Unit 6 - Medical
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/39
Last updated 3:49 AM on 3/27/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
1
New cards
Characteristics of Bacterial Infections
* DNA only
* Either gram negative or gram positive
* Antibiotics typically effective
* Biofilm - films of bacteria (attacked by antibiotic); reason people get their tonsils removed
* Cysts
* Either gram negative or gram positive
* Antibiotics typically effective
* Biofilm - films of bacteria (attacked by antibiotic); reason people get their tonsils removed
* Cysts
2
New cards
Characteristics of Viral Infections
* RNA or DNA
* Cellular takeover
* Retrovirus - inserts a DNA copy of its RNA genome into the DNA of a host
* Vaccines offer prevention
* Antibiotics typically not effective
* Potentially long contagious period
* Rapid mutations - RNA viruses can change, DNA viruses do not change (usually)
* Vaccines tend to be specific to the type of antigen
* Incredibly dangerous if uncontrolled (ex: only 3 people survived rabies)
* Cellular takeover
* Retrovirus - inserts a DNA copy of its RNA genome into the DNA of a host
* Vaccines offer prevention
* Antibiotics typically not effective
* Potentially long contagious period
* Rapid mutations - RNA viruses can change, DNA viruses do not change (usually)
* Vaccines tend to be specific to the type of antigen
* Incredibly dangerous if uncontrolled (ex: only 3 people survived rabies)
3
New cards
What types of immunity can vaccines provide? (x2)
Sterilizing immunity - take the vaccine, never get that disease
Effective immunity - moderates virus, slows down, gives the body a better chance
\
Purpose: your body can get used to a specific virus so it can fight back
Effective immunity - moderates virus, slows down, gives the body a better chance
\
Purpose: your body can get used to a specific virus so it can fight back
4
New cards
Aspects of the innate system
* Physical barriers
* Mucous Membranes
* Bactericidal Fluids
* Macrophages
* Scavenger cells
* Kills everything and doesn’t care
* Mucous Membranes
* Bactericidal Fluids
* Macrophages
* Scavenger cells
* Kills everything and doesn’t care
5
New cards
Aspects of the adaptive system
* Cell based
* T cells
* B cells
* NK cells
* Antibodies
* T cells
* B cells
* NK cells
* Antibodies
6
New cards
NK cells
NK = natural killer cells
* look for infected cells with a virus and kill them before they can produce any more of the virus
* look for infected cells with a virus and kill them before they can produce any more of the virus
7
New cards
A simple way to remember the innate and adaptive immune system…
Simple innate: think walls, inflammation, swelling, blocking
\
Complex adaptive: think assassins, precision, takes time to ramp up, specific to an invader
\
Complex adaptive: think assassins, precision, takes time to ramp up, specific to an invader
8
New cards
3 key points of cancer
1. Runaway cell division
2. Specific Cancer Pathway
3. Metasize or stay in one spot
9
New cards
Specific cancer pathway (journey) includes…
* dexposure to carcinogen
* activation of proto-oncogene
* suppression of tumor suppressor
* activated oncogene
* runaway cell growth
* disruption of physiology
* death
* activation of proto-oncogene
* suppression of tumor suppressor
* activated oncogene
* runaway cell growth
* disruption of physiology
* death
10
New cards
How can cancers be identified?
Via total body MRI’s
11
New cards
Stage 1 Cancer
Small number of cells bounded by a membrane in one location
12
New cards
Stage 2 Cancer
The cancer is growing exponentially, still bounded by a membrane and still in one location
13
New cards
Stage 3 Cancer
* Membrane ruptured
* Cells metastasized (could be everywhere)
Should cut them out and treat them with a gamma knife
* Cells metastasized (could be everywhere)
Should cut them out and treat them with a gamma knife
14
New cards
Stage 4 Cancer
Terminal cancer; people don’t come back from it (in terms of time left
15
New cards
Para-neoplastic Syndrome
A group of rare disorders that occur when the immune system has a reaction to a cancerous tumor known as a "neoplasm”
* the body’s NK cells go overdrive
* Random
* the body’s NK cells go overdrive
* Random
16
New cards
Dying and Death mean…
Sensation of effort and stopping of effort
17
New cards
Dissociation in death and dying:
* separating oneself from the environment
* creation of distance
* creation of distance
18
New cards
Gallows Humor
Processing and Deflection
* A way fro medical professionals to process and deflect themselves from the situcation
* A way fro medical professionals to process and deflect themselves from the situcation
19
New cards
CISD
CISD: Critical Incident Stress Debriefing
* The process in which teams of professional and peer counselors provide emotional and psychological support to incident personnel who are or have been involved in a critical (highly stressful) incident
\
Be aware of the steps!
* The process in which teams of professional and peer counselors provide emotional and psychological support to incident personnel who are or have been involved in a critical (highly stressful) incident
\
Be aware of the steps!
20
New cards
How does one’s passing (death) come by?
* Number of slow breaths
* Lose of moisture in eyes
* Pupils fix and dilate
* Usually people pass out before they die
* Dead Weight
* Lose of moisture in eyes
* Pupils fix and dilate
* Usually people pass out before they die
* Dead Weight
21
New cards
DNR
Do Not Resuscitate form (pink slip)
* PT doesn’t want us to perform CPR, take to an ER, etc (depends)
* Can be overriden if PT verbally overrides it
* PT doesn’t want us to perform CPR, take to an ER, etc (depends)
* Can be overriden if PT verbally overrides it
22
New cards
Mast cells
Allergy cells responsible for immediate allergic reactions
* huge, inside a blood vessel, scans the blood stream for threats
* huge, inside a blood vessel, scans the blood stream for threats
23
New cards
The process of getting an allergic reaction:
Mast cells are allergy cells responsible for immediate allergic reactions. They cause allergic symptoms by releasing products called “mediators” stored inside them or made by them. In allergic reactions, this release occurs when the allergy antibody __IgE__, which is present on the mast cell surfaces, binds to proteins that cause allergies, called allergens. This triggering is called activation, and the release of these mediators is called degranulation.
24
New cards
What happens in your body when you have an allergy?
Your body doesn’t produce mast cells, basophils, eosinophils, when a person is young and aren’t exposed to certain things/food
* should try to get exposed to many things before 9 m/o (6 m/o
* should try to get exposed to many things before 9 m/o (6 m/o
25
New cards
Anaphylaxis is a form of…
Distributive shock
26
New cards
When you have an allergic reaction, what do you do?
1. Call EMS
2. See if there is an EpiPen and help if needed
3. Keep calm or try to keep the person calm who is having an allergic reaction
4. Lie on your back or help the person lie on their back
27
New cards
key management strategies in Behavioral/Psychiatric
* Stay calm
* Stay apart
* Stay present (never leave the PT alone)
* Stay breathing
* Stay Safe - Get EMS
* Stay apart
* Stay present (never leave the PT alone)
* Stay breathing
* Stay Safe - Get EMS
28
New cards
Histamine Pathway Blockers (x3)
* Zofran
* Phenergan
* Bendryl
* Phenergan
* Bendryl
29
New cards
Adult dosage vs Geriatric dosage
Explain the difference
Explain the difference
Adult = 25 mg
Geriatric is 1/4 that amount
Geriatric = 6.25 mg
\
As you get older, drugs last and leave longer in the system
Geriatric is 1/4 that amount
Geriatric = 6.25 mg
\
As you get older, drugs last and leave longer in the system
30
New cards
Describe the stages of shock
point of assault → compensated → decompensated → irreversible
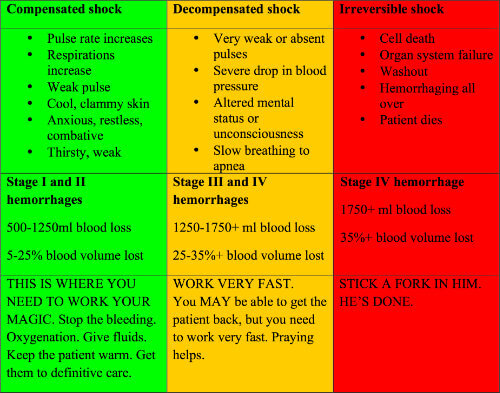
31
New cards
Types of shock
* Cardiogenic - pump failure
* Distributive - not enough fluid
* Obstructive - block in pipes
* Sepsis - bacteria breaks down capillary beds
* Extreme response after an infection
* Complication of an infection - body responds improperly to an infection
* Distributive - not enough fluid
* Obstructive - block in pipes
* Sepsis - bacteria breaks down capillary beds
* Extreme response after an infection
* Complication of an infection - body responds improperly to an infection
32
New cards
Type 1 vs Type 2 Diabetes
Type 1
* the immune system is attacking and destroying the insulin-producing cells in your pancreas
* born with it
\
Type 2
* cells don’t normally respond to insulin
* develops over time (age, obesity, diet, etc)
* the immune system is attacking and destroying the insulin-producing cells in your pancreas
* born with it
\
Type 2
* cells don’t normally respond to insulin
* develops over time (age, obesity, diet, etc)
33
New cards
Borderline personality disorder (BPD)
long period of time, impulsive, fear of abandonment, reckless behavior, over attachment
34
New cards
What happens when a male happens tearing stomach pain?
What happens when a female happens tearing stomach pain?
What happens when a female happens tearing stomach pain?
Male having tearing stomach pain → abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA)
Female having tearing stomach pain → ectopic pregnancy (if not ectopic pregnancy → AAA)
Female having tearing stomach pain → ectopic pregnancy (if not ectopic pregnancy → AAA)
35
New cards
Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC)
End point of sepsis or cancer
* Small blood clots develop throughout the bloodstream, blocking small blood vessels. The increased clotting depletes the platelets and clotting factors needed to control bleeding, causing excessive bleeding
* Not a bleeding disorder, it is a clotting disorder
* Small blood clots develop throughout the bloodstream, blocking small blood vessels. The increased clotting depletes the platelets and clotting factors needed to control bleeding, causing excessive bleeding
* Not a bleeding disorder, it is a clotting disorder
36
New cards
5Fs
5Fs - female, fat, fair, non fertile, forty
* If two or more of the 5 F's are present, your cardiac symptoms are random (ie; *not* crushing chest pain)
* If two or more of the 5 F's are present, your cardiac symptoms are random (ie; *not* crushing chest pain)
37
New cards
Parasites
* Pinworms - enter through the genitals (oral fecal route)
* Hookworm - going through the feet
* Ringworm is fungus
* Hookworm - going through the feet
* Ringworm is fungus
38
New cards
Know the Hepatitieses
* Hepatitis A is spread through the stool of an infected person
* Hepatitis B is spread through bodily fluids,
* Hepatitis C is spread through blood
None of them are spread through touching a person who is affected (oral fecal route only and bloodborne)
* Hepatitis B is spread through bodily fluids,
* Hepatitis C is spread through blood
None of them are spread through touching a person who is affected (oral fecal route only and bloodborne)
39
New cards
Toxidromes
* Anticholinergic
* Cholinergic
* Opioid
* Sedative-Hypnotic
* Sympathomimetic
* Histanergic/Nicotinic
* Cholinergic
* Opioid
* Sedative-Hypnotic
* Sympathomimetic
* Histanergic/Nicotinic
40
New cards
Coma vs seizure vs Persistent vegetative state
Coma: a state of unresponsiveness in which the patient cannot be aroused with stimulation
\
Seizure
* Absent seizures
* Focal / petit mal seizures
* Grand mal
* Diabetic
\
Persistent vegetative state: a condition in which a medical patient is completely unresponsive to psychological and physical stimuli and displays no sign of higher brain function, being kept alive only by medical intervention.
\
Seizure
* Absent seizures
* Focal / petit mal seizures
* Grand mal
* Diabetic
\
Persistent vegetative state: a condition in which a medical patient is completely unresponsive to psychological and physical stimuli and displays no sign of higher brain function, being kept alive only by medical intervention.