Microscopes, Bacteria & Lab
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
Bacteria that stains pink with Gram stain are said to be…
Gram Negative
Bacteria that’s stains purple with Gram stain are said to be…
Gran Positive
An organisms that require oxygen for metabolism and survival
Aerobe
An organism that do not require oxygen for metabolism and survival
Anaerobe
An organism that directly gets energy from the sun
Phototroph
An organism that gets its energy by breaking bonds
Chemotroph
An organism that directly produces its own food and energy
Autotroph
An organism that gets its food and energy from eating other living things
Heterotroph
The lens on the microscope closest to the eye
Ocular Lens
The lens on the microscope closest to the object
Objective Lens
Is used because it has the same refractive index as glass and it reduces the refraction
Oil Immersion
The bending of light as it passes through different substances
Refraction
The ability to distinguish two points as being separate
Resolution
Making something appear larger
Magnification
A single rod-shaped bacteria
Bacillus
A single spherical shaped bacteria
Coccus
A single spiral shaped bacteria
Spirillum
You should never use oil with non-oil objective because it might _______ into the housing
Leak
You should always work at these to prevent contaminating your samples
Angles
You should always use these techniques to prevent yourself and bacteria from becoming contaminated
Sterile
Things that cause disease or illness are called…
Pathogens
What is FOV?
The diameter of the circle of light that can be viewed with an ocular Lense
What is Fits?
How many bacteria can fit across the FOV

D.) 4

B.) 10x

D.) 100x

A.) low power lens

C.) start with coarse focus and then use the fine focus for each objective

B.) the diameter of the circle of light that can be viewed with a given objective lens

C.) use oil

D.) reduce refraction and improve resolution

B.) lens paper using a dabbing motion

D.) all of the above
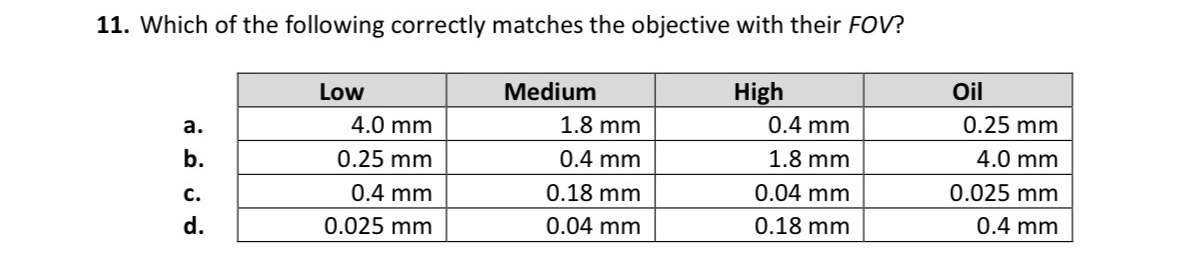
A.)
Low: 4.0mm
Medium: 1.8mm
High: 0.4mm
Oil: 0.25mm or 250μm

C.) AS = FOV/FITS

A.) I and III, only

B.) phototrophs
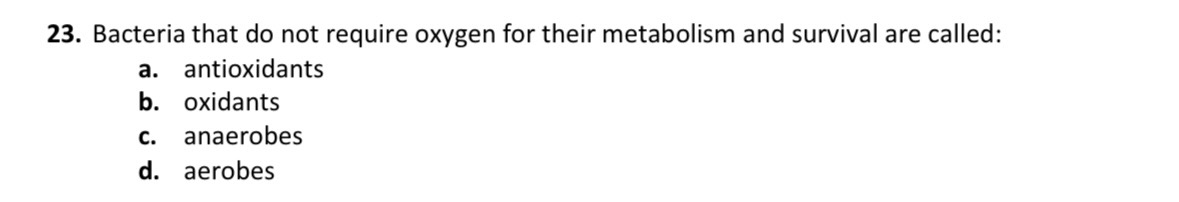
C.) anaerobes

B.) heterotrophs

C.) gram positive, diplococci

B.) capsule

B.) pili

C.) bacteria that have mutated such that they can no longer be killed by an antibiotic

C.) a zone of inhibition around the disc

D.) I, II, and III, only
What is negative control?
A group in an experiment that gets no treatment and is expected to show no effect, helping confirm that the results are valid.
What is the order of all the metric prefixes?
Mega: M
—
—
Kilo: k
Hecta: h
Deca: da
Base: g, mol, L, m
Deci: d
Centi: c
Milli: m
—
—
Micro: μ
What is the magnification of low, medium, high, and the oil and the ocular objective lens?
4x, 10x, 40x, 100x, and 10x
What is the FOVS’ for all objective lenses
4.0mm, 1.8mm, 0.4mm, and 0.25mm or 250μm
What is the difference between resolution and magnification?
Resolution is the ability to distinguish two points as being separate while magnification is making something appear larger.
Why do we use oil immersion?
We use oil immersion because the oil has a similar refractive index to glass, which reduces light refraction and allows more light into the lens. This increases resolution and gives a sharper, clearer image.
What are some do’s and don’ts’ of biological drawing?
no shading
Don’t use colour; describe colour
Large, clear; ½ of a page
Drawing should be on left
Identify structure
Right, form a vertical list
Words horizontal
Draw lines using a ruler
What does prokaryote and unicellular mean?
Prokaryotes are before nucleus or no nucleus, and is unicellular because it only made of one cell.
What are some basic structure of a bacteria?

What can be seen and can’t be seen under the microscope?
Seen:
cell
Bacteria
Can’t see:
viruses
Ribosomes
Molecules
Anything mitochondria size or smaller
What is sterile technique?
Sterile technique means preventing contamination by keeping tools clean, avoiding contact with non-sterile surfaces. This includes quickly opening plates, using sterile Q-tips or loops, flame-sterilizing equipment, and keeping your workspace and hands clean to ensure only the intended bacteria are collected and handled.
What’s is positive control and negative control?
A positive control is a part of an experiment that is expected to show a known, proving the setup works. A negative control is expected to show no reaction or change, proving that any observed effect in the experiment is due to the variable being tested and not something else.