The eye
1/18
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
What is the sclera of the eye?
The white outer layer
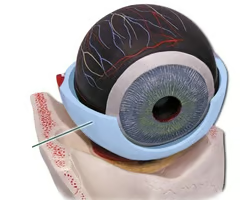
What properties does the sclera have?
Tough
What is the cornea of the eye?
Lets light in
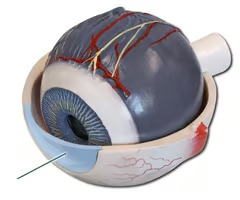
What properties does the cornea have?
- Transparent
- Curved surface
What is the Iris of the eye?
Muscles that control the size of the pupil
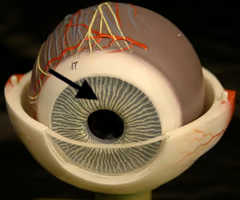
What is the lens of the eye?
Clear disc held in place by suspensory ligaments and ciliary muscles. These change the shape of the lens to focus the light rays onto the retina
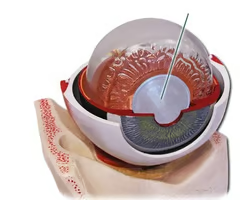
What are the suspensory ligaments of the eye?
Helps to change the lens shape
What are the ciliary muscles of the eye?
Helps to change the lens shape
What is the pupil of the eye?
The gap through which light enters the eye
What is the retina of the eye?
Contains receptors sensitive to light (roses and cones) which generates impulses when light hits them
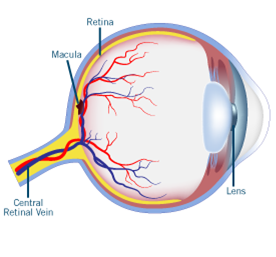
What is the optic nerve of the eye?
Sends the impulses to the brain (sensory neurone)
What is the blind spot of the eye?
Area where the optic nerve is. There are no photosensitive cells here
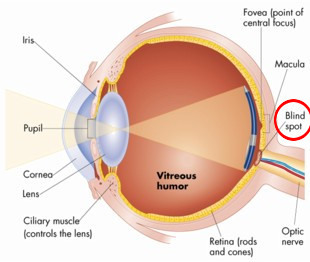
What is the jelly (vitreous humour) of the eye?
A fluid that helps to maintain its spherical shape
What happens to the eye in dim light?
The circular muscles relax and the radial muscles contract in the iris and the pupil dilates to let more light in
What happens to the eye in bright light?
The circular muscles contract and the radial muscles relax in the iris and the pupil constricts to let less light in
What is myopia of the eye?
Short - sightedness
What is hyperopia of the eye?
Long - sightedness
What is accommodation of the eye?
Refers to the eye's ability to adjust its focus and see objects clearly at different distance by changing the shape of the lens
What is adaptation of the eye?
The eye's ability to adjust to varying light conditions