macroeconomics
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
trade deals that have been signed
singapore,south korea, swtizerland, australia, new zealand, EU, member of ttp(trans pacific)
ongoing trade talks
USA,India,EU,GCC(gulf co operation council)
pros of free trade deals
trade creation and growth, prices decreasing and quantity/ choice increasing, technology diffusion(spread of technology), inward FDI
Cons of free trade deals
domestic industry harm, increased unemployment( therefore inequality), reduced standards ( us low product standards), trade deficits, over specialisation(service industry), environmental trade off
evaluation of free trade deals
time and extent of trade(trade deals with countrys we dont trade with), unfair trade practices, non tariff barriers, stakeholder tradeoffs
why some trade deals are less impactful
countrys are far, EU holds many other frictions of trade
non tariff barriers to trade with EU
proof that we meet thier standards that are manually checked at EU ports, differing EU local VAT rates
examples of unfair trade practices
subsidies, state interventions, competitive devaluations
national debt increase
80% of GDP, to 97% of GDP
what fiscal policys is bieng used currentely
contractionary
covids effect on the economy
worst recession in 300 years
why contractionary policy is currentely bieng used
huge expansionary policy due to covid ( healthcare and welfare spending, uk furlough scheme), dramatic tax cuts targeted to industrys,causing the ruining of the government budget deficit
government budget deficits
2019(£40 billion),2020/21( 15.1% of GDP/£305 billion), 2022(5.2% of GDP), 2023(4.9% of GDP), 2024(4.8% of GDP), 2025 ( 5.3% of GDP)
structural budget deficit
structural budget deficit is deficit at full employment ( 2025 2% of GDP)
consequences of covid government spending
debt interest spending high, causing opportunity cost ( over £100 billion), inflation, wage growth( wage price sprials along with inflation)
liz truss not so little budget policys
policys : unfunded tax cuts, unfunded spending to counter energy price increase
lizz truss not so little budget effects
effects: due to loss of information - gov lenders scared of bankrunpcy, mass selling of bonds, driving down bond prices, driving down bond interest rates fast ( by 3%, within 5 days), causing gov bankruptcy, panic currency selling - devaluation of pound
how did BOE stop government bankrupcy after liss truss
bailed out government
current contractionary tax rises
uk and scotland freezing income tax bands(wage increases dragging people into higher tax bands, equivalent to 7% rise) , corperation tax 19% to 25% (2024), national insurance increase(employer national insurance), windfall taxes on energy manufacturers, council tax
contractionary government spending cuts
cuts in actual and real term spending, cuts in current and capital budgets(HS2 stopped)
pros and cons of contractionary policy
pros: reduced bond interest rates ( confidence in gov finances), fiscal policy flexibility, reduced inflation cons: macro objective tradeoffs( reduced growth, increased unemployment), reduced living standards, laffer discincentives, inequalities gini ( 0.34 to 0.357)
what causes a shift in the AD curve
change in the components of AD ( C + I + G + (x-m))
what is autonomous investment and induced investment
autonomous doesnt change with income or interest rate ( gov expenditure), induced investment changes with income or interest rate ( pirvate firm invesment)
what causes shifts in SRAS
changes in production costs
what does the horizontal area of keynsian SRAS display
the economy is not operating at full capacity/ resources are not fully employed ( no increase in price level/ no inflation)
what changes effect LRAS
change in quality or quantity of goods/ services ( can be displayed by shift in ppf curve)
what is red tape
regulation which limits efficiency of firms
what is assumed about the AD curve
the supply of money available for borrowing is fixed
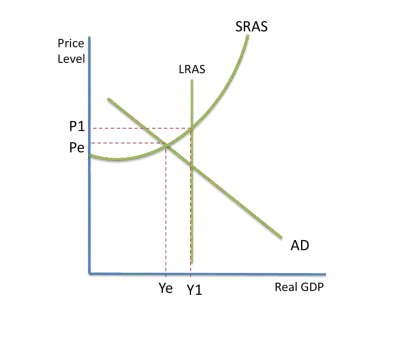
display inefficient AD producing a negative output gap due to unemployment

factors that determine national income multiplier
MPC,MPS,MPT,MPM, spare capacity
what does the significance of the multiplier depend on
the elasticity of sras
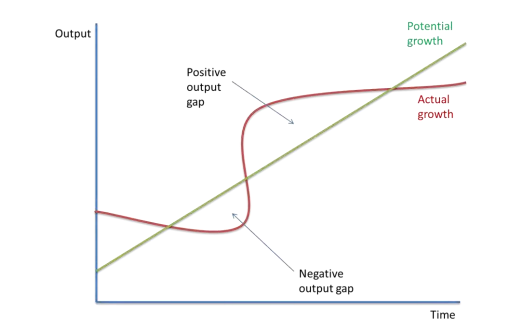
alternative output gap diagram

what is capital deepening
an increase in the size of physical capital stock
the cuases for short term and long term economic growth
short term - shifts in AD (capacity stays the same), long term - shifts in LRAS ( increase in poructive potential/ capacity)
when did trump start the trade war
2018-2019
what were trumps intial tariffs(china)
$363 billion at a 15% tariff rate
reasons for trumps intial tariffs (china)
preventing dumping, unemployment, trade deficit increases
what did joe biden raise trumps intial tariffs to (china)
up to 25%
what industry did joe bidens tariffs target (china)
climate industrys
what are examples of joe bidens tariffs towards china
100% tariffs on ev vehicles, 50% tariffs lithium ion batterys,50% tariffs on semiconductor chips, 25% tariffs on solar panels
what countrys did trump threaten with tariffs 2025
mexico and canada
trumps tariffs 2025 targeted
25% worldwide steel and aliminium, 25% cars and car parts worldwide
trumps tariffs 2025 untargeted
reciprocal tariffs up to 50%( baseline 10%)
trumps tariffs 2025 china
145%
chinese tariffs to usa
125%
reasons for 2025 tariffs
government revenue, inward investment( tariffs not faced if businesses operate in us)
risks of tariffs
retaliation(on sensitive industrys), supply side shocks(usa), demand side shocks(china), tarrifs are highly regressive and inflationary