Psych unit 3 AOS1: how does the nervous system enable psychological functioning?
5.0(6)Studied by 45 people
Card Sorting
1/46
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 9:40 AM on 3/22/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
1
New cards
Central nervous system (CNS)
\-Receives and processes sensory info from the body’s INTERNAL & EXTERNAL environments → to coordinate a response.
\-Comprises of the brain and spinal cord.
\-Comprises of the brain and spinal cord.
2
New cards
Brain (CNS)
\-**Control centre** of the entire NS.
\-Responds to sensory info & is responsible for everything that we think/do.
\-Responds to sensory info & is responsible for everything that we think/do.
3
New cards
Spinal cord (CNS)
\-Connects **brain & peripheral NS.**
\-Receives sensory info from the body & carries the messages to the brain for processing.
\-Motor info from brain is carried to organs/glands via peripheral NS.
\-Initiates involuntary **spinal reflex**.
\-Receives sensory info from the body & carries the messages to the brain for processing.
\-Motor info from brain is carried to organs/glands via peripheral NS.
\-Initiates involuntary **spinal reflex**.
4
New cards
Peripheral nervous system (PNS)
\-Carries info about body’s **peripheral & external environments towards the CNS.**
\-Carries info from **CNS to the muscles, organs & glands.**
\-Carries info from **CNS to the muscles, organs & glands.**
5
New cards
Somatic nervous system (PNS)
\-Carries **motor** info from CNS to skeletal muscles → signals them to expand/contract.
\-Carries **sensory** info from receptor sites towards CNS to enable **voluntary coordinated response** to stimuli.
\-Carries **sensory** info from receptor sites towards CNS to enable **voluntary coordinated response** to stimuli.
6
New cards
Autonomic nervous system (PNS)
\-Connects the CNS to the body’s internal organs & glands (self-regulating).
\-Changes visceral muscles, organs & glands in response to demands placed on the body.
\-Changes visceral muscles, organs & glands in response to demands placed on the body.
7
New cards
Sympathetic nervous system (ANS)
\-Increases activity of internal muscles, organs & glands to **prepare body** for **action** or **a stressor**.
\-Eg. increased heart beats, increased secretion of glucose in liver (energy), dilated pupils, expanded airways.
\-Eg. increased heart beats, increased secretion of glucose in liver (energy), dilated pupils, expanded airways.
8
New cards
Parasympathetic nervous system (ANS)
\-The counter-balance activity of the sympathetic NS.
\-Helps restore body to its normal state after action/stressor.
\-Eg. constricted pupils, resting heartbeat, constricted airways.
\-Helps restore body to its normal state after action/stressor.
\-Eg. constricted pupils, resting heartbeat, constricted airways.
9
New cards
Enteric nervous system (ANS)
\-Monitors physiological conditions of the digestive tract.
\-Integrates digestive tract’s info about its muscle contractions, gastric acid secretion and blood flow.
\-Can function independently of the brain.
\-Integrates digestive tract’s info about its muscle contractions, gastric acid secretion and blood flow.
\-Can function independently of the brain.
10
New cards
Conscious response
\-Reaction to sensory stimuli that involves awareness (voluntary).
\-Eg. shielding your eyes when its too sunny.
\-Eg. shielding your eyes when its too sunny.
11
New cards
Unconscious response
\-Reaction to sensory stimuli that doesn’t involve awareness (involuntary).
\-Eg. blinking when eyes get too dry.
\-Eg. blinking when eyes get too dry.
12
New cards
Spinal reflex
\-Unconscious and automatic response controlled by nerual circuits in the spinal cord.
\-Reflex arc: sensory info is reflected back from the spinal cord.
\-Helps body react quickly to pain.
\-Reflex arc: sensory info is reflected back from the spinal cord.
\-Helps body react quickly to pain.
13
New cards
Neurotransmitter
\-Chemical substance produced by a neuron that carries a message to other nearby neurons.
14
New cards
Synaptic gap
\-Tiny space b/w axon terminals of presynaptic neuron and dendrite of postsynaptic neuron.
1) Excitatory - stimulates a postsynaptic neuron to **perform its functions.**
3) Inhibitory - blocks/prevents a postsynaptic neuron **from firing and functioning**.
1) Excitatory - stimulates a postsynaptic neuron to **perform its functions.**
3) Inhibitory - blocks/prevents a postsynaptic neuron **from firing and functioning**.
15
New cards
Glutamate
\-Main **excitatory neurotransmitter** in CNS → enhances info transmission (postsynaptic ready to fire).
16
New cards
Gamma-amino butyric acid (GABA)
\-Main **inhibitory neurotransmitter** in CNA → makes postsynaptic less-likely to fire.
17
New cards
Neuromodulator
\-A neurotransmitter that works/influences with other neurotransmitter.
\-Can affect a large number of neurons at the same time.
\-Can affect a large number of neurons at the same time.
18
New cards
Dopamine
\-Modulatory neurotransmitter (mainly excitatory) with main functions of: moving, learning and behaviour that’s **‘rewarding’**.
\-Produced in **Substantia Nigra**.
\-Produced in **Substantia Nigra**.
19
New cards
Serotonin
\-Inhibitory modulatory neurotransmitter with functions such as: mood, emotions, processing, sleep and pain.
\-Can be described as ‘mood stabiliser’ → keeps us calm, positive and prevents anxiety.
\-Can be described as ‘mood stabiliser’ → keeps us calm, positive and prevents anxiety.
20
New cards
Synaptic plasticity
\-Ability of the synapse to change in response to experience.
\-Strengthening/weakening of connections b/w neurons at a synapse.
\-SYNAPSE IS SMALL AREA B/W 2 NEURONS.
\-Strengthening/weakening of connections b/w neurons at a synapse.
\-SYNAPSE IS SMALL AREA B/W 2 NEURONS.
21
New cards
Sprouting
\-Creations of new extensions on a neuron to allow new connections with other neurons.
22
New cards
Rerouting
\-New connections are made b/w neurons to make alternative neural pathways.
23
New cards
Pruning
\-Elimination of weak, imperfect or unused synapses.
\-Synaptic gap is destroyed.
\-Synaptic gap is destroyed.
24
New cards
Hebb’s rule
\-Neurons that fire/wire together. Presynaptic & presynaptic neurons can be so closely/tightly linked & frequently used = the fire at the same time (more efficient).
25
New cards
Long-term potentiation
\-**Long-lasting enhancement** of synaptic transmission due to repeated strong transmission.
\-Enables **postsynaptic** neurons to be more **easily activated**.
\-Enhances memory storage of info.
\-Enables **postsynaptic** neurons to be more **easily activated**.
\-Enhances memory storage of info.
26
New cards
Long-term depression
\-Long-lasting decrease in the strength of synaptic connections & transmission.
\-Results from a lack of stimulation of pre/postsynaptic neurons.
\-The basis of blocking/erasing unwanted thoughts, feelings and behaviours.
\-Results from a lack of stimulation of pre/postsynaptic neurons.
\-The basis of blocking/erasing unwanted thoughts, feelings and behaviours.
27
New cards
Stress
\-A **psychological/physiological response** produced by **internal OR external stressors.**
28
New cards
Stressor
\-Stimulus that produces stress.
\-Can be physiological (noise, temp) or psychological (running late).
\-Can be physiological (noise, temp) or psychological (running late).
29
New cards
Internal stressor
\-Originates from the individual (personal problems or physical pain).
\-Eg. stomach pain or anxiety.
\-Eg. stomach pain or anxiety.
30
New cards
External stressor
\-Originates outside the individual from environmental factors.
Eg. having too much homework.
Eg. having too much homework.
31
New cards
Acute stress
\-Stress that lasts for a short amount of time.
32
New cards
Chronic stress
\-Stress that lasts for a prolonged period of time.
33
New cards
Flight-or-flight-or-freeze response
\-An **involuntary, bodily response to a sudden and immediate threat** in readiness to fight (confront), flight (run away) or freeze (be silent and unseen).
\-Fight-flight uses sympathetic NS → increased heart rate etc.
\-Freeze uses parasympathetic → movements stop.
\-Fight-flight uses sympathetic NS → increased heart rate etc.
\-Freeze uses parasympathetic → movements stop.
34
New cards
Cortisol
\-**Primary stress hormone** which acts **slowly but effects are long-lasting** on stressors.
\-Sourced by the **adrenal cortex**.
\-Can shut down functions not needed to deal with stressor (reproductive system).
\-Immediate effects in response to stressor is **energising body** (secretion of glucose in liver).
\-Sourced by the **adrenal cortex**.
\-Can shut down functions not needed to deal with stressor (reproductive system).
\-Immediate effects in response to stressor is **energising body** (secretion of glucose in liver).
35
New cards
Having excessive cortisol
\-Impaired immune system (vulnerable to disease).
\-Weight gain (increased appetite).
\-Physiological: high blood tension, digestive problems, heart attack and strokes.
\-Psychological: impaired cognitive performance, impaired memory & learning difficulties.
\-Weight gain (increased appetite).
\-Physiological: high blood tension, digestive problems, heart attack and strokes.
\-Psychological: impaired cognitive performance, impaired memory & learning difficulties.
36
New cards
Gut-brain axis (GBA)
\-Bidirectional neural pathways that enable communication b/w bacteria in gastrointestinal tract and the brain.
\-__Vagus nerve__ helps the communication (neurotransmitter) between the gut & brain.
\-Chronic stress affects gut microbiome → illness.
\-__Vagus nerve__ helps the communication (neurotransmitter) between the gut & brain.
\-Chronic stress affects gut microbiome → illness.
37
New cards
Gut microbiota OR microbiome
\-Highly diverse and dynamic system of trillions of bacteria & other microorganisms that live in the gastrointestinal tract.
\-Disruptions to gut microbiota such as infections can trigger reactions in the body that affects physiological & psychological health.
\-Affects gut and brain → even your health!
\-Disruptions to gut microbiota such as infections can trigger reactions in the body that affects physiological & psychological health.
\-Affects gut and brain → even your health!
38
New cards
General adaptation syndrome (GAS)
\-A 3-staged **physiological** response to stress.
1st stage → alarm reaction
2nd stage → resistance
3rd stage → Exhaustion
1st stage → alarm reaction
2nd stage → resistance
3rd stage → Exhaustion
39
New cards
Alarm reaction (stage 1 of GAS)
\-Occurs when individual initially becomes aware of stressor.
1) **SHOCK** happens → drop in blood pressure, body temp and muscle tone.
2) Body rebounds from shock into **COUNTER SHOCK** → sympathetic NS (fight/flight) is activated, highly aroused & alert, adrenaline is released into blood stream.
\-Helps maintain defensive reaction to stressor (high alertness & readiness).
1) **SHOCK** happens → drop in blood pressure, body temp and muscle tone.
2) Body rebounds from shock into **COUNTER SHOCK** → sympathetic NS (fight/flight) is activated, highly aroused & alert, adrenaline is released into blood stream.
\-Helps maintain defensive reaction to stressor (high alertness & readiness).
40
New cards
Resistance (stage 2 of GAS)
-Occurs when stressor is not initially dealt with → body copes & adapts to the stressor.
\-Unnecessary physiological processes shut down (digestion, menstruation, sex drive).
\-Cortisol goes into blood stream to energise body.
\-**High levels of cortisol** = weakened immune system.
\-Unnecessary physiological processes shut down (digestion, menstruation, sex drive).
\-Cortisol goes into blood stream to energise body.
\-**High levels of cortisol** = weakened immune system.
41
New cards
Exhaustion (stage 3 of GAS)
\-Occurs when stressor is still present after 2nd stage.
\-Prolonged stress → depleted resources, resistance to disease lowers, vulnerable to physical & mental problems.
\-Symptoms → extreme fatigue, high anxiety, depression, nightmares, impaired sexual performance.
\-**High cortisol level** in blood stream = physical tear & wear on organs dealing with stress.
\-Physical disorder → hypertension, stomach problems, heart disease & potentially death.
\-Prolonged stress → depleted resources, resistance to disease lowers, vulnerable to physical & mental problems.
\-Symptoms → extreme fatigue, high anxiety, depression, nightmares, impaired sexual performance.
\-**High cortisol level** in blood stream = physical tear & wear on organs dealing with stress.
\-Physical disorder → hypertension, stomach problems, heart disease & potentially death.
42
New cards
Lazarus and Folkman’s Transactional Model of Stress & Coping
\-Proposes that stress involves an encounter between an individual and their environment, and that a stress response depends upon both an individual’s appraisal of the stressor and their ability to cope with it
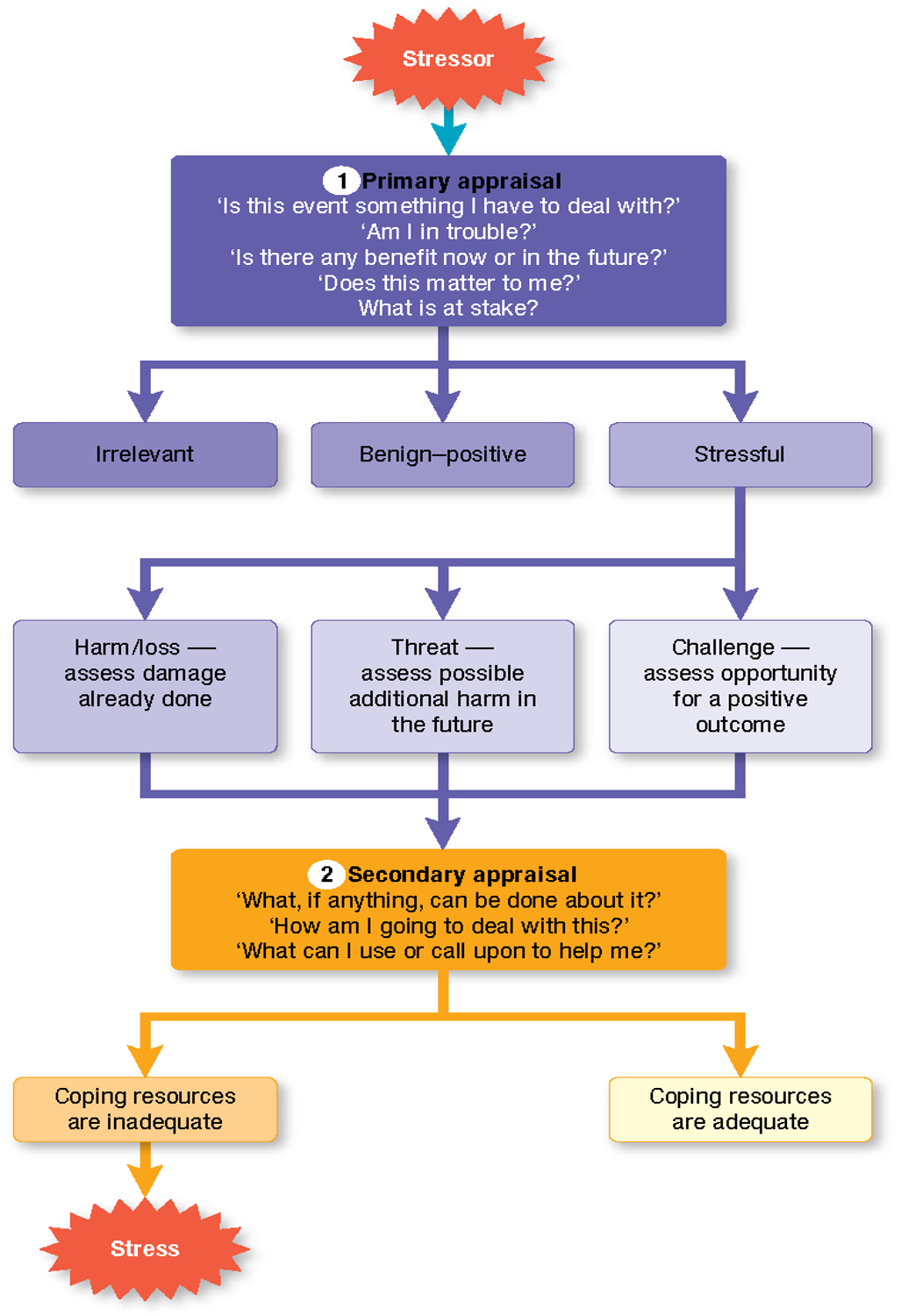
43
New cards
Coping
\-Cognitive & behavioural efforts to manage specific internal/external stressors.
44
New cards
Approach strategies
\-Effort to cope with stress by confronting the stressor & dealing directly with it.
Eg. stressed on upcoming exams so you study daily to ensure that you’re prepared.
Eg. stressed on upcoming exams so you study daily to ensure that you’re prepared.
45
New cards
Avoidance strategies
\-Effort to cope with stress by evading the stressor & indirectly dealing with it.
Eg. stressed on upcoming exams so you avoid it by playing video games.
Eg. stressed on upcoming exams so you avoid it by playing video games.
46
New cards
Coping flexibility
\-Ability to effectively modify or adjust one’s coping strategies according to the demand of stressor.
47
New cards
Context-specific effectiveness
\-When there is a match or ‘good fit’ between the coping strategy & the stressor.
Eg. upcoming sac, a positive coping strat is to study.
Eg. upcoming sac, a positive coping strat is to study.