Chemical changes
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
What is the pH scale
A measure of how alkaline or acidic a solution is
What numbers of the pH scale are acidic and what colour are they
x < 7 → less than 7 so 0-6.9
Red or yellow
What numbers of the pH scale are neutral and what colour are they
7
Green
What numbers of the pH scale are alkaline and what colour are they
x > 7 → greater than 7, 8-14
Blue or purple
How do we measure pH
use an indicator → group of chemical dyes that change depending on pH. E.g universal indicator (wide range indicator so can change colours over many pHs)
pH probe → much more accurate as it doesn’t involve humans guessing shades and so more reliable
What is an acid
Any substance that forms aqueous solutions with a pH less than 7
What’s a base
Any substance with a pH greater than 7
What are alkaline
subgroup of bases
A base that dissolves in water to form a solution wit a pH greater than 7
Form OH- ions in water → hydroxide ions
What do you get if you react an acid and base, what does it produce
neutralisation reaction
Products are a salt + water
Products are neutral and have pH 7
What is the formula for sulfuric acid
H2SO4
What is the formula for hydrochloride acid
HCl
What’s the formula for nitric acid
HNO3
What’s the formula for sodium hydroxide (base)
NaOH
What’s the formula for calcium carbonate
CaCO3
What’s titration used for
find an unknown concentration of an acid or alkali
What equipment is needed for titration (R.P)
A pipette to accurately measure a certain volume of acid or alkali (25cm3)
a comical flask to contain liquid from pipette
A burette to add alkali or acid to conical flask
White tile to place conical flask on
What is the titration method
Use the pipette to add 25cm3 of alkali to a conical flask
Add a daw drops of indicator and put the conical flask on white tile
Fill burette with acid and note the starting volume
Slowly add the acid from the burette to the alkali in the conics, flask, swirling to mix
Stop adding acid when the end point is reached (when the acid has neutralised the alkali and the indicator changes colour)
Note the final volume reading and calculate how much acid you added in total
Repeat titration u til you get concord at results which means figures if acid that are within 0.10cm3 of each other
Use concordant results to calculate the mean column of acid required to neutralise the alkali
Why is it important to swirl the flask during titration
Even,y distribute the acid and ensure the colour change ensures as soon as they neutralisation takes place
Why is it important you place the conical flask on a white tile
So you can see the colour change happen as soon as possible
What colour change happens if you add an acid into an alkali in the flask
changes from colourless to pink
What colour change happens if you add a alkaline into a acid in the conical flask
Changes from colourless to purple
What are the 3 different type of indicators
litmus
red in acidic solutions
Blue in alkaline solutions
phenolphthalein
Colourless in acidic solutions
Pink in alkaline solutions
Methyl orange
red in acidic solutions
Yellow in alkaline solutions
What is pH a concentration of
H+ ions
What do acids do to release H+ ions
Ionises
What’s a strong acid
An acid that ionises completely
all the acid particles will dissociate / turn fully into products
What’s a weak acid
An acid that hasn’t fully ionised
small amount dissociate (release H+ ions)
Reversible reactions but as it doesn’t all dissociate / doesn’t fully turn into products, the equilibrium lies to the left
What does each decrease by one on the pH scale represent
an increase of H+ ions by x 10 each time
How do you get an acidic solution with a low pH
Lots of H+ ions
Why can you only get a low pH of a weak acid in a very concentrated solution
only few acid particles ionise and release H+ ions so would need a high concentration to get more H+ ions to create a low pH
What happens during a neutralisation reaction in terms of hydrogen ions and hydroxide ions.
The positive hydrogen ions from an acid react with the negative hydroxide ions from the alkali to form molecules of water
When an acid reacts with a metal oxide what is produced
Metal oxides + acid → salt + water
When an acid reacts with a metal hydroxide what is produced
Metal hydroxide + acid → salt + water
What happens when acids react with metal carbonates
acid + metal carbonate → salt + H2O + CO2
How do u make a soluable salt
React an acid with an insoluble base
What is the method to create soluble salt crystals from a acid base reaction
part 1 - obtain a solutions of the soluble salt we want
Put dilute acid in a beaker and gently heat with a Bunsen burner
Add the insoluble base a little at a time until it stops reacting, which means it’s in excess
Isolate the salt solution by filtering out the excess stolid base using filter paper and a funnel
part 2 - Isco Kate the so,it me salt crystals from the solution
Heat the salt solution gently in a water bath until crystals start to form
Let the solution cool further, which will cause more crystals to precipitate
Filter out the soluble sat crystals using filter paper and funnel
What is the order of metals reactivity series
Most reactive :
potassium
Sodium lithium
Calcium
- - - - - - - -
Magnesium
Carbon
Zinc
Iron
— - - - - - - - -
Hydrogen
Copper
What factor determines the reactivity of a metal
How easily the atoms of that element lose there outer electrons (so they have a full outer shell and become a positive ion )
What group of metal is the most reactive
Group 1 as it is easier for them to owe electrons as they only have 1 in their outer shell
If you react metal with an acid what does it form
Metals + acid → salt + H2
What happens when potassium reacts with acid
Most reactive so reacts vigorously
could produce a flame as it releases lots of hydrogen which can catch fire
What happens when magnesium reacts with acid
Bubbles form on the surface
What is a displacement reaction
Where a more reactive metal displaces a less reactive metal
How do you measure the temperature change if the metals to test for reactivity
the most reactive metals will produce the most heat
need to make sure it’s a fair test by m
each metal has the same mass and surface area
The acid is the same type and has the same concentration each time
When you react metals and water what is formed
Metals + water → metal hydroxides + hydrogen
Only the most reactive metals can do this (potassium, sodium, lithium, calcium)
What is oxidation
The process of gaining oxygen
What is reduction
The loss of oxygen
What happens when metals react with oxygen
Most metals are fairly reactive so react and form a metal oxide
What’s an example of unreactive metals
Gold
→ because you find them as pure metals
How do you get a pure metal
reduction
React the metal with carbon if it is less reactive as it displaces the metal and reacts with the oxygen, the metal loses oxygen so becomes reduced
This produces CO2
What’s an ore
What is a redox reaction
When both oxidisation and reduction take place at the same time
What’s oxidisation in terms of electrons
Loss of electrons
What is reduction in terms of electrons
Gain of electrons
Where can redox reactions take place
displacement reactions → can write as ionic equations
What’s an ionic equation
Only Show the reactions that take part in the reaction. → remove spectator
What’s the equipment for electrolysis
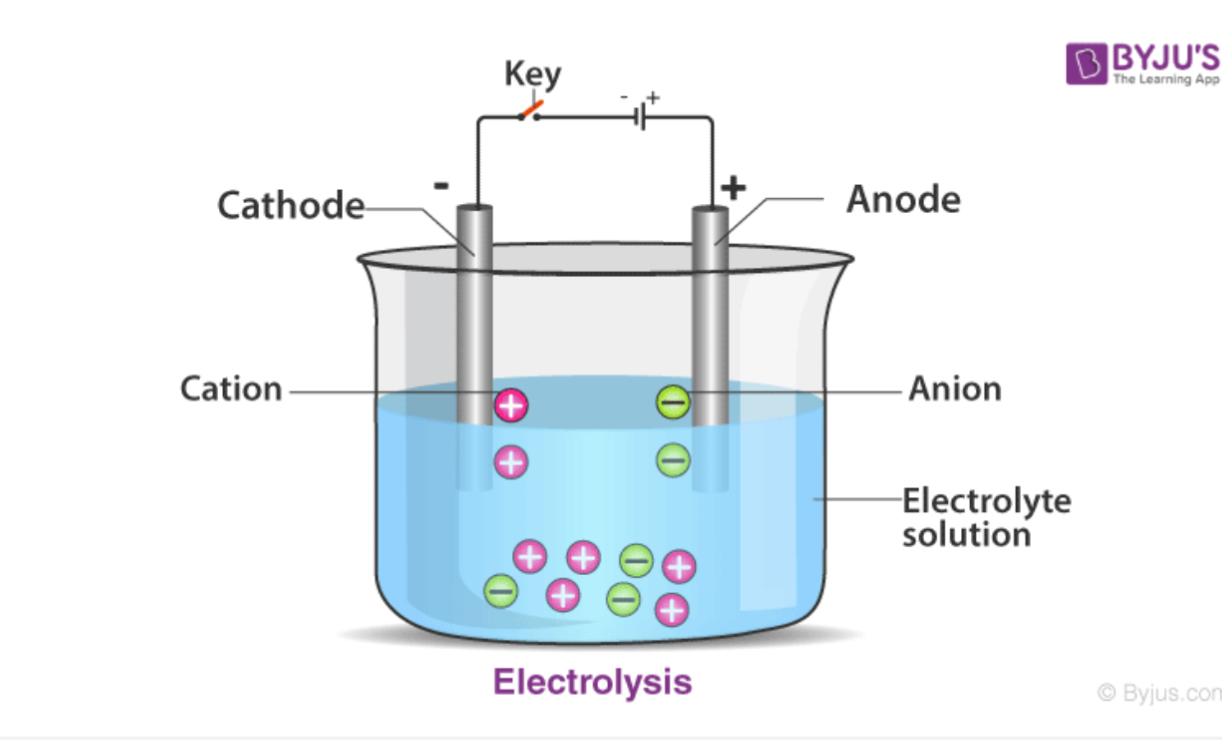
What’s an electrolyte
Liquid or solution that contains an ionic compound (ions that are free to move)
How do you get a molten liquid
Melt the insoluble product to get a liquid so ions are free to move
What are electrodes
Solid conductors
generally made of metal or carbon
What is the positive electrode called
Anode
What’s the negative electrode called
Cathode
What is the battery used for in electrolysis
Drives the flow of electrons
What does electrolysis mean
Splitting up ionic compounds into their pure elements with electricity
How does electrolysis work to separate lead bromide
the wire provides a current
Negative bromide ions will be attracted to the anode (opposites attract) and are discharged (becomes neutral). This causes the atoms to pair up and becomes bromine gas as it is oxidised→ the electrons from the bromide ions flow through to wire to the led ions where they will be reduced
The positive led ions are attracted the negative cathode (opposite charges attract) and become discharged. The led then falls to the bottom and forms a layer of molten led. The ,ed ions are reduced
In electrolysis, what direction do electrons flow
From the anode to the cathode
Why are the electrodes normally made of inert carbon
Inert means it’s unreactive, so will not take place in a reaction
In electrolysis, why do the compounds need to be molten or dissolved
So the ions are free to flow and move around
Why is electrolysis not used to extract all metals
expensive because it requires large amounts of electricity so if less reactive than carbon, reduction with carbon is used to displace the metals instead
Why is electrolysis used to extract aluminium
Aluminium is more reactive than carbon
however Al is solid (ions are fixed → bad) and it’s often found within an ore called bauxite
therefore have to turn it into molten aluminium oxide before using electrolysis
Purify the aluminium oxide from the bauxite that was mined from the ground
As it has a high melting point, we mix aluminium oxide with cryolite to lower the melting point
Then melt Aluminium oxide to make them molten
The positive 3+ ions are attracted the cathode
The negative -2 oxygen ions are attracted to the anode electrode. The oxygen ions are oxidised. The oxygen molecules can firm as a pair and form a gas
Electrons travel through the wire to the cathode where the aluminium ions are reduced. The aluminium metal forms at the bottom of the beaker
What do you do to soluble compounds in electrolysis
Dissolve them in water to from the electrolyte
in aqueous solutions, what ions are also present in the electrolyte
hydrogen ions H+
Hydroxide ions HO+
What’s the rule at the cathode in electrolysis aqueous solutions
The ion of the least reactive element will be discharged ( if the metal is more reactive than hydrogen, hydrogen is the ion present at the cathode)
What’s the rule at the anode in aqueous electrolysis
If a halide is present, it will be discharged/ present. If not hydroxide will be discharged