Unit 3.2 AP Psychology
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Learning
a relatively permanent change in an organism’s behavior due to experience
Behaviorists
psychologists focused on observable behavior
traditionally exclude processes
Learning diagram
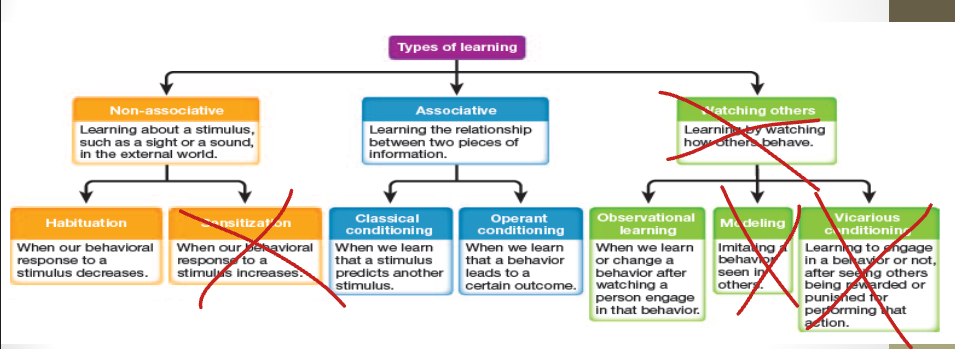
Habituation
decreases response to a stimulus; animals adapt to our environment. (Part of non-associative learning)
Expect/prepare for certain events - behavioral vs. sensory
Assume rewards/punishments will follow certain events
Insight Learning
Occurs when a solution to a problem occurs without any association, consequence, or model; recognizing relationship naturally
Conditioning
process of leaning associations
ex: when crows eventually stop getting scared from scarecrows
classical conditioning
two stimuli (associative learning)
operant conditioning
response and consequence (associative learning)
Edward Tolman
latent learning
Latent learning
learning that occurs but is not apparent until there is an incentive to demonstrate it
Ex: cognitive map - mental representation of the layout of one environment
Ex: Tolman’s Rats
Tolman’s Rats
Hungry rats → learns map with no reward (15 min)
Hungry rats → completes map once there is an incentive or cheese → we learn fast with a reward (5 min)
Classical Conditioning
type of learning in which one learns to link 2+ stimuli & anticipate events (associative learning)
Only works for involuntary responses (reflexes)
Ex: using your fav song for your alarm → now you hate that song because its your alarm
Ex: Pavlov’s dogs
Pavlov’s dogs experiment
Give dog food and ring a bell
Dog naturally drools to food
Overtime, associates food with the bell
Drools for the bell
Unconditioned Stimulus (UCS)
A stimulus that unconditionally triggers a response
Ex: Food
Unconditioned Response (UCR)
UCS automatically, intrinsically, biologically triggers this
UCR is the unlearned, naturally occuring response to an UCS
Ex: the dog drooling
Neutral Stimulus (NS)
a stimulus that does not naturally trigger a reoccurring response
Ex: the bell → bells have no impact on dogs
Conditioned response (CR)
Pair the NS with an existing UCS over and over to create CR
CR is the learned response to a previously neutral Stimulus
Ex: drooling
Conditioned Stimulus (CS)
the originally neutral stimulus that has been paired with the UCS enough times to create a response, even when the UCS isn’t present
Ex: the bell
CR
UCR
NS
CS
UCS & CS
are not intrinsically linked - illogical
Ex: bell triggers drooling—not naturally occurring
The N/CS must be present before the UCS
The point of classical conditioning is to create an expectation
Hear the bell → expect food
Participant should have same sponsor to CS and UCS
Acquisition
when one links a neutral stimulus w/ an unconditional stimulus so that the neutral stimulus begins to trigger the conditioned response
AKA: the initial conditioning response
The timing of the pairing matters
Ex: the first time the dog drooled w/ the bell, they acquired the association
You can build on to classical conditioning→ higher order conditioning
procedure in which the conditioned stimulus is paired w/ another, new, neutral stimulus
Creates a second, often weaker CS
Ex: if a dog bites you, just the sound of a dog barking may later make you feel afraid
UCS = bite, CR1= fear
Cs1 = dog, CR1 = fear
CS2 = barking, CR2 = fear
Extinction
the diminishing of a CR
happens when the UCS no longer follows the NS/CS
Ex: you ring the bell but the dogs don’t drool
Can recondition
Reconditioning
presenting the NS/CS w/ the UCS again to bring the CR back
the associated is learned more quickly this time
Ex: retraining the dogs to connect w/ the bell → will be faster this
Spontaneous Recovery
the reappearance of an extinct/weakened conditioned response
Different from reconditioning be it occurs randomly aka spontaneously
Extinction suppresses the Cr, not eliminates
Ex: Mrs. Lane’s alarm story
Ex: dog stops responding to bell, but then one day they do!
Stimulus generalization
the tendency for stimuli similar to the Cs to trigger the conditioned response
Ex: Little Albert (conditioned to be scared of mice → scared of anything white and fluffy)
Ex: dogs responding to all sorts of bells
Discrimination
the ability to distinguish between a CS and a random stimuli
Ex: the class bell vs. the announcement bell
Ex: dogs only responding to the bell
Little Albert - Jogn B. Wastson & Rosalie Raynor
were able to classically condition Little Albert to fear an object that did not originally scare him by associating it w/ a naturally fearful stimulus
UCS = loud noise
UCR = fear
NS = rat
Result: rat becomes the CS and causes the CR (fear)
Little Albert also became fearful of any object that resembled the white rat → what is this called?
One trial conditioning
the single paring of a stimulus & a response is enough to create an association or aversion
ex: dog bite
Biological preparedness
how animals are biologically predisposed to learning certain stimulus - response pairing more quickly than others - survival
Taste aversion
an acquired reaction to the smell or taste that an animal is exposed to before getting sick - much faster than normal CC
Ex: Taco Bell
Operant Conditioning
type of learning in which behavior is strengthened if followed by a reinforcer or diminished if followed by a punisher
Voluntary behaviors
Edward Throndike’s law of effect
behaviors which are rewarded will be more likely to be repeated and behaviors that are punished will be less likely to be repeated
Ex:more likely to go trick or treating when you get candy (reward); less likely to if you get a rock (punishment)
Superstition
occurs when consequences reinforce or punish unrelated behaviors
Wear lucky socks → reinforced by good test score → wear socks again because you think you think you’ll be rewarded again
Walk under a ladder →slip and fall → avoid latter’s because you think you’ll be punished again
Reinforcement
the presentation of a stimulus or event (reinforcer) that follows a behavior or response, which increase the chances of the behavior being repeated
Always increases behavior
Shaping
uses reinforcers to guide behavior gradually toward desired by following the behavior=]