CLINICAL PHARMACY 142
1/30
Earn XP
Description and Tags
HISTORY OF CLINICAL PHARMACY (PPT 1)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
HISTORY OF CLINICAL PHARMACY
1960’s - poor medicines control system which resulted to the automation of the regular pharmacists’ functions; mass production of medicines.
HISTORY OF CLINICAL PHARMACY
In the USA, unit dose dispensing was initiated and they pursued decentralization of pharmacy services.
HISTORY OF CLINICAL PHARMACY
In the UK, the unification of the prescription and administration record paved the way for pharmacists to visit the wards and handle the ordering of medicines.
HISTORY OF CLINICAL PHARMACY
Clinical pharmacy has emerged due to the presence of of the pharmacists in the patient areas (clinical setting) and their interest in promoting safe medication use.
HISTORY OF CLINICAL PHARMACY
From ward pharmacist (UK), the term clinical pharmacy was adopted.
HISTORY OF CLINICAL PHARMACY
In the 1980’s, clinical pharmacy practice grew because of its outcome-cost-effective medicine use in the hospital.
HISTORY OF CLINICAL PHARMACY
The positive economic and clinical outcomes were recognized by institutions and governments and the clinical pharmacy practice was established. (Walker R. and Whittlesea C. (2012). Clinical Pharmacy and Therapeutics)
HISTORY OF CLINICAL PHARMACY
Impact of clinical pharmacy on patients and institutions were studied and high acceptance of the practice was shown by doctors and other Hospital pharmacists.
HISTORY OF CLINICAL PHARMACY
Clinical pharmacy was introduced into pharmacy education in the 1970’s.
HISTORY OF CLINICAL PHARMACY
Specializations stared in the 1980s and continued on to the present time.
HISTORY OF CLINICAL PHARMACY
Pharmaceutical care as the new philosophy of the practice was developed in the 1990 by Dr. Charles Hepler and Linda Strand.
HISTORY OF CLINICAL PHARMACY
Clinical pharmacy finds its application in the community setting as well in the 1990s.
HISTORY OF CLINICAL PHARMACY
Medication Therapy Management became a clinical pharmacy service provided to various institutions outside of the hospital and community pharmacy settings in early 2000s.
CLINICAL PHARMACY
The area of pharmacy concerned with the science and practice of rational medicine use; It is patient-oriented, evidence-based, and designed to promote health, wellness and disease prevention in order to improve quality of life of patients.
CLINICAL PHARMACIST
A pharmacist in any practice setting who provides a substantial amount of of direct patient-oriented care with emphasis on the science and practice of rational drug use.
CURRENT SPECIALIZATIONS
Adult Medicine
Ambulatory Care
Cardiology
Clinical Administration
Clinical Informatics
Critical Care
Drug Information
Emergency Medicine
Endocrinology/Diabetes
Geriatrics
Hematology/Oncology
Women’s Health
Immunology/Transplantation
Infectious Diseases
Managed Care
Medication Therapy Management
Nephrology
Nutrition Support
Outcomes and Economics
Pain and Palliative Care
Pediatrics
Psychiatry and Central Nervous System
Pharmacotherapy
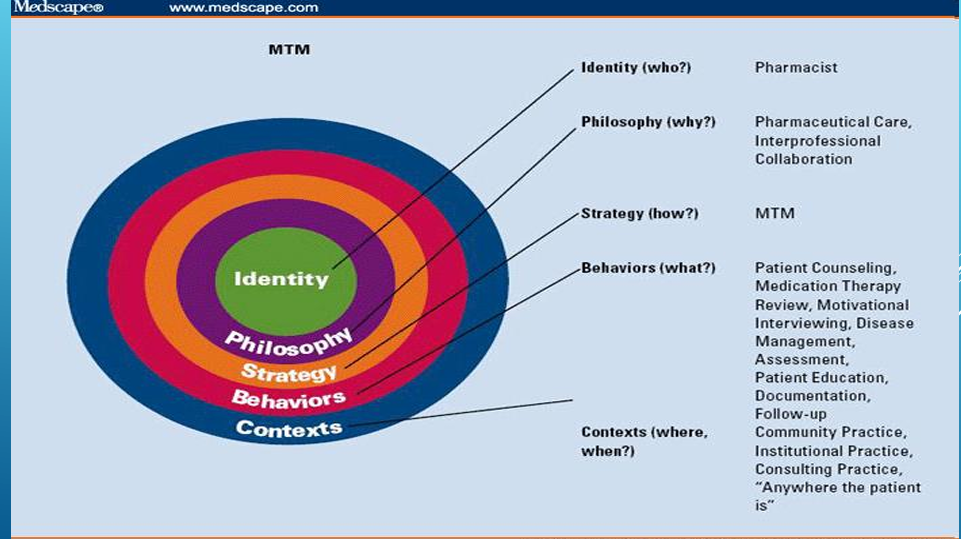
MEDICATION THERAPY MANAGEMENT
Identity (who) - Pharmacist
Philosophy (Why?) - Pharmaceutical Care, Interprofessional Collaboration
Strategy (How?) Medication Therapy Management
Behaviors (What?) - Patient Counseling, Medication Therapy Review, Motivational Interviewing, Disease Management Assessment, Patient Education, Documentation, Follow-up
Contexts (where, when?) - Community Practice, Institutional Practice, Consulting Practice, “Anywhere the Patient is”
DISCUSSION NOTES - CLINICAL PHARAMACY OVERVIEW
Pharmacy evolved from just making and dispensing medicines to having a role in clinical settings.
CLINICAL PHARAMACY OVERVIEW
Clinical Pharmacy emerged as a new area of practice, especially from the 1980s onwards.
CLINICAL PHARAMACY OVERVIEW
Realization that it reduced healthcare costs by:
Preventing wrong medications.
Reducing hospital stays.
Avoiding additional medications and complications.
Preventing malpractice suits for doctors, nurses, and pharmacists.
CLINICAL PHARAMACY OVERVIEW
Avoids malpractice suits for doctors, nurses, and pharmacists.
HISTORY AND DEVELOPMENT OF CLINICAL PHARMACY IN THE PHILIPPINES
Clinical Pharmacy introduced by US-trained professionals in the 1970s.
Early adoption in institutions like Makati Medical Center and PGH.
Clinical pharmacists started being consulted by doctors regarding medications.
Though it started early, it hasn’t become mainstream.
Still practiced but with limited integration into the system.
IMPACT OF CLINICAL PHARMACY - CLINICAL OUTCOMES
Studies show that having clinical pharmacists lessened the length of stay of patients, the expenses for the patients, and there are some studies showing that having clinical pharmacists even lowered the mortality.
IMPACT OF CLINICAL PHARMACY - ECONOMIC OUTCOMES
lessened the expenses for the patients
lowered the cost on the side of the institution
IMPACT OF CLINICAL PHARMACY - HUMANISTIC OUTCOMES
patient-centered care and satisfaction
IMPACT OF CLINICAL PHARMACY
Clinical Pharmacy introduced in the BS Pharmacy curriculum in the 1970s.
Over time, specializations developed: e.g., cardiovascular pharmacy. Increasing over time.
Modern curriculum includes pharmacotherapy in 4th year (previously only 3–5 units).
Clinical exposure and real-life case discussions enhance practical learning.
PHARMACISTS’ ROLE IN THE CLINICAL TEAM
Doctors may lack detailed knowledge of medicine formulation and excipients.
Pharmacists are critical for:
Modified release formulations.
Dosing for NGT (nasogastric tube) patients.
Preventing drug/food interactions.
Pharmacists can intervene and correct prescribing errors effectively.
MEDICATION THERAPY MANAGEMENT
MTM emerged as an extension of clinical pharmacy and pharmaceutical care.
Focuses on rational medicine use.
Ensures appropriate medicines are given and therapeutic outcomes achieved.
FROM CLINICAL PHARMACY TO PHARMACEUTICAL CARE TO MTM
Evolution of practice:
Clinical Pharmacy
Pharmaceutical Care
Medication Therapy Management (MTM)
Includes:
Patient counseling
Medication therapy review
Motivational interviewing (for adherence issues)
Disease management
Education and documentation
Follow-up
PHARMACEUTICAL CARE PROCESS
Assessment
Review patient meds, interview patient, gather history.
Identification of Medication-related Problems
Care Plan Development
Create interventions/solutions.
Follow-up & Evaluation
Assess success of the care plan.