IB Business Management HL
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/249
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
250 Terms
1
New cards
Entrepreneur
An individual who demonstrates enterprise and initiative in order to make a profit
2
New cards
Intrapreneur
An individual employed by a large organization who demonstrates entrepreneurial thinking in the development of new products or services
3
New cards
Primary Sector
The portion of the economy concerned with the direct extraction of materials from Earth's surface, generally through agriculture, although sometimes by mining, fishing, and forestry.
4
New cards
Secondary Sector
The portion of the economy concerned with manufacturing useful products through processing, transforming, and assembling raw materials.
5
New cards
Tertiary Sector
The portion of the economy concerned with transportation, communications, and utilities, sometimes extended to the provision of all goods and services to people in exchange for payment.
6
New cards
Quaternary Sector
Provides services which are especially focused on knowledge eg. e-commerce and services involving IT, the media and web based services
7
New cards
Chain of Production
"The different stages of making, distributing and selling a good or service from the initial production of parts, through to the final product through to distribution and sale of the product."
8
New cards
Horizontal Growth
When a business acquires or merges with another business engaged in the same activity/in the same market
eg. Two grocery stores merging
eg. Two grocery stores merging
9
New cards
Vertical Growth
When a business acquires another business involved in earlier or later stages in the chain of production, or when a business begins operations in an earlier stage via internal growth.
Backward Vertical Integration - Eg. A lumber company purchasing a reserve of trees
Forwards Vertical Integration - Eg. A business purchasing another business
Backward Vertical Integration - Eg. A lumber company purchasing a reserve of trees
Forwards Vertical Integration - Eg. A business purchasing another business
10
New cards
Possible problems for a start-up
- Poor location
- Unreliable supplies
- Poor research
- Inappropriate target market
- Goals are too vague
- Accounts not kept properly
- Limited success
- Unreliable supplies
- Poor research
- Inappropriate target market
- Goals are too vague
- Accounts not kept properly
- Limited success
11
New cards
Purpose of a business plan
Support launch of new org or business idea; attract finance; support strategic planning, provide a focus for development, work as a measure of business success
12
New cards
Elements of a business plan
- Business idea, aims, and objectives
- Business organization
- HR
- Finance
- Marketing
- Operations
- Business organization
- HR
- Finance
- Marketing
- Operations
13
New cards
Sole Trader
A business owned and operated by one person.
Features:
- Sole trader owns and runs the business
- No legal distinction between owner and business
- Limited finance
- Business is close to the customer
Features:
- Sole trader owns and runs the business
- No legal distinction between owner and business
- Limited finance
- Business is close to the customer
14
New cards
Advantage of a sole trader
- Complete control over decisions
- Flexibility in working hours and salary
- Minimal legal formalities
- Flexibility in working hours and salary
- Minimal legal formalities
15
New cards
Disadvantage of a sole trader
- High competition with established companies
- Limited opportunities for expansion
- Limited capital
- Unlimited liability
- Limited opportunities for expansion
- Limited capital
- Unlimited liability
16
New cards
Partnership
A business is formed by two or more people, generally friends, associates, or people of similar skills.
Features:
- Joint decision making
- No legal distinction between business and owners
- More available finance
Features:
- Joint decision making
- No legal distinction between business and owners
- More available finance
17
New cards
Advantage of a partnership
- Range of skills and ideas
- Partners bring more expertise
- Lower risk, more access to finance
- Partners bring more expertise
- Lower risk, more access to finance
18
New cards
Disadvantage of partnership
- unlimited liability
- less access to loans from financial institutions
- profits must be shared
- chance of disagreements
- less access to loans from financial institutions
- profits must be shared
- chance of disagreements
19
New cards
Company
A business organization established for a specific purpose and registered according to local or national legislation
20
New cards
Micro-financiers
Provide small amounts of finance to those who traditionally would not have access to it
21
New cards
Vision Statement
A philosophy, vision or set of principles which steers the direction and behavior of an organization
22
New cards
Objectives
Strategic - long term to guide company in right direction
Tactical - medium to short term objectives to achieve strategic objectives
Operational - day-to-day objectives to reach tactical objectives
SMART: Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-Specific
Tactical - medium to short term objectives to achieve strategic objectives
Operational - day-to-day objectives to reach tactical objectives
SMART: Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-Specific
23
New cards
Business Strategy
A plan to achieve a strategic objective in order to work towards the aims of the business
24
New cards
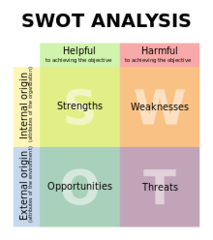
SWOT Analysis
Helps managers brainstorm perceived Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats for the business
25
New cards
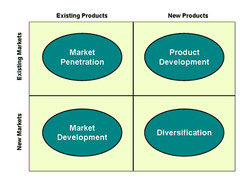
Ansoff Matrix
Helps a business set objectives and plan growth strategies. Looks at growth potential in terms of the market and product.
26
New cards
Market Penetration
A marketing strategy that tries to increase market share among existing customers by selling more of an existing product
27
New cards
Market Development
Company growth by identifying and developing new market segments for current company products
28
New cards
Diversification
A strategy of increasing sales by introducing new products into new markets
29
New cards
Stakeholder
An individual or group who has an interest, often financial, in the activities and success of the organization.
30
New cards
Shareholder
An individual who owns a share or shares in a company
31
New cards
Competitor
Another business or organization offering very similar goods or services
32
New cards
Internal and External Stakeholders
Internal - individuals or groups that work within the business eg. shareholders, managers, employees etc.
External - individuals or groups that are outside the business eg. government, suppliers, customers, pressure groups
External - individuals or groups that are outside the business eg. government, suppliers, customers, pressure groups
33
New cards
Interests of Internal Stakeholders
1) Shareholders - focus on returns from investments
2) Managers - focus on business strategy, strategic objectives, tactical objectives
3) Employees and their unions - focus on protecting rights and working conditions
2) Managers - focus on business strategy, strategic objectives, tactical objectives
3) Employees and their unions - focus on protecting rights and working conditions
34
New cards
Interests of External Stakeholders
1) Government - focus on how business operates, impacts economy
2) Suppliers - focus on maintaining stable relationship
3) Customers/Consumers - focus on getting products to meet needs/wants
4) Community - impact of business of local area
5) Financers - eg. banks, return on their investments
6) Pressure groups - focus on how business impacts area of concern
2) Suppliers - focus on maintaining stable relationship
3) Customers/Consumers - focus on getting products to meet needs/wants
4) Community - impact of business of local area
5) Financers - eg. banks, return on their investments
6) Pressure groups - focus on how business impacts area of concern
35
New cards
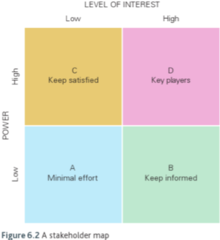
Johnson and Scholes
A power-interest model, maps stakeholders against power and interest
36
New cards
STEEPLE Analysis
Social, Technological, Economic, Ecological, Political, Legal and Ethical

37
New cards
Fixed and Variable Costs
Fixed - costs which do not change according to the amount of goods or services produced by the business eg. rent
Variable - costs which increase or decrease due to the amount of goods or services produced eg. supplies
Variable - costs which increase or decrease due to the amount of goods or services produced eg. supplies
38
New cards
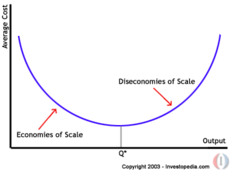
Economies/Diseconomies of Scale
Economies of Scale - achieved when the business increases its scale of productions and in the process becomes more efficient
Diseconomies of Scale - when a business experiences inefficiency due to increasing scale of production
Diseconomies of Scale - when a business experiences inefficiency due to increasing scale of production
39
New cards
Advantages of being a large business
- survival (less likely to fail/be taken over)
- economies of scale (more common for large businesses, higher profits)
- market leader status (can influence market habits)
- market share (allows them to determine prices, customer base)
- economies of scale (more common for large businesses, higher profits)
- market leader status (can influence market habits)
- market share (allows them to determine prices, customer base)
40
New cards
Advantages of being a small business
- greater focus (are able to focus on smaller tasks/product range)
- exclusiveness (allows them to charge higher prices)
- greater motivation (prestige can motivate workers)
- competitive advantage (personalized service gives comp. adv)
- less competition (likely in smaller markets)
- exclusiveness (allows them to charge higher prices)
- greater motivation (prestige can motivate workers)
- competitive advantage (personalized service gives comp. adv)
- less competition (likely in smaller markets)
41
New cards
Internal Growth (Organic)
Occurs when a business expands its existing operations
42
New cards
External Growth
Business expansion achieved by means of merging with or taking over another business, from either the same or a different industry
43
New cards
Horizontal Integration
The integration of two businesses which are in the same industry and same chain of production
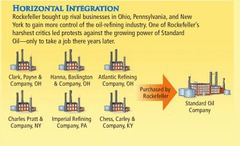
44
New cards
Backward Vertical Integration
Occurs when a business integrates with another further back in the chain of production, usually to protect their supply chain. In same industry.
45
New cards
Forward Vertical Integration
When a business integrates with another in the same industry further down the chain of production (usually to secure an outlet for products)
46
New cards
Conglomeration
When two businesses in separate industries integrate (to reduce overall corporate risk)
47
New cards
Joint Venture
When two businesses agree to combine resources for a specific goal and over a finite time period

48
New cards
Strategic Alliance
A long-term partnership between two or more companies established to reach a specific goal.
Differs from Joint Venture as there can be more than two businesses involved and the businesses remain independent.
Differs from Joint Venture as there can be more than two businesses involved and the businesses remain independent.
49
New cards
Franchise
A business established or operated under an authorization to sell or distribute a company's goods or services in a particular area

50
New cards
Franchisee advantages and disadvantages
Advantages:
- the product exists and is usually well known
- set-up costs are reduced
- secure stock supply
- franchisor can provide legal/financial etc. help
Disadvantages:
- unlimited liability
- has to pay royalties to the franchiser
- no control over products
- no control over supplies
- the product exists and is usually well known
- set-up costs are reduced
- secure stock supply
- franchisor can provide legal/financial etc. help
Disadvantages:
- unlimited liability
- has to pay royalties to the franchiser
- no control over products
- no control over supplies
51
New cards
Franchisor advantages and disadvantages
Advantages:
- quick access to wider markets
- does not have risks/liabilities of running franchise
- gains high profits and sign-up fees
Disadvantages:
- loses control in day-to-day running of business
- brand image will suffer if franchisee acts improperly
- quick access to wider markets
- does not have risks/liabilities of running franchise
- gains high profits and sign-up fees
Disadvantages:
- loses control in day-to-day running of business
- brand image will suffer if franchisee acts improperly
52
New cards
Globalization
The process by which the worlds regional economies become one integrated global unit
53
New cards
Multinational Company
A business that operates in more than one country and is legally registered in more than one country
54
New cards
Advantages and Disadvantages of multinational companies on host countries
Advantages:
- economic growth (employment, taxes etc)
- new ideas
- skill transfer
- more choice of products
- infrastructure
Disadvantages:
- majority of profits do not go to host country
- local businesses may experience loss of market share
- may be short term (may not remain in host country)
- economic growth (employment, taxes etc)
- new ideas
- skill transfer
- more choice of products
- infrastructure
Disadvantages:
- majority of profits do not go to host country
- local businesses may experience loss of market share
- may be short term (may not remain in host country)
55
New cards
Fishbone diagram
A visual identification of many potential causes of a problem
Benefits:
- motivating, discussing problems
- flexible
- simple, visually attractive
- can single out cause of problem
Limitations:
- does not necessarily show solutions
- can lead to arguments
- requires knowledge + honesty
- requires follow up process
Benefits:
- motivating, discussing problems
- flexible
- simple, visually attractive
- can single out cause of problem
Limitations:
- does not necessarily show solutions
- can lead to arguments
- requires knowledge + honesty
- requires follow up process
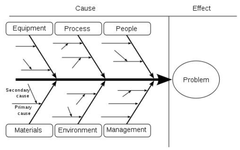
56
New cards
Decision Tree
A planning tool used to help make strategic decisions, using probabilities of success and failure
Benefits:
- gives clear answer to complex problem
- flexible
- simple, visually attractive
Limitations:
- based on estimates
- based on quantitative data, not qualitative
- can be difficult to make if many possible situations
Benefits:
- gives clear answer to complex problem
- flexible
- simple, visually attractive
Limitations:
- based on estimates
- based on quantitative data, not qualitative
- can be difficult to make if many possible situations
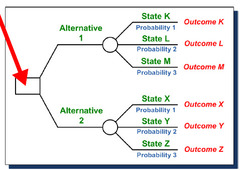
57
New cards
Force Field Analysis
A technique for determining which forces drive a proposed change and which forces restrain it. Used to decide whether to make a change or not
Benefits:
- gives clear answer to complex question
- flexible
- simple, visually attractive
Limitations:
- involves interpretations of which factors to include
- based on estimates on weighing each factor
- based on qualitative data, not quantitative issues
Benefits:
- gives clear answer to complex question
- flexible
- simple, visually attractive
Limitations:
- involves interpretations of which factors to include
- based on estimates on weighing each factor
- based on qualitative data, not quantitative issues
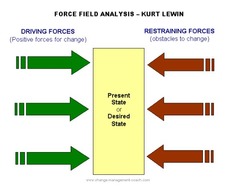
58
New cards
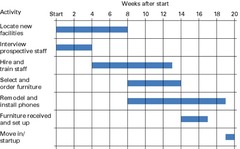
Gantt Charts
planning charts used to schedule resources and allocate time
Benefits:
- gives clear picture of current progress of tasks
- gives picture of overall project
- flexible
- allows managers to plan use of resources to remain efficient
Limitations:
- based off estimates
- difficult to apply to complex projects
- based on qualitative data not quantitative (eg costs)
- cannot separate interdependent tasks
- pressure to meet deadlines can stress workers
Benefits:
- gives clear picture of current progress of tasks
- gives picture of overall project
- flexible
- allows managers to plan use of resources to remain efficient
Limitations:
- based off estimates
- difficult to apply to complex projects
- based on qualitative data not quantitative (eg costs)
- cannot separate interdependent tasks
- pressure to meet deadlines can stress workers
59
New cards
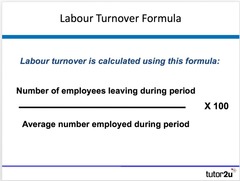
Labour turnover
A measure of how many people leave a business over a given period of time. It is usually expressed as a percentage of the total labour force
60
New cards
External factors influencing potential workforce
- technological change (eg. working at home)
- government regulations (eg. minimum wage etc)
- demographic change (ageing population, birth rate etc)
- social trends
- state of economy (boom or recession)
- education (courses available, skill sets etc)
- labour mobility (changing occupations, locations etc)
- government regulations (eg. minimum wage etc)
- demographic change (ageing population, birth rate etc)
- social trends
- state of economy (boom or recession)
- education (courses available, skill sets etc)
- labour mobility (changing occupations, locations etc)
61
New cards
Internal Factors influencing HR plan
- changes in business organization
- changes in labour relations
- changes in business strategy
- changes in business finance
- changes in labour relations
- changes in business strategy
- changes in business finance
62
New cards
The Human Resources Plan
1) Recruitment (choosing the right worker)
2) Training (making sure worker has correct skills)
3) Appraisal (performance evaluation)
4) Termination or Dismissal
2) Training (making sure worker has correct skills)
3) Appraisal (performance evaluation)
4) Termination or Dismissal
63
New cards
Stages of Recruitment
1) Identification
- Job description
- person specification
- internal or external recruitment?
2) Application
- job advert
- application form or resume (CV)
- internal or external agency
3) The Selection Process
- shortlisting
- testing (aptitude, team based etc)
- interviews
- Job description
- person specification
- internal or external recruitment?
2) Application
- job advert
- application form or resume (CV)
- internal or external agency
3) The Selection Process
- shortlisting
- testing (aptitude, team based etc)
- interviews
64
New cards
Induction Training
Focuses on making a new employee familiar with business functions, lines of authority etc. Helps them settle in quickly
65
New cards
On-the-job training
When employees are trained while doing their normal job. Normally occurs through mentoring, eg. an experienced employee guiding new workers.
Shadowing is also common, when the new employee follows another to learn a skill
Shadowing is also common, when the new employee follows another to learn a skill
66
New cards
Off-the-job training
When the employee is given time off work to attend training for the job. eg. in a workshop, conference, or external agency.
67
New cards
Appraisal
The performance of the employee is reviewed.
Methods:
1) Formative - Giving employees feedback after appraisal to help them learn and improve
2) Summative - measures employees performance according to set standards. Employees can pass or fail. Usually conducted at end of project or contract
3) 360 Degree - provides employees with opportunity to receive performance appraisal from managers AND co-workers, and even customers. Involves upwards appraisal
4) Self-appraisal - employees can reflect on their own work, usually with the aid of a form. Helps identify their strengths and weaknesses.
Methods:
1) Formative - Giving employees feedback after appraisal to help them learn and improve
2) Summative - measures employees performance according to set standards. Employees can pass or fail. Usually conducted at end of project or contract
3) 360 Degree - provides employees with opportunity to receive performance appraisal from managers AND co-workers, and even customers. Involves upwards appraisal
4) Self-appraisal - employees can reflect on their own work, usually with the aid of a form. Helps identify their strengths and weaknesses.
68
New cards
Termination, Dismissal and Redundancy
- Termination: Employee terminates or leaves the business at the end of their contract
- Dismissal: When an employee breaks terms of the contract and is dismissed as a result
- Redundancy: When a business no longer has any work for an employee (can be either voluntary/involuntary)
- Dismissal: When an employee breaks terms of the contract and is dismissed as a result
- Redundancy: When a business no longer has any work for an employee (can be either voluntary/involuntary)
69
New cards
Outsourcing
When a business subcontracts a process, such as manufacturing or packaging, to another business or organization
70
New cards
Offshoring
When a business outsources a process or service to another country in order to reduce costs
71
New cards
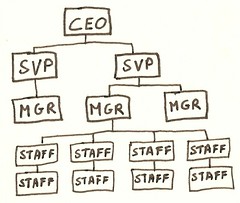
Organizational chart
A diagram that outlines the formal roles, responsibilities and reporting lines
72
New cards
Levels of hierarchy
The number of layers of management and supervision existing in an organization
73
New cards
span of control
How many subordinates are directly below the authority of the manager and whom a manager is responsible for
74
New cards
Chain of command
The formal route through which a decision must travel through the organization/commands going from top of hierarchy to bottom
75
New cards
Delegation
Transferring authority to a person for a task
76
New cards
Centralization
A high degree of centralization indicates that all major decision is maintained within a small group of manager operating close to the head of the business
77
New cards
Decentralization
Senior managers maintain core strategic decisions, but other decision making authority is delegated to middle managers
78
New cards
de-layering
The process of flattening out an organisational hierarchy. This means reducing the number of layers of management.
79
New cards
Tall Organization Structure
- many levels of hierarchy
- narrow spans of control
- centralized decision making
- long chains of command
- autocratic leadership
- limited delegation
- narrow spans of control
- centralized decision making
- long chains of command
- autocratic leadership
- limited delegation

80
New cards
Flat organizational structure
- Few levels of hierarchy
- Wider spans of control
- Decentralized decision making
- Shorter chains of command
- Democratic leadership
- Increased Delegation
- Wider spans of control
- Decentralized decision making
- Shorter chains of command
- Democratic leadership
- Increased Delegation
81
New cards
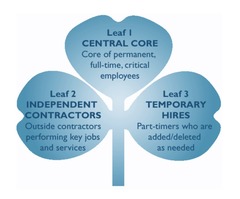
Charles Handy Shamrock Model
Model suggests that businesses can reduce costs, gain competitive advantage and increase response time by trimming their workforce and retain only a multiskilled core
82
New cards
Verbal communication
- interviews
- meetings
- lectures
- presentations
- telephone conversations
- face to face conversations
*quick, direct, effective, immediate feedback
*misunderstandings
- meetings
- lectures
- presentations
- telephone conversations
- face to face conversations
*quick, direct, effective, immediate feedback
*misunderstandings

83
New cards
Visual communication
- presentations
- videos
- notice boards
- signs
- symbols
- body language
*effective, permanent, recognizable
*incorrect interpretations
- videos
- notice boards
- signs
- symbols
- body language
*effective, permanent, recognizable
*incorrect interpretations

84
New cards
Written communication
- reports
- letters
- notices
- bulletins
- forms
- press releases
- memos
- emails
*effective, permanent, can be revised
*impersonal, minunderstandings
- letters
- notices
- bulletins
- forms
- press releases
- memos
- emails
*effective, permanent, can be revised
*impersonal, minunderstandings
85
New cards
Functions of management
Planning (setting strategic/tactical/operational objectives)
Organizing (resources, people etc)
Commanding (making sure employees perform correct tasks)
Coordinating (parts of production, areas etc)
Controlling (quality, production levels etc)
Organizing (resources, people etc)
Commanding (making sure employees perform correct tasks)
Coordinating (parts of production, areas etc)
Controlling (quality, production levels etc)
86
New cards
Autocratic leadership
Leadership style that involves making managerial decisions without consulting others
87
New cards
Paternalistic leadership
A leadership style where the leader has authority over employees but regards them as 'family' and is concerned for their wellbeing.
88
New cards
Democratic leadership
A leadership style that promotes the active participation of workers in making decisions
89
New cards
Laissez-faire leadership
A leadership style that leaves much of the business decision-making to the workforce - a 'hands off' approach
90
New cards
Situational leadership
Effective leadership varies with the *task* in hand and situational leaders adapt their leadership style to each situation
91
New cards
Intrinsic Motivation
Motivation which comes from the satisfaction of carrying out a particular activity
92
New cards
Extrinsic Motivation
Motivation derived from external factors, such as money
93
New cards
Frederick Winslow Taylor
American mechanical engineer, who wanted to improve industrial efficiency. He is known as the father of scientific management, and was one of the first management consultants
Thought standardization of work methods and enforced adoption of ideal ways of working were key to maximizing output.
Thought standardization of work methods and enforced adoption of ideal ways of working were key to maximizing output.

94
New cards
Abraham Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs
Maslow's pyramid of human needs; must satisfy levels below before reaching to next; can go up and down pyramid stages
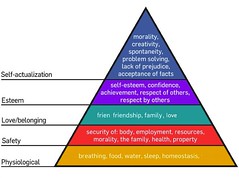
95
New cards
Frederick Herzberg's Motivation-Hygiene Theory
Workers must have both hygiene and motivation factors to be truly motivated.
Hygiene needs:
- company policy/administration
- work conditions
- salary
- status
- personal life
Motivation factors:
- achievement
- recognition
- the work itself
- responsibility
- advancement
Hygiene needs:
- company policy/administration
- work conditions
- salary
- status
- personal life
Motivation factors:
- achievement
- recognition
- the work itself
- responsibility
- advancement
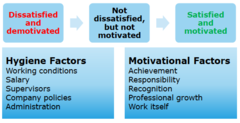
96
New cards
John Adams: "Equity Theory"
based on concepts of inputs, outputs and equity. Employees will be motivated when they perceive that their inputs into the business are equal to the outputs they receive
Inputs (what employee brings to business)
- ability/skills
- dedication
- effort
- hard work
- loyalty
- knowledge
Outputs (what employee receives from business)
- fringe benefits
- job security
- praise
- recognition
- responsibility
- salary
- sense of acheivement
Inputs (what employee brings to business)
- ability/skills
- dedication
- effort
- hard work
- loyalty
- knowledge
Outputs (what employee receives from business)
- fringe benefits
- job security
- praise
- recognition
- responsibility
- salary
- sense of acheivement
97
New cards
Daniel Pink Motivation Theory
Thought older motivation theories were outdated and flawed.
Though businesses must focus on INTRINSIC motivation
Though businesses must focus on INTRINSIC motivation
98
New cards
Power culture (Charles Handy)
Concentrating power among a few people
99
New cards
Role culture (Charles Handy)
Each member of staff has a clearly defined job title and role
100
New cards
Task culture (Charles Handy)
Used in situations where short term teams address specific problems - power shifts based on the skill set of workers on team