(Edited) Speech Anatomy Final
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
Where is the limbic system found?
On the inner border of the cerebrum (between the hemispheres), above the diencephalon
What is the main function of the cerebellum?
Balance and coordination
Two hemispheres of the cerebrum
right and left
what separates the brain's hemispheres
longitudinal fissure
How do the two hemispheres communicate
corpus callosum
What are the three types of fibers of the cerebrum?
Projection - convey/receive information from remote regions to cortex
Association - interconnect regions in same hemisphere, ex: Arcuate fasciculus
Commissural - interconnect areas in one hemisphere to other (Corpus Callossum)
Broca's area is located in
left frontal lobe
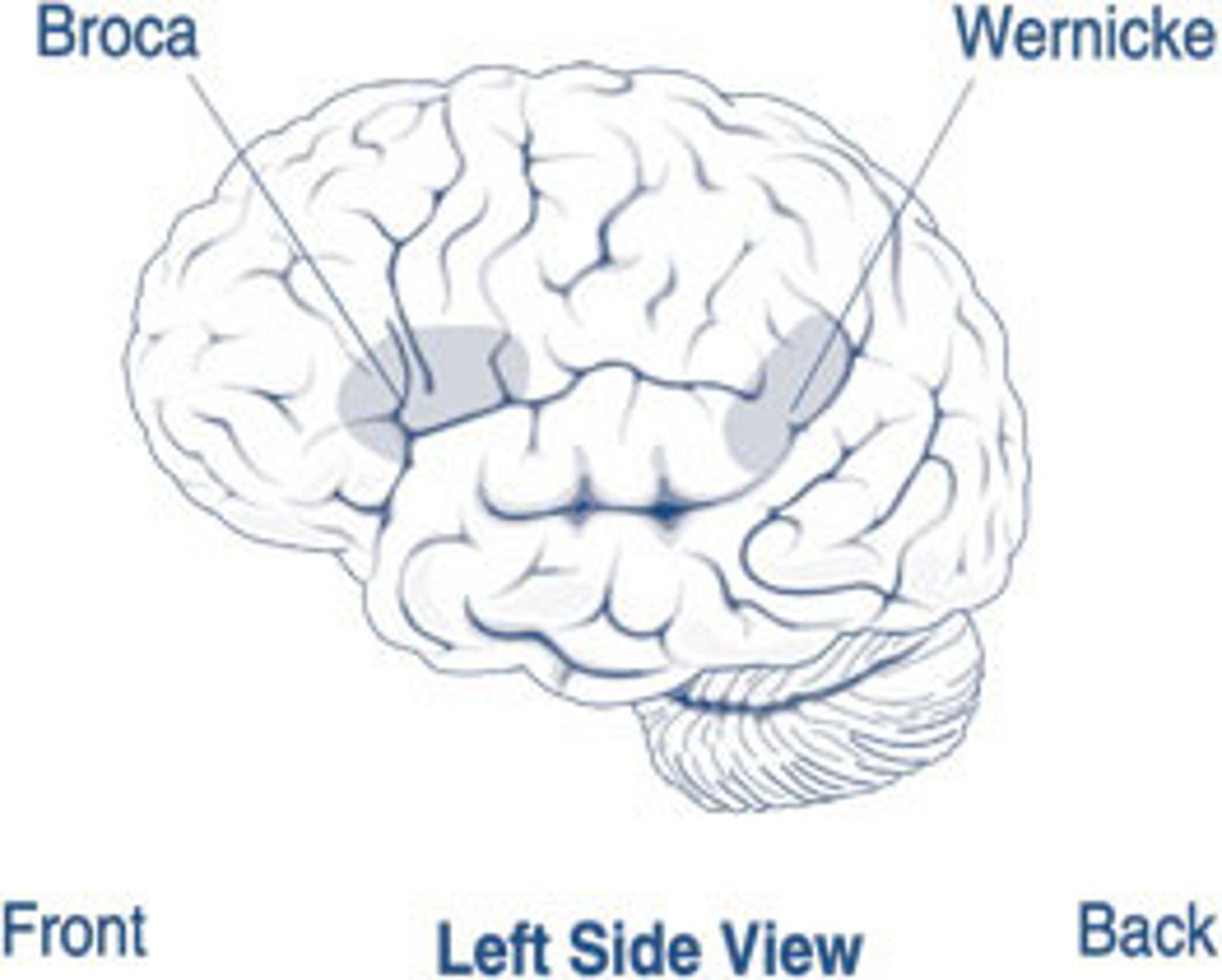
Broca's area function
speech production
Wernicke's area location
left temporal lobe
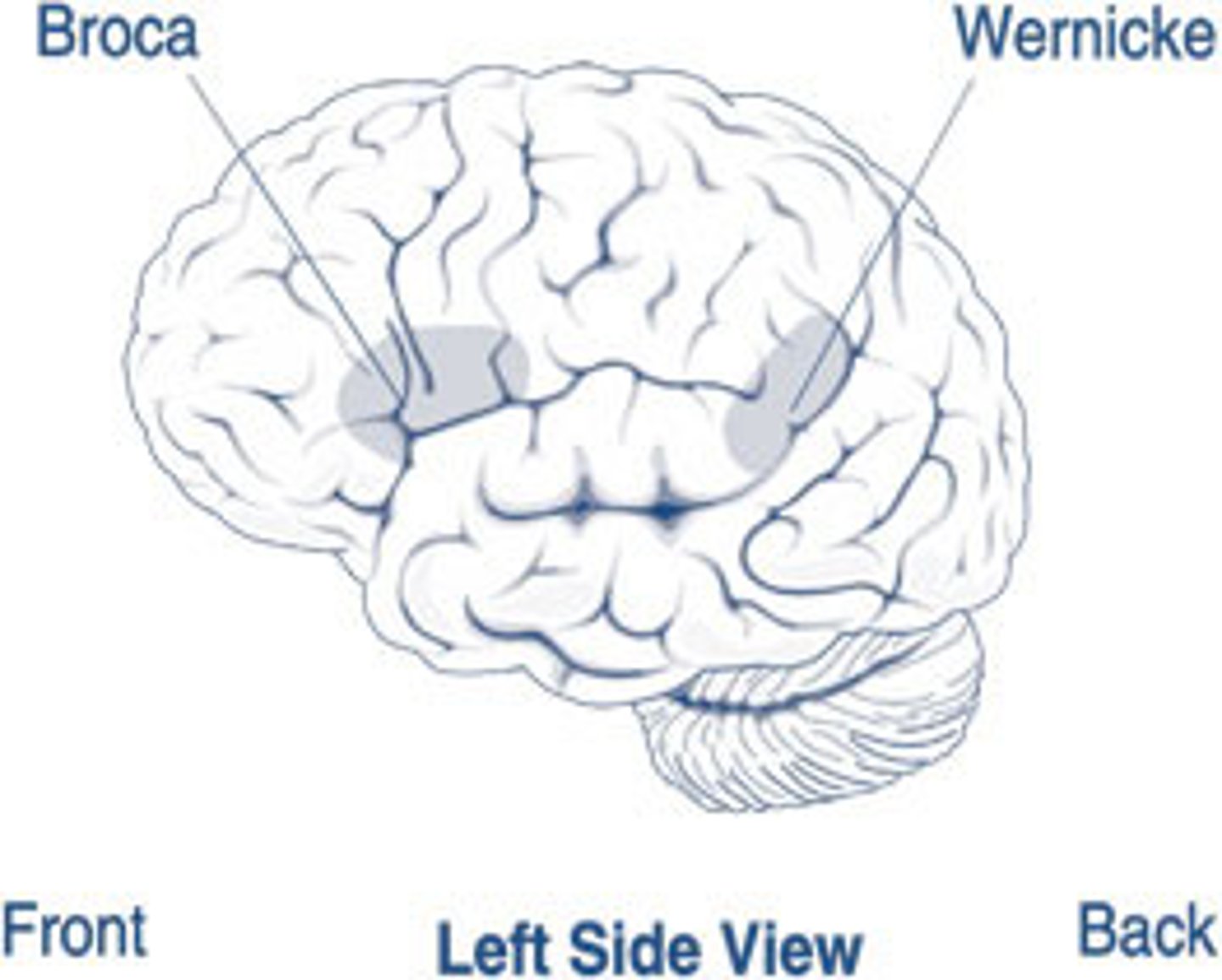
Wernicke's area function
language comprehension
Broca vs wernicke neumonic: BLondes For President? We Can't Let Them!
(to all my blonde friends I am so sorry I'm just desperate for acronyms)
Broca Left Frontal Production
Wernicke Comprehension Left Temporal
Primary motor cortex location
frontal lobe
Primary sensory cortex location
parietal lobe
Basal ganglia function
Receives input from most of cerebral cortex, especially motor area
-Regulates motor function
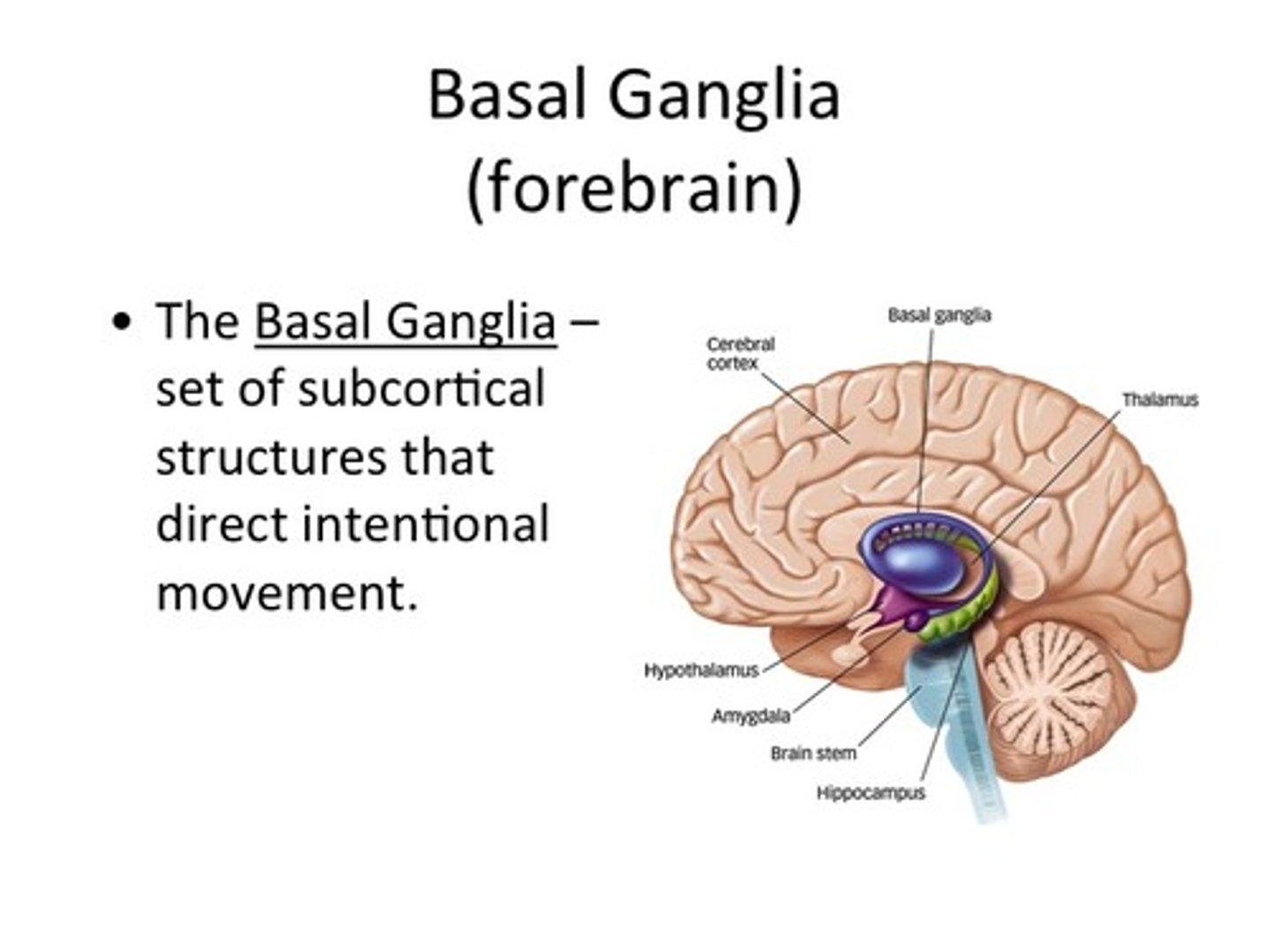
Why is the limbic system considered primitive
holds autonomic nervous system, which is the automatic, fight or flight system, emotion and memory systems
what do lesions of the basal ganglia cause
Hypokinetic movement disorders, such as parkinsonism, in which movement becomes infrequent, slow, rigid; Hyperkinetic movements disorders such as Huntington's disease, which are characterised by dance like involuntary movements.
What do lesions of the cerebellum cause
motor movement disorders as ataxia tremors and ataxic dysarthria
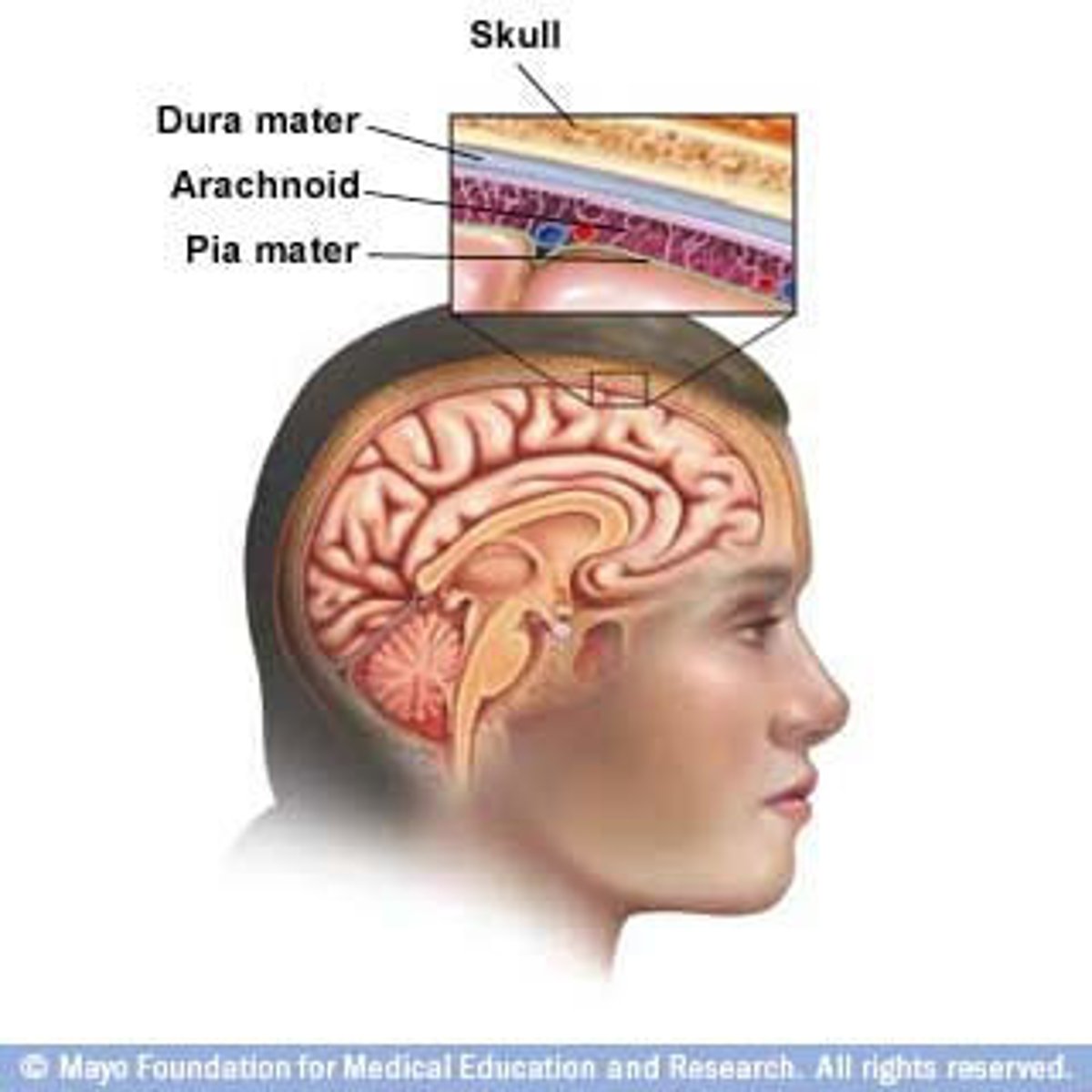
Three layers of the meninges (inner to outer) (PAD)
piameter, arachnoid mater, and dura meter (
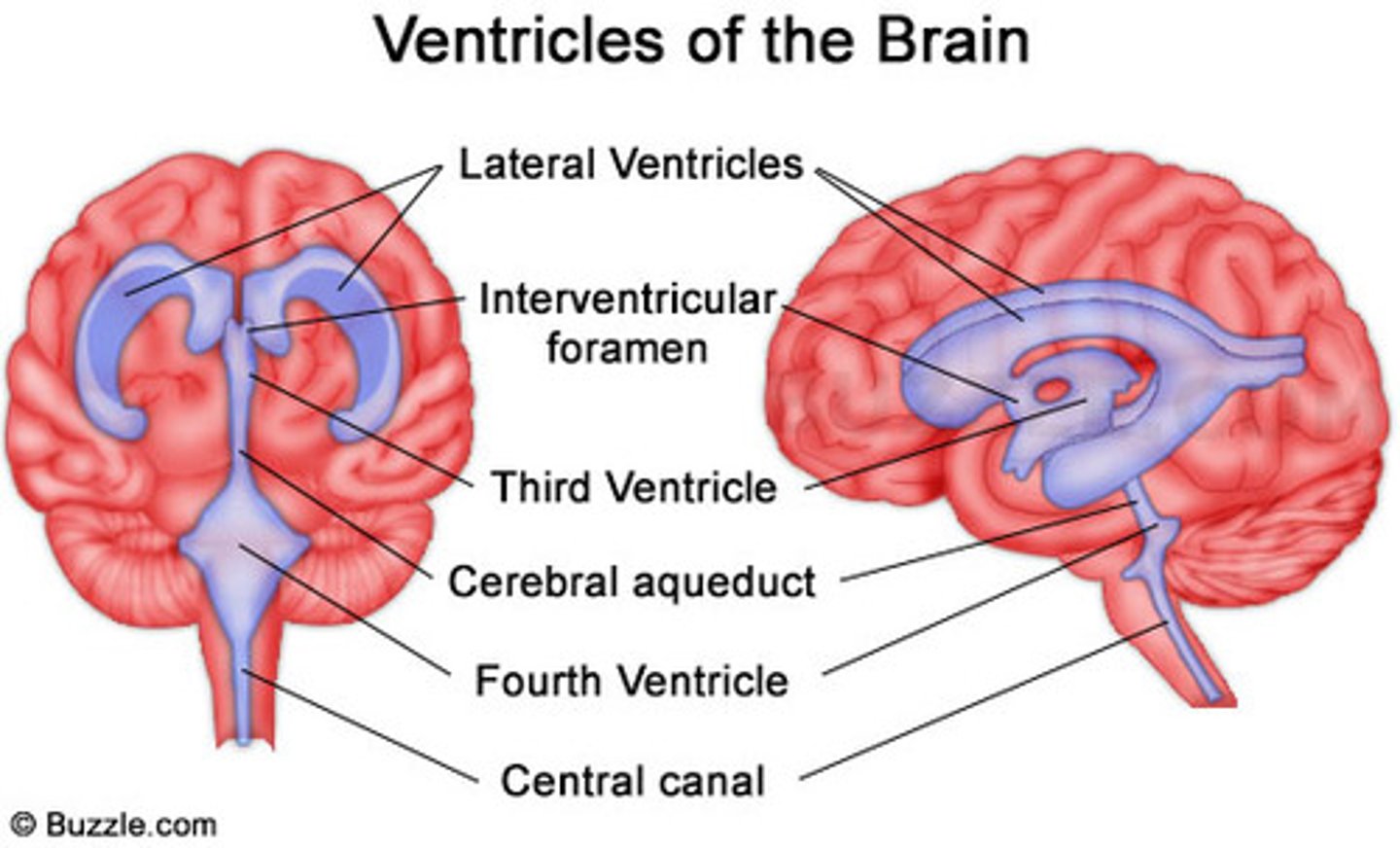
What are the ventricles of the brain
Cavities CSF flows through. 2 lateral ventricles, third ventricle, fourth ventricle
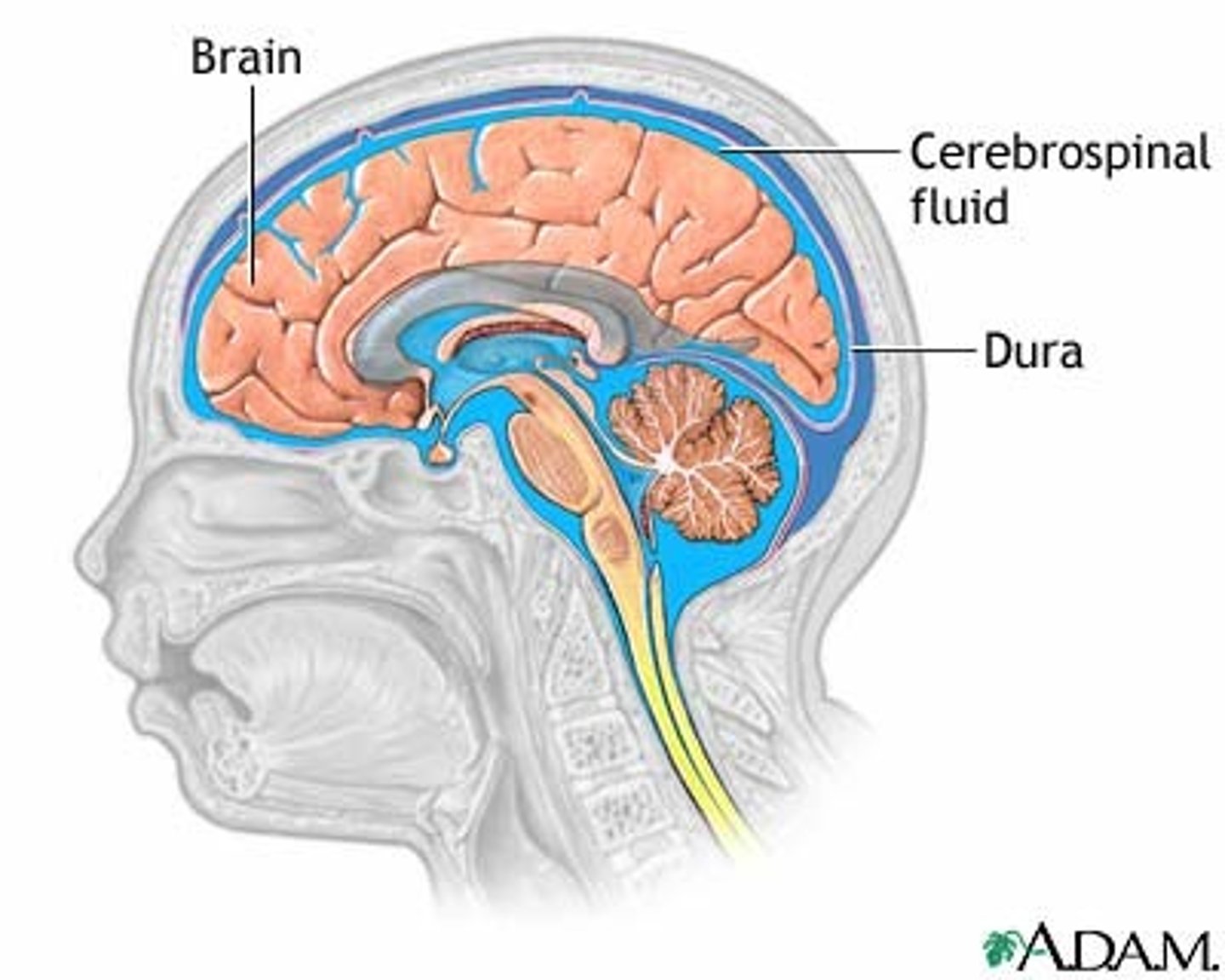
chloroid plexus
produces CSF
CSF function
buoyancy
protection: shock absorption
homeostasis: distribute substances between brain cells
clearing waste: removed into bloodstream
circle of willis
A circle of arteries at the base of the brain that supply blood to the brain
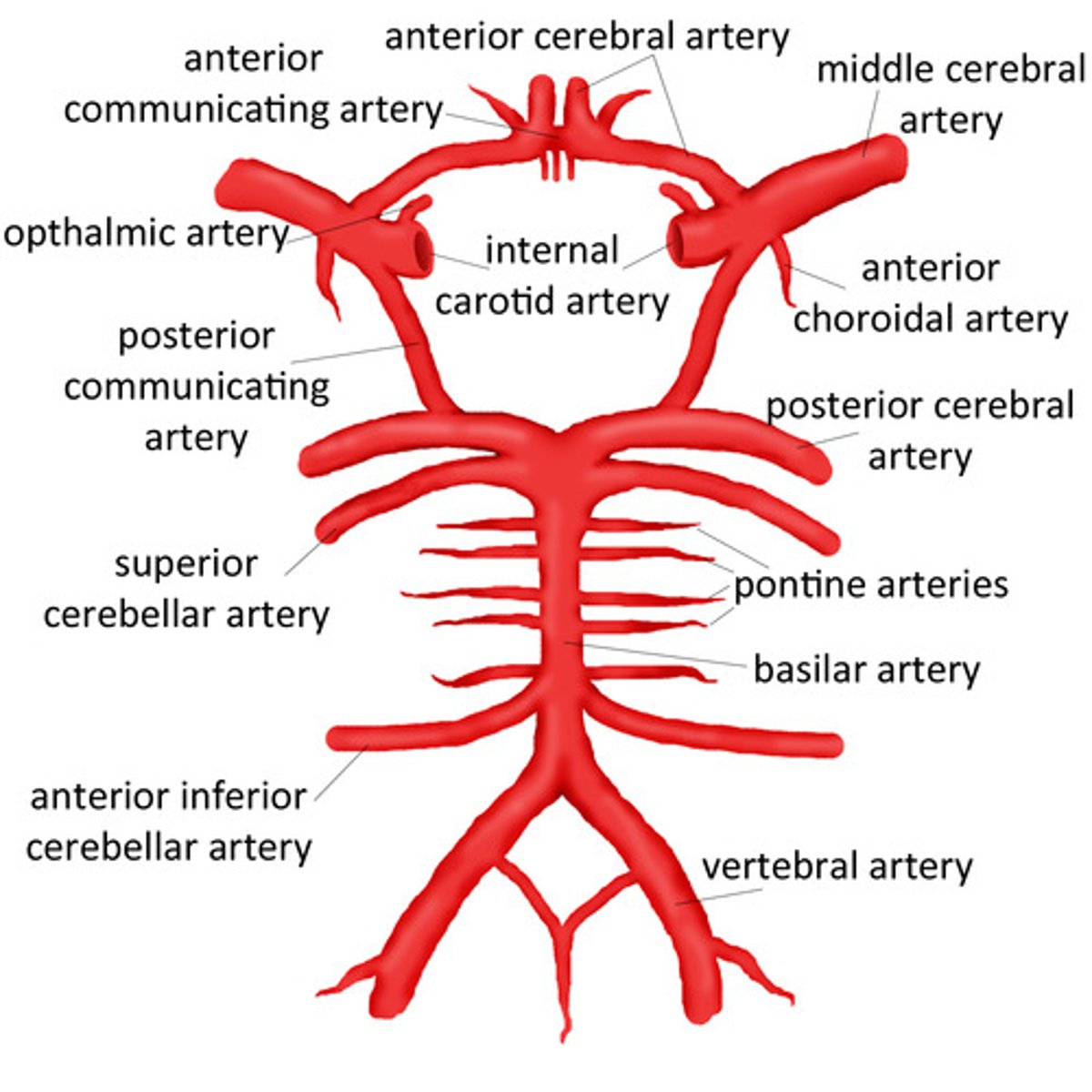
What two pairs of arteries supply the structures of the brain?
Carotid arteries + vertebral arteries
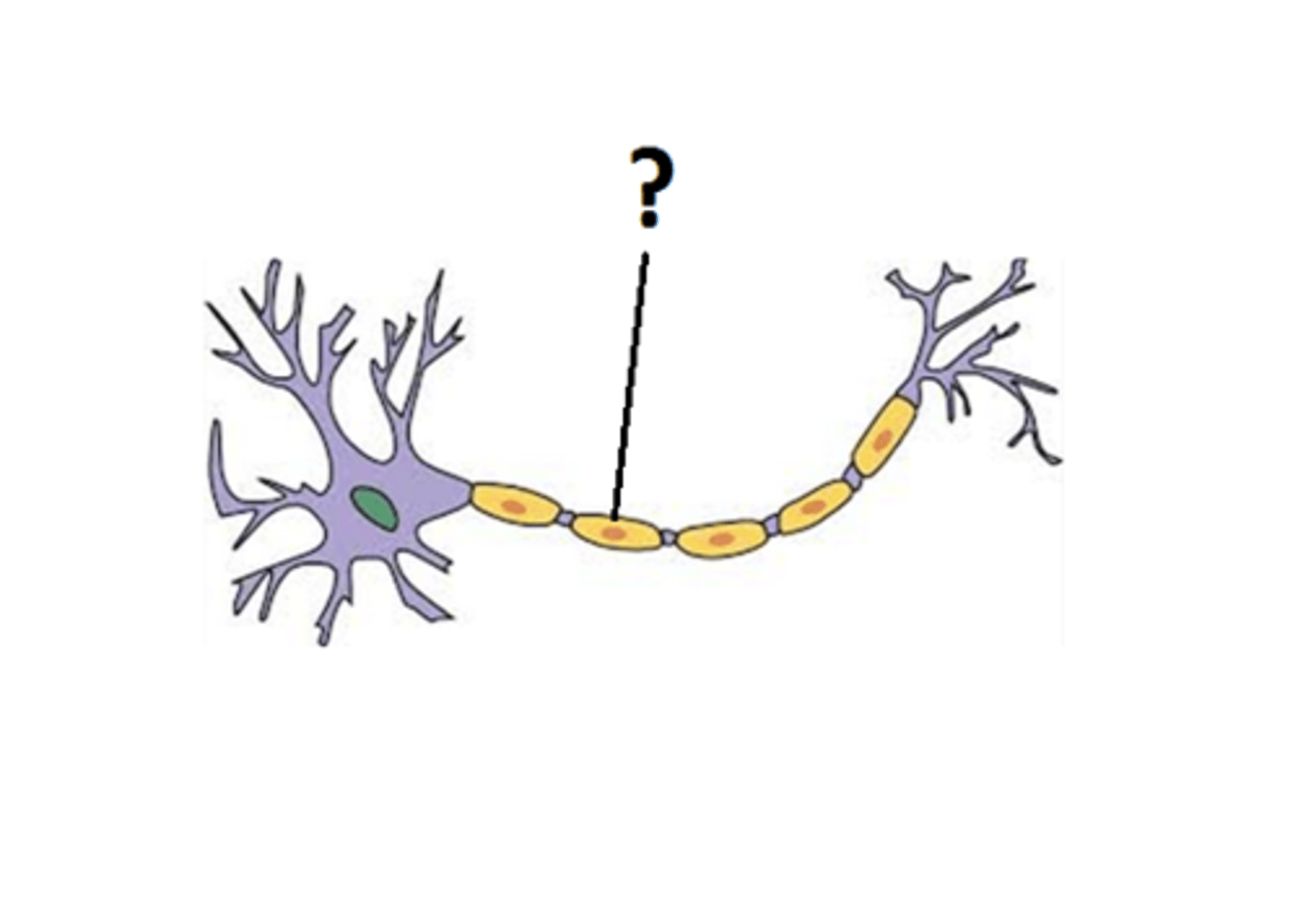
Axon vs dendrites of a neuron
Axon is the "ranch" of a neuron--what the message travels along. Covered by myelin and nodes of Ranvier. Dendrites receive signal and supply it to the axon.
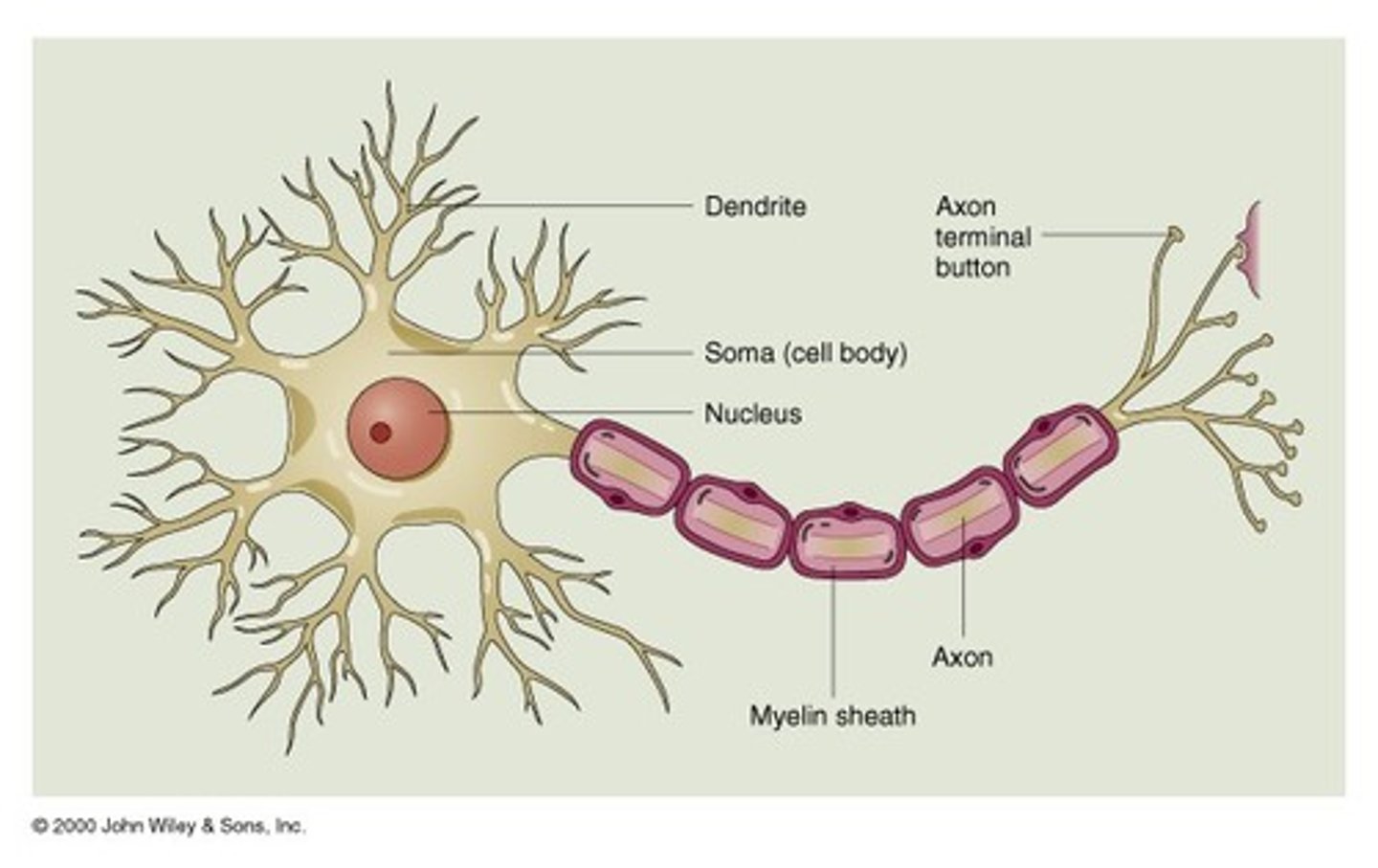
Myelin
a fatty substance that helps insulate neurons and speeds the transmission of nerve impulses
What is a synapse?
Gap between neurons
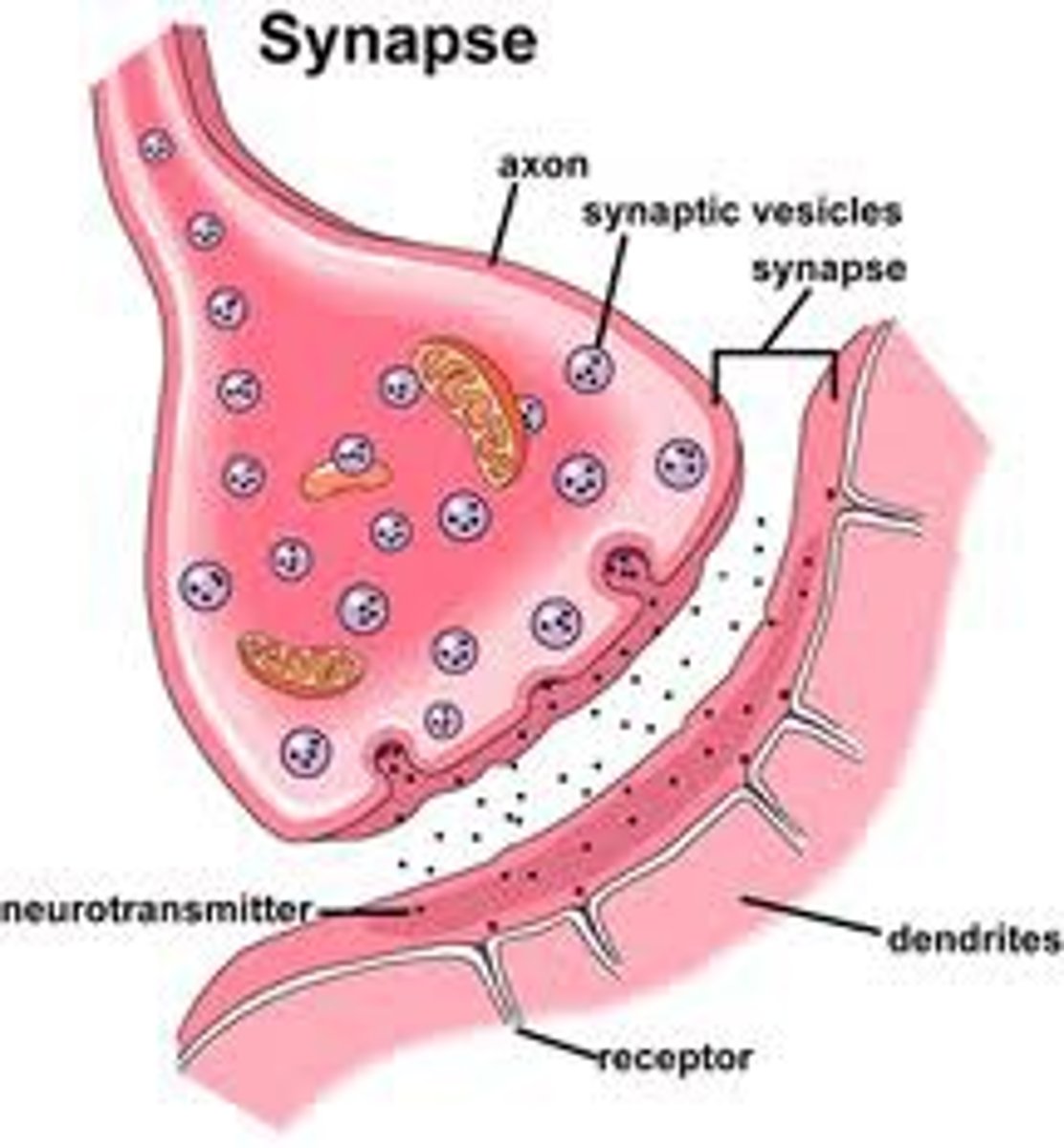
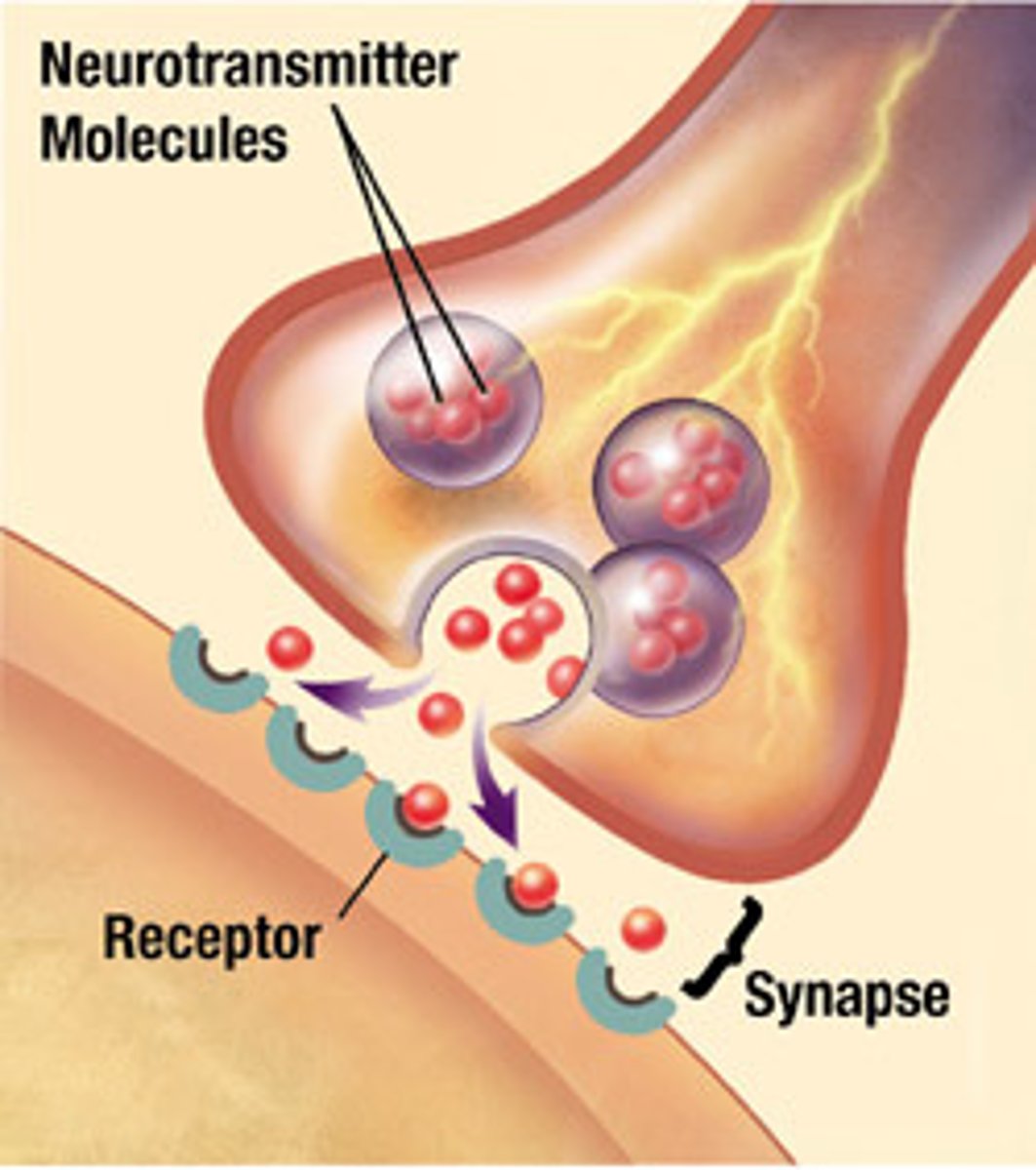
What is released into the synapse
neurotransmitters
Cranial Nerves
12 pairs of nerves that carry messages to and from the brain
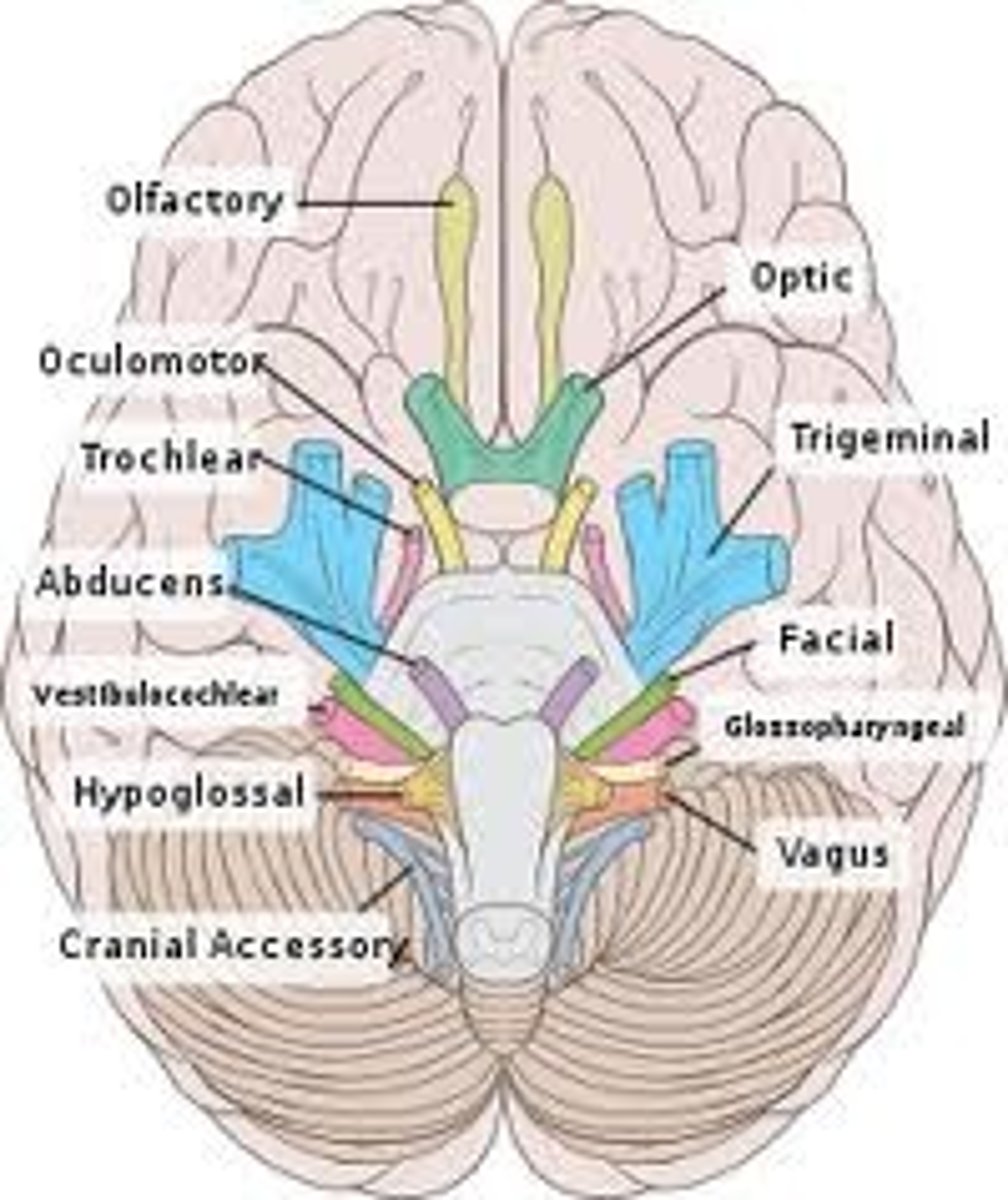
Cranial Nerve neumonic
On Old Olympus' Towering Top A Friend, Ariana Grande, Voiced Songs Hopefully
Olfactory, Optic, Oculomotor, Trochlear, Trigeminal, Abducens, Facial, Auditory, Glossopharyngeal, Vegus, Sensory Hypoglossal
olfactory nerve
the nerve that carries smell impulses from the nose to the brain
optic nerve
the nerve that carries neural impulses from the eye to the brain
oculomotor nerve
eye movement
trochlear nerve
eye movement
trigeminal nerve function
sensory: face, teeth, tongue
motor: muscles of mastication
abducens nerve function
lateral eye movement
facial nerve function
facial expression, taste
Auditory nerve function
sends messages from cochlea to the brain (cerebrum)
glossopharyngeal nerve function
Sensory-Taste, respiration, blood pressure
Motor- Swallowing & gagging
vagus nerve function
Taste, hunger, and GI Tract
sensory cranial nerve function
include special senses such as vision and general senses such as touch and pain (ex: optic, olfactory)
hypoglossal nerve function
tongue movement
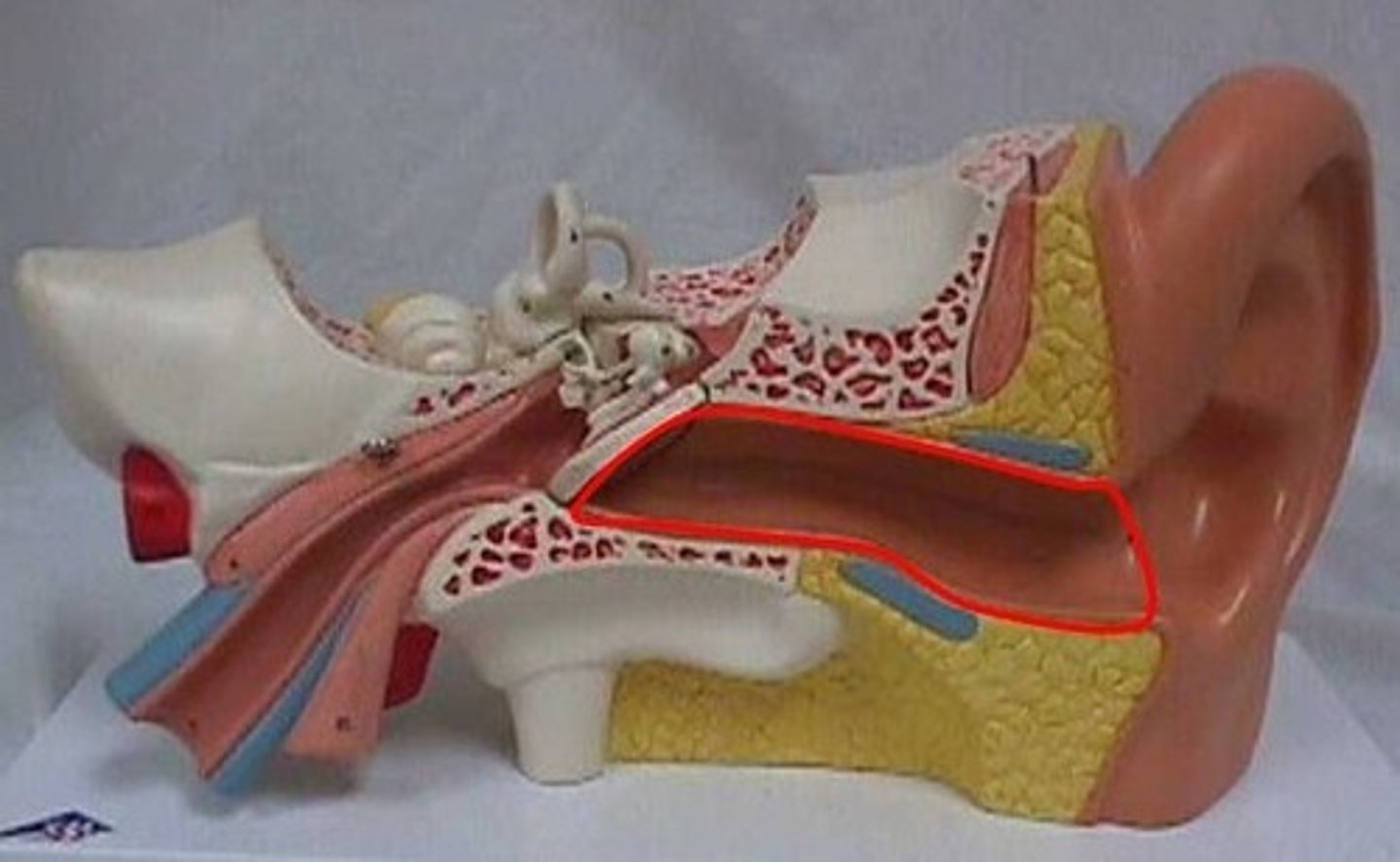
What physical protection does the external auditory meatus (Ex) provide?
Hair cells + cerum (earwax) trap germs + outer enemies
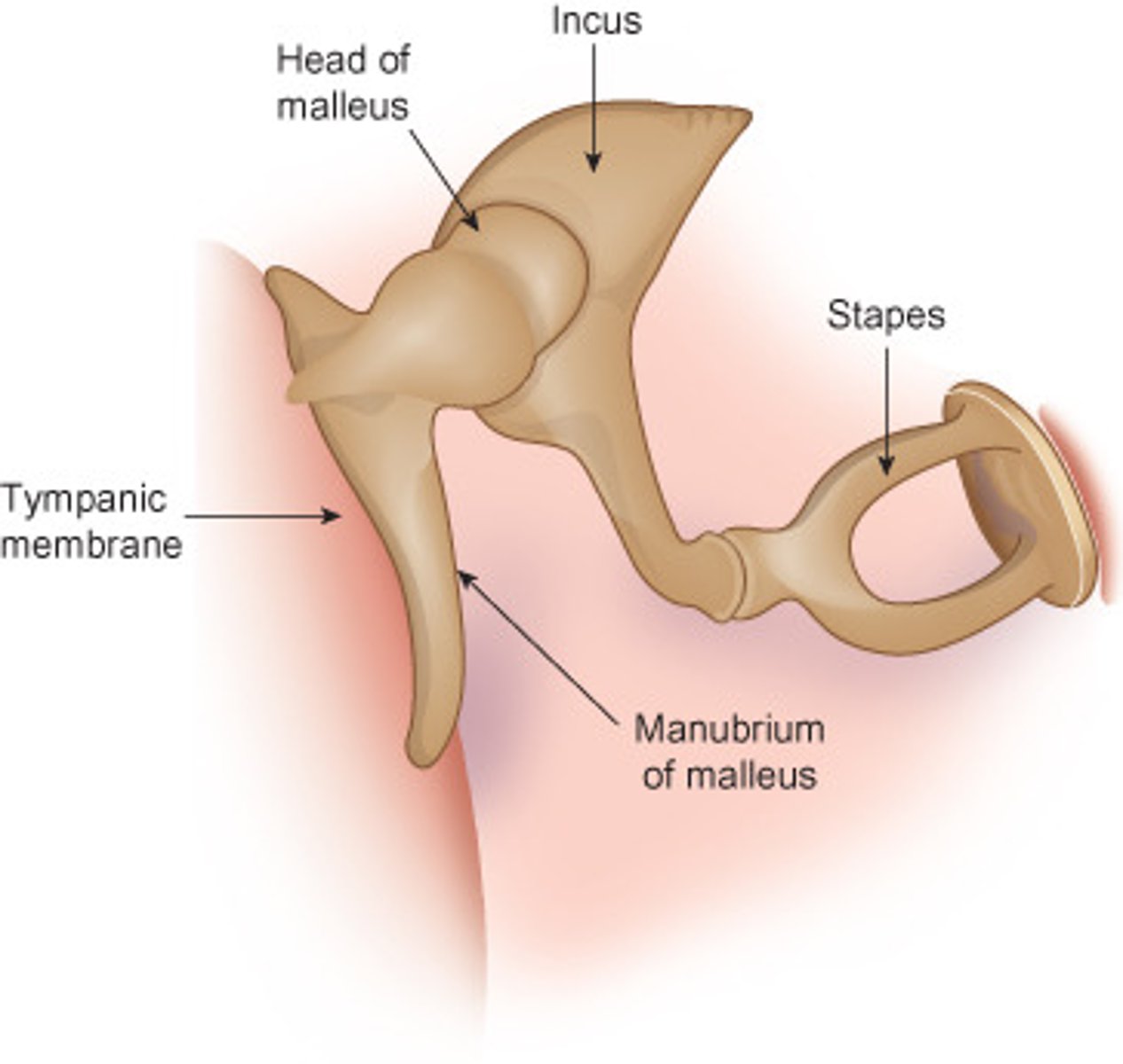
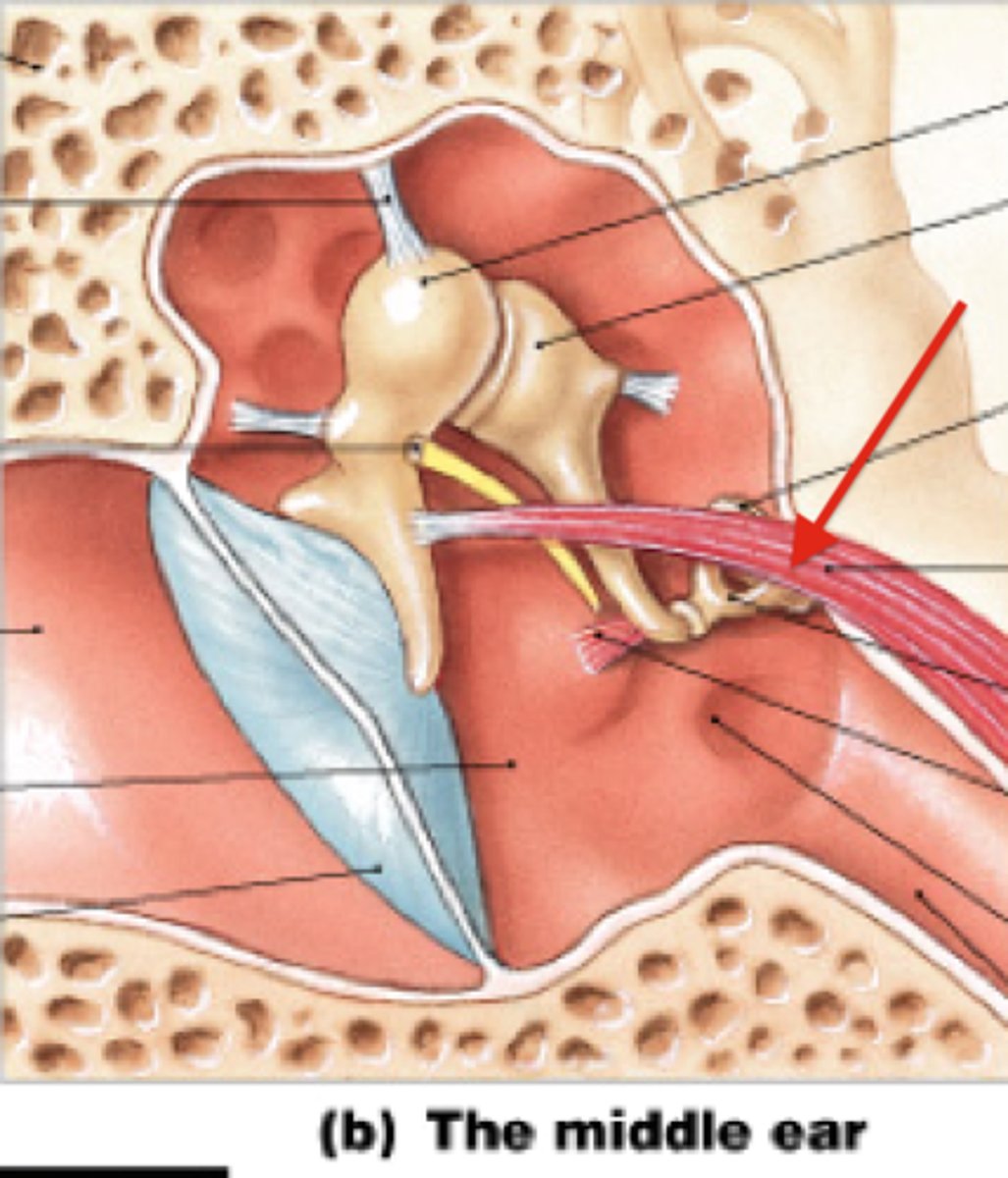
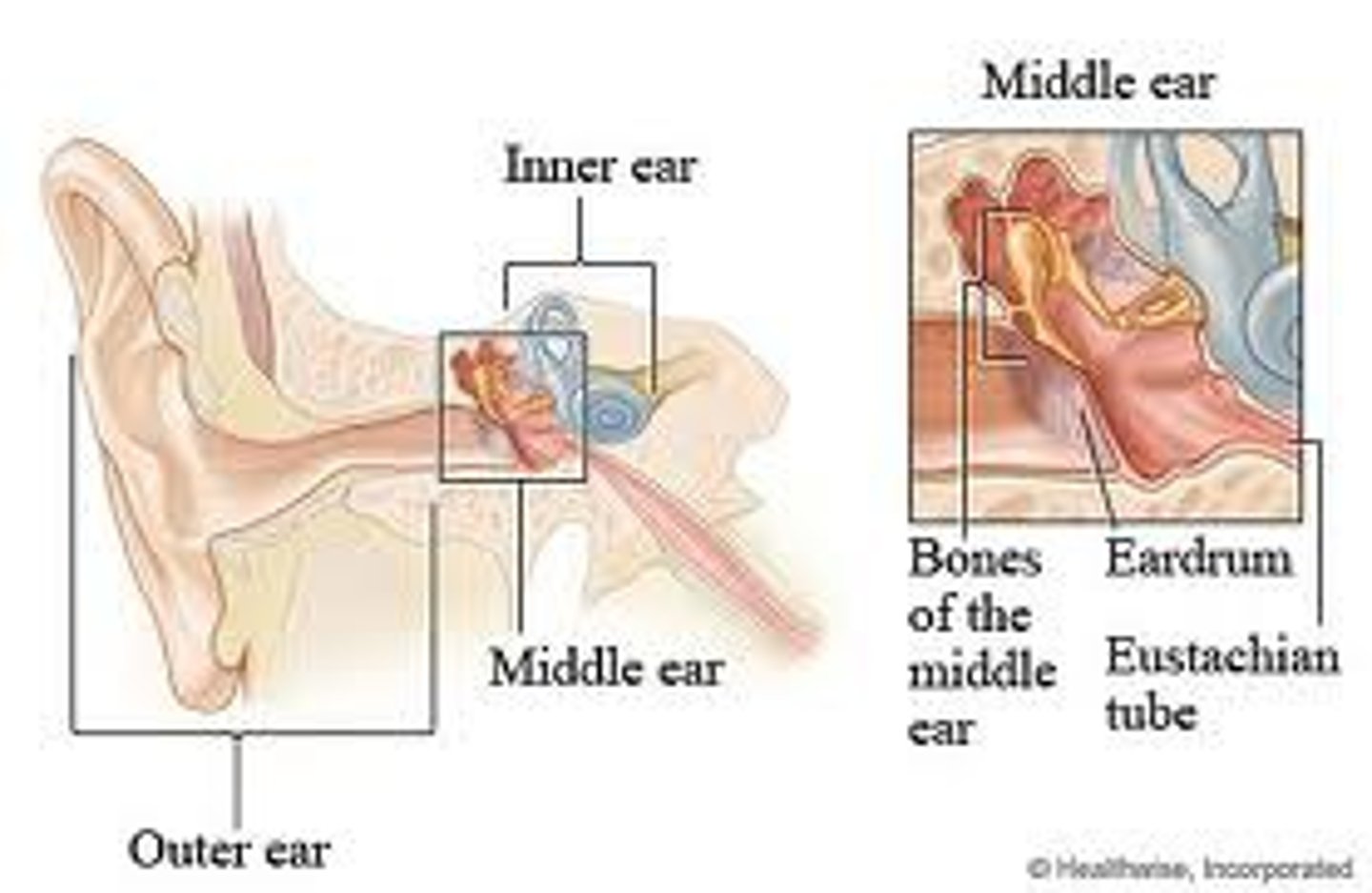
Bones of the middle ear
malleus, incus, stapes (ossicles)
Smallest muscles of the body
stapedius and tensor tympani
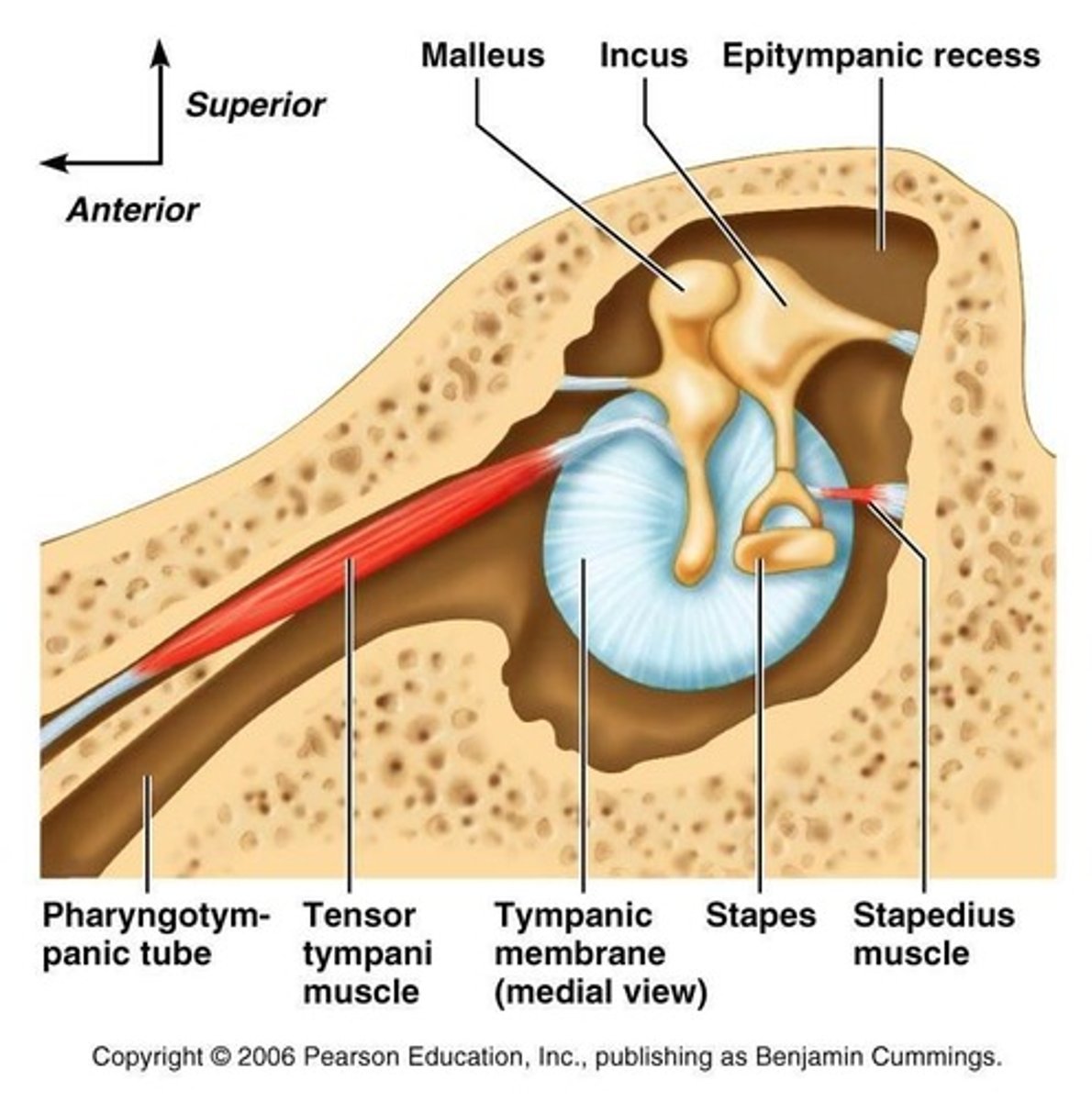
Stapedius
the muscle attached to the stapes; tensing the stapedius decreases vibration
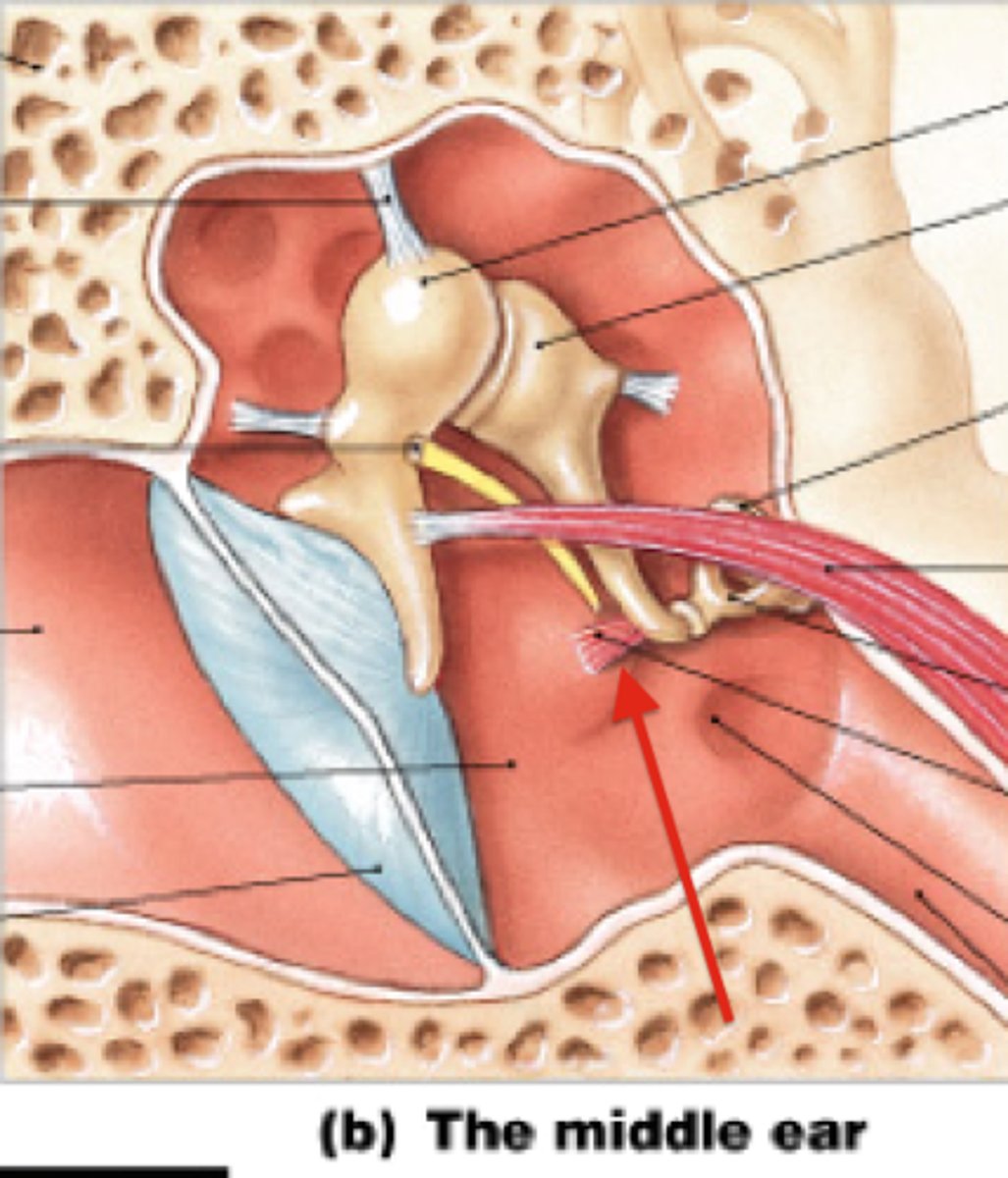
tensor tympani
the muscle attached to the malleus; tensing the tensor tympani decreases vibration
Membrane between scala vestibuli and scala media
vestibular membrane/ Reissner's membrane
Membrane between scala media and scala tympani
basilar membrane
Function of the outer ear
collecting sound and sending it to the eardrum through the auditory canal
What is the function of the middle ear?
Matches airborne acoustic signal with fluid medium of cochlea
-tympanic membrane vibrates, stimulates malleus, incus, stapes, eventual mechanical energy
impedance matching device
term used to refer to the primary function of the middle ear; it must to overcome the difference in impedances of the fluid-filled cochlea and the air-filled middle ear. The middle ear boosts acoustic energy by approximately 30 -33 dB to overcome the impedance mismatch.
What is the function of the Eustachian tube?
Equalize pressure in the middle ear with the outside atmosphere
-angled for drainage
What is the function of the vestibular system?
controls posture and balance
-understands where the head is in the world
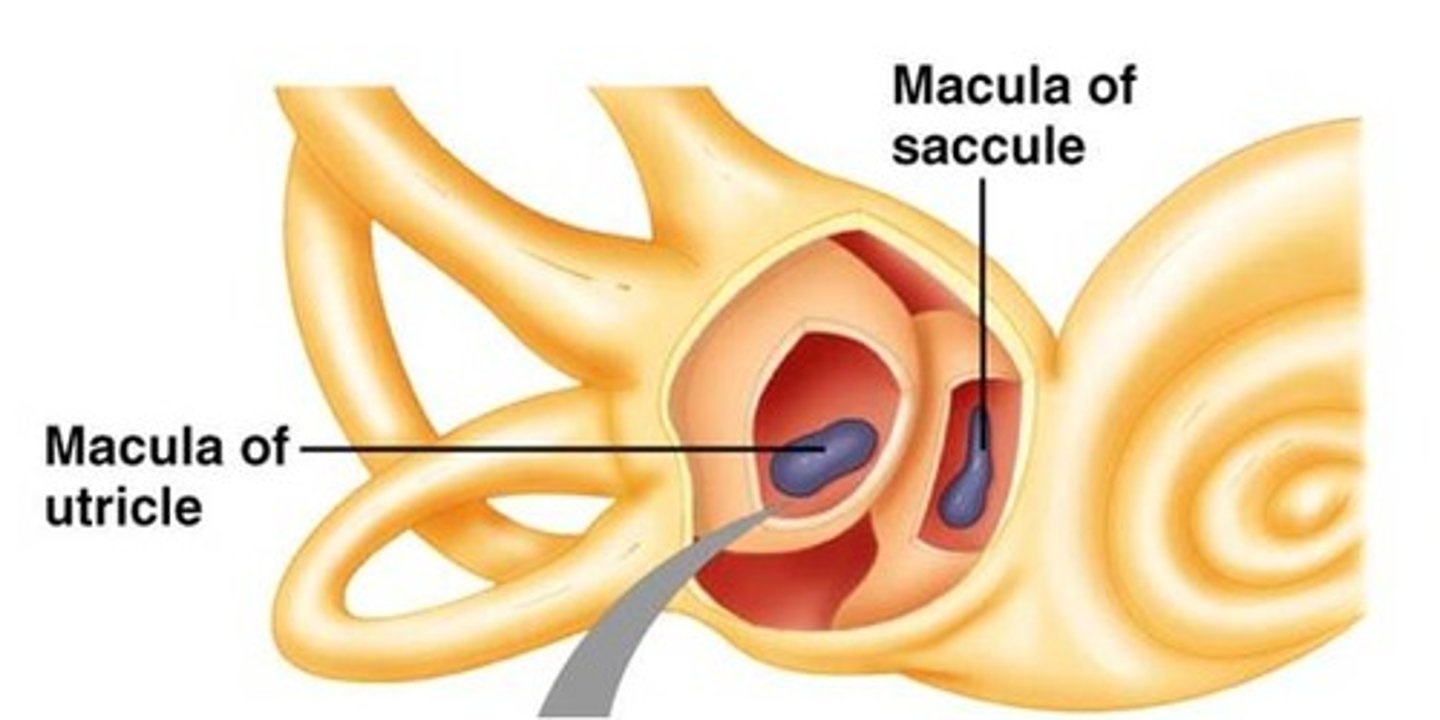
utricle and saccule
Organs of vestibular system
Utricle purpose
Lies in horizontal plane; detects static displacements and linear accelerations (tilting and translational)
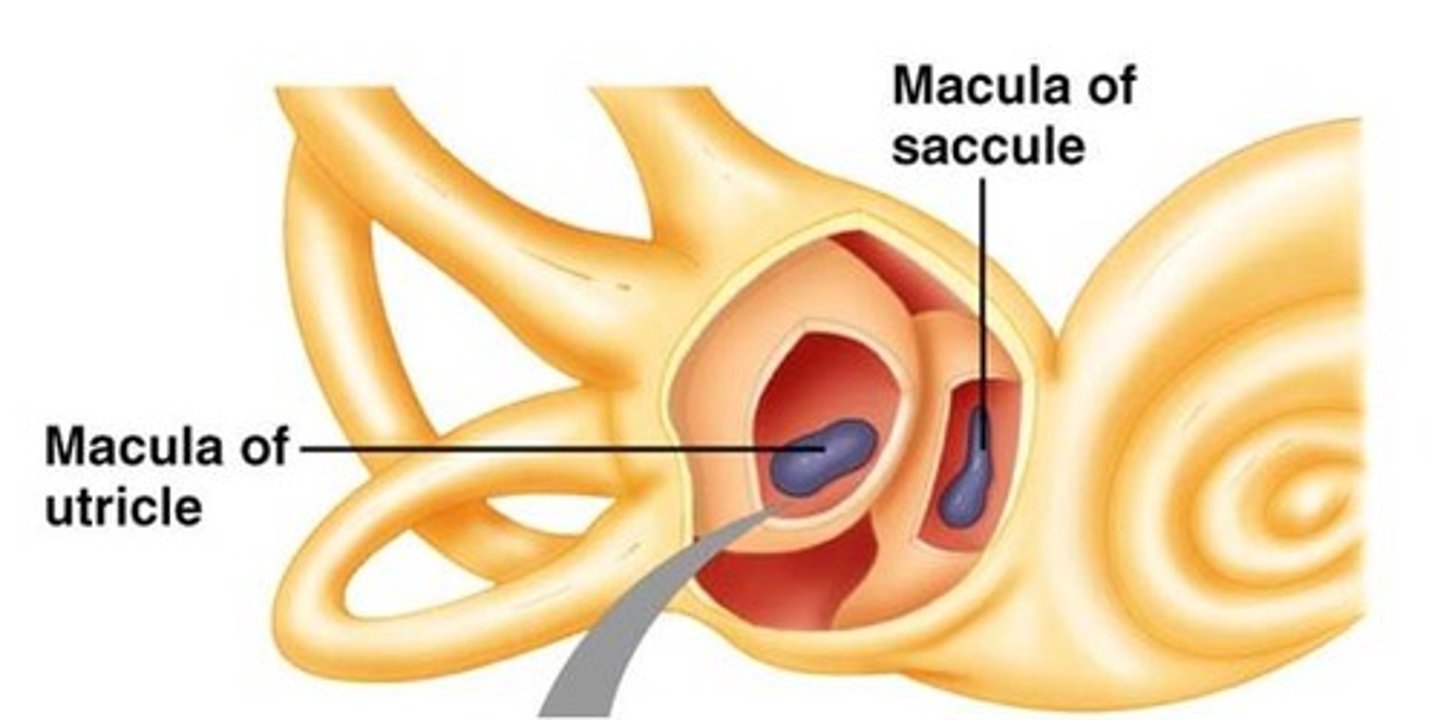
Saccule function
detects vertical acceleration
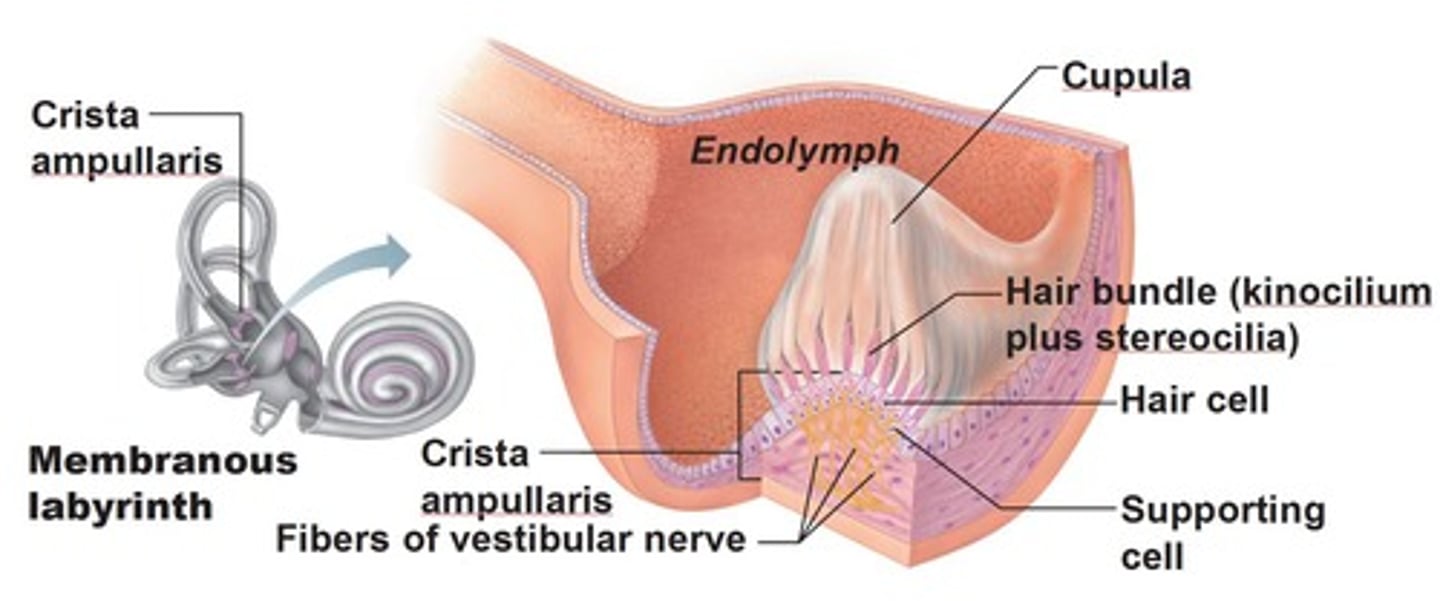
crista ampullaris
A specialized receptor located within the semicircular canals that detects head movements
function of the inner ear
convert mechanical sound waves to neural impulses that can be recognized by the brain for hearing and balance
Fluid of the Scala media
endolymph
fluid in scala tympani + vestibuli
perilymph
Three types of hearing impairment
conductive, sensorineural, mixed
Conductive hearing impairment
Outer or middle ear
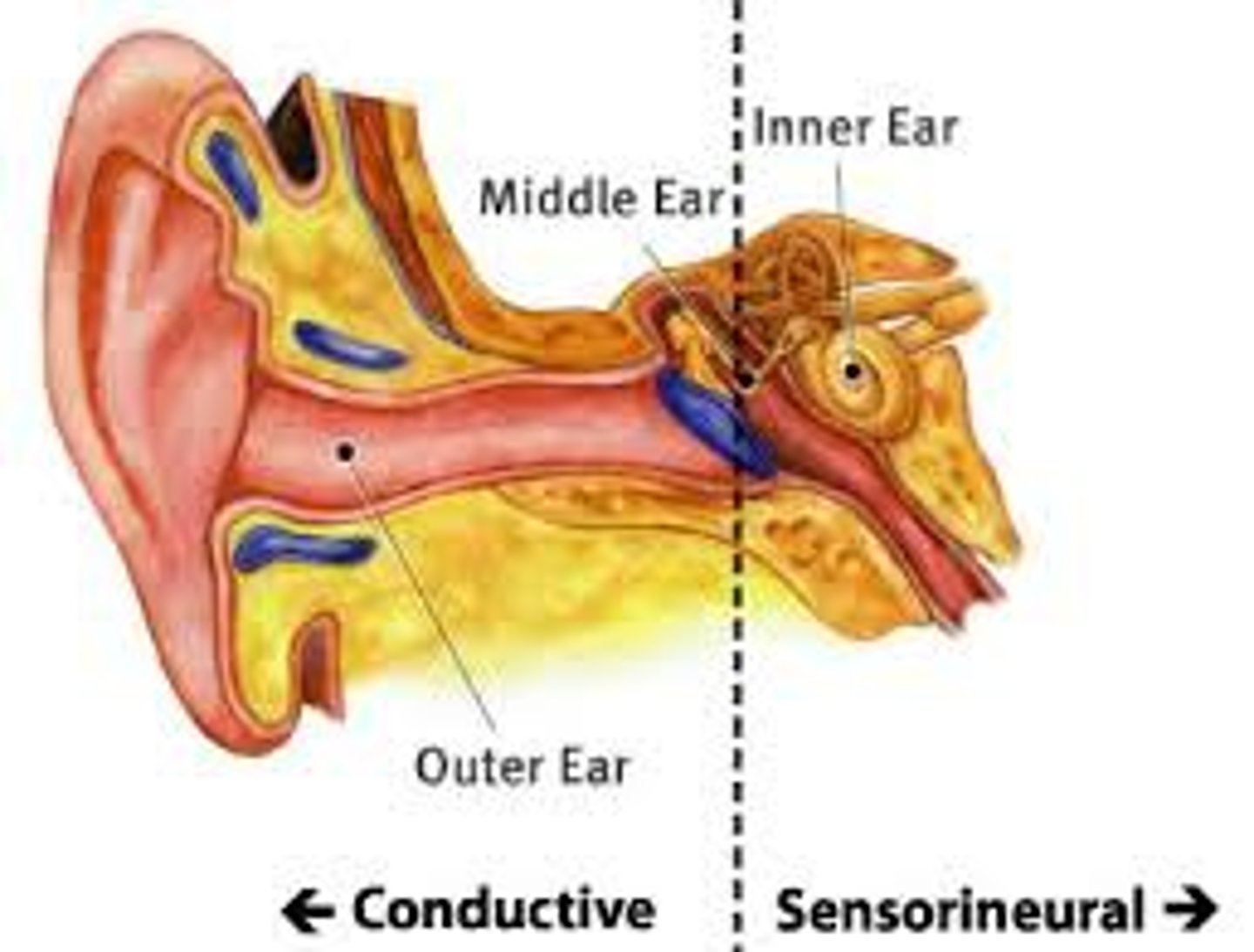
Sensorineural hearing loss
hearing loss caused by damage to the cochlea's receptor cells or to the auditory nerves; also called nerve deafness
-Inner ear
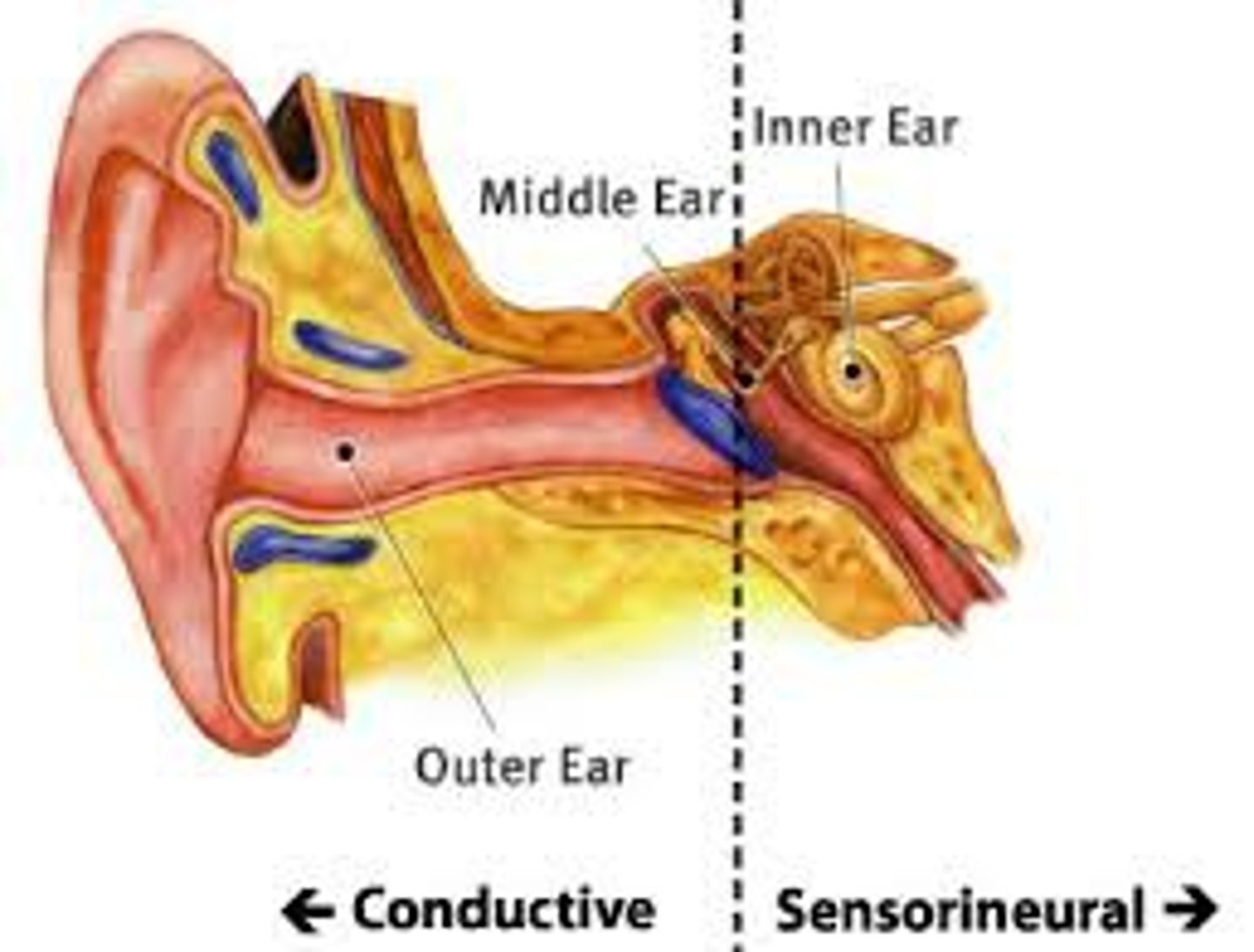
Mixed hearing loss
combination of sensorineural and conductive hearing loss
Hair cells activated by high frequency tones
Base of the basilar membrane
Hair cells activated by low frequency tones
Apex of basilar membrane
Function of the basilar membrane
acts as a spectral analyzer that translates vibration frequencies within the cochlear fluid pressure waves into positions of maximal displacement along its length.
cochlear nerve
the branch of the auditory nerve that transmits auditory information from the cochlea to the brain
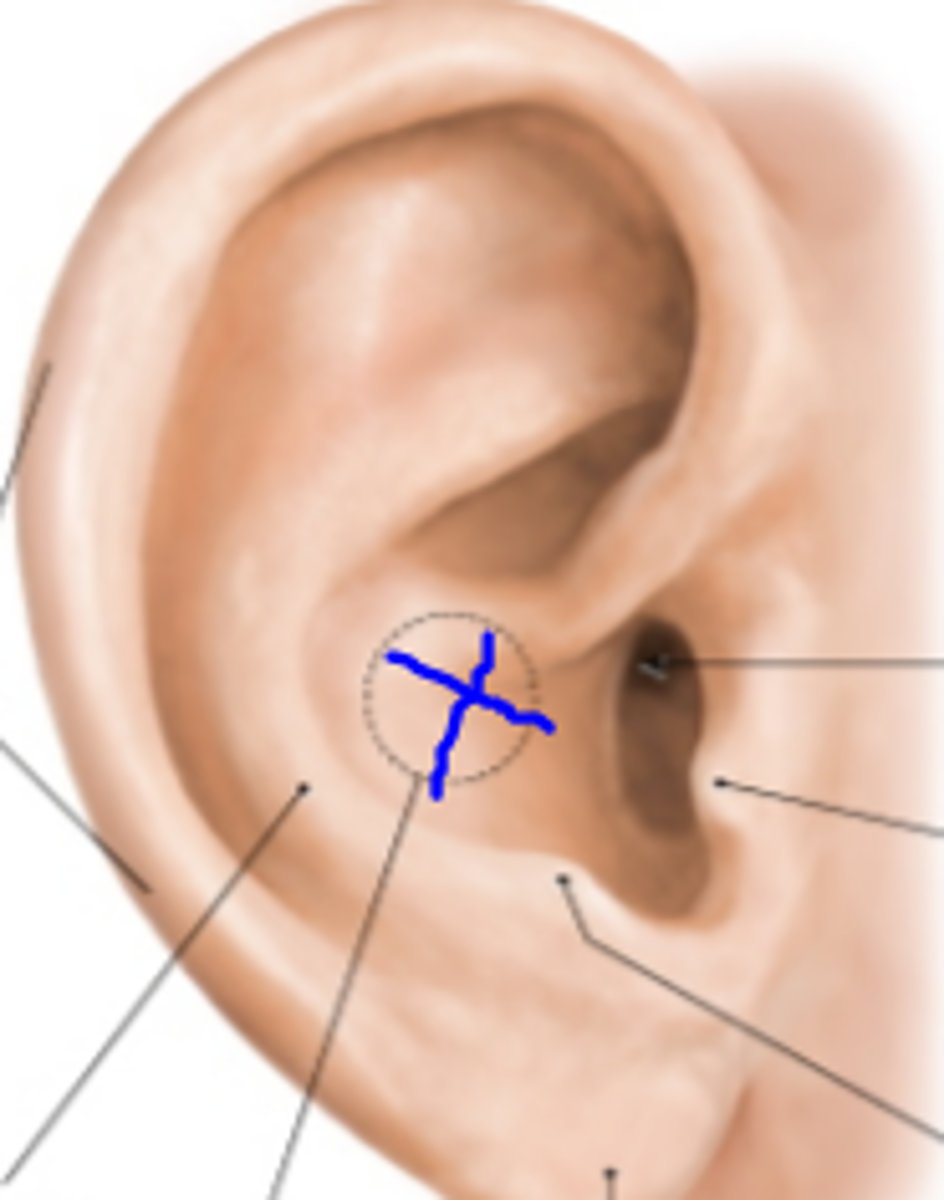
Concha
the concave shell of the ear; the deepest depression of the ear
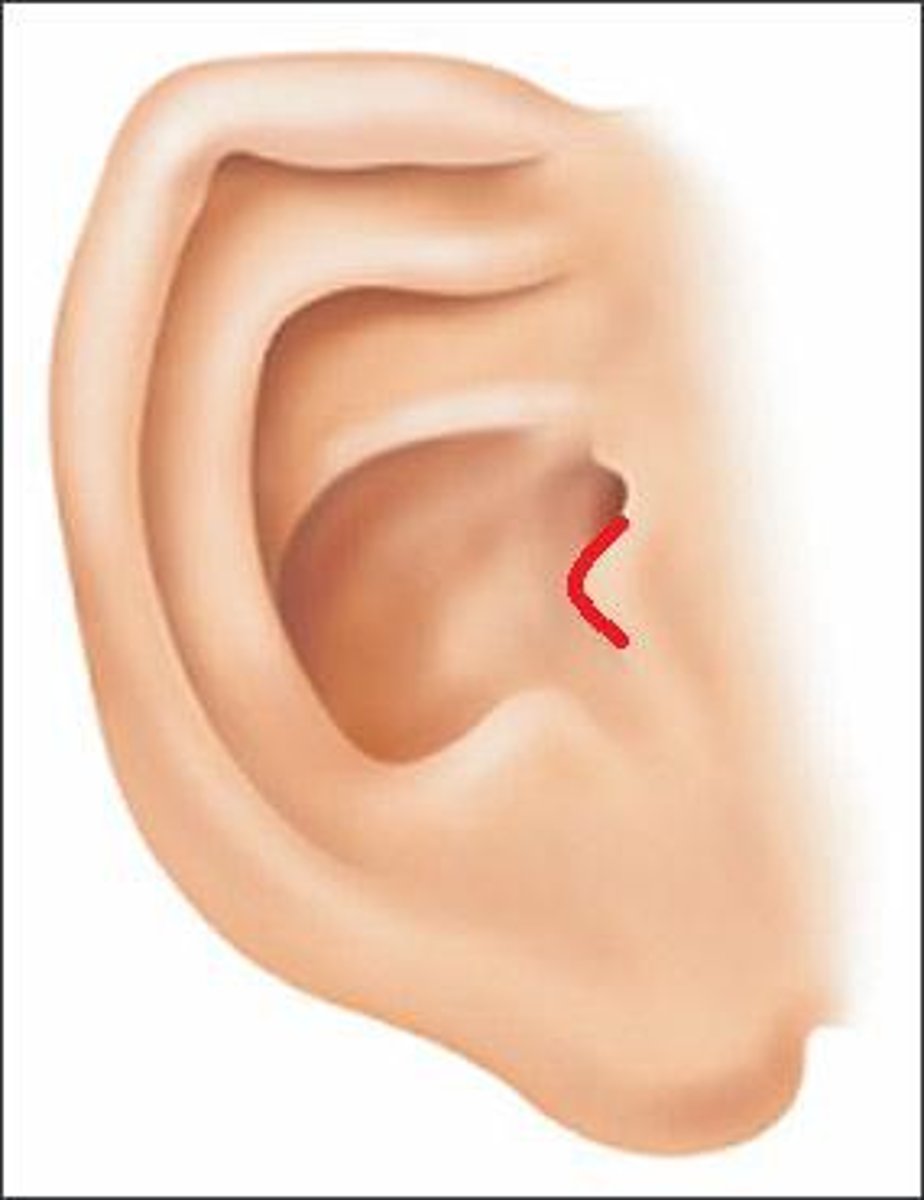
Tragus
Cartilaginous projection anterior to the external opening of the ear
external auditory meatus
ear canal