Bony Pelvis and Pelvic Floor
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
ox coxae
hip bones
3 bones fused together, anteriorly connected at the pubic symphysis and posteriorly at the sacrum
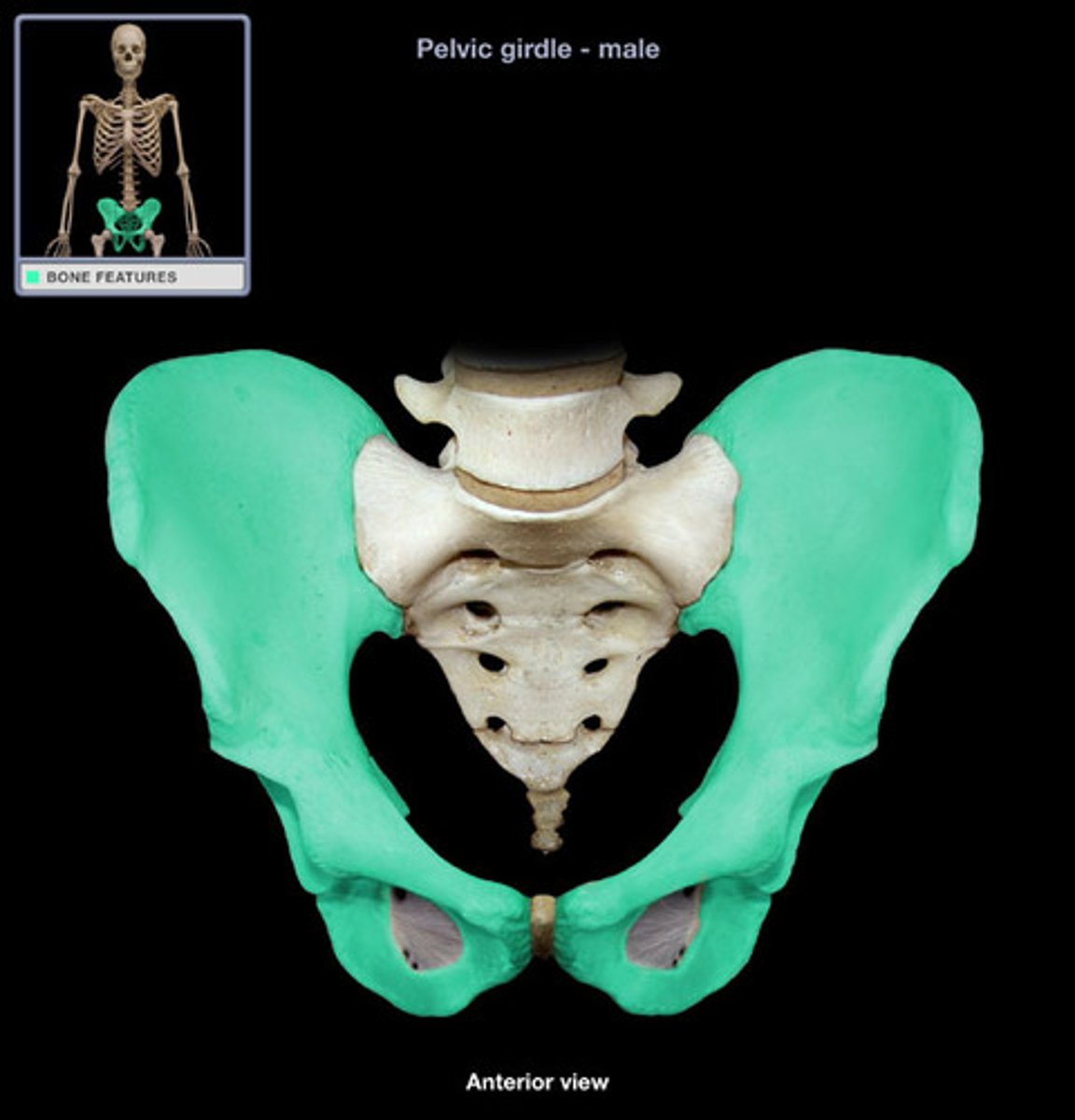
bony pelvis
2 coxal bones, sacrum, coccyx
ilium
weight bearing during sitting
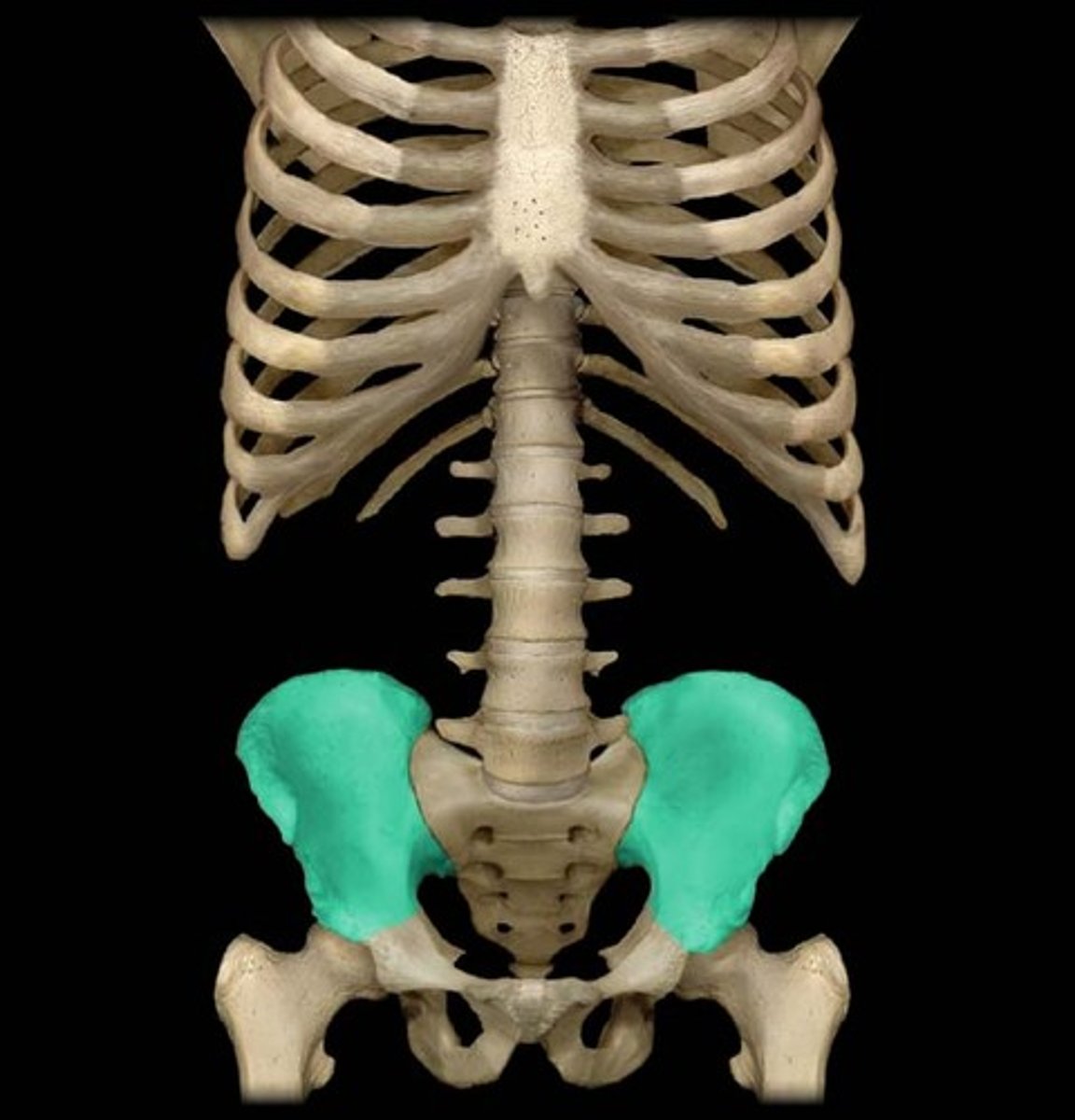
pubis
The medial anterior portion of the pelvis
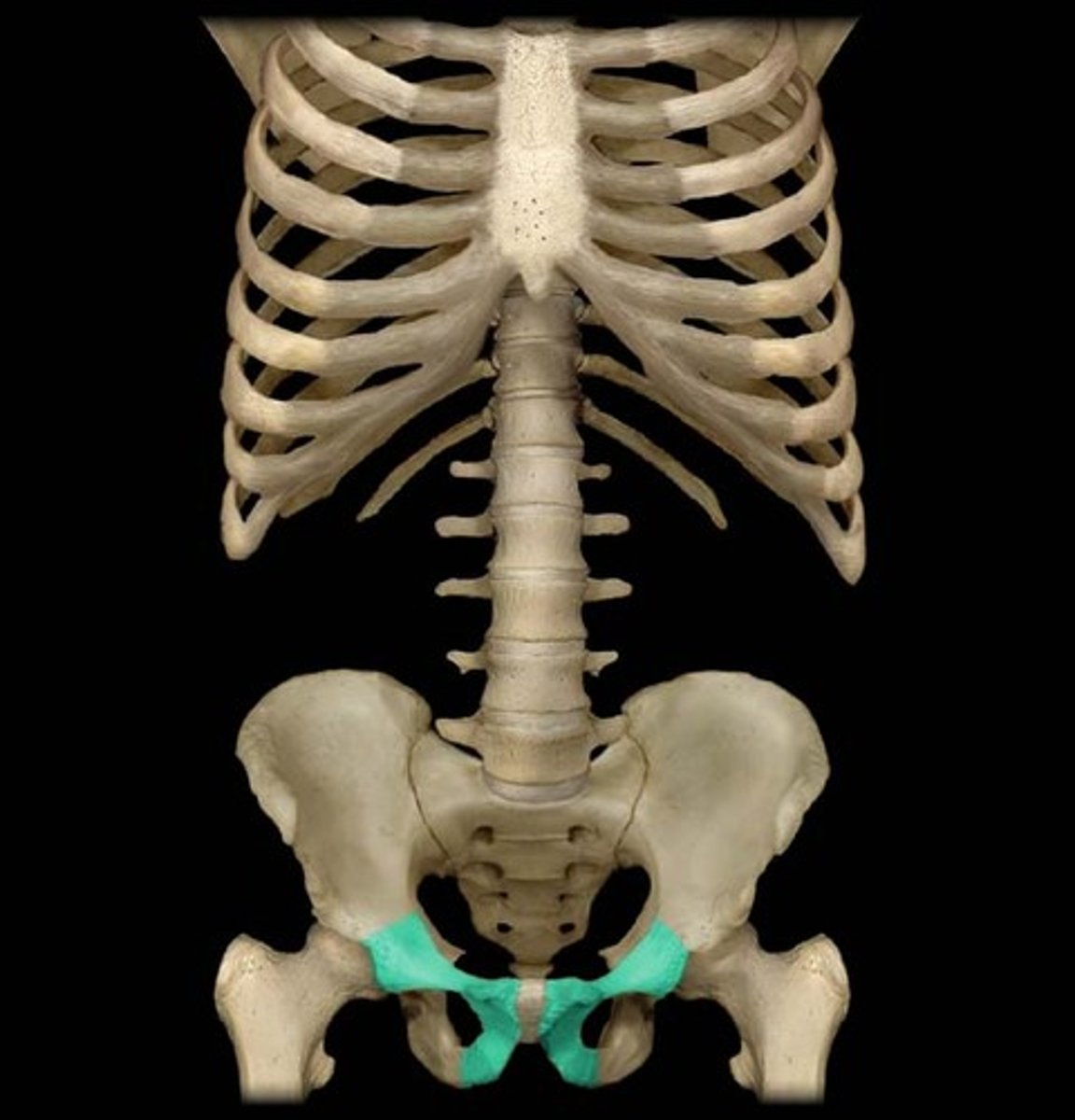
ischium
the lower, posterior portions of the pelvis
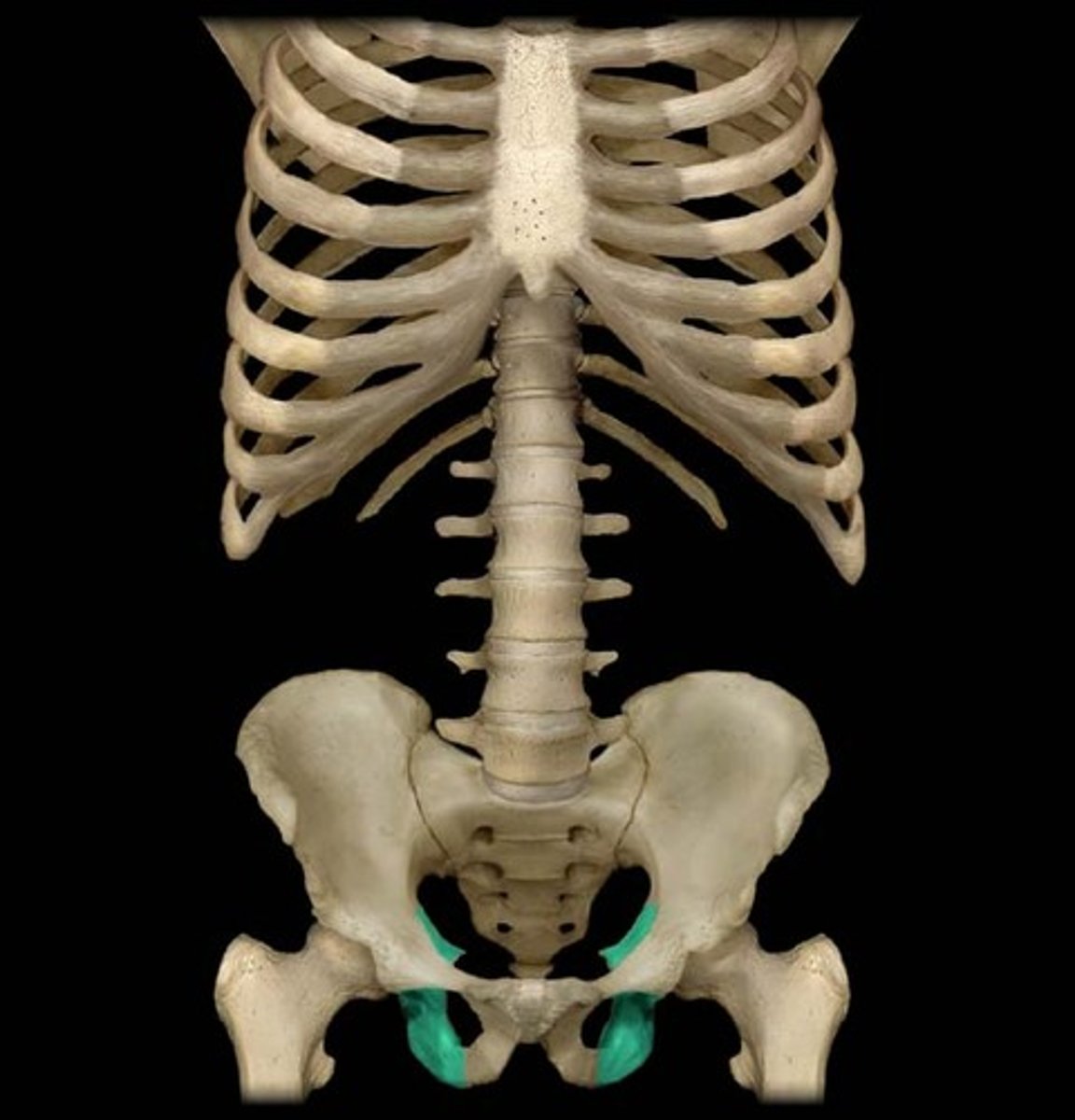
iliac crest
upper margin of iliac bones
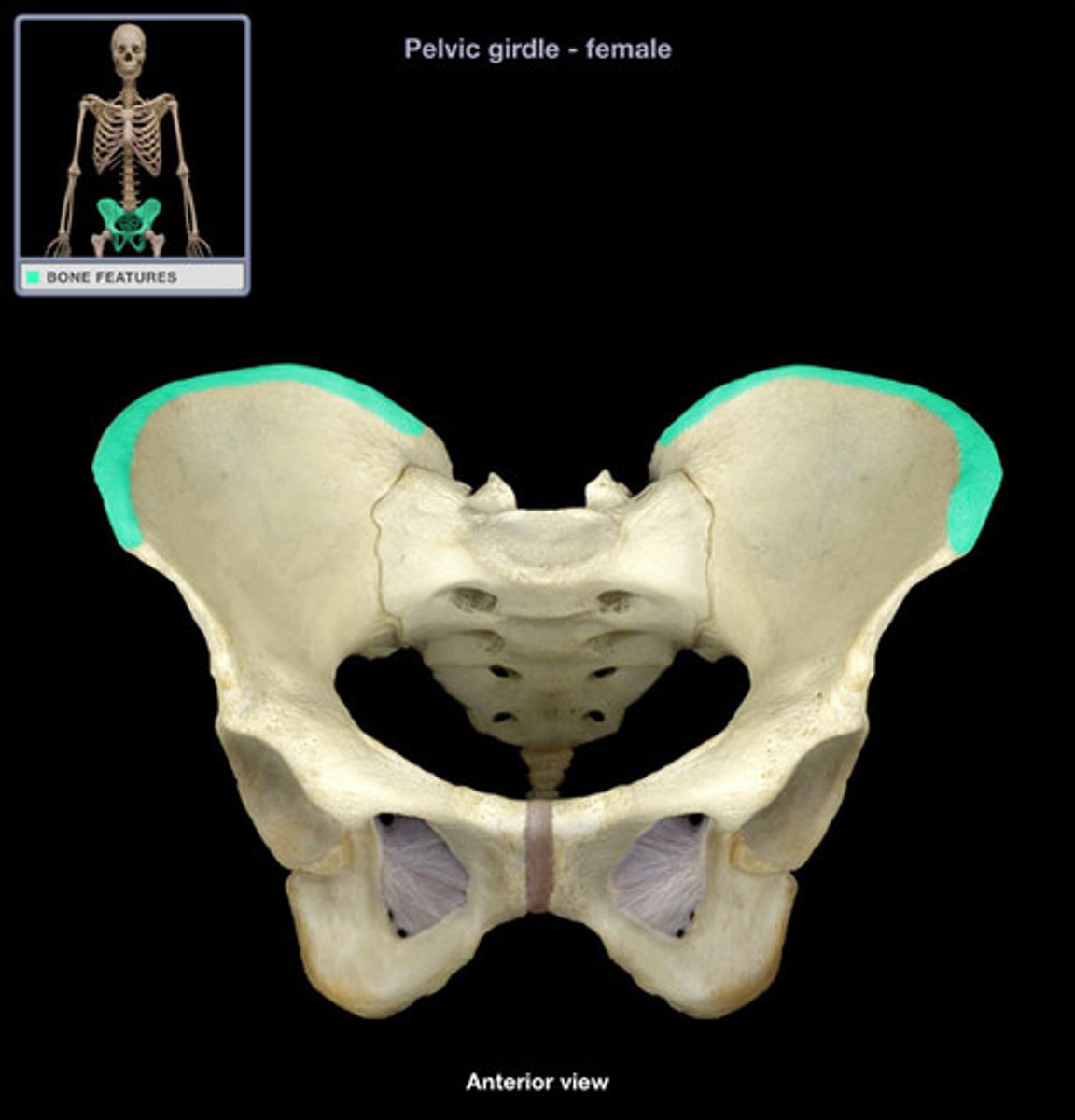
posterior superior iliac spine
the sharp posterior end of the iliac crest
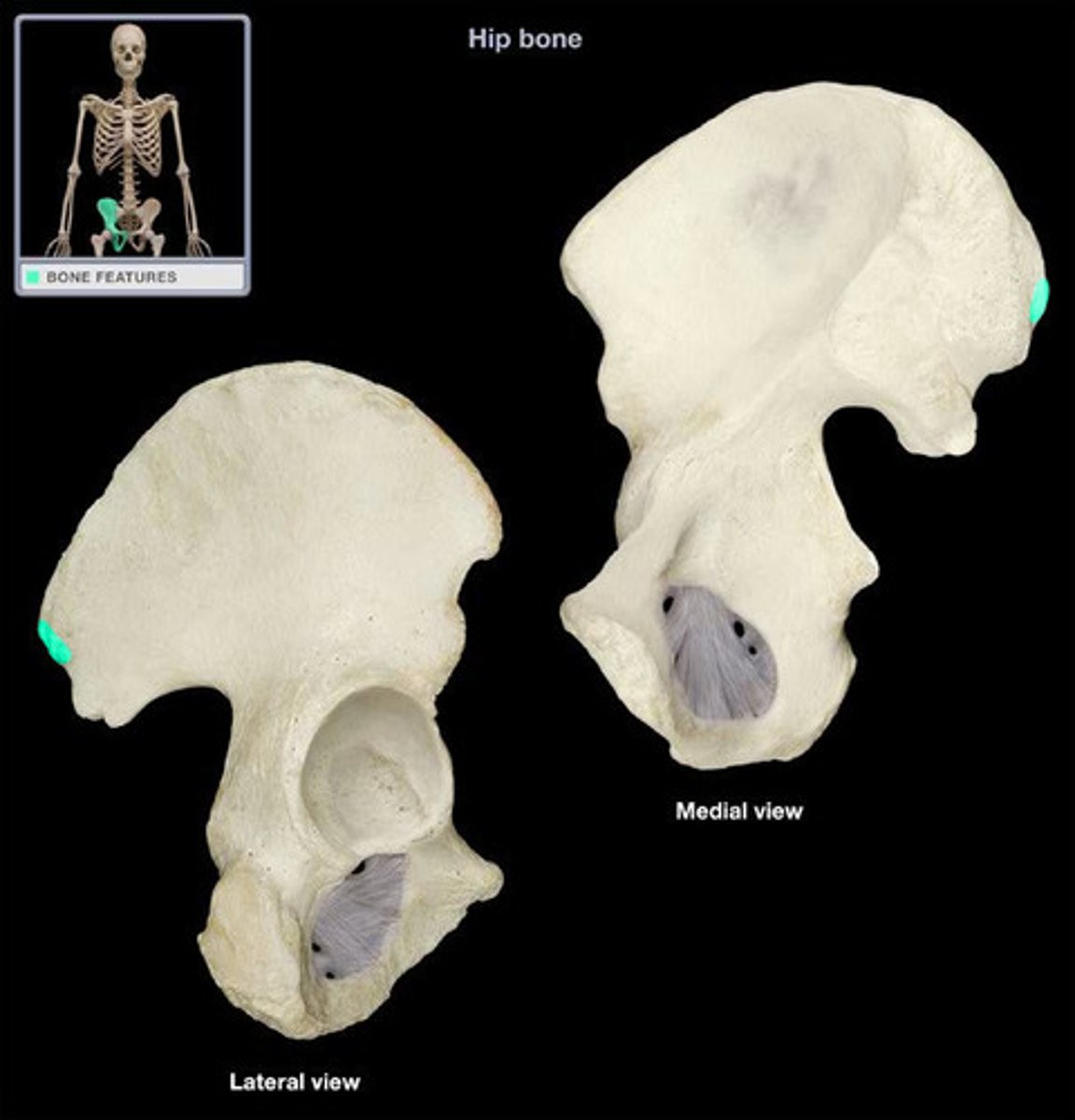
posterior inferior iliac spine (PIIS)
a bony projection located inferior to the posterior superior iliac spine
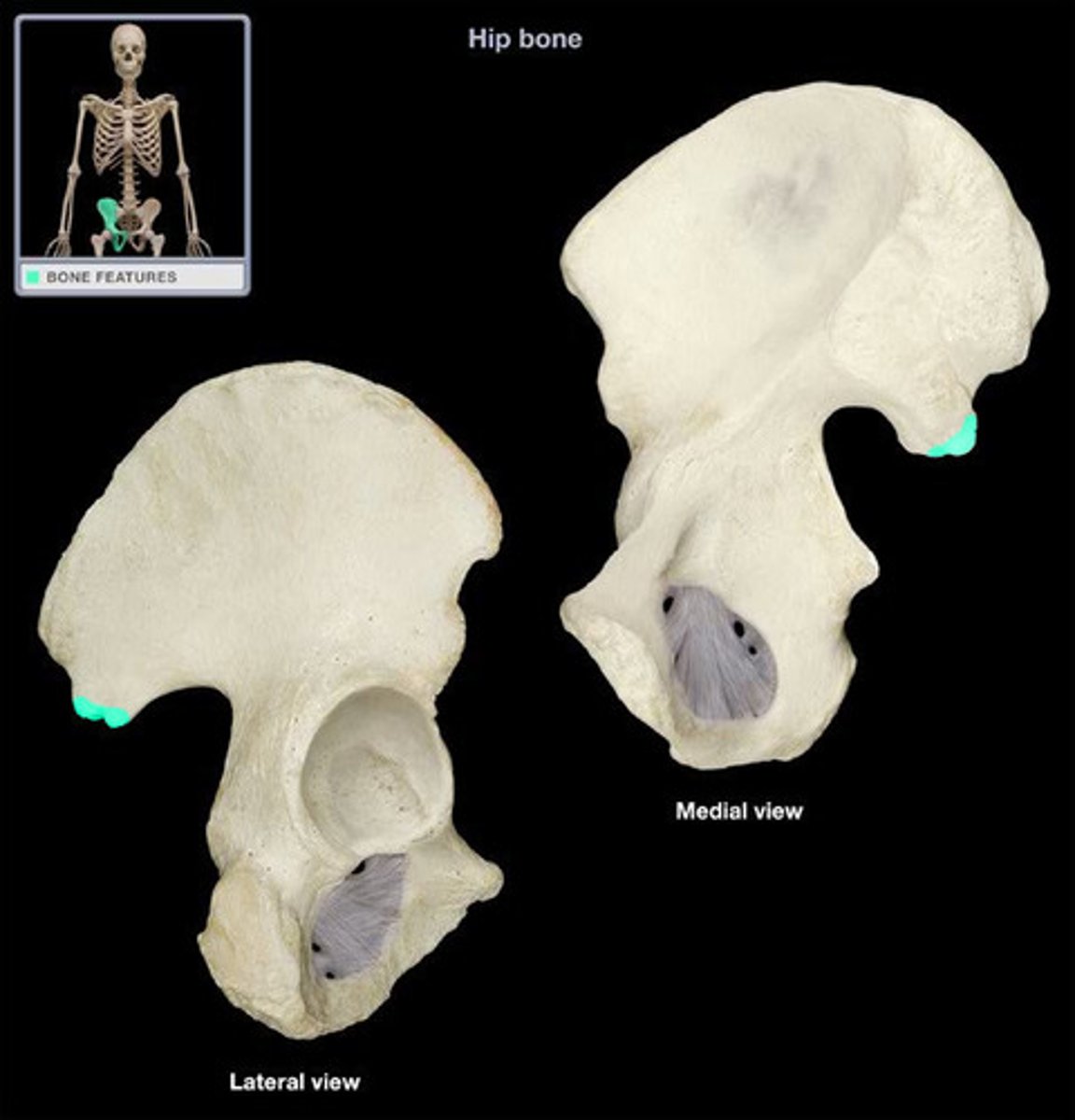
anterior superior iliac spine
origin of sartorius
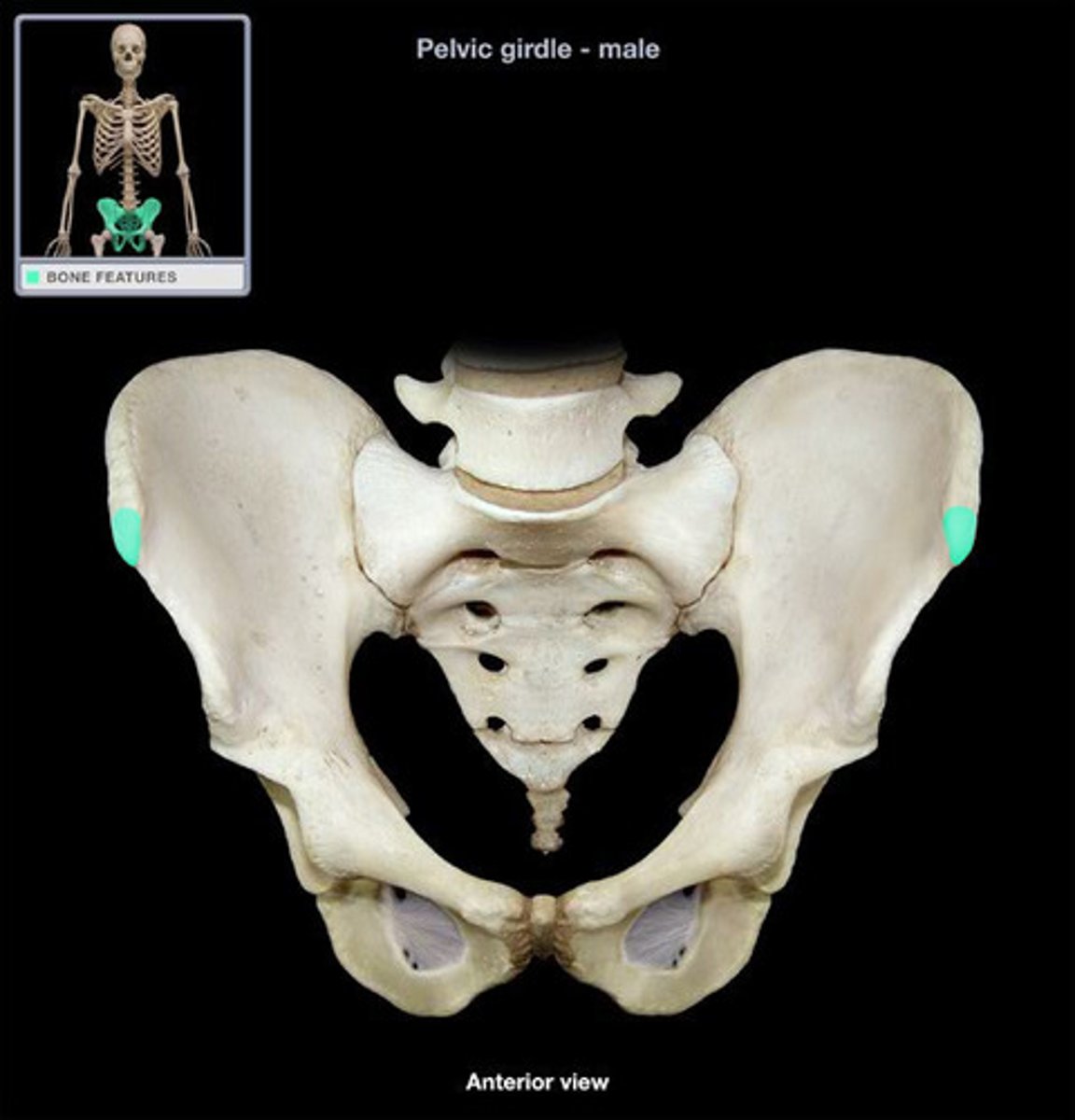
anterior inferior iliac spine (AIIS)
origin of rectus femoris
iliac fossa
The broad, slightly concave inner surface of the ilium.
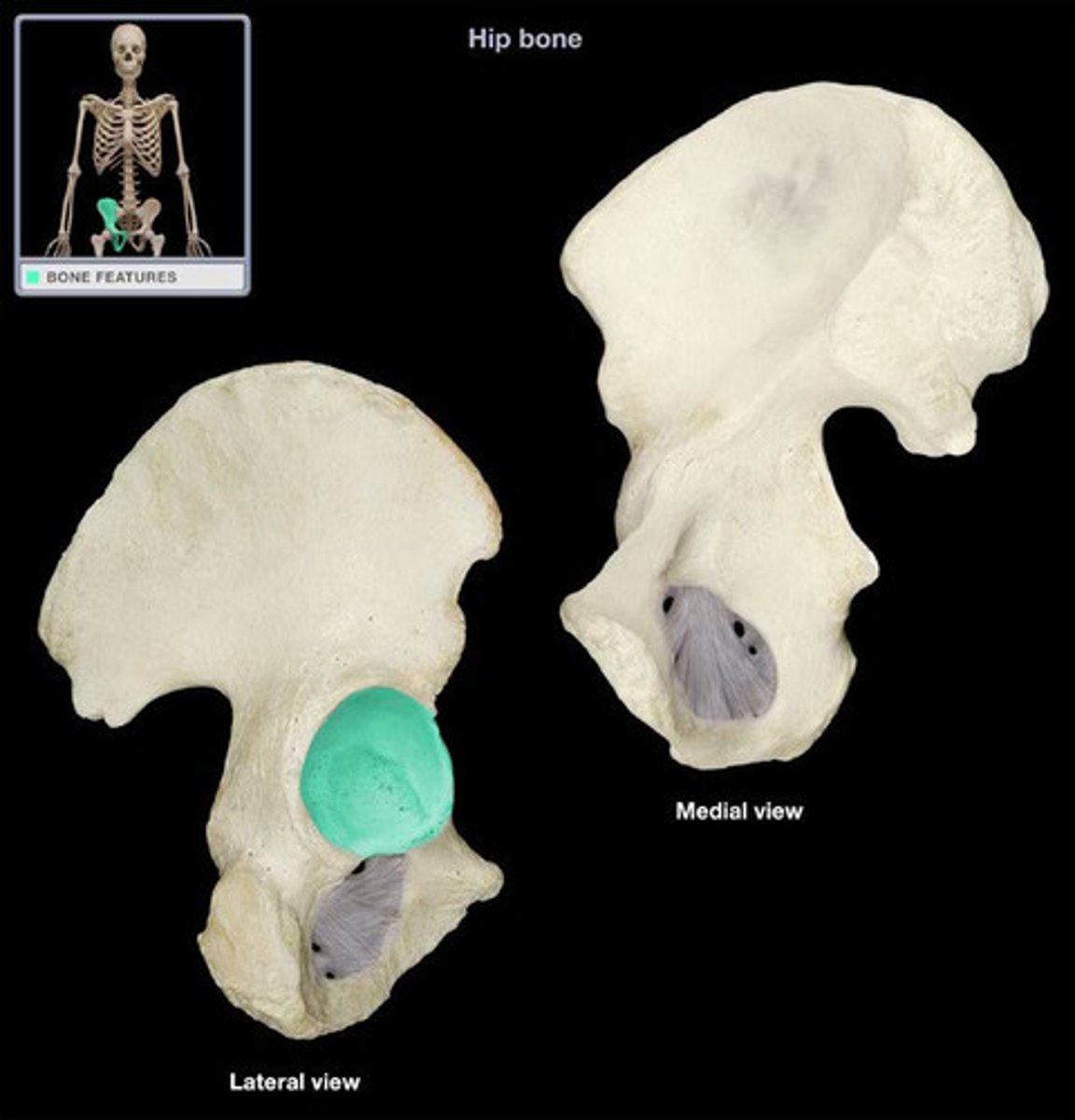
Acetabulum
large socket in the pelvic bone for the head of the femur
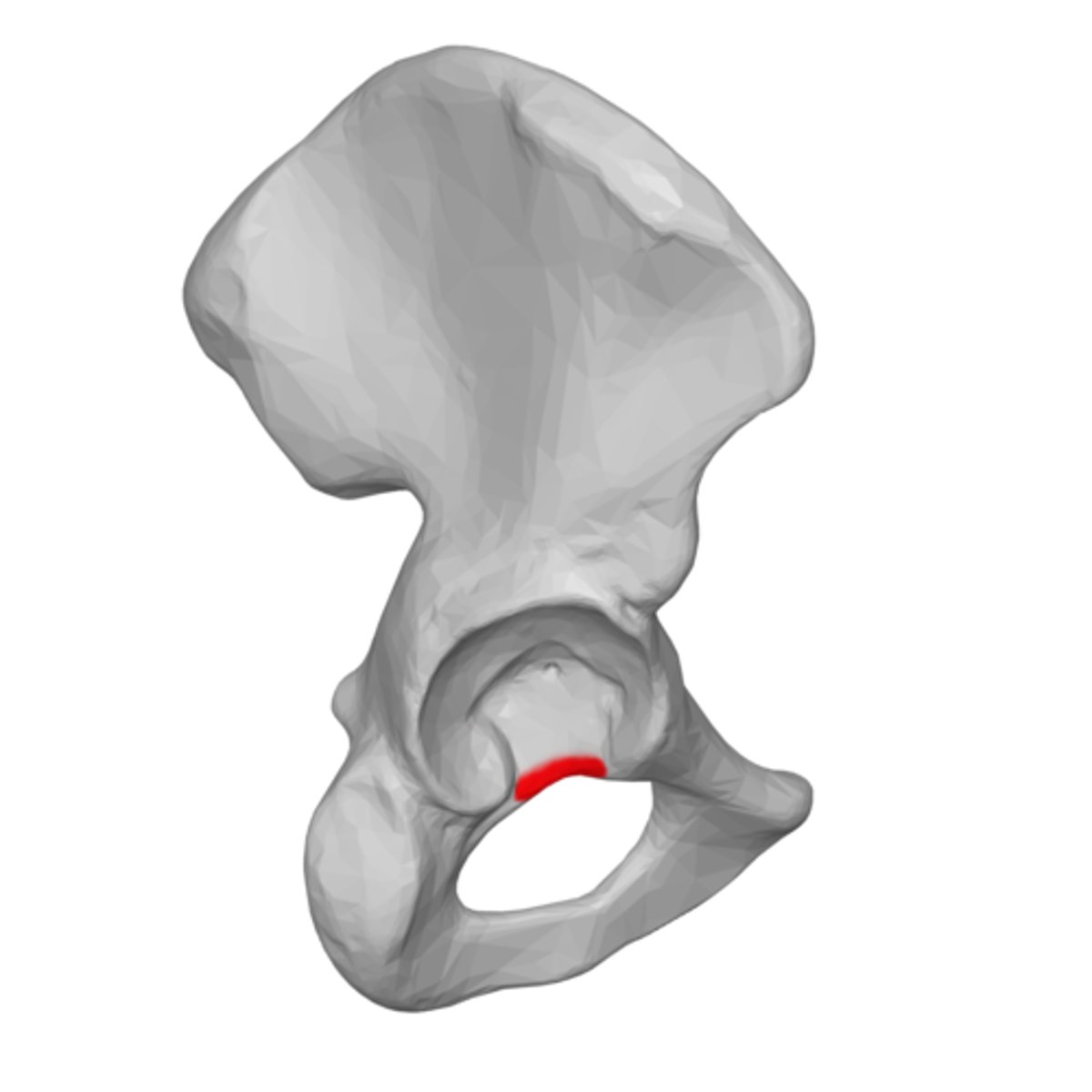
acetabular notch
deep notch in the inferior part of the brim
greater sciatic notch
allows blood vessels and the large sciatic nerve to pass from the pelvis posteriorly into the thigh
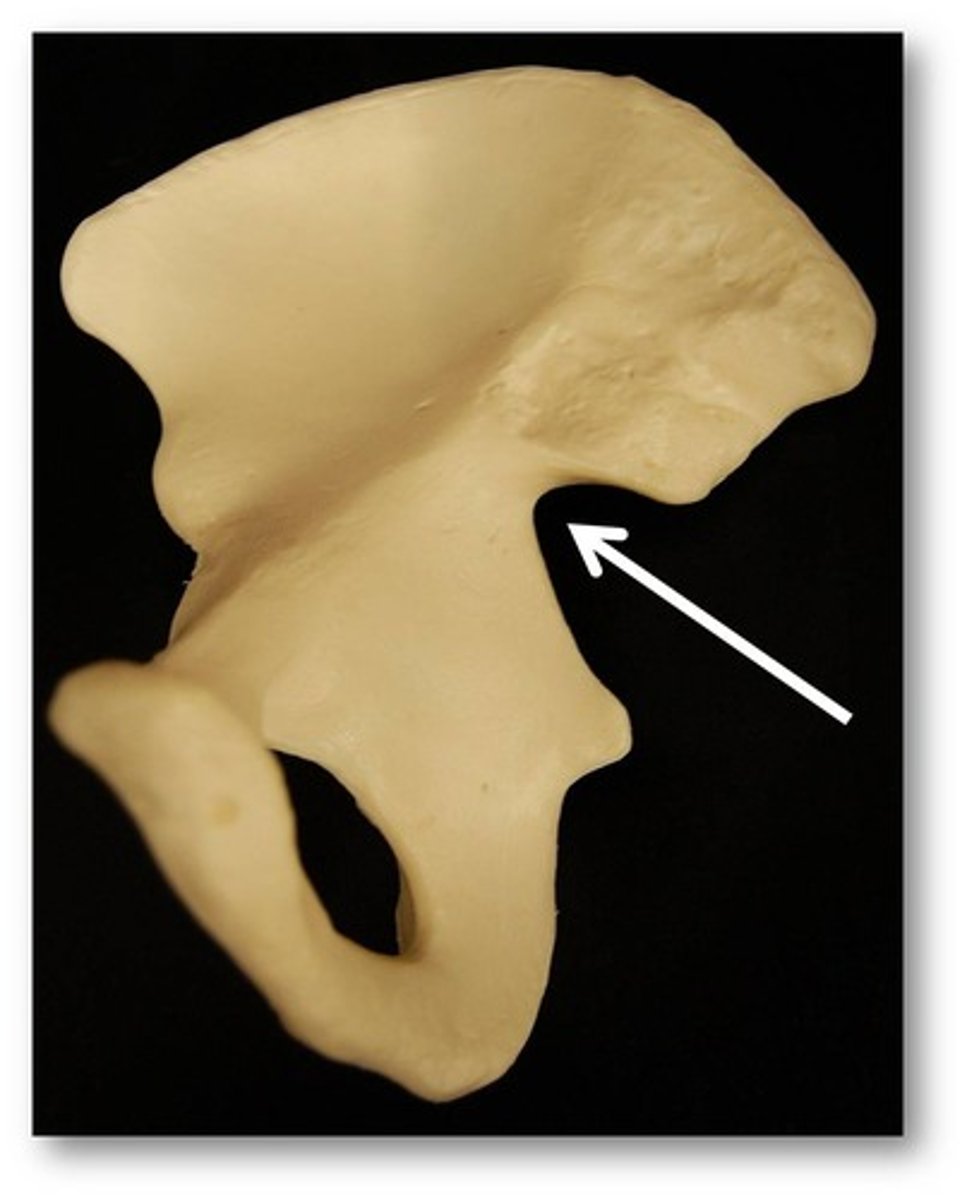
ischial tuberosity
receives the weight of the body when sitting
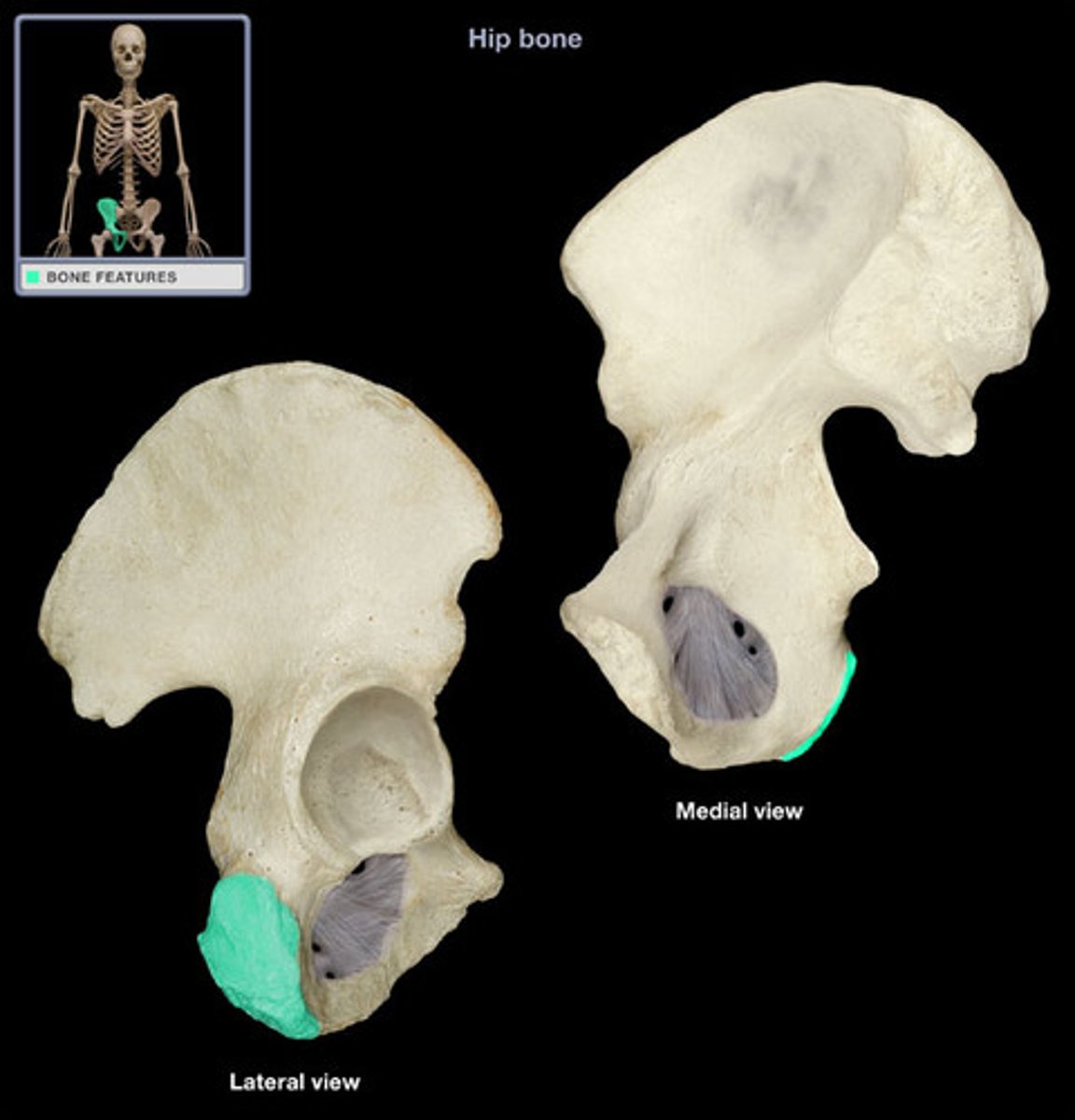
body of ischium
Makes up all of the ischium superior to the tuberosity
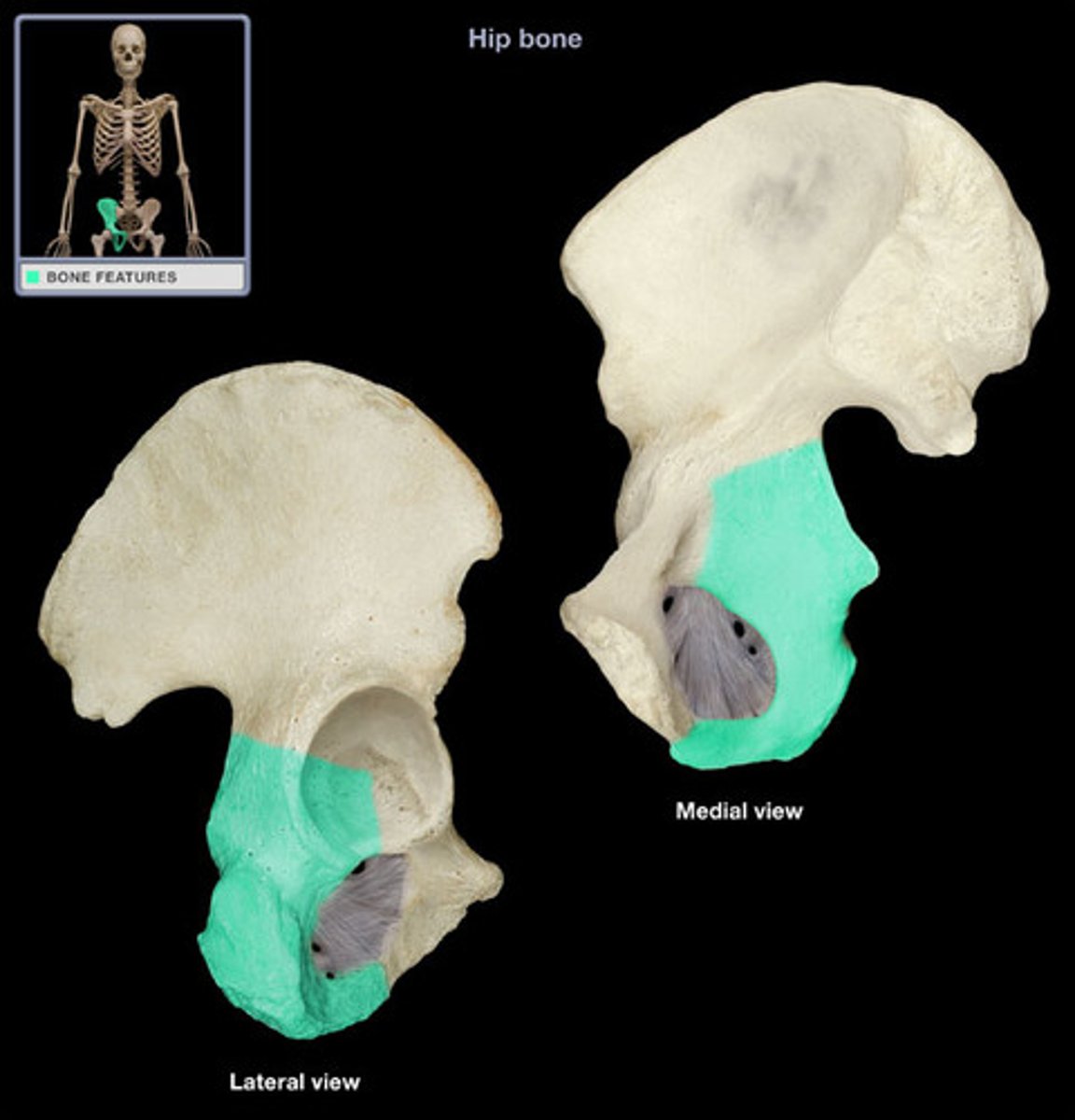
ramus of ischium
joins the inferior ramus of the pubis anteriorly
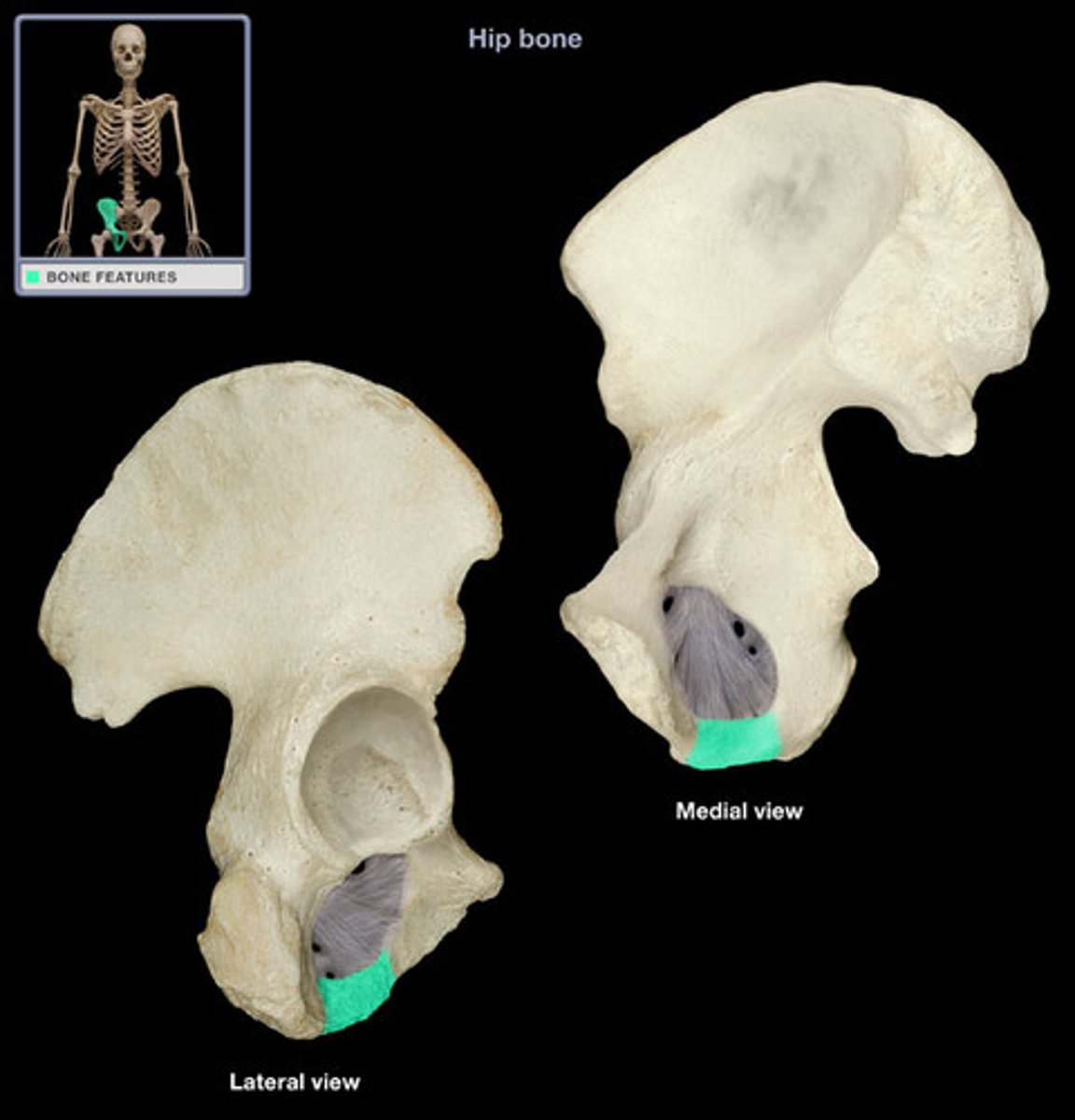
obturator foramen
opening in hip bone formed by the pubic and ischial rami
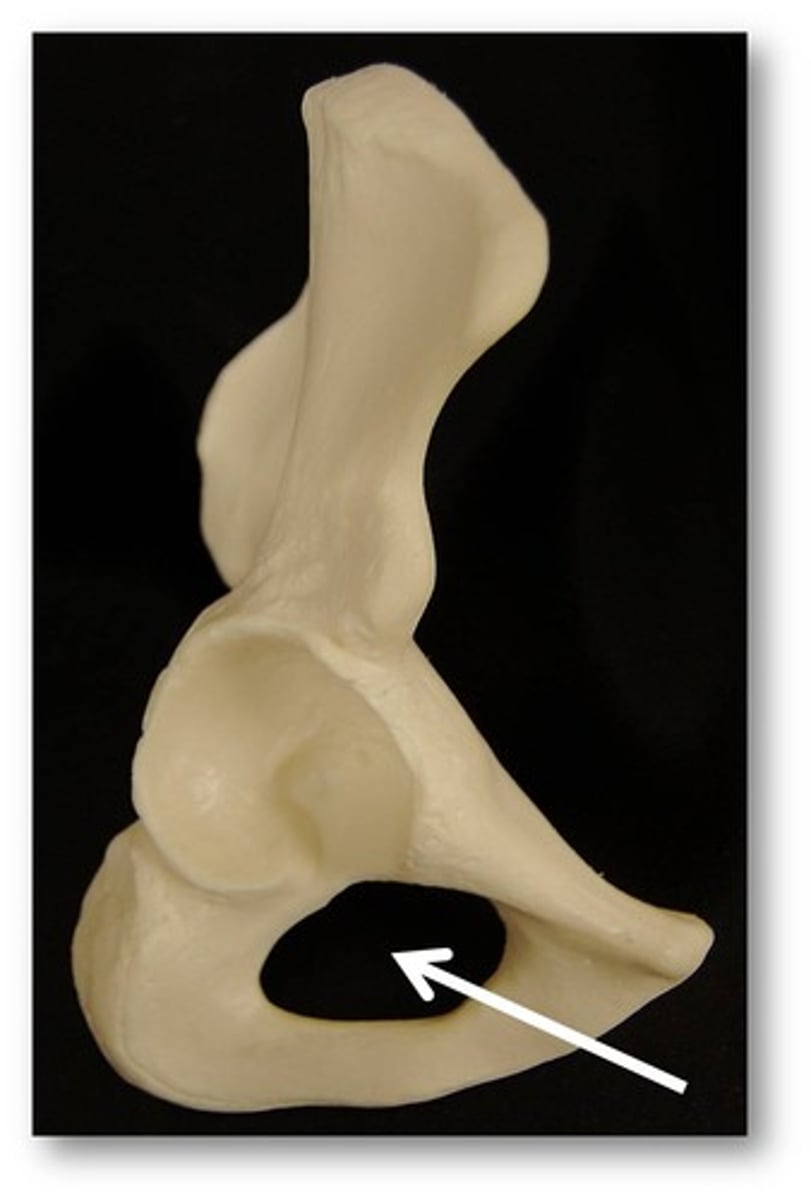
body of pubis
origin of adductor longus
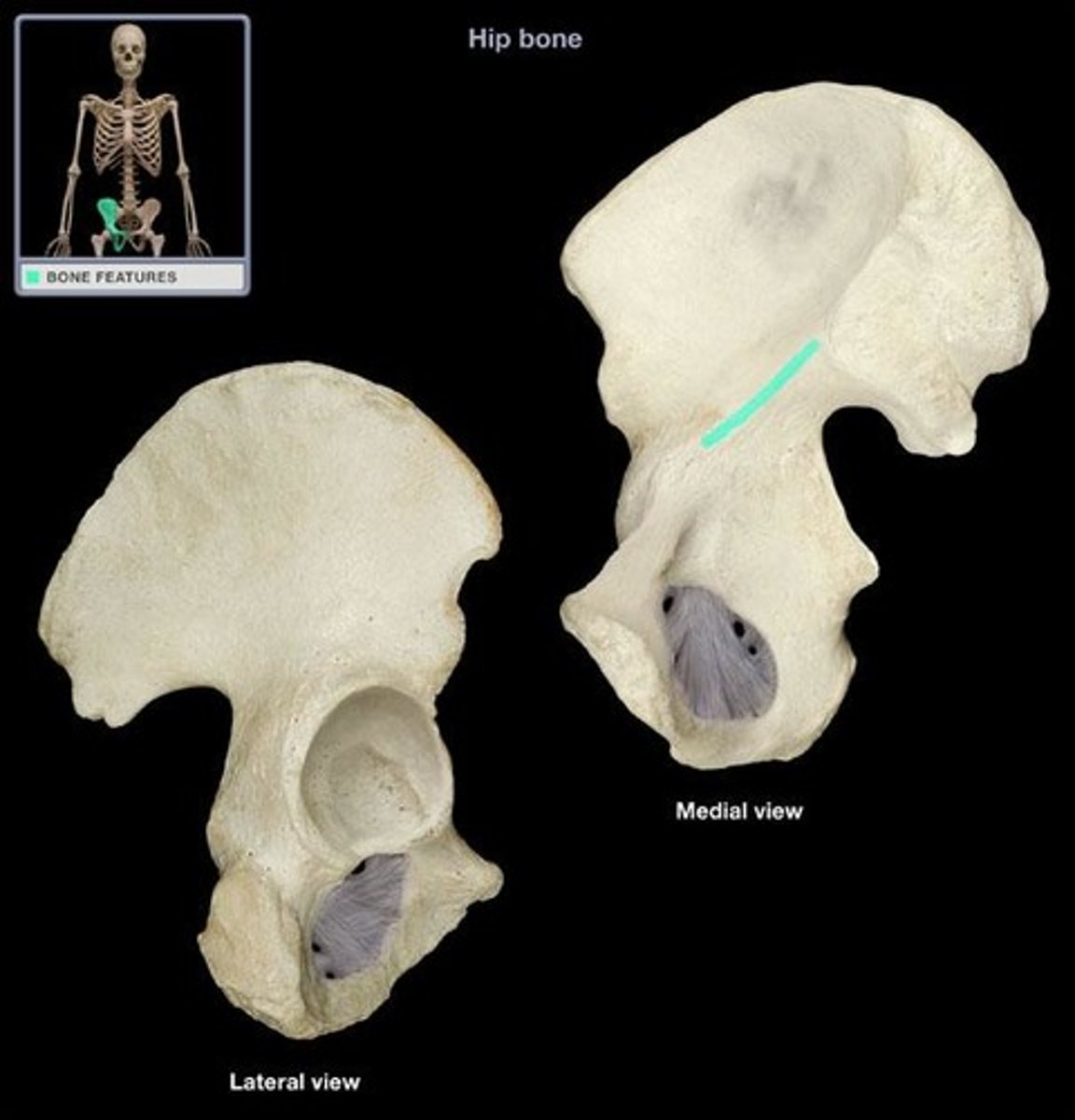
arcuate line
a ridge of bone that runs inferiorly and anteriorly from the auricular surface, forms pelvic brim
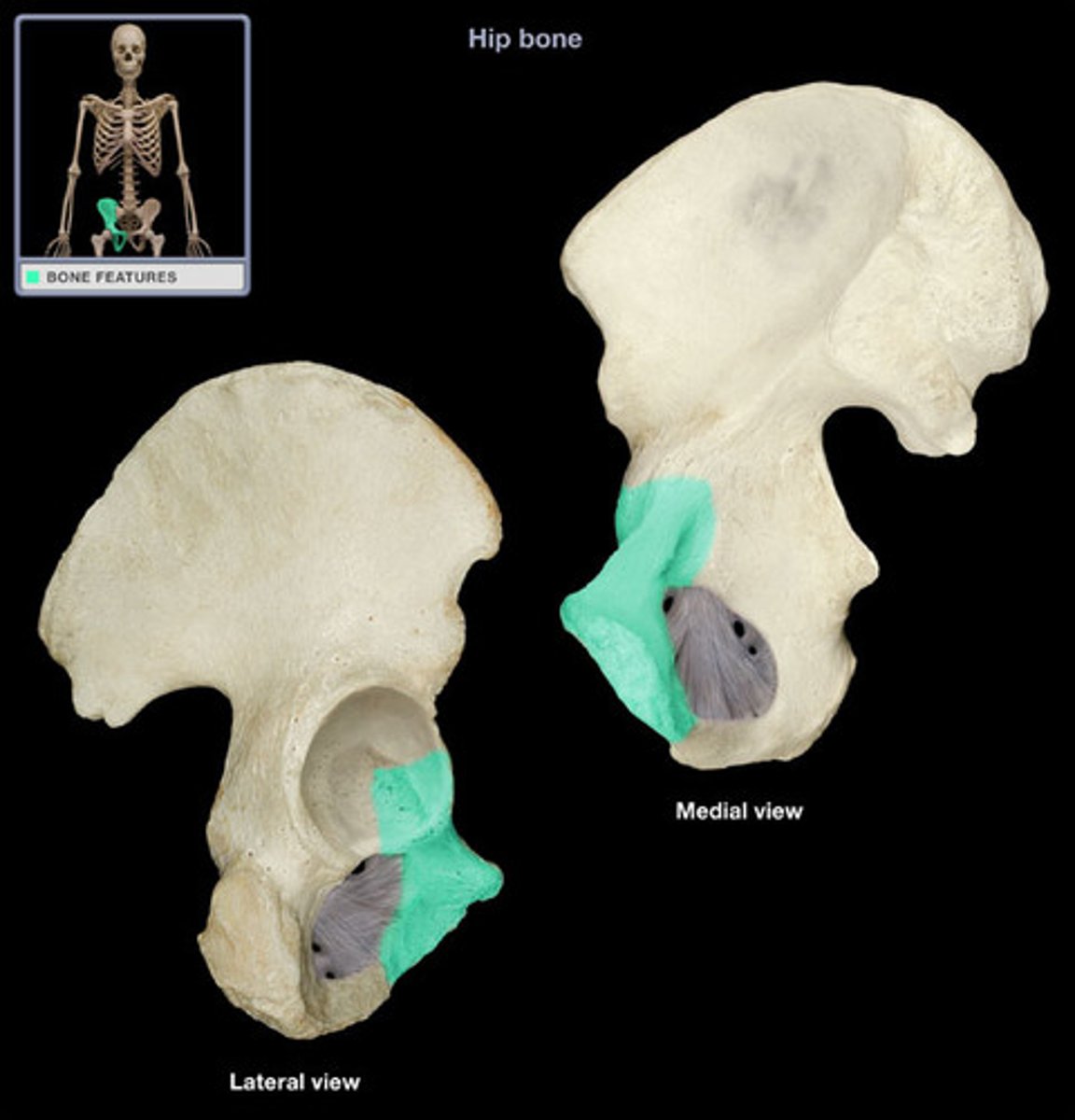
iliopubic eminence
marks the point of union of the ilium and the pubis just lateral to the arcuate line
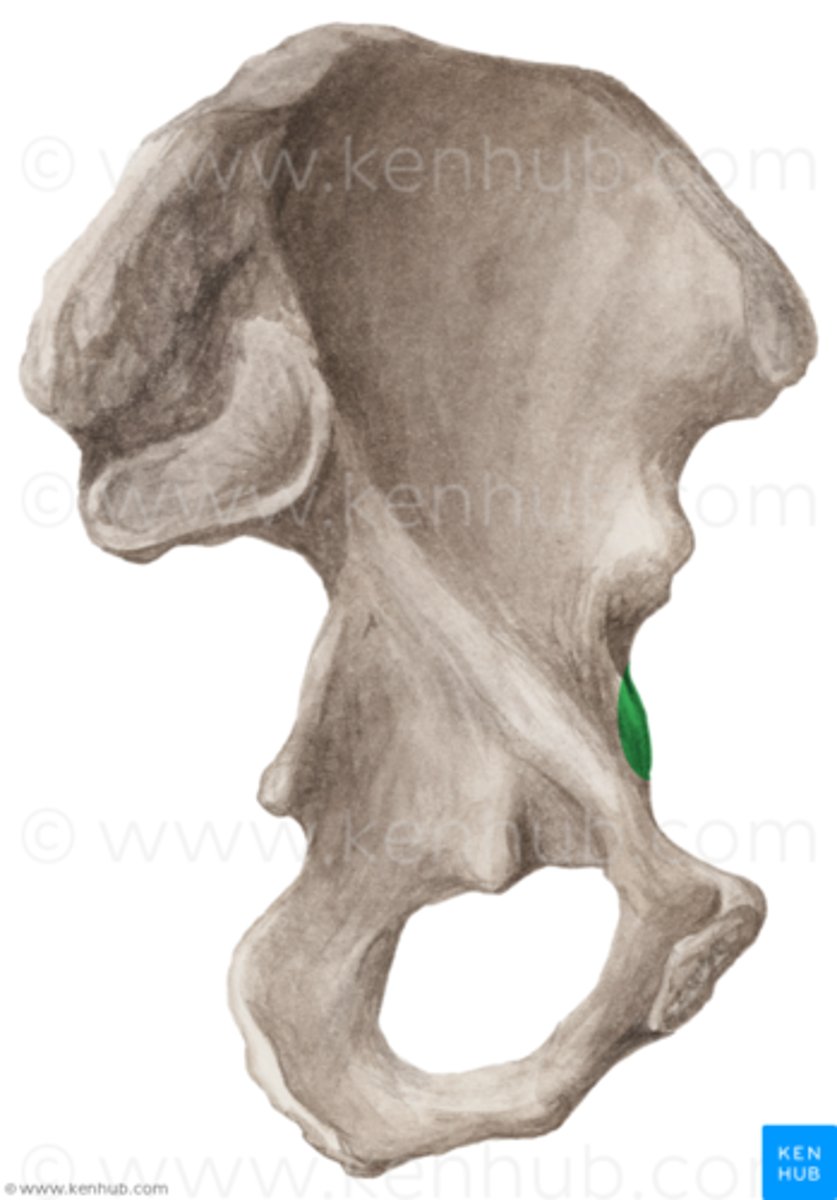
pubic tubercle
An attachment point for the inguinal ligament.
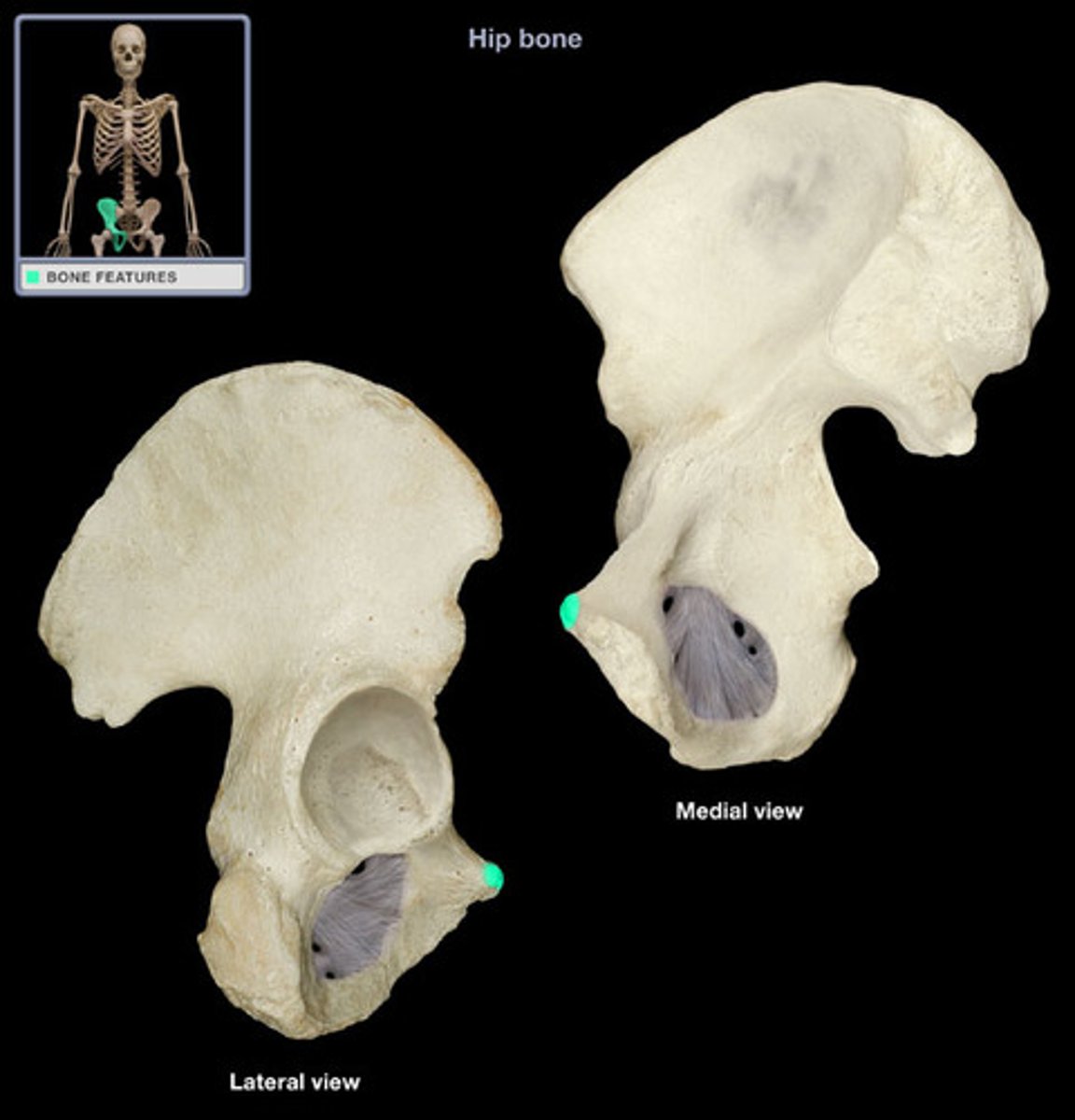
superior ramus of pubis
origin of pectineus
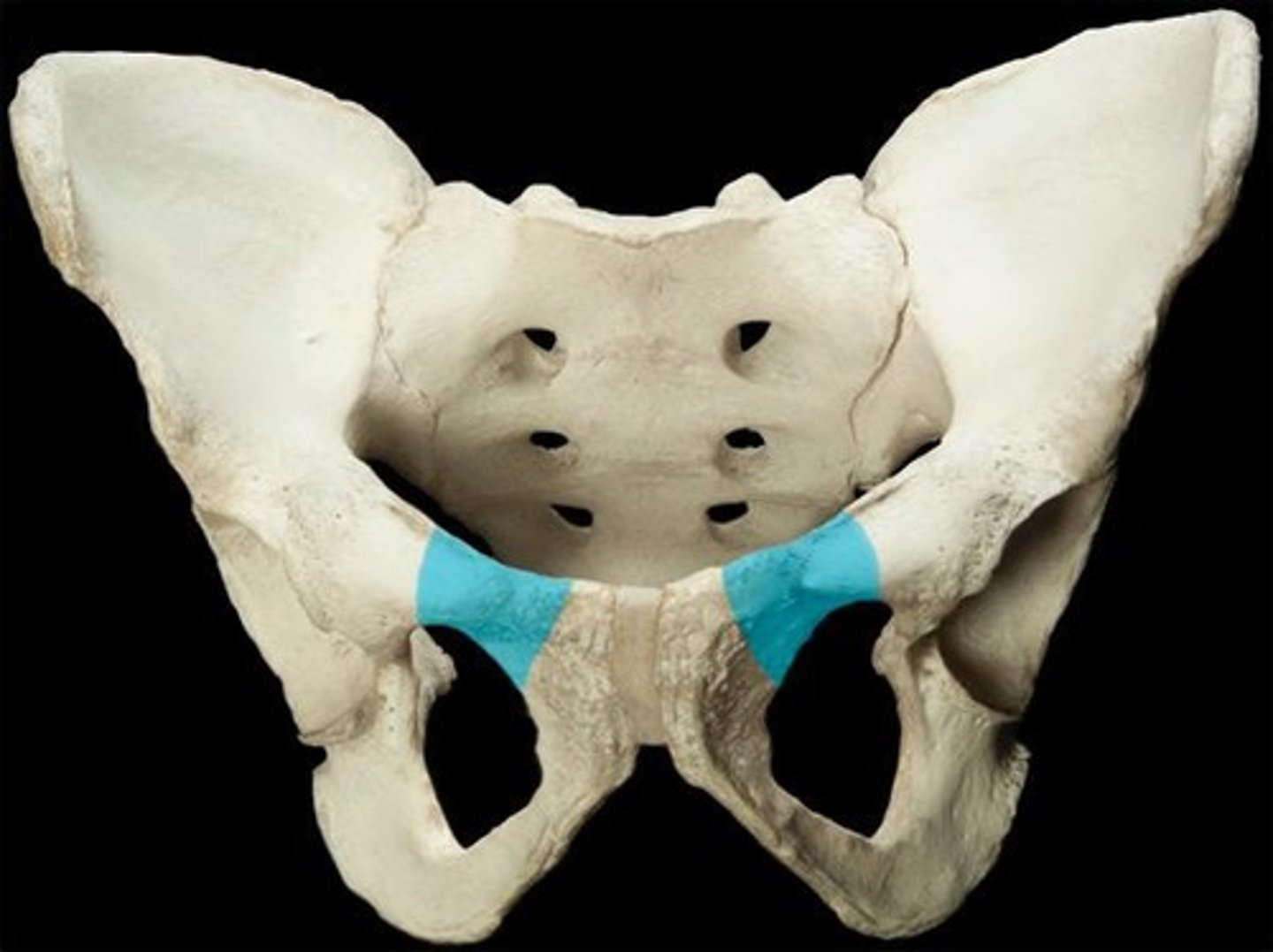
inferior ramus of pubis
origin of adductor brevis
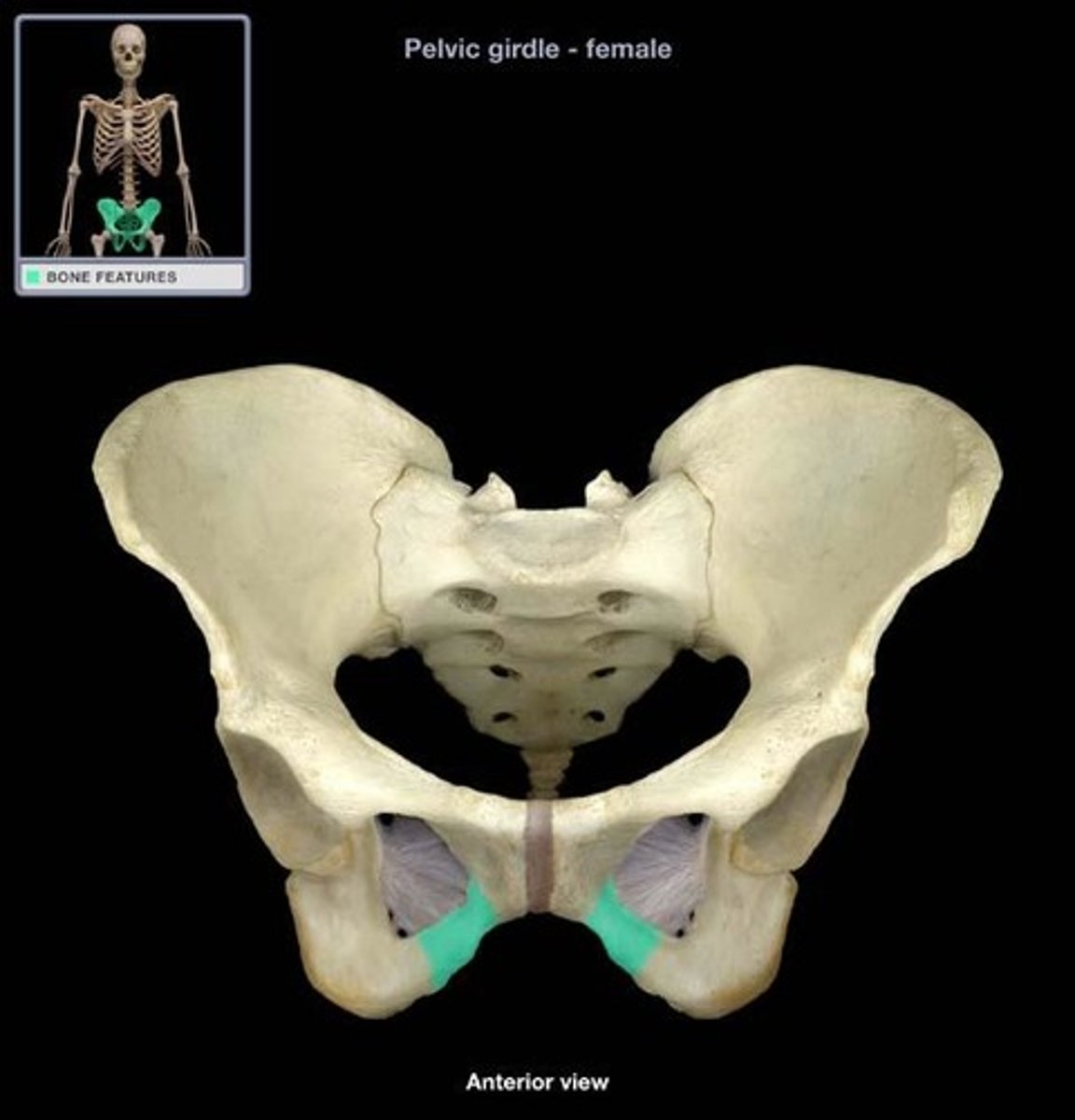
pubic symphysis
cartilaginous joint at which two pubic bones fuse together
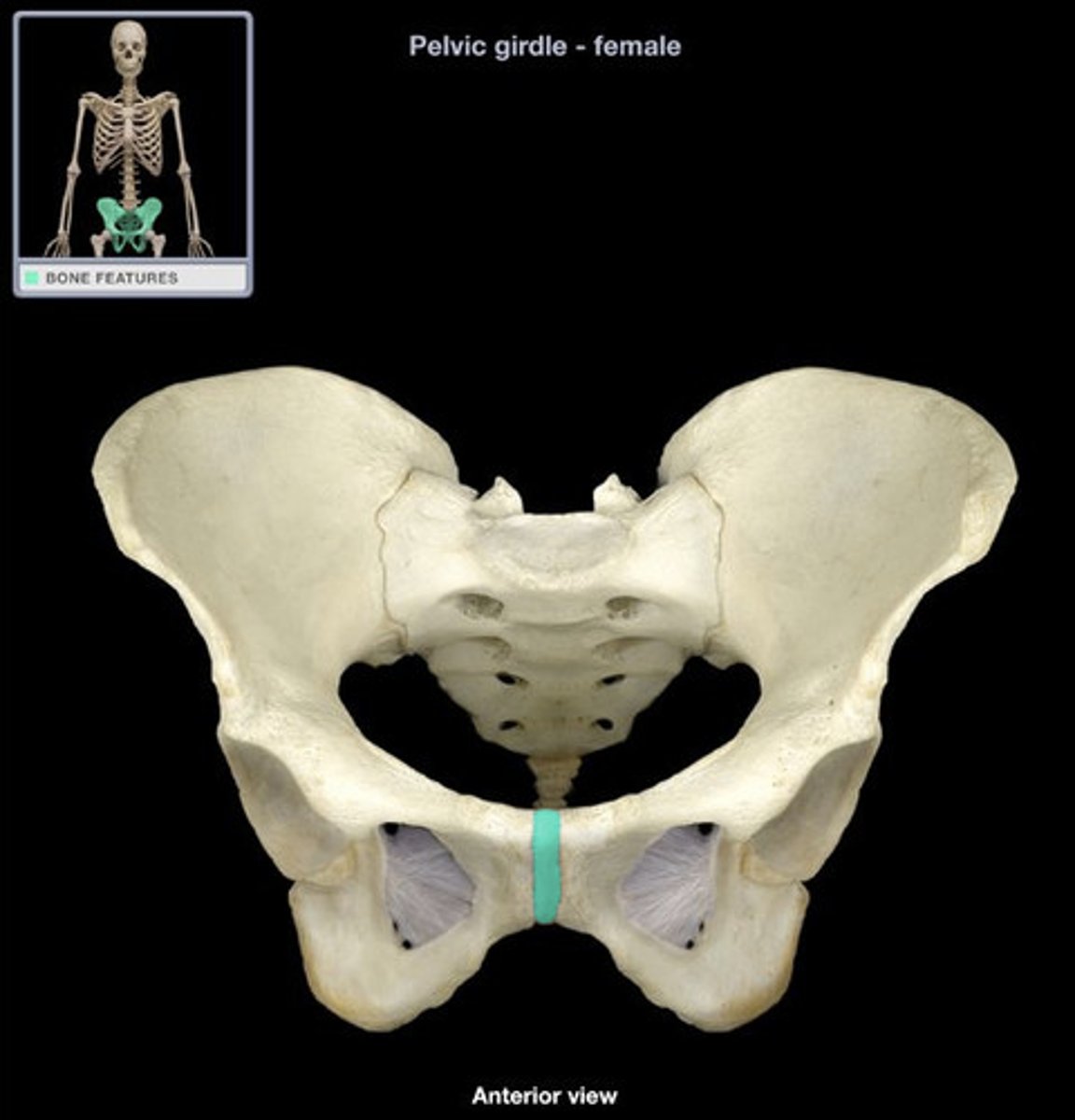
pelvic floor
The muscular base of the abdomen attached to the pelvis, supports pelvic organs, influence urination, defecation, sexual function
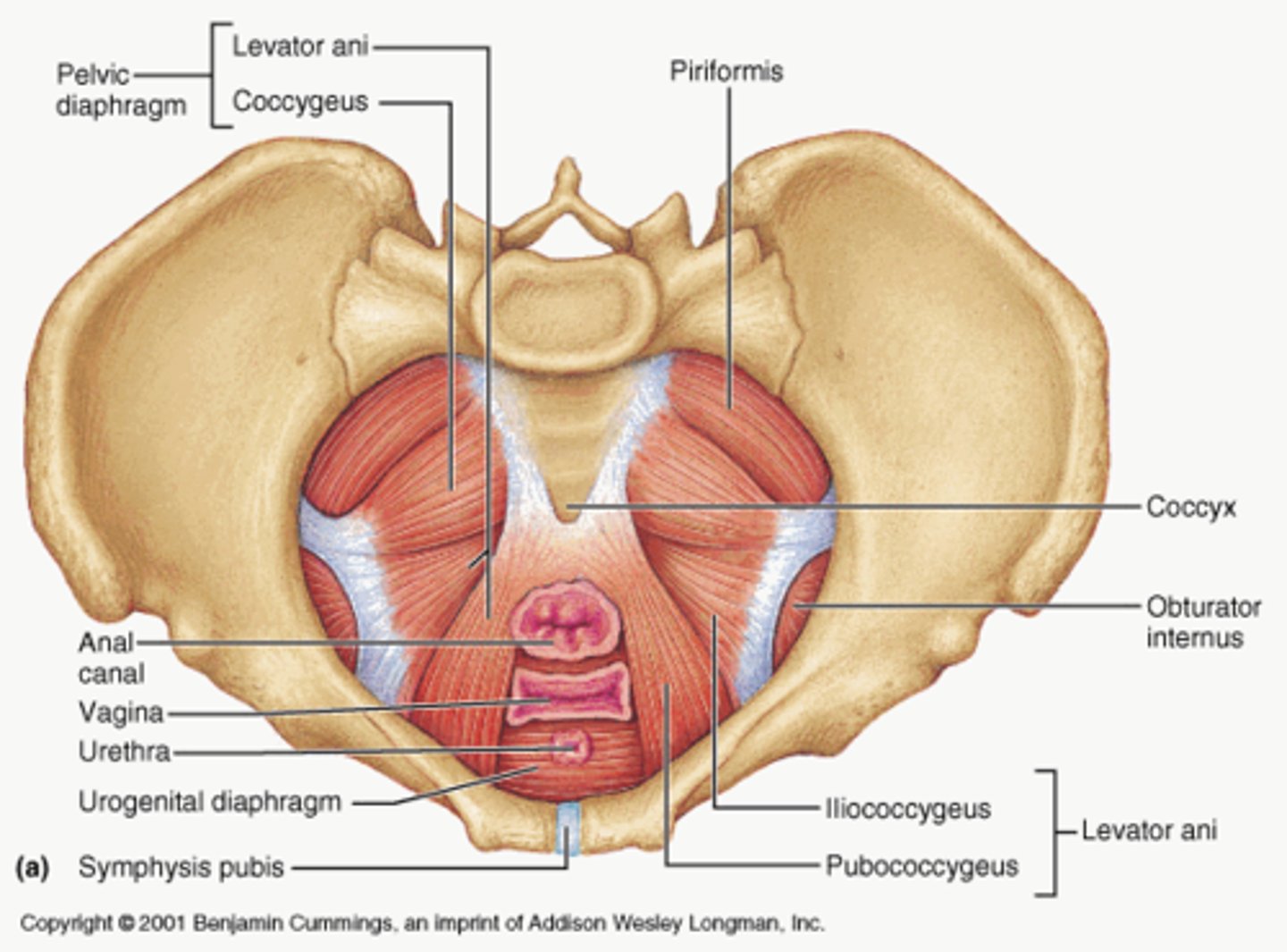
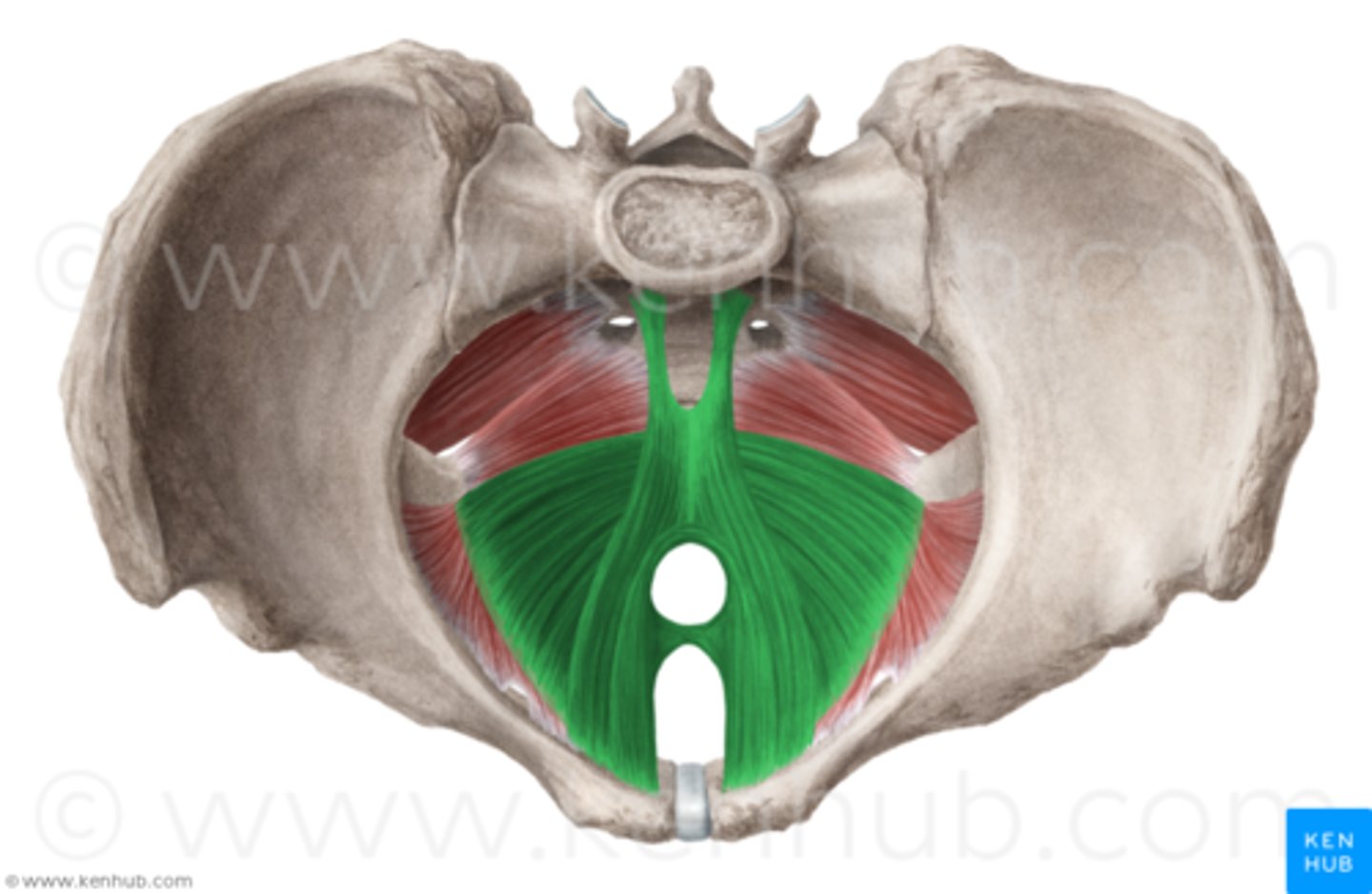
levator ani muscles
puborectalis, pubococcygeus, iliococcygeus
urethral canal
lumen of urethra that drains urine from bladder in male and female, and semen from reproductive system in male
hiatuses in pelvic floor
urethral canal, rectal canal, vaginal canal
rectal canal
Most posterior opening in the pelvic floor, bordered by puborectalis
vaginal canal
middle opening in the pelvic floor that allows passage of the fetus during birth
How can the pelvic floor be exercised?
since control is voluntary, kegal exercises and control of urine can be practiced
pelvic diaphragm (proper)
levator ani and coccygeus
pelvic diaphragm (all groups)
includes pelvic diaphragm proper, urogenital diaphragm, sphincters and erectile muscles of urogenital tract
Puborectalis
O: anteriorly, from pubic symphysis
I: posteriorly, around anorectal junction
A: inhibits and also aids in defecation, and flatulence
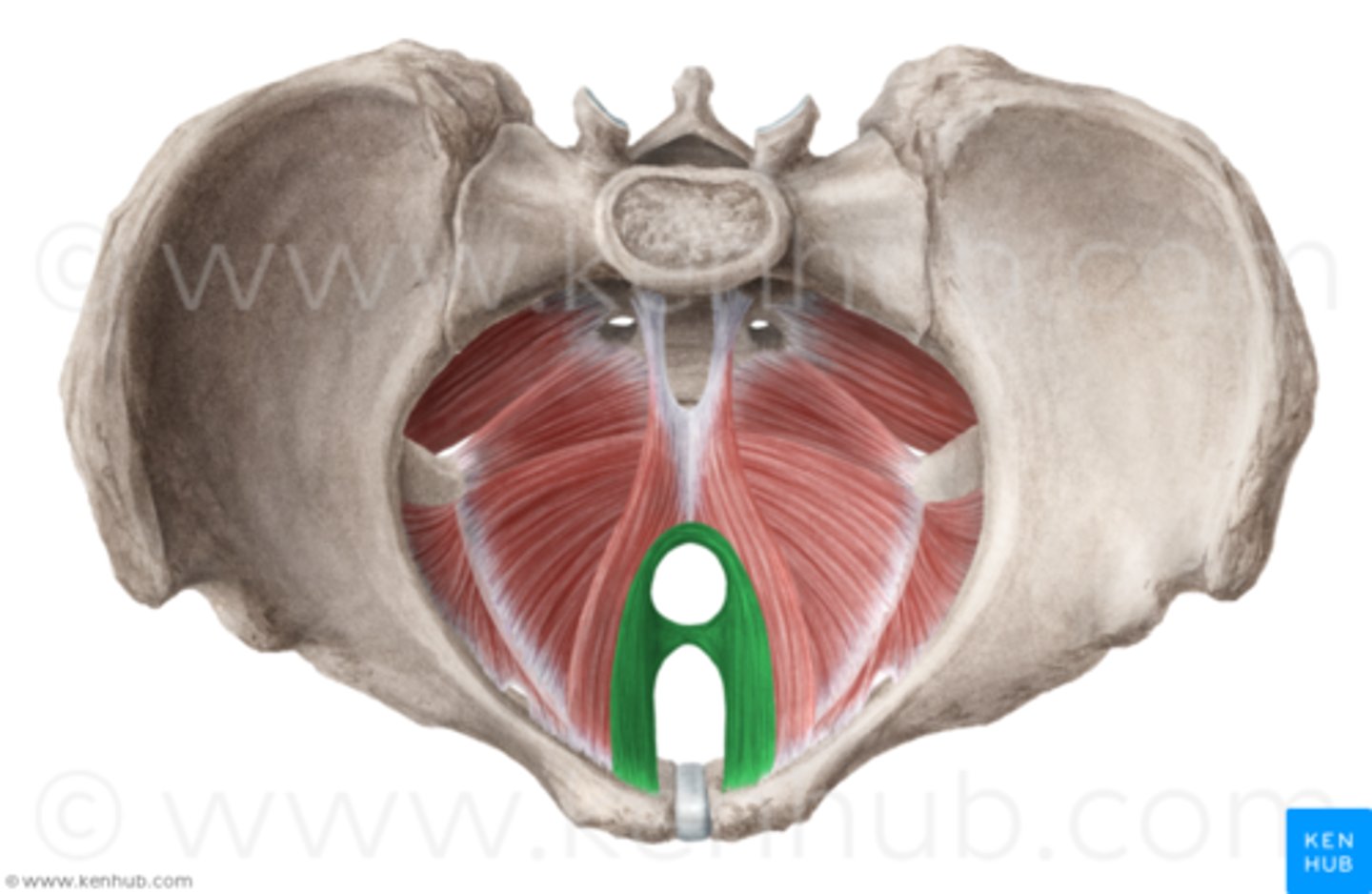
What is the result of damage to puborectalis?
involuntary farting and defecation
Pubococcygeus
O: pubic bone (lateral to puborectalis)
I: coccyx
A: controls urine flow, contracts during orgasm
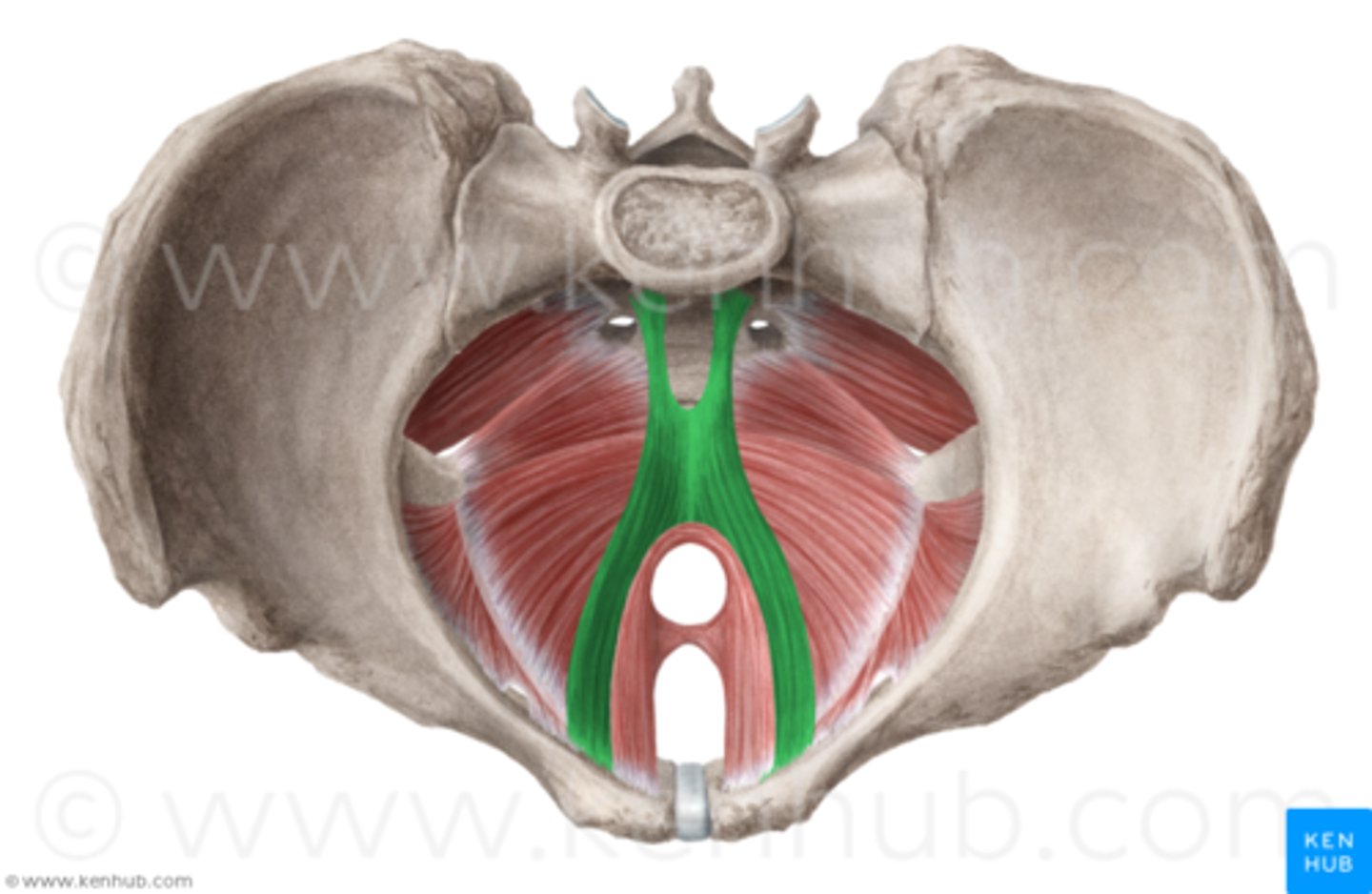
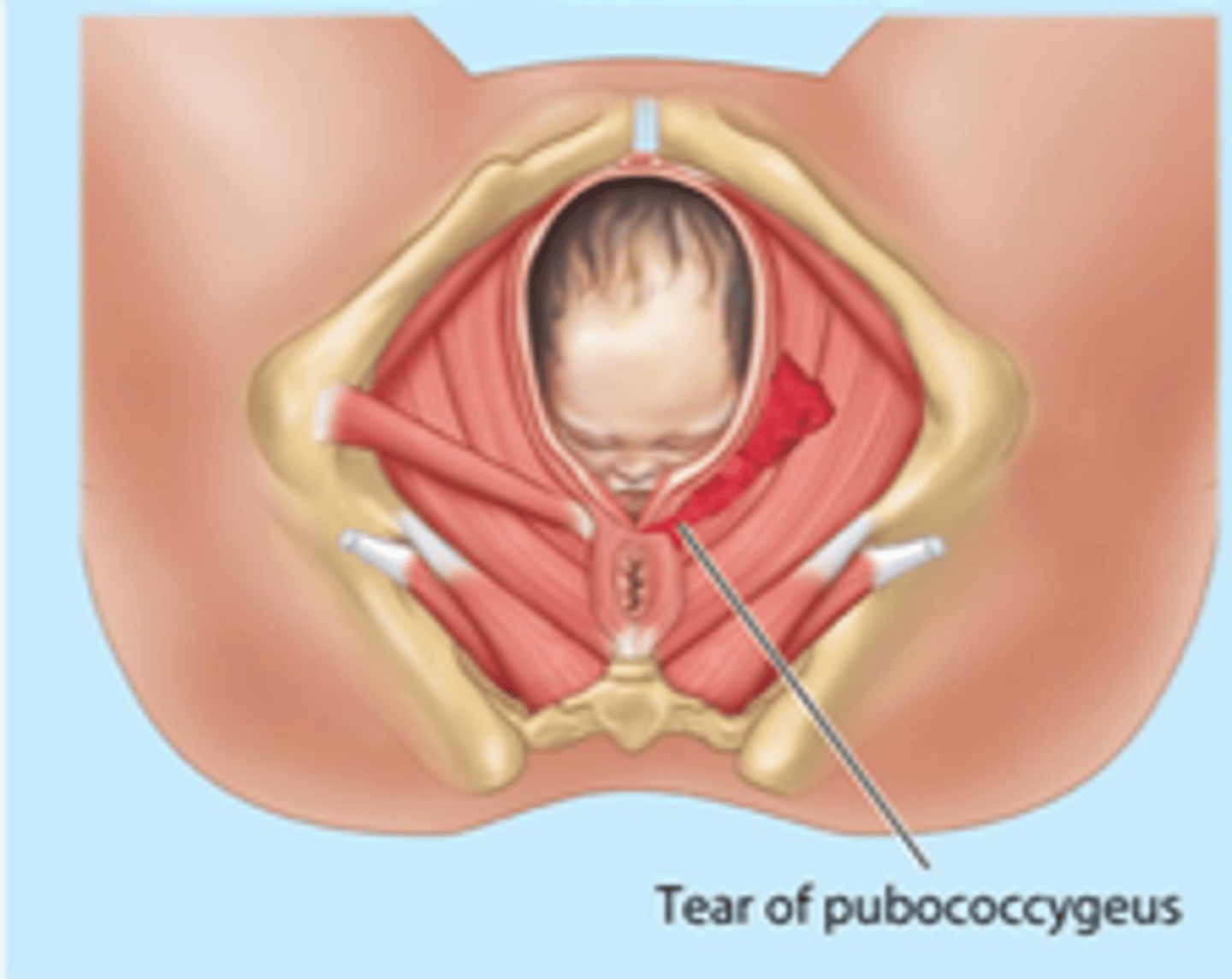
pelvic floor injury
-extremely common consequence of vaginal delivery
-puborectalis and pubococcygeus are most common muscles damaged, causing incontinence and sexual dysfunction
fundus of uterus
Most superior & widest portion of uterus, used to track fetal development based on position
What are common symptoms that arise from the fetus compressing abdominal organs?
shortness of breath, heartburn, reduced stomach capacity, issues moving chyme/feces