Week 13 - Physiology of visual acuity
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
What is visual acuity?
Finest detail that can be seen at high contrast
How many minutes of arc are in a degree?
60
How many minutes of arc is produced when reading a 6/6 line on a snellen chart
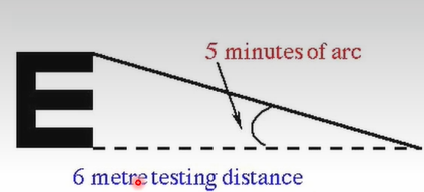
How can you read a letter on a Snellen Chart?
If you can view each limb
What is minimum angle of resolution?
Minutes of arc required to recognise the letter
What does 6/6 mean?
Viewing distance / distance each letter subtends 5 minutes of arc
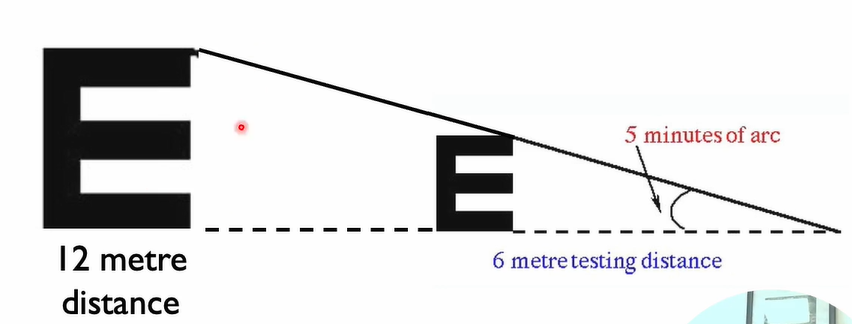
Why is a 6/12 letter bigger?
At a distance of 12 meters, that is the size for 5 minutes of arc
What is a cycle?
Ability to resolve one black bar and one white bar
What is a cycle per degree?
How many cycles are able to fit in a degree
What are the 4 types of acuity?
Detection
Resolution
Recognition
Localisation
What is detection?
Ability to see something (whether it is there or not)
What is the angle for types of acuity?
0.5-1.5 seconds per arc
How many seconds are in a minute of arc?
60
What is resolution acuity?
Smallest angle at which subjects can distinguish between critical elements
How is resolution acuity measured?
Landolts C or tumbling Es where letters are facing different directions
What is recognition acuity?
Subject must be able to detect, resolve and identify the target
E.g. Snellen
What type of relationship is between Snellen and MAR?
Linear relationship when both are logged aka logMAR
What is a bailey lovie chart?
Gives visual acuity in logMAR
Each letter is 0.02
Viewed at 6m
What is vernier acuity?
Localisation acuity
Small offset between 2 targets
What is Helmholtz sampling technique
Need at least one unstimulated neuron between 2 stimulated neurons to resolve
What would be required to get 2 different signals to the brain?
2 Different ganglion cells
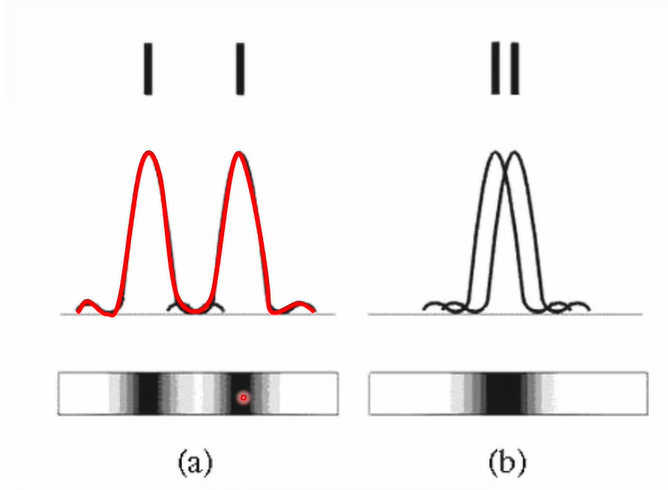
What happens when we try to resolve 2 spots of light?
Some overlap, must be separate enough so peaks do not overlap
Where can we see the sharpest detail?
Centre of vision / fovea
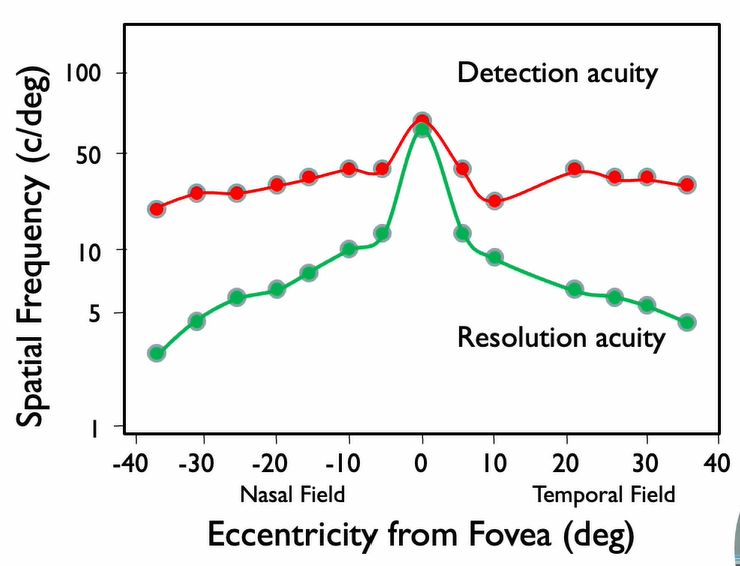
What type of arrangement has good acuity?
Dense arrangement of receptive fields
What is the relation between cycles of degree and visual acuity?
Higher cycles of degree the better the visual acuity
Does acuity increase or decrease from rod mediated vision to cone mediated vision
Increase, as smaller receptive field in cone photoreceptors
Where is the peak VA?
5 degrees off the fovea
Is minimum angle of resolution greater with letter recognition than grating acuity?
Letter recognition
More difficult to detect, lower visual acuity
How does letter spacing affect visual acuity?
Crowding effect
Cramming them closer diminishes ability to read them
What is self crowding?
When a letter crowds itself, e.g. a W
How do smaller pupils limit VA?
Diffraction entering and then spreading
How do larger pupils decrease visual acuity?
Optical aberrations
What is the optimal pupil size
3-5mm