Lecture 15 - Protein Synthesis, Mutations, & Regulation of Gene Expression
1/82
Earn XP
Description and Tags
BIO Flashcards
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
83 Terms
Form of specific sequences of DNA nucleotides
“information content” of GENES is…
Synthesis of proteins and of RNA molecules invovled in protein synthesis
Specific sequence of DNA nucleotides codes for…
Allele
Variation in the nucleotide sequence of a specific gene
Variation in the proteins synthesized
Nucleotide variances among alleles translates into ____
Traits, features, biochemistry, and physiology among different individuals within the same and across different species
Variation proteins leads to different _______
Proteins
Link between genotype and phenotype
Gene expression
Process by which DNA directs protein synthesis
Genes
Instructions for making specific proteins
mRNA
Bridge between DNA and protein synthesis
Backbone sugar is ribose (not deoxyribose)
Uracil replaces thymine
Single strand of nucleotides (vs double helix)
Differences between RNA and DNA
Transcription
RNA processing
Translation
Three major stages of DNA to proteins
Transcription
DNA-direct synthesis of mRNA
RNA Polymerase
Separates DNA strands and joins RNA nucleotides complementary to the DNA template strand, only works 5’ —> 3’, do NOT need a primer
Promoter
Where RNA attaches and begins transcription
Terminator
Sequence that signals the end of transcription
Transcription in Eukaryotic Cells
Occurs in nucleus of cells, results in pre-mRNA
Primary Transcript
Initial RNA transcript, further processing yields mRNA
RNA Processing
When eukaryotic cells modify RNA after transcription… occurs in nucleus.
Both ends of primary transcript are changed
Specific interior sequences are cut out and removed; remaining sequences are spliced back together
Head and Tail Modifications
Facilitate the export of mRNA from the nucleus
Help protect mRNA from hydrolytic enzymes
Help the ribosomes attach to the 5’ cap of the mRNA
Examples: 5’cap & poly-A tail
5’ cap
At 5’ end of pre-mRNA, modified form of guanine is added
Type of head/tail modification
Poly-A Tail
At 3’ end, enzyme adds 50-250 adenine nucleotides
RNA splicing
Removes introns and joins exons to create a shortened mRNA molecule with a continuous coding sequence
Introns
Noncoding segment of nucleotides that lie between coding regions
Exon
Region of mRNA that is eventually expressed… meaning they are translated into amino acid sequences
Translation
RNA-directed synthesis of a polypeptide
transfer RNA (tRNA)
Transfers amino acids from the “cytoplasmic pool” to a growing polypeptide chain on a ribosome, bears one specific amino acid at one end on the other has an anticodon
Codon
Sequence of three adjacent nucleotide bases within a strand of mRNA that provides the genetic code for a particular amino acid
Anticodon
Group of three bases on a tRNA molecule that are complementary to an mRNA codon
Peptide Bonds
Ribosomes join the amino acids into a chain via _____ bonds
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
Combine with proteins to form the large and small subunits of the ribosome, in eukaryotic cells the formation of these subunits occurs in the nucleolus. Catalyzes the formation of the polypeptide bond
P site
Found in a ribosome, holds the tRNA carrying the growing polypeptide chain
A site
Found in a ribosome, Holds the tRNA carrying the next amino acid to be added to the chain
E Site
Part of ribosome, where discharged tRNA leaves the ribosome
Occurs at the carboxyl end of polypeptide
Ribosomes attach each new amino acid with a peptide bond on which end of the polypeptide?
Polyribosomes or Polysomes
Multiple ribosomes simultaneously translating a single mRNA strand to make multiple copies of polypeptide
Chaperonin
Is a protein that helps the polypeptide fold correctly… primary structure determines secondary and tertiary structure
During and After synthesis
When does polypeptide folding occur?
Post-translational Modification
Addition of sugar, lipids, or phosphate groups to polypeptide to make it functional
Quaternary Structure
2 or more polypeptides join to form a protein with a ______ structure.
Central Dogma
Francis Crick named the concept of DNA transcribed to RNA which is translated to Protein the _____.
Mutations
Changes in the genetic material of a cell, ultimate source of new alleles/genes, if it has an adverse effect on phenotype, it is referred to as a genetic disorder/hereditary disease
Large-scale mutations
Long segments of DNA are affected by translocations, duplications, or inversions
Point Mutations
Chemical changes in just one nucleotide pair of a gene, if occurs in gamete may be transmitted to future generations
Sickle-cell disease
Caused by a mutation of a single nucleotide pair in the gene (point mutation), genetic disorder.. leads to an abnormal protein
Nucleotide-Pair substitution
Replacement of one nucleotide and its partner with another pair of nucleotides, some have no effect on protein function (due to redundancy of genetic code)
Silent Mutation
A change in nucleotide pair transforms one codon into another that is translated into the same amino acid
Missense Mutation
A change in nucleotide pair transforms one amino acid for another with little effect on protein function
Nonsense Mutations
A change of an amino acid codon into a stop codon, causing early termination of translation leading to a nonfunctional protein
Insertions and Deletions
Additions or losses of nucleotide pairs in a gene, more likely than substitution to have disastrous effect on protein made
Frameshift Mutation
All nucleotides downstream of a deletion or insertion become improperly grouped into codons, resulting in extensive missense
DNA replication, DNA repair, or DNA recombination
When do mutations occur?
Mutagens
Chemical or physical agents that interact with DNA to cause mutations
radiation like X-ray, ultraviolet light
Forms of Physical agents
Chemical Mutagens
Cause Mutations in different ways… nucleotide analogs that may be subbed into DNA, pair incorrectly during DNA replication OR interfere with DNA replication by inserting into DNA OR cause chemical changes in bases changing pairing properties
Gene
Region of DNA that can be expressed to produce a final functional product that is either a polypeptide or a protein
By transcription into RNA and then translation into a polypeptide that performs a specific function
How are genes expressed?
Proteins
What brings about an organism’s observable phenotype?
Cell only expresses a small subset of its genes, gene expression is precisely regulated
A typical cell expresses?
Changes in environmental conditions
Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells alter their patterns of gene expression in response to…
Each cell contains the same, complete set of genes but expresses a different subset of genes
Can modulate protein making to match demand
Multicellular eukaryotes develop and maintain multiple cell types (Cell diversity)
In bacteria it is often regulated at the transcription stage… Eukaryotes regulate at various stages
When is gene expression regulated?
Cancer or other disorders
Disruptions in gene regulation may lead to _____.
Bacteria that express only the genes whose products are needed by the cell.
Ex: bacterium in tryptophan-rich environment stops producing tryptophan to conserve its resources
Natural selection favors bacteria that ____.
Feedback Inhibition
The pathway’s end product blocks the activity of the first enzyme in the pathway.
Typical of anabolic pathways.
Allows cell to adapt to short-term fluctuations in supply of a needed substance
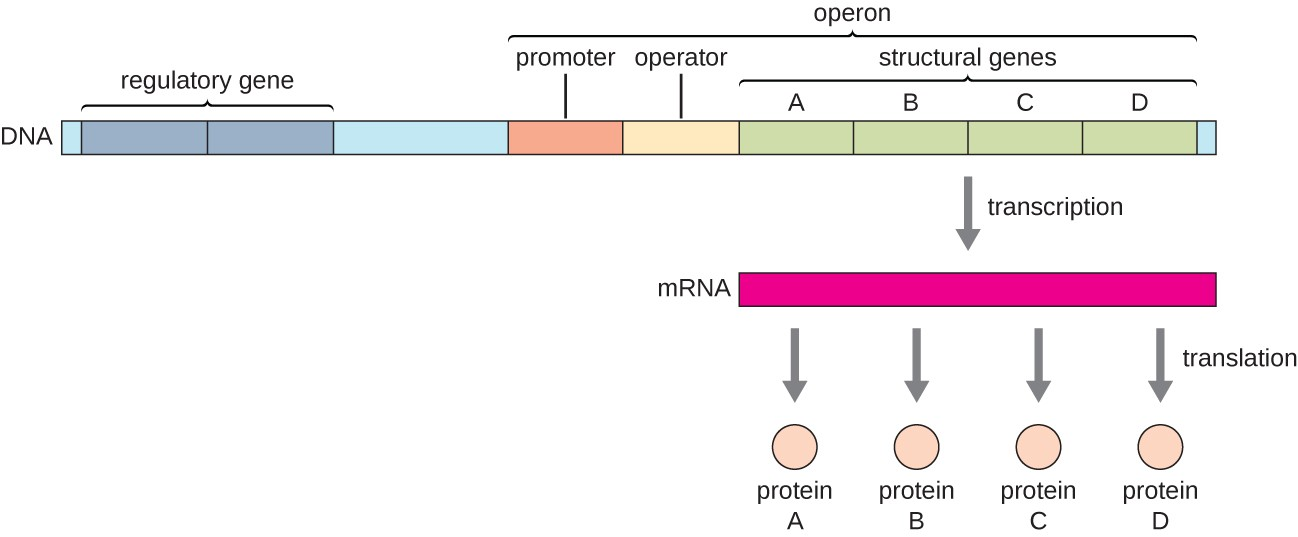
Operon Model - Operator, repressor, and operon
Basic mechanism for control of gene expression in bacteria… regulation of one gene by another that operates as a “master” switch. Control of enzyme production occurs at transcription.
Differential gene expression OR Cell Differentiation
Expression of different genes by cells with the same genome. All cells in organism have identical genome, but subset of genes expressed in cell of each type is unique.
20%
Typical human cell expresses about ____ of its genes at any given time.
Imbalances and diseases like cancer
Problems with gene expression and control can lead to ______.
True
True or False… Genes of densely condensed heterochromatin are usually not expressed.
N-terminus
Protrudes outwards from the nucleosome, found on each histone molecule
Histone Acetylation
Addition of an acetyl group called ______ promotes transcription… or deacetylation of lysines in histone tails play a direct role in regulation of gene transcription
Attachment of methyl group (methylation)
Addition of ____ to histone tail leads to condensation of chromatin (i.e. no transcription)
Addition of phosphate group
Called Phosphorylation… added to an amino acid next to a methylated amino acid leads to decondensation of chromatin
DNA methylation
Reduces gene expression. Can occur at tails of histone proteins or on certain bases in DNA, usually cytosine
Occurs in most plants, animals and fungi.
Occurs more on inactive DNA than on actively transcribed regions
Removal of extra methyl groups can turn on some of these genes.
Individual genes are usually more heavily methylated in cells where they are not expressed. How to turn on gene?
Deficient DNA methylation leads to abnormal embryonic development. Once methylated, genes usually stay that way through successful cell divisions.
DNA methylation causes the long-term inactivation of genes during cellular differentiation
Control elements
Noncoding DNA segments that serve as binding sites for protein transcription factors
Transcription Factors
Collection of proteins that mediate the binding of RNA polymerase and onset of transcription
Enhancers
Distal control elements… binds to activator proteins which turn on transcription. Composed of about ten control elements, which can only bind to one or two specific transcription factors
Binding of specific transcription factors, either activators or repressors, to control elements of enhancers
Gene expression in Eukaryotic cells can be altered by…
Repressors
Inhibit gene expression by blocking the binding of activators to their control element
Can bind directly to control-element DNA, turning off transcription even in the presence of activators
Alternative RNA splicing
Different mRNA molecules are produced from the same primary transcript, different RNA segments are treated as exons/introns.
Increases number of possible human proteins.
75% - 100% of human genes probably undergo this process
Regulatory Proteins
Control intron-exon choices by binding to regulators sequence within primary transcript, specific to cell type