lecture 3 getting together: marriage, cohabitation and partnering
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
intimacy
“a close, familiar and usually affectionate or loving personal relationship w another person or group”
psychological concept used to describe the feelings garnered from the lvl of quality, frequency or exposure to a physical or emotional relationship w ones self and w everything else; places, things, and people
sexual relationships w and w out emotional closeness
for some commitment may develop from intimacy
for others intimacy may grow out of commitment
commitment can be personal/private (between you and a partner or family), legally recognized, religious, or linked to expectations/ideals
most important developmental task in young adulthood = establishment of intimacy
ability and freedom to disclose innermost self to another
important developmental tasks in young adulthood
establishment of intimacy
ability and freedom to disclose innermost self to another
building relationship foundation
types of intimate relationships
romantic relationships
casual, short-term relationships
hooking up
friends w benefit
courtship - dating to find a long-term partner
cohabition
alt to living alone
precursor to marriage
alt to marriage
marriage
monogamous: having one mate
polygamous: more than one mate
polyamorous: having more than 1 loving intimate relationship at a tie w full knowledge and consent of everyone involved
polyandrous: more than 1 husband
polygyny: more than 1 wife
platonic: intimate and affectionate but not sexual
friendship
siblings
parent-child
single
celibate, dating and/or sexually active
to be single
26.8% of households are single people
singlehood may be viewed as negative
selfish, lonely, immature, unfulfilled, weirdo
ideologies or marriage and family assume that romantic relationships are always beneficial
may offer autonomy, fulfilling career goals, building friendships, self-development
dating
in the 19th century, “dating” was supervised by adults and expected to lead to marriage
today the dominant dating culture approves of dating between young people without assuming these relationships will lead to marriage
dating or courtship is still currently the most common way of beginning a romantic relationship in canada
technology has shaped the way people experience dating relationships and meet partners
16% of canadians report finding love online
datings main functions
add to a person’s status
form of socialization
form of recreation
part of courtship w the purpose of marriage
exchange theory in dating
men more than women show off material assets
education, job, income, car
women tend to emphasize physical appearance
both men and women display sympathy, kindness, helpfulness, good manners and humour as attraction mechanisms
wheel theory of love
4 stages
rapport
complementarity of needs: needs of 1 partner fit the needs of another
needs are influenced by social values
self revelation
development of mutual dependencies
personal need fulfillment
communication
women use communication to build connections and solve problems
closeness built on communication
men closeness comes from shared experiences
communication about feelings is often non-verbal
mate selection
social homogamy
similar backgrounds
theory of propinquity
we select people we know
friends, high school sweetheart, coworkers
complementarity of needs
attracted to those who have desirable qualities you do not have
mate selection: filter theory
geography
mutual attraction
meeting core needs
compatibility
social exchange - best choice?
similarities
mutual commitment
marriage
A SOCIAL INSTITUTION, LEGAL STATUS AND RELIGIOUS
DUTY
• WHO CAN MARRY AND LEGAL PROTECTIONS DICTATED BY
LAW AND RELIGION
• MARITAL DISSOLUTION ALSO GOVERNED BY LAWA PERSONAL AND FAMILY EXPERIENCE
A SOCIAL NORM & EXPECTATION
• TYPICAL AND EXPECTED IN MOST SOCIETIES
rights of marriage
sexual access
kind treatment
faithfulness
use of family assets
matrimonial home
financial support of each other and any children
arranged marriage
MARRIAGE THAT INVOLVES SOME PARTICIPATION OR
CONTROL BY PARENTS AND EXTENDED FAMILIES
• MAY NOT MEET UNTIL THE WEDDING DAY OR BOTH THE
PARENTS AND THE INDIVIDUAL MAY BE INVOLVED IN THE
PROCESS OF FINDING A MARITAL PARTNERWHAT ARE THE PREDOMINANT PERCEPTIONS OF
ARRANGED MARRIAGES IN NORTH AMERICA?
marriage statistics
2006 CENSUS DATA:
• 69% OF ALL CENSUS FAMILIES IN CANADA ARE HEADED
BY A MARRIED COUPLE (DOWN FROM 71% IN PREVIOUS
CENSUS)
• COMMON-LAW COUPLE HEADED FAMILIES = 16%
• LONE-PARENT HEADED FAMILIES = 15.9%COMMON-LAW MORE PREVALENT IN QUEBEC
• LESS FINANCIAL AND SOCIAL PRESSURE TO MARRY
why people get married
status
economic
financial support and joint property
sex
regulation of sexual behaviour
children
identity
family identity
economic identity
love and support
enforceable trust
most superior form of adult relationship
models of marriage
historical classic
emphasizes biological and social complementarity between men and women (heteronormative, trad gender roles)
hunter/gatherer
considers this the best social system to raise children
choice model
private agreement between individuals
sexuality = self expression and should not involve the state
commitment model
intimate, committed relationship centralizing emotional support
highest social recognition
modern marriage
conventional roles
separate spheres
shared roles
both partners participate in paid and unpaid labour
dual-career roles
priority on career
reverse conventional roles
structural functionalist
courtship and marriage are social processes and institutions that contribute to the smooth functioning of the society
courtship or dating:
form of socialization into the customs, values, and trads of a society - learning how to engage intimately w others
form of recreation
means of assessing a potential partner for marriage
benefit to the economy - dating ppl spend $$$
ppl get married because society needs them to
regulates sexual behaviour
provides a container for the care and raising of children
creates a sense of social identity that fits w social norms
provides for the emotional needs of both/all partners
critical theory
DATING AND MARRIAGE ARE NOT ONLY SOCIAL NORMS...
THEY ARE ALSO NORMATIVE
• MEANING THAT DATING AND BEING MARRIED ARE PART OF
WHAT QUALIFIES A PERSON TO FIT INTO THE CATEGORY OF
'NORMAL' IN WESTERN SOCIETIES.THE DESIRES TO COURT AND MARRY ARE SOCIALLY CREATED
AND BENEFIT PARTICULAR GROUPS AND THEIR INTERESTSDATING AND MARRIAGE ARE IDEALIZED SOCIAL IDEAS AND
INSTITUTIONS THAT HIDE VIOLENCE AND OPPRESSIONTHE CONCEPTS OF DATING AND MARRIAGE REPRESENT THE
BELIEFS AND LIFESTYLES OF WHITE, MIDDLE CLASS,
WESTERNERSWHEN WE FOCUS ON DATING AND MARRIAGE ONLY, WE MISS
MANY OTHER VALID FORMS OF BEING ALONE AND TOGETHER
cohabitation
fastest growing family structure in canada
a pathway to marriage for young adults
an alt to marriage (more often for olde adults)
influenced by changes in employment, housing problems, convenience, response to pregnancy
expectations to marry a higher among those cohabiting than those who are not
• INCREASINGLY ACCEPTED, ESPECIALLY AMONG YOUNGER PEOPLE
• MEN ARE MORE WILLING THAN WOMEN TO COHABIT
• COUPLES ARE OFTEN MORE EGALITARIAN
• LESS RELIGIOUS
• QUEBEC FRANCOPHONES ARE MORE LIKELY TO COHABITATE
• HIGHER LEVELS OF MARITAL DISCORD AND LOWER LEVELS OF WELL-BEING
THAN MARRIED INDIVIDUALS
• MARRIAGE MAY NOT BE NOT DISCUSSED UNTIL THE COMPLETION OF GOALS –
COMPLETION OF EDUCATION, STABLE JOB
• NOT ALWAYS A PRECURSOR TO MARRIAGE
• 2/3 DO NOT SEE THE NEED TO GET MARRIEDDESPITE THIS, COHABITATION IS BECOMING MORE
ACCEPTED AS A SETTING TO RAISE CHILDRENCOHABITATION (BOTH WITH AND WITHOUT CHILDREN) IS THE FASTEST GROWING FAMILY STRUCTURE
when cohabiTATING before marriAGE LEADS TO POORER RELATIONSHIP QUALITY
IF PARTNER’S “SLIDE” INTO COHABITATION WITHOUT MAKING A
FORMAL DECISIONIF IT IS PRIMARILY FOR FINANCIAL REASONS OR TOO EARLY IN THE
RELATIONSHIPIF PARTNERS ARE ON THE “SAME PAGE” ABOUT THE FUTURE OF THEIR
RELATIONSHIPIF ONE OR MORE OF THE PARTNERS FEELS “STUCK” IN THE
RELATIONSHIP AND/OR FORCED INTO MARRIAGEIF ONE OR MORE ARE “SERIAL COHABITATORS”
COHABITING COUPLES RECEIVE THE SAME RIGHTS AS MARRIED COUPLES EXCEPT…
CUSTODY RIGHTS
INSURANCE BENEFITS
FINANCIAL SUPPORT
JOINT DIVISION OF PROPERTY
COHABITION AND LAW
FEDERALLY, IF A COUPLE HAS LIVED TOGETHER LONG ENOUGH,
THEY COUNT AS SPOUSES FOR:
• INCOME TAX
• LIFE INSURANCE
• PENSION BENEFITSOBLIGATION FOR SUPPORT VARIES FROM PROVINCE TO PROVINCE
IN MOST CASES, COHABITATING COUPLES DO NOT HAVE THE SAME
PROPERTY RIGHTS AS MARRIED COUPLES
• DO NOT SHARE ASSETS AFTER BREAK, UNLESS PROOF THEY
CONTRIBUTED
SAME SEX marriage
IN 2005, BILL C-38 GRANTED EQUAL MARRIAGE
RIGHTS TO SAME SEX COUPLESIN 2006, THE FIRST CENSUS THAT COLLECTED DATA
ON SAME SEX MARRIED COUPLES
• 45,300 SAME-SEX COUPLES (7,500 – 16.5% WERE
MARRIED)
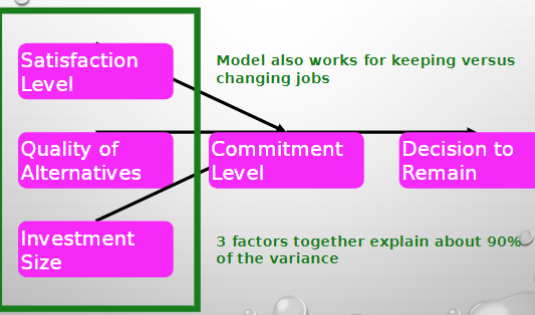
factors determine commitment lvl
satisfaction lvl: relationship quality, good interactions, “makes me happy”
quality of alternatives: if you left this relationship, what would replace it?
investment size: what you have put into the relationship that will be lost if you leave (sunken cost fallacy)
investment model of commitment
MARITAL SATISFACTION
WHAT INDIVIDUALS BRING TO THE MARRIAGE
• EMOTIONAL/PERSONALITY CHARACTERISTICS
• RESOURCESHOW COUPLES INTERACT
EXTENDED FAMILIES AND SOCIAL CONTEXTS
GOTTMANS FINDINGS
CONFLICT IS INEVITABLE IN A RELATIONSHIP
• HOW COUPLES FIGHT CONTRIBUTES TO RELATIONSHIP
DISSOLUTIONPOSITIVE AFFECT THE ONLY PREDICTOR OF MARITAL STABILITY
AND HAPPINESS AMONG STABLE COUPLES“... NO EVIDENCE... TO SUPPORT THE IDEA THAT ANGER IS THE
DESTRUCTIVE EMOTION IN MARRIAGES.”NEVER HAVING FIGHTS IS NOT BENEFICIAL TO A RELATIONSHIP
HAPPY COUPLES HAVE 5 POSITIVE INTERACTIONS FOR EVERY 1
NEGATIVE INTERACTION
HORSEMEN OF NEGATIVITY
CRITICSM
DEFENSIVENESS
CONTEMPT
STONEWALLING (UNCOOPERATIVE, UNWILLING TO DISCUSS OR ACKNOWLEDGE)
sexuality
approaches to sex among unmarried
puritanical: sex only in marriage, to produce children
double standard: men allowed more sexual freedom than women
sex-with-affection: acceptable w in committed relationships
sex-for-pleasure: more egalitarian
changes over time
attitudes toward premarital sex became more permissive from 50s to 80s
recent stats suggest that by grade 11:
over half had oral sex
40% of boys and 46% of girls have had sex
hiv/aids and safer sex
casual relationships
ONE STUDY FOUND THAT APPROXIMATELY 64-75% OF
AMERICAN ADOLESCENTS HAD EXPERIENCED “HOOKING UP” –
HAVING SEX OUTSIDE OF A DATING RELATIONSHIPDIFFERENT TYPES OF CASUAL SEX RELATIONSHIPS, SUCH AS
“FRIENDS WITH BENEFITS” (WENTLAND & REISSING, 2011)ONGOING SEXUAL RELATIONSHIP WITHOUT ROMANTIC
COMMITMENT
RESEARCH INDICATES POSITIVE AND NEGATIVE EXPERIENCES
infidelity
ANYWHERE FROM 25-40% OF RELATIONSHIPS
MEN MORE LIKELY TO BE UNFAITHFUL BUT RATES ARE
BECOMING MORE ALIKEGAY MEN MORE LIKELY THAN LESBIANS TO HAVE
RELATIONS OUTSIDE THEIR RELATIONSHIPDECREASES IN LONG-TERM UNIONS
• PEAKS FOR WOMEN AT 7 YEARS
• MEN AT 18 YEARS