Neural Tissue and Cranial Nerves Extra Credit
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
define and memorize
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
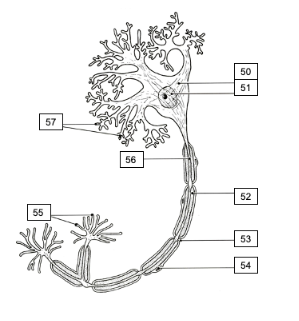
Parts of the Neuron
Soma
Nucleus
Myelin sheath
Nodes of Ranvier
Schwann cells
Axon terminal
Axon
Dendrite
Acetylcholine (ACH)
The most common excitatory neurotransmitter
Afferent (sensory) neurons
Carry impulses from receptors towards the CNS
Axon
Longer process (up to 3-4 ft) that conveys signals away from the soma.
Central nervous system
Brain and spinal cord
Dendrite
Typically shorter processes that convey impulses toward the soma.
Depolarization
A membrane will shift the membrane potential from -70 mv to +30 mv.
Effector
muscles and glands (organs)
Efferent (motor)
Carry impulses away from the CNS and to effectors (muscles or glands)
Interneuron (associative) neurons
Lie between sensory and motor neurons in the CNS and integrate incoming and outgoing signals.
Myelin sheath
Increase the speed of impulse transmissions.
Neuroglia
Support cells for the neurons.
Receptor
The body's receiver for different stimuli, converting them into signals the body can understand and react to.
Peripheral nervous system
Part of the nervous system outside the CNS
Polarized
A stimulus is applied to a polarized membrane, which causes the membrane to become permeable to Na.
Synapse
Occur between the axon of one cell and the dendrite of the next cell.
Olfactory
Type- sensory
Effect- smell
Optic
Type- sensory
Effect- vision
Oculomotor
Type- motor
Effect- focus, pupil, eyelids
Trochlear
Type- motor
Effect- move eyes
Trigeminal
Type- mixed
Effect- tears, move eyes, senses forehead
Abducens
Type- motor
Effect- move eyes
Facial
Type- mixed
Effect- taste, facial expression
Auditory
Type- sensory
effect- hearing, equilibrium
Glossopharyngeal
Type- mixed
Effect- swallowing, salivary glands
Vagus
Type- mixed
Effect- various thoracic organs
Spinal accessory
Type- motor
Effect- muscle of the neck and back
Hypoglossal
Type- motor
Effect- move tongue