Comprehensive Guide to Amplitude and Frequency Modulation in Communication Systems
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
What is the electromagnetic spectrum?
The range of frequencies of electromagnetic radiation and their respective wavelengths and energies.
What are the different bands of the electromagnetic spectrum?
Radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma rays.

What are the basic components of a communication system?
Information source, input transducer, transmitter, communication channel, receiver, output transducer, and destination.
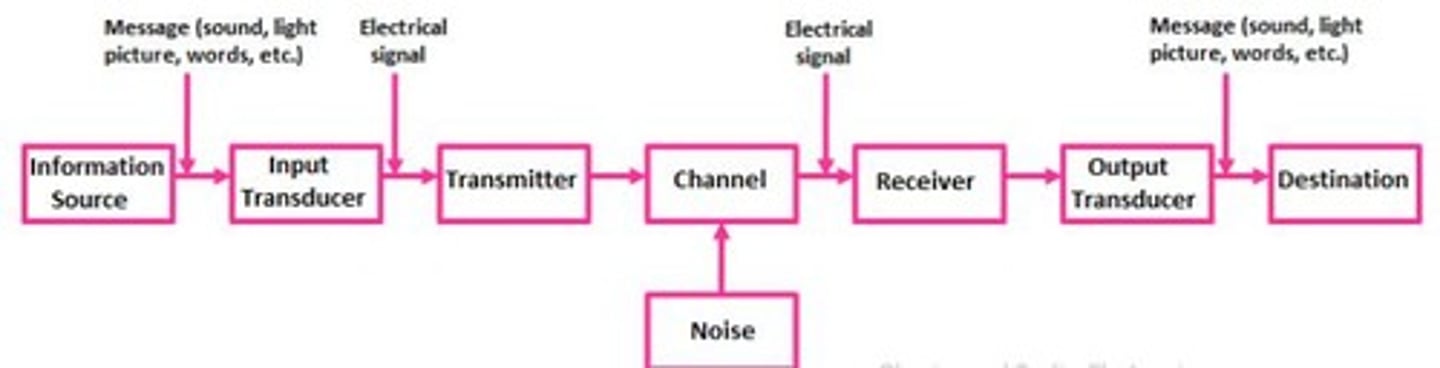
What is the role of an input transducer in a communication system?
It converts non-electrical signals (like sound or light) into electrical signals.
What device is a common example of an input transducer?
A microphone.
What is the function of a transmitter in a communication system?
To convert the signal produced by the source into a form suitable for transmission.
What is modulation?
A technique used by transmitters to convert electrical signals into a form suitable for transmission.
What is the communication channel?
The medium (wired or wireless) through which the signal travels from the transmitter to the receiver.
What is noise in a communication system?
An unwanted signal that interferes with the transmitted signal, degrading its quality.
What is the role of a receiver in a communication system?
To receive the electrical signal from the channel and convert it back to its original form for human understanding.
What does an output transducer do?
It converts electrical signals back into non-electrical signals (like sound or light).
What is the primary purpose of modulation?
To generate a modulated signal that is well suited to the characteristics of the transmission medium.
List some reasons for the need for modulation.
To reduce antenna height, overcome hardware limitations, reduce interference, multiplex signals, assign channel frequencies, narrow band signals, reduce transmission complexity, and increase bandwidth.
What is amplitude modulation?
A technique where the amplitude of the carrier signal varies according to the instantaneous amplitude of the modulating signal.
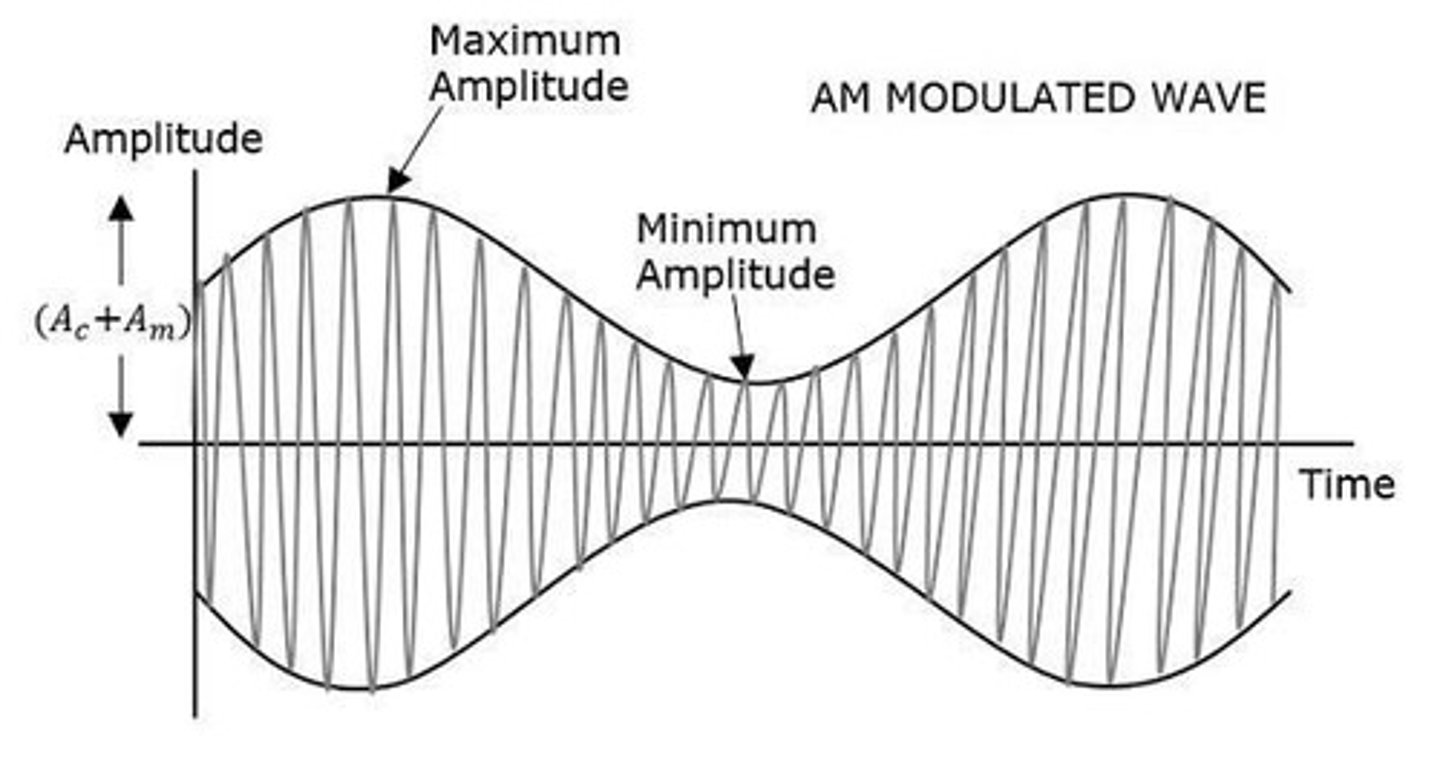
What is the envelope in amplitude modulation?
An imaginary line that connects the positive and negative peaks of the carrier wave, representing the shape of the modulating signal.
What is the mathematical representation of the modulating signal?
m(t) = Am cos(2πfmt), where Am is the amplitude and fm is the frequency of the modulating signal.
What is the equation for the amplitude modulated wave?
s(t) = [Ac + Am cos(2πfmt)] cos(2πfct), where Ac is the amplitude of the carrier signal.
What is the modulation index?
The ratio of the amplitude of the modulating signal to the amplitude of the carrier signal, denoted as μ = Am/Ac.
What does a modulation index of 1 indicate?
Perfect modulation, meaning the percentage of modulation is 100%.
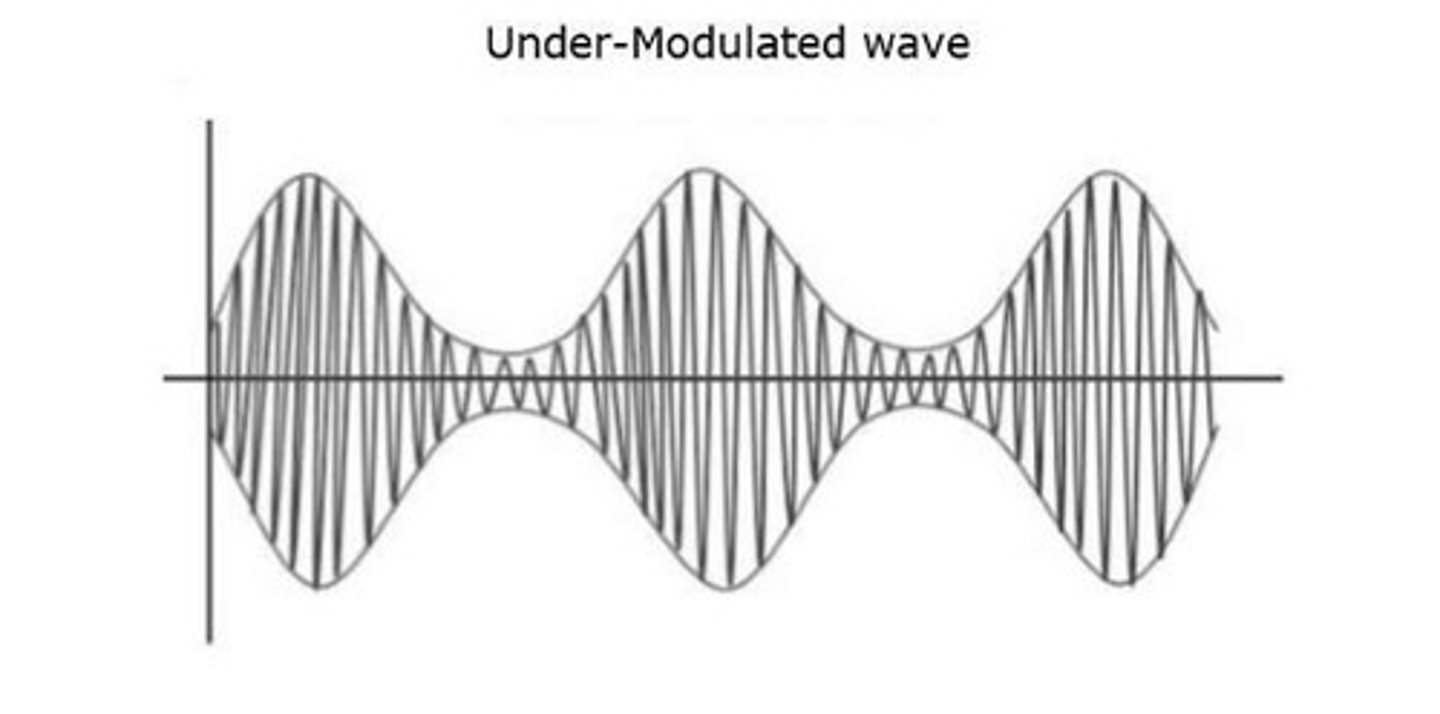
What is under-modulation?
When the modulation index is less than 1, resulting in a modulated wave that does not fully represent the modulating signal.
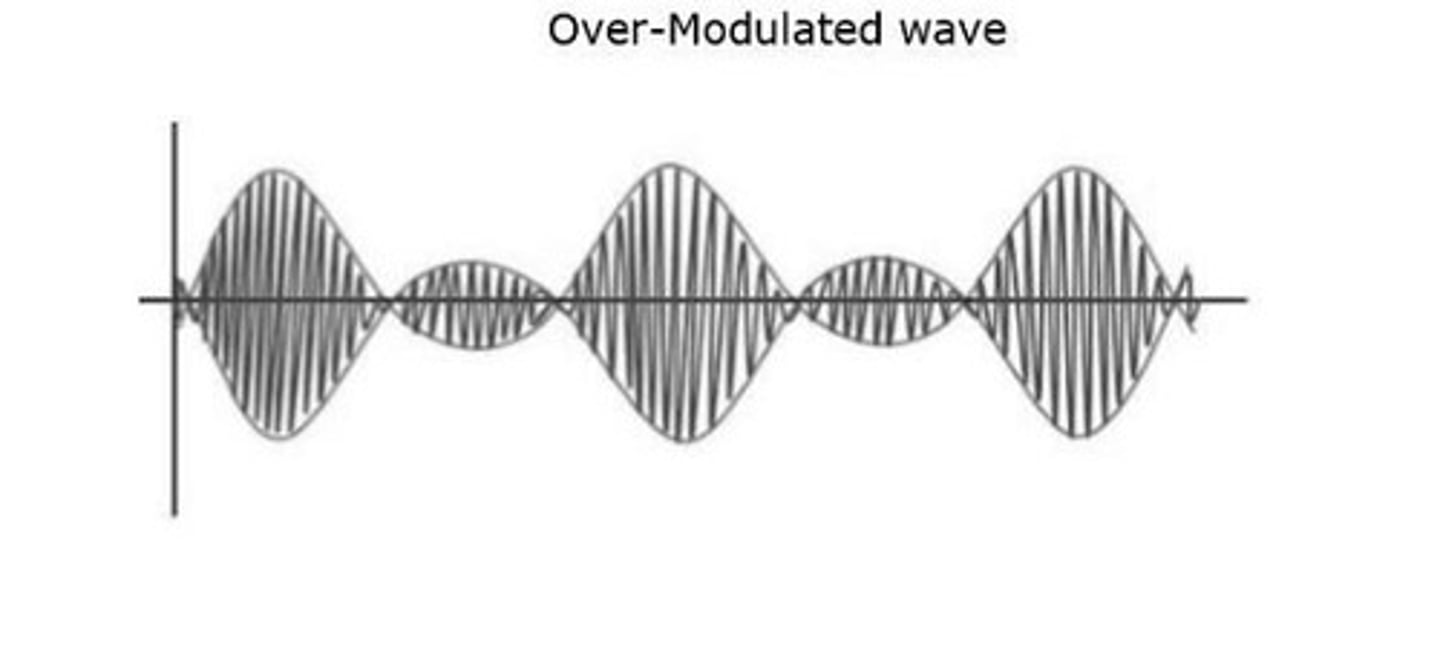
What is over-modulation?
When the modulation index is greater than 1, causing distortion and interference in the modulated wave.
What is the power distribution in amplitude modulation?
The power of an AM wave is the sum of the powers of the carrier, upper sideband, and lower sideband frequency components.
How is the power of an AM wave calculated?
Using the formula that includes the carrier power and the modulation index.
What happens to the carrier wave during over-modulation?
It experiences a 180° phase reversal, leading to additional sidebands and distortion.
What is the power relationship for an AM wave with a modulation index μ=1?
The power of the AM wave is equal to 1.5 times the carrier power.
What is the purpose of a balanced modulator in AM signal generation?
It modifies a signal to output only the sideband signals by suppressing the carrier signal.
What components are used in a balanced modulator built with FETs?
It typically includes three transformers (T1, T2, T3) and FETs.
What happens to the output of a balanced modulator when no modulating signal is applied?
The FET currents cancel each other, resulting in no output.
How does a modulating signal affect the output of a balanced modulator?
The modulating signal causes FET currents to flow that do not cancel, producing DSB output.
What is the function of the local oscillator in AM_SSB generation using the Phase Shift Method?
It generates the carrier signal for modulation.
What is the role of the summer block in the AM_SSB generation process?
It produces an output that is either the sum or difference of two inputs based on their polarity.
What is the output of the upper product modulator in the AM_SSB generation process?
It is the product of the modulating signal and the carrier signal.
What does the lower product modulator output in the AM_SSB generation process?
It outputs the product of the phase-shifted modulating signal and the carrier signal.
What is the purpose of the band pass filter in the SSB suppression method?
It allows only a single sideband (USB or LSB) to pass through.
What is Vestigial Sideband (VSB) modulation?
It is a technique that transmits part of the lower sideband along with the upper sideband to avoid information loss.
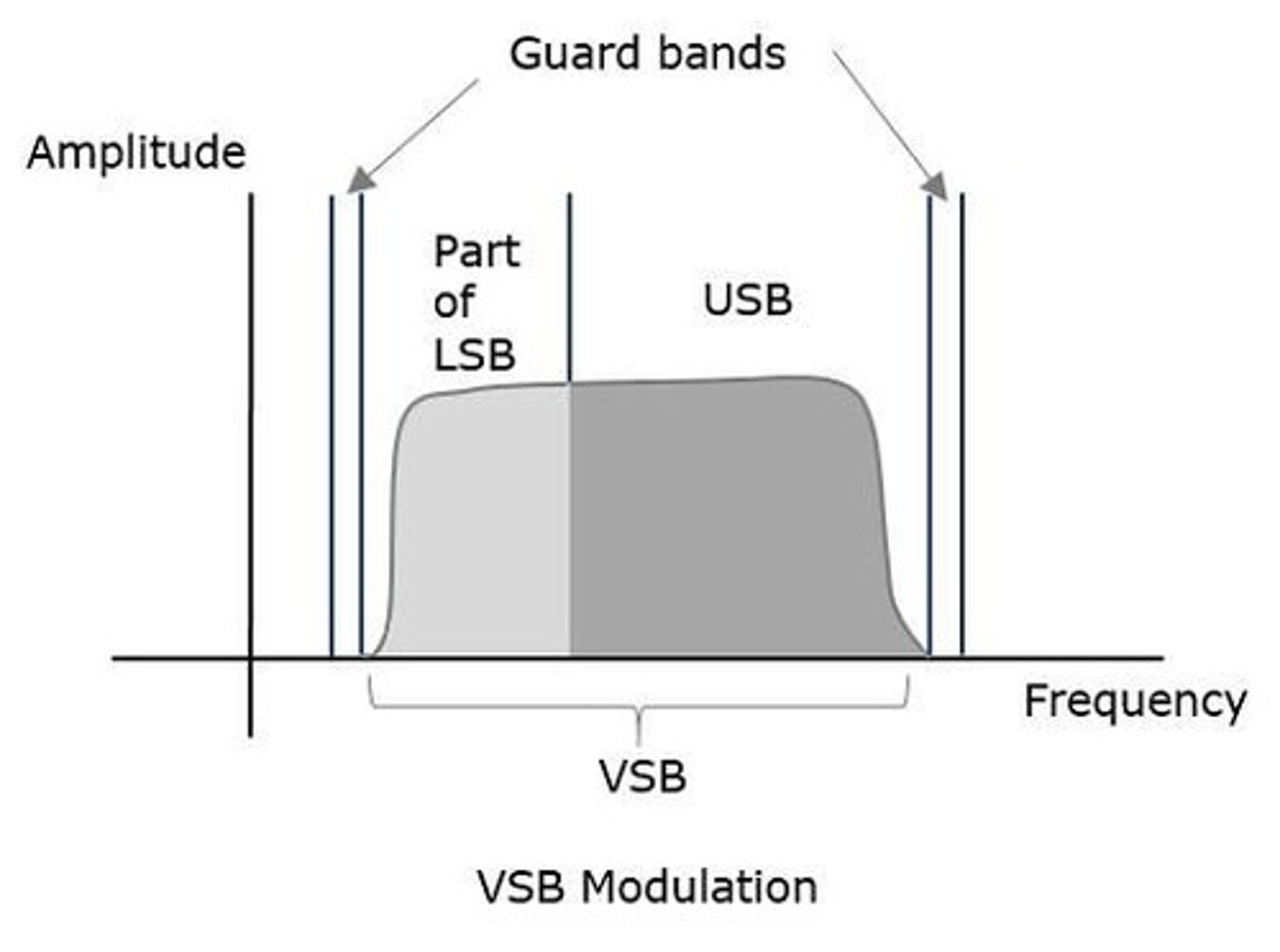
What is the transmission bandwidth formula for a VSB modulated wave?
B = (fm + fv) Hz, where fm is the message bandwidth and fv is the width of the vestigial sideband.
List two advantages of VSB modulation.
1. Highly efficient. 2. Reduction in bandwidth.
What is a significant disadvantage of VSB modulation?
The bandwidth is greater compared to SSB, and demodulation is complex.
What is the primary application of VSB modulation?
It is primarily used for the transmission of television signals.
What is the function of an envelope detector in AM systems?
It provides an output proportional to the amplitude of the envelope of the AM signal.
What are the two main components of an AM diode detector?
1. Diode/rectifier. 2. Low pass filter.
Why are Schottky diodes preferred in AM diode detectors?
They have a lower turn-on voltage, making them suitable for low signal levels.
What is the purpose of the low pass filter in an envelope detector?
To remove high frequency elements remaining after detection.
What should be considered when selecting the capacitor value in an envelope detector?
It should be large enough to hold the peak of the RF waveform but not so large as to attenuate modulation.
What is the typical source impedance in an envelope detector circuit?
It typically has a relatively high source impedance.
What is the primary function of an envelope detector in an AM radio receiver?
To rectify the RF signal and provide an output equivalent to the envelope of one half of the signal.
What is the significance of the resistor placed across the capacitor in an envelope detector?
It determines the time constant of the capacitor and the load, ensuring RF is removed while audio modulation is preserved.
What happens if the envelope detector is loaded too much?
The operation of the detector will be impaired.
Why is the value of the resistor providing the DC return path critical in an envelope detector?
It helps provide the required match without absorbing too much signal.
What is diagonal clipping in the context of envelope detectors?
It occurs when the time constant of the detector is not properly selected, leading to distortion in the recovered baseband signal.
What is the effect of keeping the time constant RC large in an envelope detector?
It reduces spikes in the detected envelope but can lead to diagonal clipping if too large.
What is the relationship between the modulation index and the envelope in AM signals?
The modulation index affects the slope of the envelope, which must be greater than or equal to the rate of fall of the capacitor to avoid distortion.
What is the mathematical representation of instantaneous frequency in FM modulation?
fi = fc + kt * m(t), where fc is the carrier frequency, kt is the frequency sensitivity, and m(t) is the message signal.
What is frequency deviation in FM modulation?
The difference between the FM modulated frequency and the normal carrier frequency, denoted by Δf.
What does Carson's Rule state about the bandwidth of an FM system?
The bandwidth B is double the sum of the maximum frequency deviation and the highest modulating frequency: B = 2(fd + fm).
What are the characteristics of Narrowband FM?
It has a small bandwidth, a modulation index less than 1, and consists of the carrier and sidebands, used in mobile communications.
What distinguishes Wideband FM from Narrowband FM?
Wideband FM has infinite bandwidth, a modulation index greater than 1, and is used in broadcasting applications like FM radio.
What is the role of a varactor diode in FM modulation?
It varies its junction capacitance linearly with the applied bias and must be reverse biased to function.
What is the output of the AM diode detector?
The output is equivalent to the envelope of the modulated signal, rectifying the waveform to leave only one half.
What happens to the frequency of the modulated wave when the amplitude of the modulating signal increases in FM?
The frequency of the modulated wave increases.
What is the effect of a zero amplitude modulating signal in FM?
The frequency of the modulated wave remains constant and equal to the carrier frequency.
What is the modulation index of FM?
The ratio of frequency deviation to the modulating frequency.
What is the purpose of filtering in the diode envelope detector?
To remove high-frequency elements, allowing the output waveform to be suitable for audio transducers.
What can cause diagonal clipping in an envelope detector?
Improper selection of the time constant, increased modulation index, or insufficient capacitor discharge rate.
How does the slope of the envelope relate to the capacitor discharge in an envelope detector?
The rate of fall of the capacitor must be algebraically greater than or equal to the slope of the envelope to avoid distortion.