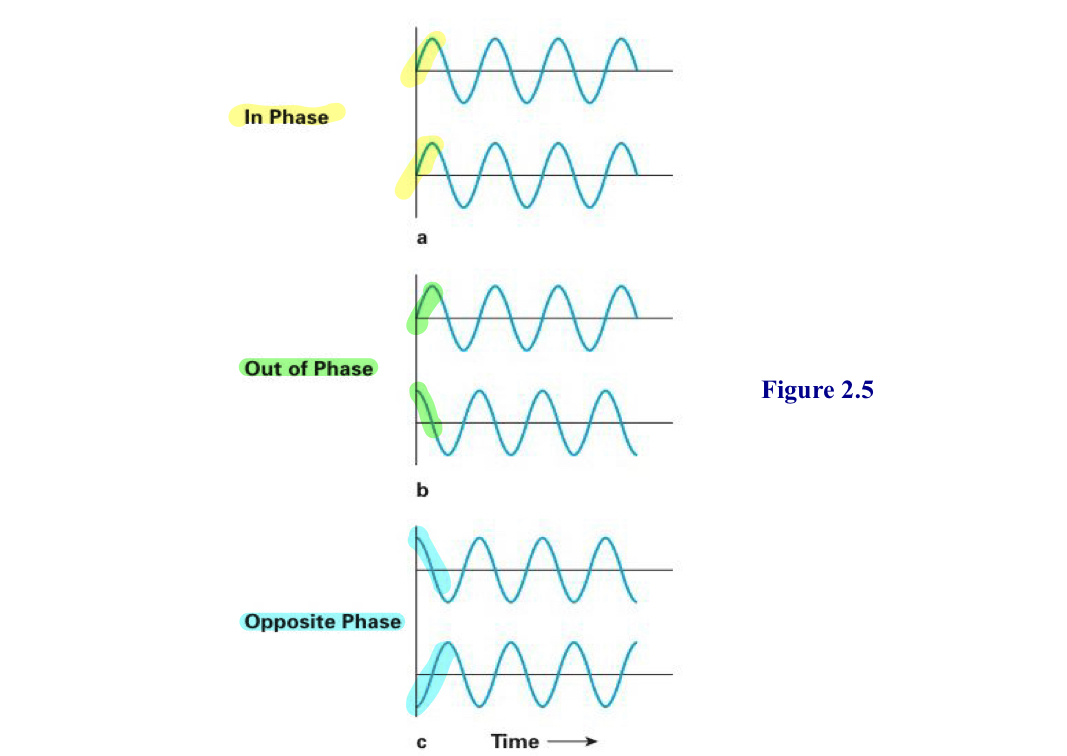
Phase
where the wave begins
waves starting at the same point are in phase
waves starting at different points are out of phase
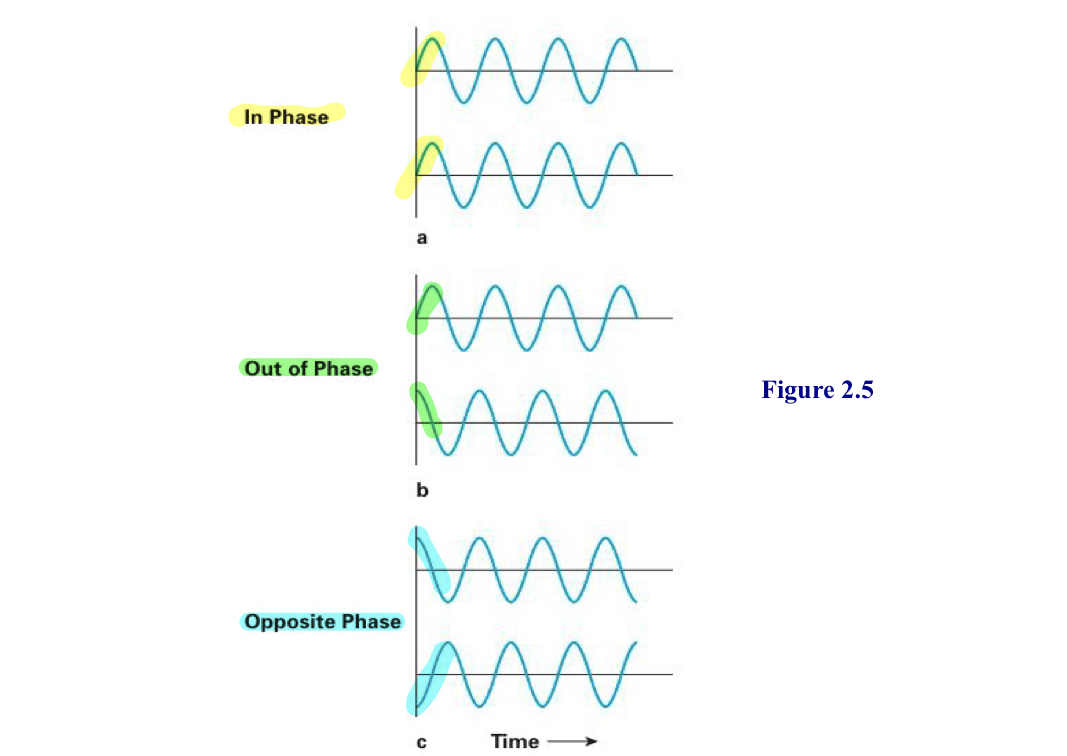
Opposite phase
waveforms that are 180 degrees out of phase
Cycle
air particle movement from rest to max. displacment one one direction, back to rest, and max. displacement in other direction (one condensation and rarefaction)
Period
amount of time it takes to complete one cycle
Frequency
the number of cycles completed in period of time
Resonant frequency
the frequency where an object naturally vibrates on its own
As the mass of the vibrating body increases…
the frequency decreases
As the mass of the vibrating body decreases…
the frequency increases
As stiffness decreases, resonant frequency…
decreases
Fundamental frequency
lowest rate of a complex sound’s vibration
Formants
frequencies in a complex periodic sound that occur over the fundamental frequency
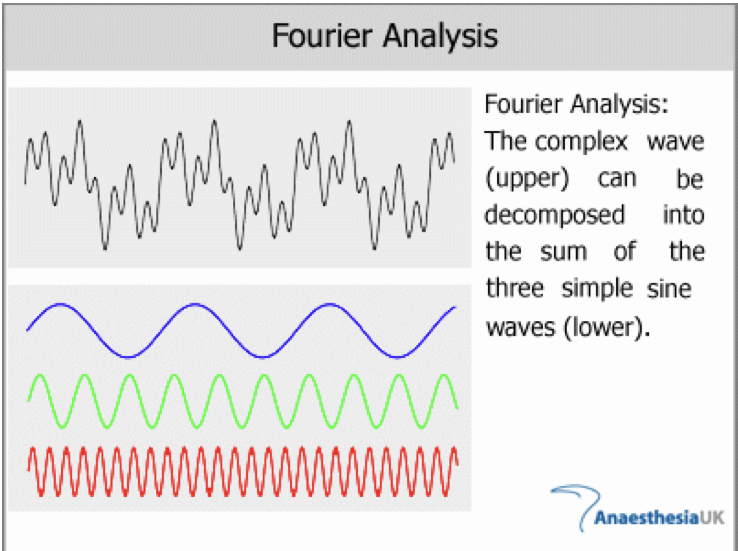
Fourier analysis
breaks down a given speech sound into individual parts
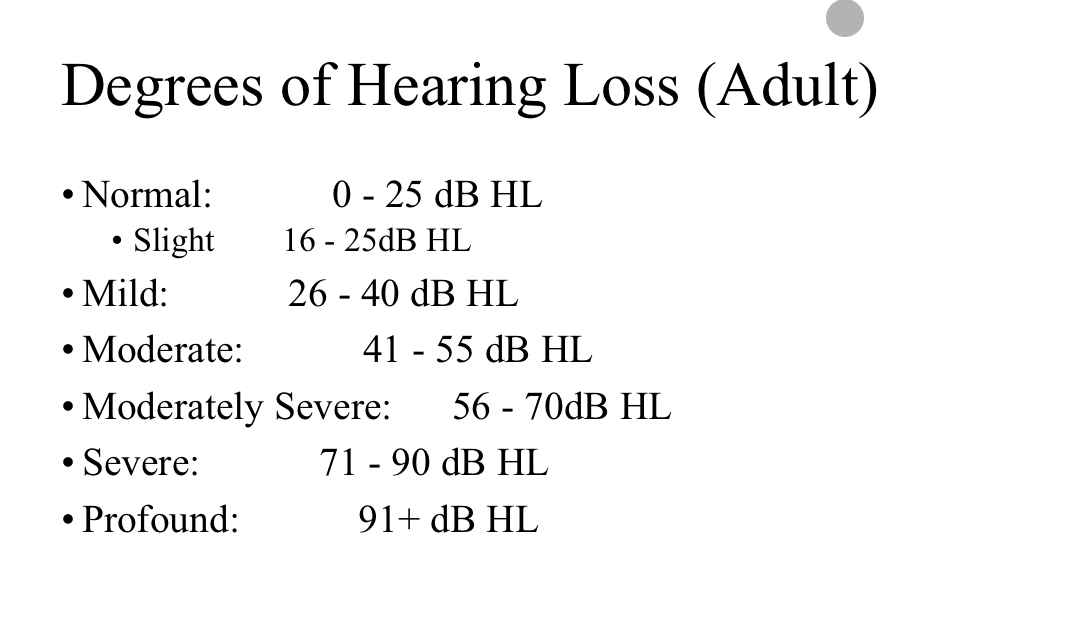
Degrees of Hearing Loss (Adult)
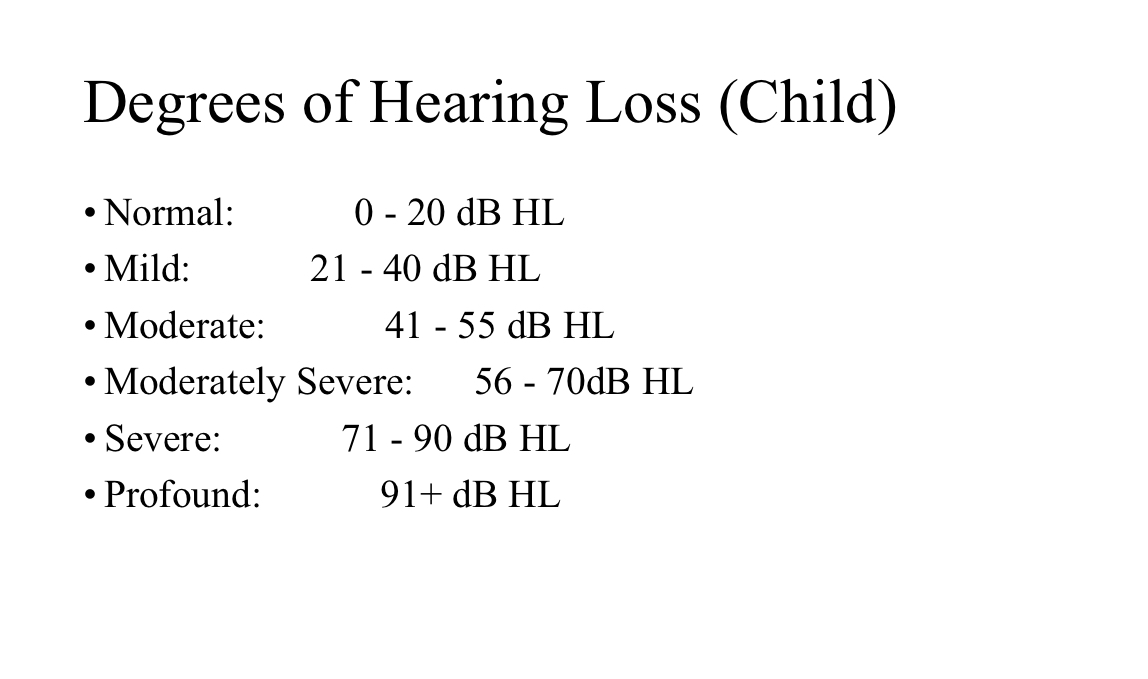
Degrees of Hearing Loss (Child)
Threshold
lowest level at which a person can detect a sound 50% of the time at a given frequency
Types of hearing loss
conductive
sensorineural
mixed
Conductive Hearing Loss
sound breaks down at the pinna and middle ear
cerumen stopping sound
fluid or infection
hole in TM
ossicular chain not connected
Sensorineural Hearing Loss
affecting inner ear or auditory nerve
hair cells damaged
auditory nerve cells damaged
Mixed Hearing Loss
affecting outer/middle/inner ear or auditory nerve
combo of conductive and sensorineural
Unilateral Hearing Loss
present in only one ear, the other is normal
can be any hearing loss
Air-Bone Gap
the difference in sound transmission between air and bone conduction
air conduction should be equal bone conduction threshold in normal hearing