Development Dynamic
1/35
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
GDP
The total value of goods and services produced by a country annually.
HDI
Measures development on a scale of 0 to 1 based of mulitple factors such as: education, healthcare, income, life expectancy and others.
CPI
Measures how corrupt a country is. Ranges from 0 - 100 (100 being least corrupt).
Gini Coefficient
Measures how much of the countries income goes to the richest people in that country. 1 means all of it go to the richest people.
Demographic
Geography that is about population.
Population structure
number/proportion of males and females for each age group.
Birth rate
Number of live births per 1000 people / year.
Death rate
Number of deaths per 1000 / year.
Maternal mortality
Number of mothers per 100 000 who die in childbirth.
Dependency ration
Proportion of below not in working age (0-14 years) and (65+) / working population *100
fertility rate
Average number of births per woman.
Infant mortality
Number of children per 1000 live births who die before their first birthday.
Life expectany
Average number of years and months a person can expect to live.
Why are women so important in development in a country?
less educated women tend to have more children
This leads to more money needs to be spent in support for healthcare, education and housing.
If women are well educated they can improve the learning of children when they are home.
What is the brant line?
A line seperating the devloped countries from developing countries on the world map, stating that the countries south of the world are less developed than the north.
Development gap
The difference between the irch and poor
Absolute Poverty
Where people struggle to survive day to day
Relative poverty
When people are less wealthy than the majority of people (can’t afford a normal living pattern).
Reasons for a development gap
Colonialism
International relations
Trade blocs
Natural resources
Topography and climate
Systems of governance
The top 20% of the world’s countries own ___% of the worlds wealth
82.8%
Barriers to development (Malawi)
Landlocked
Rural isolation
Climate Change
Increased Pollution
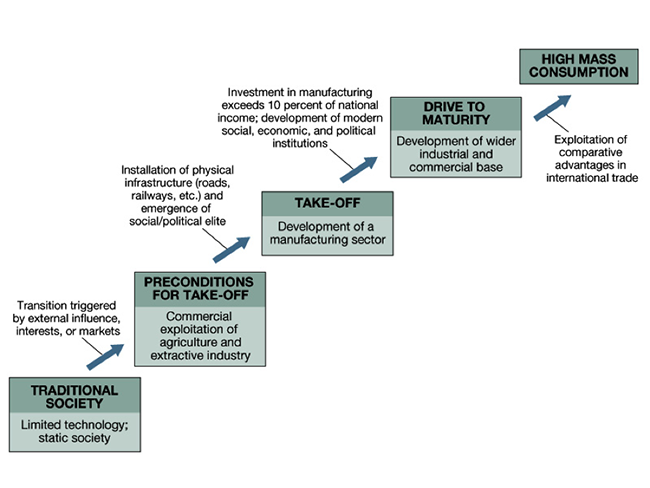
Rostovs Development Theory
Franks dependacy Theory
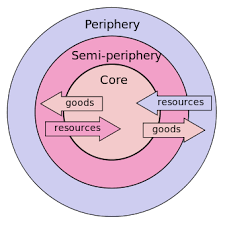
Periphery
Countries of low development.
Cannot sell many processed goods - tariffs are put on them.
Core gives aid, but then forces them to buy something they dont want - tied aid
Little amounts of factories
Semi-periphery
More developed than periphery (emerging)
Core gives aid, but then forces them to buy something they dont want - tied aid
Factories manufacture goods at low costs
Good transport links
Reliable electricity
Power over periphery, but not the core
Core
Very delveoped country that the periphery depends upon.
Buy raw materials off periphery and process it for lots of profit.
Give loans to Periphery/Semi-periphery, but charge interest
Globalisation
Where people and places become more connected over time.
Reasons for Globalisation
Technology and the internet
People can manage businesses overseas on the internet.
Transport and containerisation
More goods can be imported/exported
TNCs
Keep wage costs low to gain more profits. Locate in developing/emerging countries.
Trade Blocs
Tariffs on import/exports from a group of countries (e.g. EU).
Why do some countries benefit mre from globalisatin?
International Relations
Geographical location
Colonialism
Neo-Colonialism
(Taking advantage by buying rawe materials then selling processed goods back for a higher price).
Environmental Challenges
NGO
Non-Governmental organisation
IGO
Inter-Governmental Organisation
Intermediate Technology
Technology that is appropriate - suitable for their needs.
Low-Tech soloutions
Local materials and labour
Local Expertise
Top Down
Where decisions are made by governments/large companies and forced on people
Bottom Up
Where decisions are made by local communities/people abd local people work together to make it happen.
FDI
Foreign Direct Income
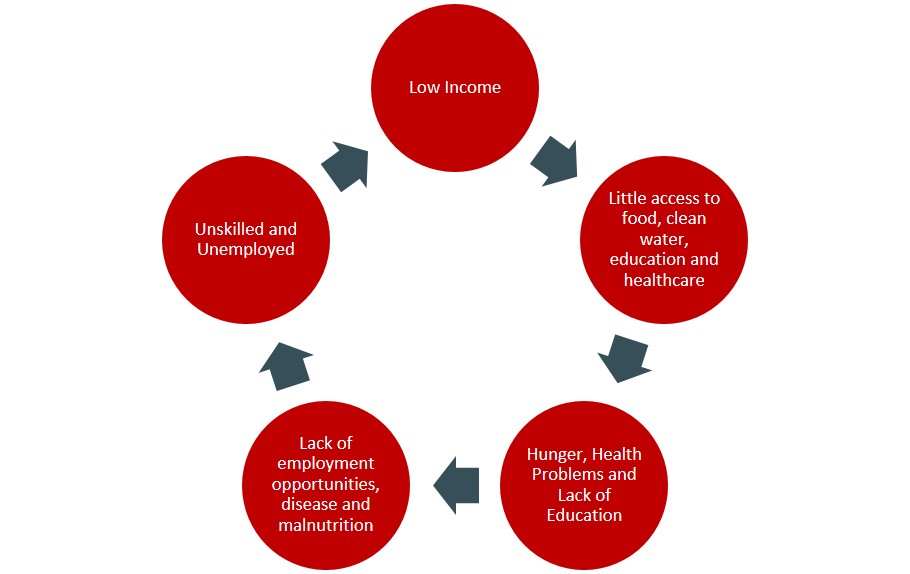
Poverty Cycle