CH. 6 Bone Tissue - Dr. Jones
1/107
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
108 Terms
osteoprogenitor cells
Bone-forming cells originate from __. (bone stem cell)
skeletal cartilage
made of highly resilient, molded cartilage tissue that consists primarily of water; contain no blood vessels or nerves
perichondrium
dense connective tissue surrounding cartilage like a girdle
-helps cartilage resist outward expansion
-contain blood vessels for nutrient delivery to cartilage
chondrocytes
what cartilage is made up of; cells encased in small lacunae within jelly-like extracellular matrix
hyaline cartilage
most prominent and abundant cartilage
-provides support, flexibility, resilience
hyaline cartilage
cartilage found in:
-Articular (joints)
-costal (ribs)
-respiratory (larynx & respiratory pathways)
-nasal cartilage (external nose)
elastic cartilage
similar to hyaline cartilage, but contains both collagen and elastic fibers
elastic cartilage
cartilage found in:
-external ear
-epiglottis
fibrocartilage
thick collagen fibers that provide great tensile strength
fibrocartilage
cartilage found in:
-menisci of knee
-pubic symphysis
-intervertebral discs
appositional growth
cartilage increase in WIDTH
interstitial growth
cartilage increase in LENGTH
osteocytes
The lacunae of bone contain __.
7 functions of bone
Support for body + organs
Protection of brain, spinal cord, vital organs
Anchorage as levers for muscle action
Mineral Storage of calcium and phosphorus
Blood cell formation; hematopoiesis - occurs in red bone marrow
Triglyceride (fat) storage used for energy source stored in bone cavity
Hormone production of osteocalcin
206
how many bones are in the human body?
80
how many bones in axial skeleton?
126
how many bones in appendicular skeleton?
long bones
bones that are longer than they are wide eg. humerus, finger bone
short bones
bones that resemble cubes. eg. carpal, tarsals
flat bones
bones that are thin, flattened, a bit curved. eg. sternum, ribs, shoulder blade, most skull bones
irregular bones
bones with complicated shape eg. vertebral bones, hip bone
sesamoid bone
bones form within tendons
ex. patella
compact bone
dense outer layer on every bone that appears smooth and solid
spongy bone
made up of honeycomb of small needle-ike or flat pieces of bone called trabeculae
-spaces between trabeculae filled with red or yellow bone marrow
compact bone
__ are sandwiched between connective tissue membranes
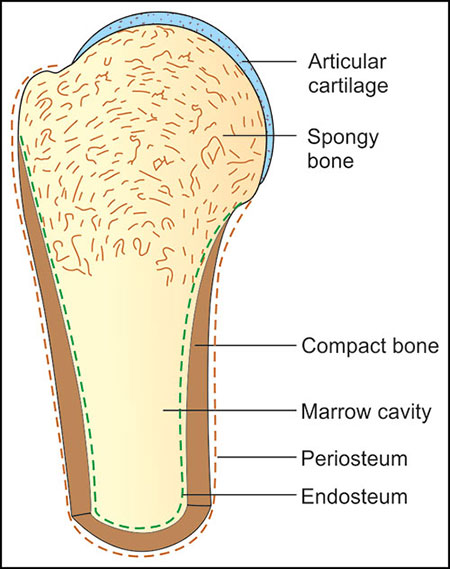
periosteum
covers the OUTSIDE of compact bone
endosteum
covers INSIDE portion of compact bone
hyaline cartilage
__ covers the area of the bone that is part of a moveable joint
diaphysis
shaft of bone
epiphyses
bone ends
diaphysis
filled with yellow bone marrow in adults
epiphyseal line
remant of childhood epiphyseal plate where bone growth occurs
periosteum
white, double membrane that covers external surfaces except joints
fibrous layer
outer layer consisting of dense irregular connective tissue consisting of Sharpey’s fibers that secure to bone matrix
osteogenic layer
inner part of periosteum; contains osteogenic stem cells which give rise to most all bone cells
endosteum
covers internal bone surfaces
covers trabeculae of spongy bone, lines canals that pass thru compact bone
-also contain osteogenic cells that can differentiate into other bone cells
red bone marrow
found in newborns in their medullary cavities and all sponge bone
red bone marrow
found in adults located in heads of femur and humerus
-most active areas of hematopoiesis are flat bone diploe and some irregular bones (hipbone)
dipole
another name for spongy bone
yellow bone marrow
a tissue that may revert back to red marrow if a person needs more red blood cells (in extreme cases)
tuberosity
large rounded projection; may be roughened
trochanter
very large, blunt, irregularly shaped process eg. on femur
turbercle
small rounded projection or process
epicondyle
raised area or above condyle
groove
furrow
fissure
narrow, slit-like opening
process
any bony prominence
spine
sharp, slender, often pointed projection
head
bony expansion carried on a narrow neck
facet
smooth, nearly flat articular (joint) surface
condyle
rounded articular projection; often articulates with a corresponding fossa
foramen
round or oval opening through a bone
notch
indentation at the edge of a structure
meatus
canal-like passageway
sinus
cavity within bone filled with air and lined with mucous membrane
fossa
shallow,basin-like depression in a bone
red bone marrow
Hematopoiesis occurs in
vitamin D production
what does the skeletal system NOT do?
long bone
A bone which has an epiphysis at each end is a
perforating (Sharpey's) fibers
The periosteum is attached to the underlying bone through
osteoclast
When there is too little calcium in blood, which cells begin resorption of bone to release calcium to the blood?
collagen
Bone is somewhat flexible due to the presence of
the epiphyses of long bones
Spongy bone is found in:
osteoclast
breaks down bone matrix
chondrocytes
what is found in the epiphyseal plate?
osteon
structural unit of compact bone
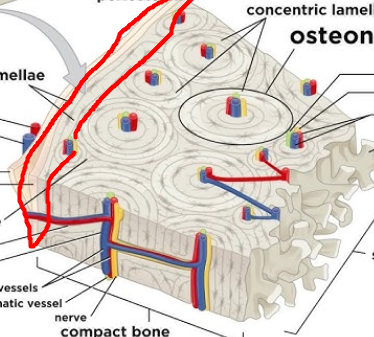
lamellae
layers of bone tissue; contain collagen fibers that run in different directions of adjacent rings, withstands stress and resist twisting
central canal
runs through core of osteon; provides oxygen and nutrients via blood vessels and nerve fibers
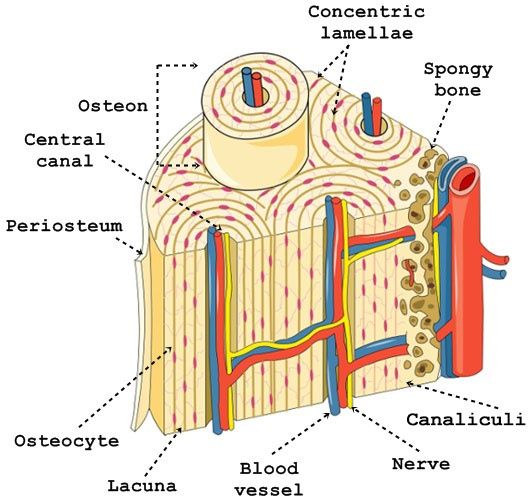
perforating canals
canals lined with endosteum that occur at right angles to central canal; poke holes in connecting osteon
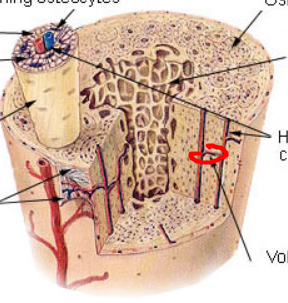
canaliculi
hairlike canals that connect lacunae to each other; enables communication between all osteocytes of osteon “sidewalk or street”
lacunae
small cavities containing osteocytes “house”
interstitial lamellae
lamellae that are not part of osteon, fills gaps between forming osteons
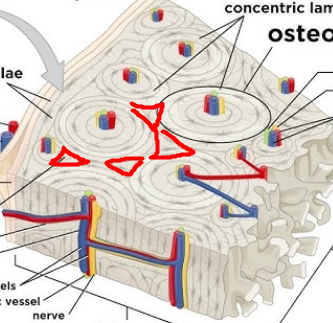
circumferential lamellae
layers of lamellae that extend around entire surface of diaphasis and AROUND and OUTSIDE the various osteons
spongy bone
appears poorly organized but organized along lines of stress to help bone resist any stress, contain trabeculae and no osteons
trabeculae
like cables on a suspension bridge, giving strength to bone… found in spongy bone
osteoid
protein of bone
hydroxyapatites (mineral salts)
calcium which contributes to hardness of bone + resistance
compression
bone is HALF as strong as steel in resisting ___
tension
bone is as strong as steel in resisting ___
ossification (osteogenesis)
process of bone tissue formation
endochondral ossification
bone forms by replacing hyaline cartilage
cartilage (endochondral) bone
bones formed by hyaline cartilage and provides framework for skeleton
intramembranous ossification
bone develops fibrous membrane (membrane bones)
interstitial growth
long bones grow lengthwise
appositional growth
bones increase thickness
epiphyseal plate closure
occurs when epiphysis and diaphysis close
nondisplaced fracture
fracture where ends retain normal postion
displace fracture
fracture where ends are out of norml alignment
complete fracture
broken all the way through
incomplete fracture
not broken all the way through
open (compound) fracture
skin is penetrated
closed (simple) fracture
skin is not penetrated
comminuted fracture
type of fracture
-bone fragments into 3 or more pieces
-common in older adults who have brittle bones
spiral fracture
type of fracture
-ragged break occurs when excessive twisting forced are applied to bone
-common sports fracture
-also seen in abuse cases
depressed fracture
type of fracture
-Broken bone portion is pressed inward
-typical of skull fracture
compression fracture
type of fracture
-bone is crushed
-common in porous bones (osteoporotic bone) subjected to extreme trauma like a fall
epiphyseal fracture
type of fracture
-epiphysis separates from the diaphysis along the epiphyseal plate
-tends to occur where cartilage cells are dying and calciication of matrix is occuring
greenstick fracture
type of fracture
-bone breaks incompletely, much in the way a green twig breaks.
-only one sie of shaft breaks; other side bends
-common in children whose bones are more flexible than those of adults
closed reduction
physician manipulates to correct position of broken bone
open reduction
surgical pins or wires secure ends of bone