Abstract Data Types and Data Structures Overview Cartes | Quizlet
1/239
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
240 Terms
Abstract Data Type (ADT)
A type (or class) for objects whose behavior is defined by a set of values and a set of operations.
Abstraction
The process of providing only the essentials and hiding the details.
List ADT
A list contains elements of the same type arranged in sequential order.
get()
Return an element from the list at any given position.
insert()
Insert an element at any position of the list.
remove()
Remove the first occurrence of any element from a non-empty list.
removeAt()
Remove the element at a specified location from a non-empty list.
replace()
Replace an element at any position by another element.
size()
Return the number of elements in the list.
isEmpty()
Return true if the list is empty, otherwise return false.
isFull()
Return true if the list is full, otherwise return false.
Stack ADT
A Stack contains elements of the same type arranged in sequential order.
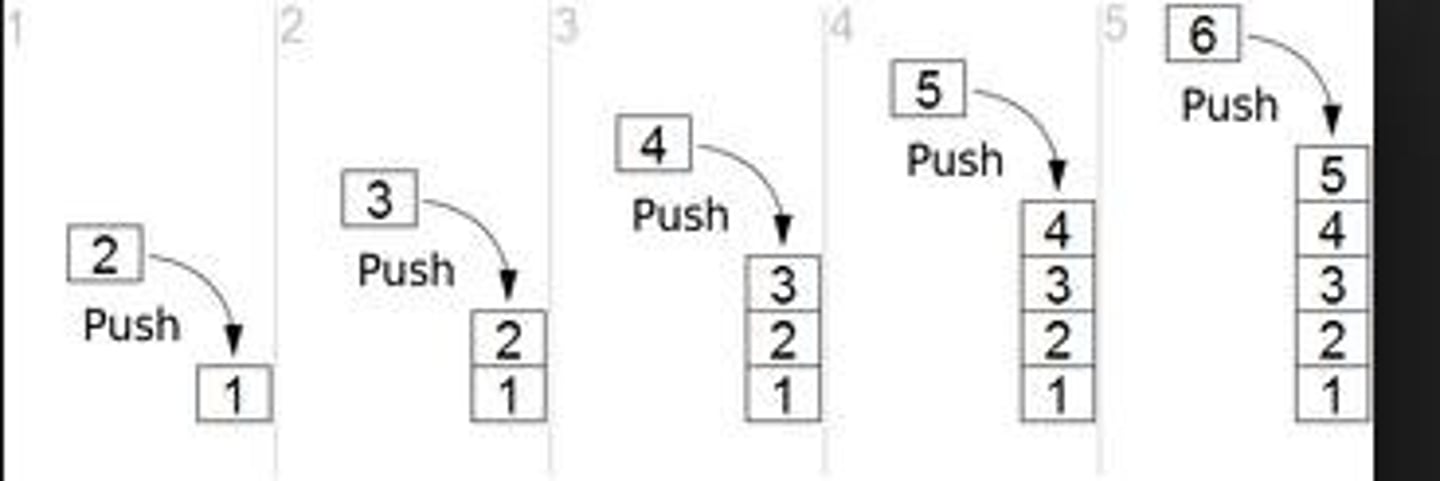
push()
Insert an element at one end of the stack called top.
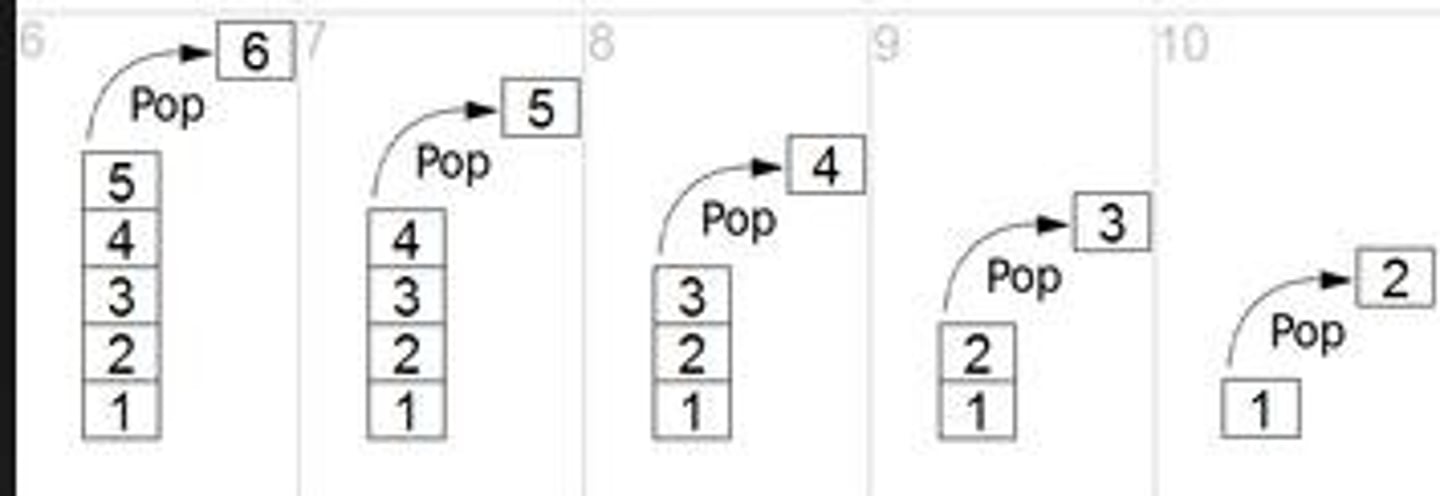
pop()
Remove and return the element at the top of the stack, if it is not empty.
peek()
Return the element at the top of the stack without removing it, if the stack is not empty.
size()
Return the number of elements in the stack.
isEmpty()
Return true if the stack is empty, otherwise return false.
isFull()
Return true if the stack is full, otherwise return false.
Queue ADT
A Queue contains elements of the same type arranged in sequential order.
enqueue()
Insert an element at the end of the queue.
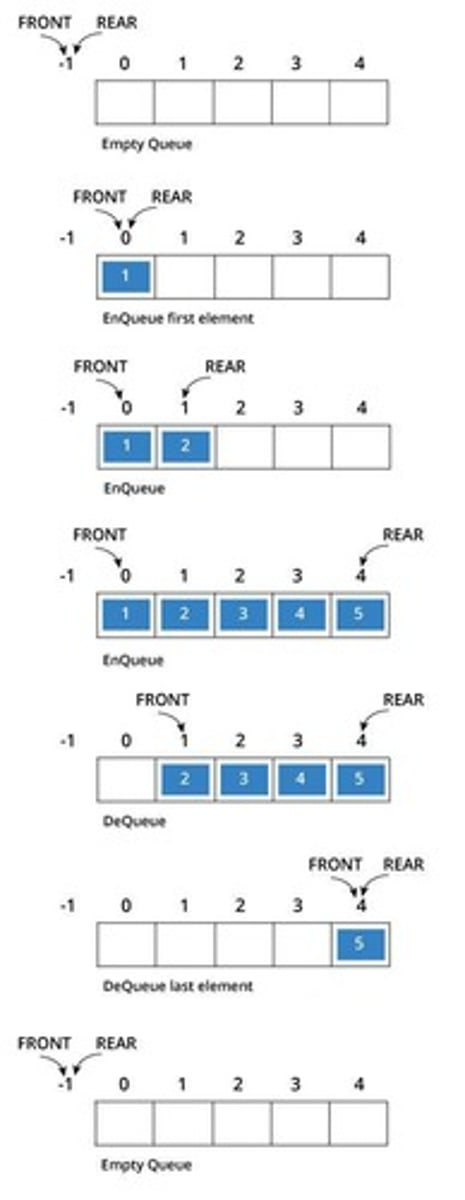
dequeue()
Remove and return the first element of the queue, if the queue is not empty.
peek()
Return the element of the queue without removing it, if the queue is not empty.
size()
Return the number of elements in the queue.
isEmpty()
Return true if the queue is empty, otherwise return false.
isFull()
Return true if the queue is full, otherwise return false.
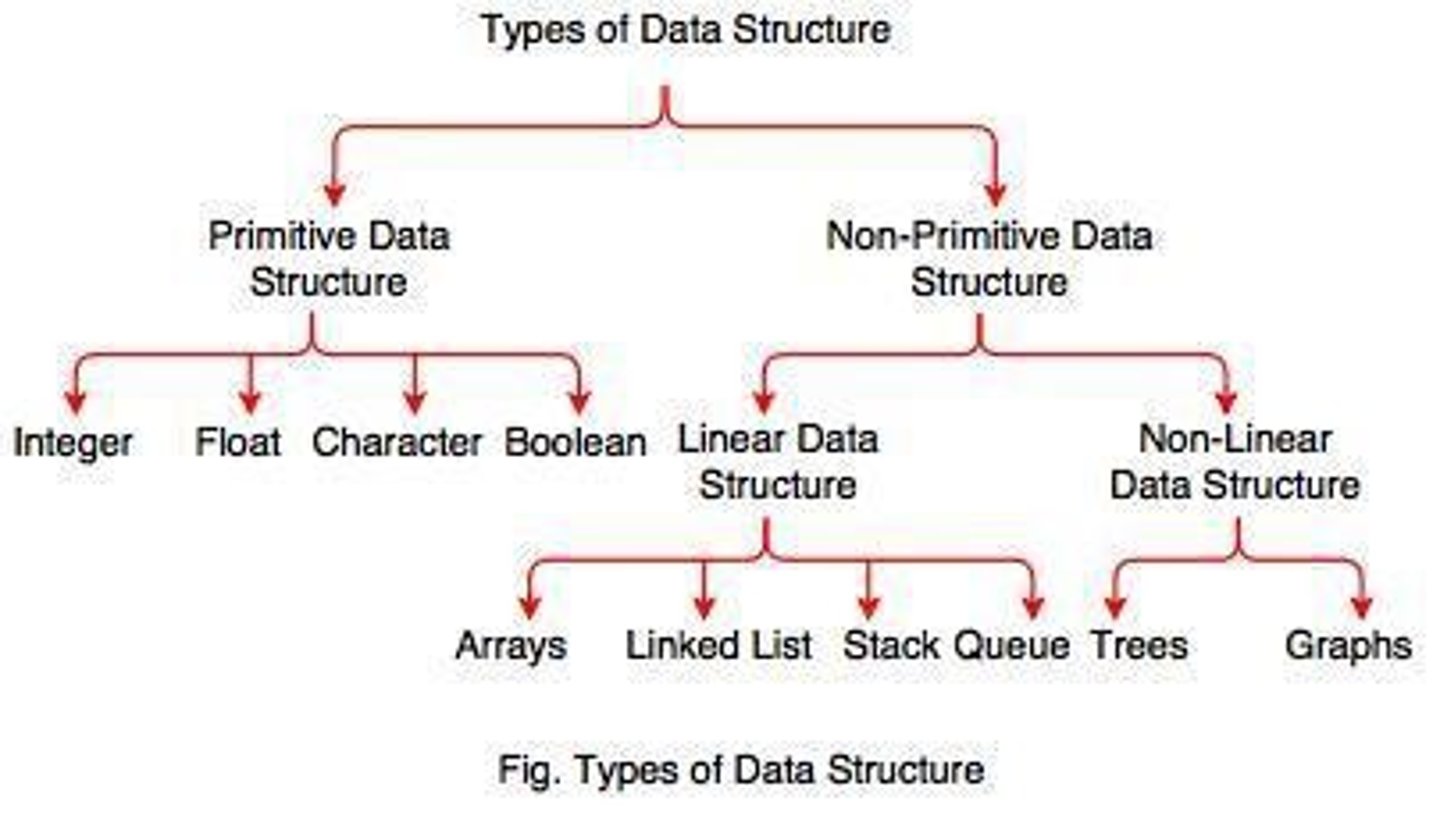
Data Structure
A specialized format for organizing, processing, retrieving and storing data.
Advantages of Data Structure
Data structures allow information storage on hard disks, management of large datasets, design of efficient algorithms, safe storage of information, and easier processing of data.
Data Structures
A way to organize and store data in a computer so that it can be accessed and modified efficiently.
Arrays
An array stores a collection of items at adjoining memory locations, allowing easy calculation or retrieval of each element.
Stacks
A stack stores a collection of items in a linear order, following the last in first out (LIFO) principle.
Queues
A queue stores a collection of items where the operation order is first in first out (FIFO).
Linked Lists
A linked list stores a collection of items in a linear order, where each node contains a data item and a reference to the next item.
Trees
A tree stores a collection of items in a hierarchical way, with nodes linked to other nodes and possibly having multiple children.
Graphs
A graph stores a collection of items in a non-linear fashion, made up of nodes (vertices) and edges connecting them.
Linear Data Structures
Data structures where data items are arranged in a linear sequence, such as arrays.
Non-Linear Data Structures
Data structures where data items are not in sequence, such as trees and graphs.
Homogeneous Data Structures
Data structures where all elements are of the same type, such as arrays.
Non-Homogeneous Data Structures
Data structures where elements may or may not be of the same type.
Static Data Structures
Data structures whose sizes and memory locations are fixed at compile time, such as arrays.
Dynamic Data Structures
Data structures that can expand or shrink depending on program needs, such as linked lists.
Stack Data Structure
An Abstract Data Type (ADT) that follows a particular order for operations, typically LIFO.
Push Operation
The procedure of inserting a new element to the top of the stack.
Stack Overflow
An attempt to insert a new element into a full stack, resulting in an overflow condition.
Pop Operation
The procedure of removing an element from the top of the stack.
Peek or Top
Returns the top element of the stack.
isEmpty
Returns true if the stack is empty, else false.
isFull
Checks if the stack is full.
Stack Underflow
Any attempt to delete an element from already empty stack results into Stack Underflow.
Push Operation
The process of putting a new data element onto stack.
Steps of Push Operation
1. Checks if the stack is full. 2. If the stack is full, produces an error and exit. 3. If the stack is not full, increments top to point next empty space. 4. Adds data element to the stack location, where top is pointing. 5. Returns success.
Algorithm for Push Operation
begin procedure push: stack, data; if stack is full return null; top ← top + 1; stack[top] ← data; end procedure
Pop Operation
Accessing the content while removing it from the stack.
Steps of Pop Operation
1. Checks if the stack is empty. 2. If the stack is empty, produces an error and exit. 3. If the stack is not empty, accesses the data element at which top is pointing. 4. Decreases the value of top by 1. 5. Returns success.
Algorithm for Pop Operation
begin procedure pop: stack; if stack is empty return null; data ← stack[top]; top ← top - 1; return data; end procedure
peek()
Get the top data element of the stack, without removing it.
Algorithm of peek() function
begin procedure peek; return stack[top]; end procedure
isempty()
Check if stack is empty.
Algorithm of isempty() function
begin procedure isempty; if top less than 1 return true; else return false; end procedure
isfull()
Check if stack is full.
Algorithm of isfull() function
begin procedure isfull; if top equals to MAXSIZE return true; else return false; end procedure
Applications of stack
Infix to Postfix/Prefix conversion, Redo-undo features at many places like editors, photoshop, Forward and backward feature in web browsers, Used in many algorithms like Tower of Hanoi, tree traversals, stock span problem, histogram problem.
Implementation of Stack
There are two ways to implement a stack: Using array, Using linked list.
MAX
Defined as 5 in the stack implementation program.
top
An integer variable initialized to -1 indicating the current position in the stack.
Stack Overflow
Occurs when trying to push an element onto a full stack.
C Program Structure
Includes standard libraries, defines MAX, initializes stack and top, and contains main function with a loop for stack operations.
Menu Options
1. Push, 2. Pop, 3. Display, 4. Exit.
Push Function
Prompts user for an element to push onto the stack and updates the stack accordingly.
Display Function
Not explicitly defined in the notes but implied to show stack contents.
pop()
A function that removes the top element from the stack.
Stack Underflow
An error that occurs when trying to pop an element from an empty stack.
display()
A function that prints all elements in the stack.
Expression
A collection of operators and operands that represents a specific value.
Operator
A symbol that performs a particular task like arithmetic, logical, or conditional operation.
Operand
The values on which the operators can perform tasks, which can be direct values, variables, or addresses.
Infix Expression
An expression where the operator is placed between the operands.
Postfix Expression
An expression where the operator is placed after the operands.
Prefix Expression
An expression where the operator is placed before the operands.
Infix to Postfix Conversion
The process of converting an infix expression into a postfix expression using a stack.
Infix to Prefix Conversion
The process of converting an infix expression into a prefix expression.
Stack Data Structure
A data structure that follows the Last In First Out (LIFO) principle.
Higher or Equal Precedence
Refers to operators that have the same or greater priority than the current operator in expression evaluation.
Final Postfix Expression
The result of converting an infix expression into postfix notation.
Example of Infix Expression
( A + B ) * ( C - D )
Example of Final Postfix Expression
A B + C D - *
Example of Infix Expression with Exponent
A + (B C - (D / E ^ F) G) * H
Left Parenthesis
The symbol '(' used in expressions to denote the start of a sub-expression.
Right Parenthesis
The symbol ')' used in expressions to denote the end of a sub-expression.
Push
To add an element to the top of the stack.
Pop
To remove the top element from the stack.
To output a value or message to the console.
Symbol
Any character that represents an operator or operand in an expression.
Result (Output)
The final output after processing an expression.
Infix to Prefix Conversion
A method that involves reversing the input string before conversion and then reversing the final output string before displaying it.
Step 1
Reverse the infix expression i.e A+BC will become CB+A. Note while reversing each '(' will become ')' and each ')' becomes '('.
Step 2
Obtain the postfix expression of the reversing expression i.e CB*A+.
Step 3
Reverse the postfix expression. Hence in our example prefix is +A*BC.
Example Expression
Infix expression = (A+B^C)*D+E^5.
Step 1 Example
Reverse the infix expression: 5^E+D*(C^B+A).
Step 3 Example
Convert expression to postfix form: (5^E+D*(C^B+A)).